
Age-related cataract is a multifactorial disease with various risk factors associated with each different type of senile cataract. Also, cortical and posterior subcapsular cataracts were related closely to environmental stresses including diabetes and drug ingestion.
What age is most likely to develop cataracts?
Cataracts are a natural part of the aging process for most people. In fact, 90% of people will develop a cataract by age 65, though many may not experience symptoms for months or even years after the cataract develops. However, there are a number of additional cataract risk factors that can cause cataracts to develop more quickly or earlier in ...
What age should I worry about cataracts?
Age-related cataracts can begin to form any time from age 40 onwards. However, because they take many years to cause symptoms, they generally don’t cause any vision problems before the age of 60. Once diagnosed, your eye doctor will monitor the condition as it progresses. Preventative measures during this time include eyeglass and/or contact ...
What is a cortical cataract and how is it treated?
Cortical cataract surgery is the most common surgical procedure in the world. In many cases, the refractive power of the natural lens is preserved by a permanent artificial intraocular lens placed inside the eye.
When should I see Doctor about cataracts?
You may have found yourself needing to update your eyeglasses or contact lens prescriptions more often because your vision keeps worsening. If you are over the age of 40 and are experiencing any of the symptoms above, you should make an appointment with your ophthalmologist to have your eyes checked for cataracts.
What is the treatment for cortical cataracts?
The long-term treatment for cortical cataract is cataract surgery. It is a common surgery and carries low risk. The surgeon removes the cloudy natural lens and replaces it with a clear artificial lens called an intraocular lens (IOL).
What are the 3 main types of age-related cataract?
The 3 main types of age-related cataract are nuclear sclerotic, posterior subcapsular and cortical.
What is the cause of cortical cataract?
Aging of the eye is the primary cause of cortical cataracts. As we get older, our eyes' lenses become weaker, less flexible and thicker. This increases the likelihood of our lenses becoming cloudy. This increased cloudiness limits the amount of light through our lens to the retina, resulting in blurred vision.
What is the most common type of age-related cataract?
nuclear cataractA nuclear cataract is the most common type of age-related cataract. It is caused by the hardening and discoloration (yellowing) of the lens. This type of cataract forms deep in the central area, or nucleus of the lens. Over time, this type of cataract changes the eye's ability to focus.
How long can you have a cataract before you go blind?
The National Eye Institute publishes that age-related cataracts can form in a person's 40s or 50s, but they generally progress slowly enough that they do not start to really impair vision until age 60 or so.
When is a cataract ready for removal?
When you have cataracts, you'll notice that your vision is tinted yellow or brown. This means that you'll see less, and your vision has become distorted. When this becomes difficult to ignore, it could be a sign that you are ready for cataract surgery!
Do cortical cataracts require surgery?
Cortical Cataract treatment While surgery is often opted to treat cataracts, early stages of the disorder can be managed with prescription glasses. Getting spectacles with a stronger lens will help make the vision better for a while. However, one cannot put off surgery for too long.
Can cortical cataracts affect vision?
The typical symptoms that come with cortical cataracts include: Increased difficulty driving at night. Blurry lines that affect vision. Blurred vision.
What does cortical cataract mean?
Cataracts that affect the edges of the lens (cortical cataracts). A cortical cataract begins as whitish, wedge-shaped opacities or streaks on the outer edge of the lens cortex. As it slowly progresses, the streaks extend to the center and interfere with light passing through the center of the lens.
Are age related cataracts hereditary?
Most recently, the twin eye study demonstrated significant genetic influence of age-related cortical cataract, with heritability accounting for 53–58% of the liability for age-related cortical cataract (Hammond et al., 2001).
What type of cataract is the fastest growing?
Trauma-related cataracts are typically the most fast-growing type of cataracts. Radiation: Radiation-related cataracts, sometimes listed under trauma-related cataracts, occur after the lens has been exposed to radiation. Exposure to high levels of radiation can result in clouded vision in as little as two years.
How do you test for cortical cataracts?
Using a slit lamp or a special device called an ophthalmoscope, your eye doctor can examine your lens for signs of a cataract. Applanation tonometry. This test measures fluid pressure in your eye. There are multiple different devices available to do this.
What is Level 3 cataract?
