
Meaning
- Cost of goods manufactured are the production costs incurred on finished goods produced in a specific accounting period.
- Cost of goods sold are the production costs incurred on goods actually sold in a specific accounting period.
How can I calculate costs of goods sold?
Cost of Goods Sold Formula. Following is the COGS formula on how to calculate cost of goods sold. Cost of Goods Sold = Beginning Inventory + Purchases - Ending Inventory For example, if a business has a beginning inventory worth of $200,000 and ending inventory of $50,000 with new purchases of $300,000, the cost of goods sold can be solve with the above COGS formula.
How to calculate the cost of goods sold?
How to calculate the cost of goods sold. The basic formula for calculating the cost of goods sold is: COGS = Beginning inventory + Purchases - Ending inventory. Beginning inventory: Inventory remaining from a previous period. Purchases: Inventory purchased or produced in current period. Ending inventory: Remaining product that was not sold.
Can you calculate your cost of goods sold?
You can get the final cost of goods sold by using the following formula: Beginning inventory + new purchases – ending inventory = cost of goods sold For example, you had a beginning inventory of $100,000 and you purchased $50,000 of additional materials and products during the year.
How to decrease cost of goods sold?
- Use less expensive materials in production
- Find ways to reduce waste in manufacture and in the supply chain
- Investigate ways to reduce material storage and transportation costs
- Negotiate ceaselessly on every materials order you place: If you can’t get a price discount, seek other benefits, such as free or reduced-rate shipping
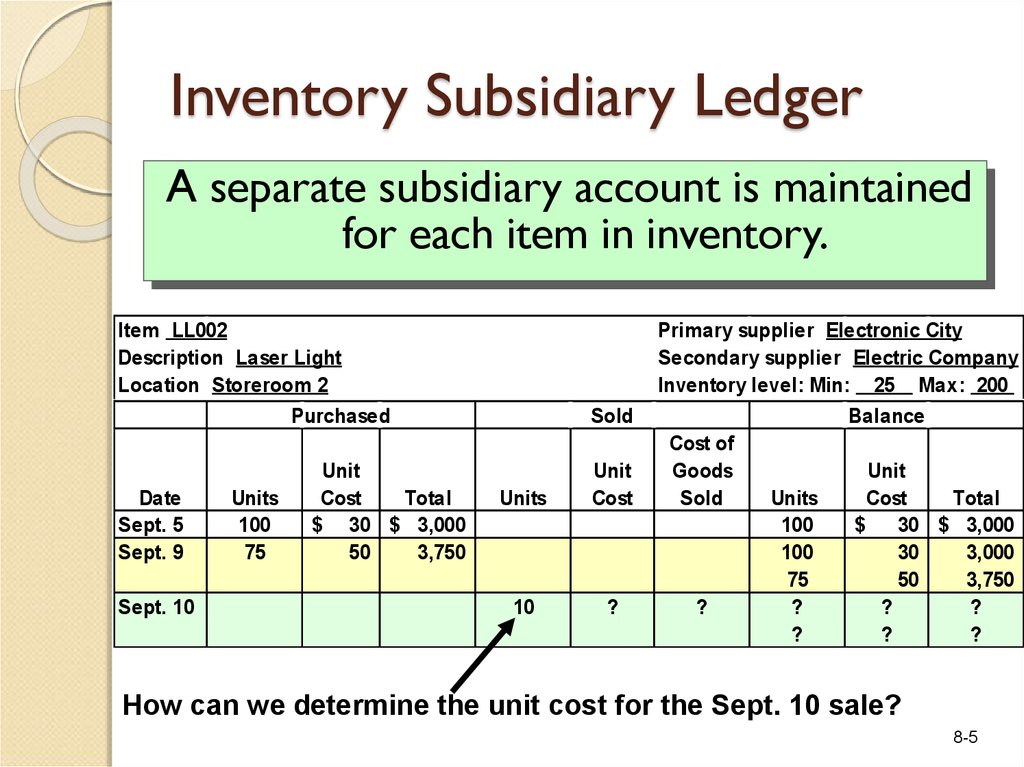
How do you calculate cost of goods sold for a manufacturing company?