Stage 3: The 'Clear' Cataract The lens is still clear, however the lens material no longer bends light consistently. The image that is generated is a little blurry even though the lens material is clear. This type of blur cannot be corrected with glasses or contacts. Contrast goes down, and glare becomes noticeable.
What are the 4 types of cataracts?
Cataract types include:Cataracts affecting the center of the lens (nuclear cataracts). ... Cataracts that affect the edges of the lens (cortical cataracts). ... Cataracts that affect the back of the lens (posterior subcapsular cataracts). ... Cataracts you're born with (congenital cataracts).
Which type of cataracts is most common?
Nuclear Sclerotic Cataracts A nuclear cataract is the most common type of cataract, beginning with a gradual hardening and yellowing of the central zone of the lens also known as the nucleus. Over time, this hardening and yellowing will expand to the other layers of the lens.
What are the 2 types of cataract surgery?
Types of Cataract SurgeryPhacoemulsification, or phaco. A small incision is made on the side of the cornea, the clear, dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye. ... Extracapsular surgery. Your doctor makes a longer incision on the side of the cornea and removes the cloudy core of the lens in one piece.
Causes of Cortical Cataracts
The key causes of cortical cataracts are eye injury, aging, and a family history of cataracts.
Risk Factors
Some of the risk factors for cortical cataracts include medical conditions that can be influenced by lifestyle choices, such as diabetes and hypertension. Autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, may also be a risk factor.
Prevention of Cortical Cataracts
The risk of developing cortical cataracts can be reduced with lifestyle changes. Even if you have a family history of cataracts, you can still reduce other risk factors by making some changes.
Treatment for Cortical Cataracts
Treatment can be managed progressively to match the rate of cataract growth.
What is the effect of cortical cataracts on the eye?
A cortical cataract affects the outer edge of our eye’s lens and creates cloudy “spokes” that impair our vision. These spokes begin at the outside edge of the lens cortex (the outermost layer of the lens) and slowly work their way toward the center of the eye. Eventually, these spokes will converge until the entirety of the cortex is covered, and vision is completely impaired.
How common are cataracts?
Cataracts are a natural condition that affect us as we get older. They are quite common, especially in adults over 40, and they are often easily treated with corrective lenses or surgery. Many people don’t realize there are three types of cataracts that impact different parts of our eye.
How do you know if you have cortical cataracts?
Someone with cortical cataracts will notice a blurry or cloudy area along the outer boundary of their vision. It may be barely noticeable at first and won’t cause a huge amount of inconvenience.
Is cataract surgery safe?
Cataract surgery is quite routine and very safe, as more than three million Americans undergo the process each year. Cortical cataract surgery involves removing the old lens and replacing it with an artificial one.
Can trauma to the eye cause cataracts?
Injury can also damage the eye’s lens and lead to cataracts. Any other trauma to the eye, such as surgery or disease can also weaken the tissue of the lens and lead to cataracts. Genetic history makes some people more susceptible to cortical cataracts as they grow older.
Can you have both eyes at once with cataracts?
Cortical cataracts typically affect both eyes simultaneously, but it’s not uncommon for one eye to suffer more severe symptoms than the other.
Can glasses help with cataracts?
Although prescription lenses don’ t necessarily cure the cataract, they can overcome the blurry symptoms caused by the cataracts to help you see more clearly. If you already wear corrective lenses, your eye doctor may increase the power of your prescription.
How common are cortical cataracts?from allaboutvision.com
According to the Beaver Dam Eye Study, the incidence of cortical cataracts is around 1 in 10 for people between 43-86 years old . It is a widespread age-related condition and becomes more common as we get older.
What is a cortical cataract?from allaboutvision.com
A cortical cataract is an opacity in the outer layer, or cortex, of the natural lens. It is more common in people with diabetes and hypertension. Symptoms of cortical cataracts include glare, blurred vision and a decreased ability to perceive color, contrast and depth.
What is the treatment for cortical cataract?from allaboutvision.com
A short-term treatment for cortical cataracts may be a new glasses prescription. The long-term treatment for cortical cataract is cataract surgery. It is a common surgery and carries low risk. The surgeon removes the cloudy natural lens and replaces it with a clear artificial lens called an intraocular lens (IOL). The surgery takes about 15 minutes, and you will be able to go home that day.
What causes a cataract in the eye?from allaboutvision.com
A cortical cataract is caused by the buildup of protein fibers in the outer layer (cortex) of the lens. These clusters of clumped proteins disrupt the transparency of the lens fibers, resulting in opacities in the lens.
How to treat secondary cataract?from nei.nih.gov
Your doctor will use a laser to make an opening in the membrane behind the artificial lens in your eye — this is called YAG laser capsulotomy. Most people will notice their vision is back to normal a few days after the procedure. Last updated: August 3, 2019.
Why is it important to treat cataracts early?from nei.nih.gov
It’s important to treat these cataracts early on so your child doesn’t develop other vision problems, like amblyopia ( lazy eye ). Other pediatric cataracts are so small that they won’t hurt your child’s vision. Your child’s doctor can monitor these smaller cataracts to make sure they don’t cause vision problems.
What is secondary cataract surgery?from nei.nih.gov
Secondary cataract is common, but it’s easy to fix with a laser treatment in your eye doctor’s office. During cataract surgery, your doctor removes the lens from your eye and replaces it with a clear artificial lens.
What are the Most Common Symptoms of a Cortical Cataract?
Each of the three types of cataracts comes with its own set of symptoms, so don't be fooled into thinking what you're experiencing isn't a cataract because it doesn't meet the symptoms you've read about for other types of cataracts.
How many people have cataracts?
Cataracts are an extremely common eye condition among middle-aged and older adults. In fact, more than 22 million American adults over the age of 40 suffer from them. Not all cataracts are the same though. There are actually three distinct types of cataracts.
What is the best way to help a cataract sufferer?
Prescription eyeglasses or bifocals are usually a first step to help improve a cataract-sufferer's vision. If you already have glasses, your prescription may be updated to a greater power in an attempt to help you see more clearly. Cataracts, left untreated, will continue to grow and change, so getting a new pair of glasses is usually a short-term solution at best.
Can you get glasses if you have cataracts?
Cataracts, left untreated, will continue to grow and change, so getting a new pair of glasses is usually a short-term solution at best. Cataract surgery, performed by a skilled eye surgeon, is the next step when prescription glasses aren't doing the trick any more, and your cataracts are impacting your everyday life.
What causes cataracts in children?
Most cataracts are the result of aging, the World Health Organization (WHO) explains. Congenital cataracts can also occur, which is when babies are born with them, or they develop early in childhood. Cataracts can also be result of the following: 1 Eye injury (traumatic cataract). 2 Illness, health problems, or previous eye surgery (secondary cataract). 3 Exposure to radiation (radiation cataract). 4 Behaviors like smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, extended exposure to ultraviolet sunlight, and poor nutrition (risk factors for developing cataracts).
What are the risk factors for cataracts?
Exposure to radiation (radiation cataract). Behaviors like smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, extended exposure to ultraviolet sunlight, and poor nutrition (risk factors for developing cataracts).
What is posterior subcapsular cataract?
A posterior subcapsular cataract forms in the back of the lens, often directly in the path that light needs to pass through for sight. Mayo Clinic warns that a subcapsular cataract generally creates increased sensitivity to light, halos and glares around lights, impaired reading abilities, and reduced vision in bright lights. Certain medications, including corticosteroids and diabetes medications, can increase the risk for developing a posterior subcapsular cataract.
Why do you need cataract surgery?
A cataract surgery is done when the cataract impairs your vision and interferes with your daily life. Surgery may also be needed if and when a cataract might interfere with treatment for other issues related to vision or the eyes, even if it is not impairing vision directly.
How do cataracts form?
Cataracts form when proteins that make up the lens of the eye begin to clump together. This is common as a person ages and the lens becomes more rigid and less flexible.
Why do cataracts occur?
Most cataracts are the result of aging, the World Health Organization (WHO) explains. Congenital cataracts can also occur, which is when babies are born with them, or they develop early in childhood. Cataracts can also be result of the following: Eye injury (traumatic cataract). Illness, health problems, or previous eye surgery (secondary cataract).
Where does a nuclear cataract occur?
A nuclear cataract is most often associated with aging and forms in the center of the lens (the nucleus). Nuclear cataracts can occur in one or both eyes, and they often impact distance vision.
What is a cortical cataract?