Therefore, to calculate the cost of goods sold (COGS) for a manufacturing company, is to use the following formula: Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) = Cost of Goods Manufactured (COGM) + Beginning Inventory of Finished Goods – Ending Inventory of Finished Goods.
What defines cost of goods sold?
Cost of goods sold is the total amount your business paid as a cost directly related to the sale of products. Depending on your business, that may include products purchased for resale, raw materials, packaging, and direct labor related to producing or selling the good.
Is cost of goods sold the same as manufacturing cost?
The cost of goods manufactured is not the same as the cost of goods sold. Goods manufactured may remain in stock for many months, especially if a company experiences seasonal sales. Conversely, goods sold are those sold to third parties during the accounting period.
What is COGS and how is it calculated?
Cost of goods sold (COGS) is calculated by taking the value of inventory at the beginning of the period being studied, adding the cost of any new inventory purchased over the covered period, and subtracting the value of inventory held at the end of the period. COGS = Beginning Inventory + Purchases – Ending Inventory.
What is not included in cost of goods sold?
COGS does not include general selling expenses, such as management salaries and advertising expenses. These costs will fall below the gross profit line under the selling, general and administrative (SG&A) expense section.
What is the formula of cost of goods manufactured?
COGM includes all expenses related to the manufacturing process from inventory and factory overhead to labor. It is calculated by adding together the total costs of manufacturing and beginning work in process (or WIP) inventory and subtracting the ending WIP inventory from their sum.
How does a manufacturing company report cost of goods manufactured?
The formula and format for presenting the cost of goods manufactured is: The cost of the direct materials used. PLUS the cost of the direct labor used. PLUS the cost of manufacturing overhead assigned.
How do you prepare a statement of cost of goods manufactured?
How Do We Calculate Cost of Goods Manufactured? To calculate the cost of goods manufactured, you must add your direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead to get your businesses' total manufacturing cost.
How do you calculate cost of goods of sold?
Costs of Goods Sold (COGS) represent the expenses involved into producing your goods over a certain period of time. The COGS formula is: COGS = the starting inventory + purchases – ending inventory.
What is the difference between cost of sales and cost of goods sold?
Key takeaways: The difference between cost of goods sold and cost of sales is that the former refers to the company's cost to make products from parts or raw materials, while the latter is the total cost of a business creating a good or service for purchase.
What is included in COGS for a service company?
Cost of Goods Sold, (COGS), can also be referred to as cost of sales (COS), cost of revenue, or product cost, depending on if it is a product or service. It includes all the costs directly involved in producing a product or delivering a service. These costs can include labor, material, and shipping.
Is cost of goods sold the same as cost of sales?
Both these sums are accounted for in the income statement following sales income. The vital distinction between the cost of goods sold and the cost of sales is that the cost of sales isn't tax-deductible, while the cost of goods sold is tax-deductible.
Why is it important to have a schedule for cost of goods manufactured?
In general, having the schedule for Cost of Goods Manufactured is important because it gives companies and management a general idea of whether production costs are too high or too low relative to the sales they are making.
What is finished goods inventory?
Finished Goods Inventory, as the name suggests, contains any products, goods, or services that are fully ready to be delivered to customers in final form. The following T-account shows the Finished Goods Inventory. Beginning and ending balances must also be considered, similar to Raw materials and WIP Inventory.
What is COGM in accounting?
Just like the name implies, COGM is the total cost incurred to manufacture products and transfer them into finished goods inventory for retail sale. To learn more, launch CFI’s free accounting courses!
What is raw materials inventory?
Raw materials inventory refers to the inventory of materials that are waiting to be used in production. For example, if a company were to make a raw material purchase for use, these would be recorded in the debit side of the raw materials inventory T-Account.