A cortical cataract begins as whitish, wedge-shaped opacities or streaks on the outer edge of the lens cortex. As it slowly progresses, the streaks extend to the center and interfere with light passing through the center of the lens. Cataracts that affect the back of the lens (posterior subcapsular cataracts).
What is a cataract in the right eye?
Overview. A cataract occurs when the lens of your eye becomes cloudy. Eventually, a cataract can advance to the degree of the one shown in this person's right eye. Normal vision (left) becomes blurred as a cataract forms (right). A cataract is a clouding of the normally clear lens of your eye.
What is the name of the cataract that affects the back of the eye?
Cataracts that affect the back of the lens (posterior subcapsular cataracts). A posterior subcapsular cataract starts as a small, opaque area that usually forms near the back of the lens, right in the path of light. A posterior subcapsular cataract often interferes with your reading vision, reduces your vision in bright light, and causes glare or halos around lights at night. These types of cataracts tend to progress faster than other types do.
How does cataract affect vision?
How a cataract affects your vision. Normal vision (left) becomes blurred as a cataract forms (right). A cataract is a clouding of the normally clear lens of your eye. For people who have cataracts, seeing through cloudy lenses is a bit like looking through a frosty or fogged-up window. Clouded vision caused by cataracts can make it more difficult ...
Why is my cataract turning brown?
As the cataract slowly progresses, the lens may even turn brown. Advanced yellowing or browning of the lens can lead to difficulty distinguishing between shades of color. Cataracts that affect the edges of the lens (cortical cataracts).
How do you know if you have cataracts?
Symptoms. Signs and symptoms of cataracts include: At first, the cloudiness in your vision caused by a cataract may affect only a small part of the eye's lens and you may be unaware of any vision loss. As the cataract grows larger, it clouds more of your lens and distorts the light passing through the lens.
What causes nearsightedness in the eye?
Cataracts affecting the center of the lens (nuclear cataracts). A nuclear cataract may at first cause more nearsightedness or even a temporary improvement in your reading vision. But with time, the lens gradually turns more densely yellow and further clouds your vision.
How to diagnose cataracts?
Diagnosing Cataracts. Your doctor will perform a comprehensive eye exam to check for cataracts and to assess your vision. This will include an eye chart test to check your vision at different distances and tonometry to measure your eye pressure.
When is cataract surgery recommended?
Surgery is recommended when cataracts prevent you from going about your daily activities, such as reading or driving. It’s also performed when cataracts interfere with the treatment of other eye problems.
What is a cloudy area that forms in the lens of the eye?
A cataract is a dense, cloudy area that forms in the lens of the eye. A cataract begins when proteins in the eye form clumps that prevent the lens from sending clear images to the retina. The retina works by converting the light that comes through the lens into signals.
What causes a cataract to turn yellow?
Nuclear cataracts form in the middle of the lens and cause the nucleus, or the center, to become yellow or brown. Cortical cataracts are wedge-shaped and form around the edges of the nucleus. Posterior capsular cataracts form faster than the other two types and affect the back of the lens.
What are the symptoms of cataracts?
Common symptoms of cataracts include: blurry vision. trouble seeing at night. seeing colors as faded. increased sensitivity to glare. halos surrounding lights. double vision in the affected eye. a need for frequent changes in prescription glasses.
Can cataracts cause blindness?
Cataracts can interfere with daily activities and lead to blindness when left untreated. Although some stop growing, they don’t get smaller on their own. The surgical removal of cataracts is a very common procedure and is highly effective roughly 90 percent#N#Trusted Source#N#of the time, according to the National Eye Institute.
Can prednisone cause cataracts?
The use of the steroid prednisone and other medications can sometimes lead to cataracts. Traumatic cataracts develop after an injury to the eye, but it can take several years for this to happen. Radiation cataracts can form after a person undergoes radiation treatment for cancer.
How long does it take for cataracts to develop?
It can be difficult to pinpoint exactly how, and how quickly, a cataract will progress, but the general rule is that when they form later in life and due to aging, they typically form slowly over a period of years, while those that begin earlier in life and due to other circumstances can progress more rapidly.
Why do cataracts progress so slowly?
Cataracts related to aging often progress very slowly, giving you time to think about treatment and how best to address the issue. ( Learn More) Cataracts can also form due to genetics, environmental factors, illness, and injury, and these types of cataracts can progress more rapidly. ( Learn More)
What is cataract surgery?
Cataract eye surgery is a very common and medically necessary procedure to remove and replace the eye’s natural lens when the vision has been clouded by a cataract. We offer laser-assisted cataract surgery and lifestyle lenses as options for our patients.
What are the symptoms of cataracts?
Cataract Symptoms and When Treatment Is Needed 1 Blurry or cloudy vision 2 Yellowish tint to things 3 Double vision 4 Glares or halos around lights 5 Poor night vision 6 Increased sensitivity to light 7 Lack of contrast 8 Colors that appear dull 9 Regular changes to prescription glasses or contacts
Why do cataracts form in the eye?
Illness like diabetes, use of medications like corticosteroids, injury to the eye, exposure to radiation, congenital disease, and previous eye surgery can cause cataracts to form earlier in life. Again, these cataracts can often progress faster. Cataracts that begin by forming on the back of the lens (posterior subcapsular cataract) ...
Why do cataracts grow?
A lot of direct exposure to sunlight, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, poor nutrition, and a genetic predisposition can speed up the progression of a cataract.
How long does cataract surgery take?
Cataract surgery is common, and it can be done in an hour or so. It is relatively fast-healing, safe, and widely accessible. An artificial lens can provide clarity and improve your quality of life, helping to restore vision. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that cataract surgery is highly successful.
What are the different types of age-related cataracts?
There are three main types of age-related cataracts defined by their clinical appearance: nuclear, cortical, and posterior subcapsular ( figure 3 ). They can present alone or in combination. Typically the changes are bilateral, but they are commonly asymmetrical. Figure 3 Types of cataracts.
Where are cataracts found?
These cataracts are granular opacities occurring mainly in the central posterior cortex just under the posterior capsule. They can be present in younger patients, are commonly associated with a complaint of glare, such as when driving at night, and tend to reduce near vision more than distance visual acuity.
Why is social history important for cataract surgery?
Social history will help assessment of the need for surgical intervention and the availability of assistance in postoperative care.
What is the cortex of a lens?
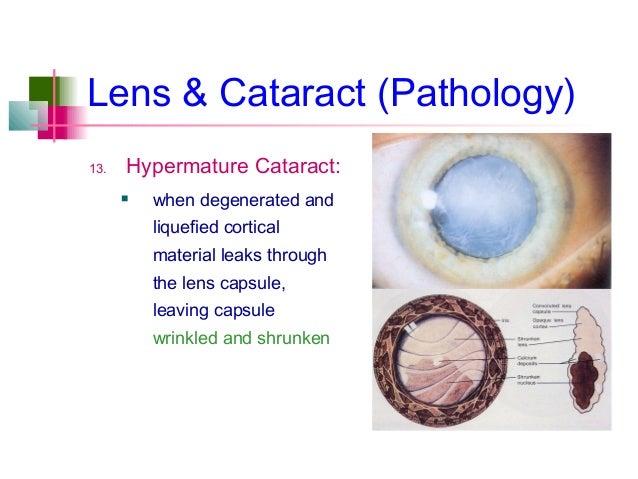
The cortex of the lens is made of the newest lens fibres. No fibres are lost with ageing, and new fibres are added to the outside of the lens, under the outer coating or capsule of the lens. With ageing, discrete opacities (cortical spokes) can develop within the cortex of the lens that typically cause no visual symptoms unless they involve the visual axis or the entire cortex, in which case the lens becomes white and is said to be mature.
Where is the cataract lens located?
The lens is the optically clear structure located behind the iris and in front of the vitreous body and retina ( figure 1 ). 1.
How does nuclear sclerosis affect vision?
Nuclear sclerosis progresses slowly, over years. In some cases it does not significantly affect vision or causes only a change in refraction (myopic shift), sometimes called second sight, since glasses might no longer be needed for reading. With further progression there can be loss of colour discrimination and also loss of vision, typically greater for distance than for near vision.
What causes a cataract?
Cataract, opacification of the lens, is one of the commonest causes of loss of useful vision, with an estimated 16 million people worldwide affected. Several risk factors have been identified in addition to increasing age—genetic composition, exposure to ultraviolet light, and diabetes. However, no method to halt the formation ...