What is marginal cost formula?
Marginal Cost Formulas Marginal Cost FormulaThe marginal cost formula represents the incremental costs incurred when producing additional units of a good or service. The marginal cost
Why is COGM Important for Companies?
In general, having the schedule for Cost of Goods Manufactured is important because it gives companies and management a general idea of whether production costs are too high or too low relative to the sales they are making.
What is Cost of Goods Sold?
Cost of Goods Sold, also known as Cost of Sales, is a key metric in determining a company’s Gross Profit and Gross Margin. It measures only the direct costs associated with the production of goods within a manufacturing company. For accounting purposes, Cost of Goods Sold is listed under “current assets” on a balance sheet. Current assets are goods expected to be converted to cash within one year and include cash, accounts receivable, stock inventory, work in progress inventory and other liquid assets.
How to calculate cost of goods sold?
Calculating Cost of Goods Sold requires taking the beginning and inventory value, minus ending inventory value plus factory overhead and direct labor. The steps include: 1 Start with the Beginning Raw Materials Inventory value and add all raw materials purchased during the selected accounting period. Then, subtract the ending inventory value. This is the valuation of the direct materials used in production. 2 Next, add the value of the direct labor and factory overhead. (Factory overhead will include factory expenses like rent and utilities). Then, add this sum to the direct materials from step 1. This is the Total Manufacturing Cost. 3 Using the beginning Work in Process (WIP) inventory, subtract the ending WIP inventory value and add to the Total Manufacturing Costs in step 2. This is the Cost of Goods Manufactured (COGM). 4 Finally, use the Finished Goods beginning inventory value and subtract the Finished Goods ending inventory value and add this sum to the Cost of Goods Manufactured. This is the total Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
How to calculate COGM?
Using the beginning Work in Process (WIP) inventory, subtract the ending WIP inventory value and add to the Total Manufacturing Costs in step 2. This is the Cost of Goods Manufactured (COGM).
Why is accurate inventory counting important?
Having accurate inventory counting and adhering to a strict COGS calculation can help determine which products may be too low, or too high, and allows a company to set appropriate pricing.
What is current asset?
Current assets are goods expected to be converted to cash within one year and include cash, accounts receivable, stock inventory, work in progress inventory and other liquid assets. To obtain an accurate Cost of Goods Sold, a company must have accurate control of its inventory functions. This includes the physical or automated functions ...
Why is the value of COGS important?
The value of COGS is important for several reasons: Helps to Set Profitable Pricing – In complex manufacturing systems, costing each step of production is a challenge.
What is raw material inventory?
Raw Materials Inventory – This includes unprocessed materials used in finished goods as well as components. Raw material costs are based on the total “landed costs” of the goods.
What is the cost of goods sold?
Cost of goods sold is defined as the complete cost legitimately brought about by a company to sell products and services. During the manufacturing process, the expense of goods sold is otherwise called the cost of goods manufactured.
How to determine cost of product?
To decide the cost of the product, the raw materials prepared toward the start of the production time frame must be added to non-fundamental raw materials (for example, labor and overhead), afterward deducted by the things staying in the stockroom toward the finish of the period.
Why do manufacturers need raw materials?
Essentially, raw materials are the principal necessity for determining the expense of goods sold. Manufacturers are responsible for deciding the number of raw materials that will be utilized to make a thing.
How to calculate raw materials utilized?
Here are how to compute all the raw materials utilized for the production process: Raw materials utilized = starting balance of raw materials + raw material which are bought – end balance of raw materials.
What is inventory purchase?
Inventory Purchases. Inventory purchases incorporate all crude material bought by the company, both money and credit exchanges. They likewise incorporate the expense of transportation, excluding discounts and returns.
What is starting inventory expense?
The starting inventory expenses are the whole , the inventory expenses toward the start of the period or the current monetary year. The equalization of the starting inventory expenses can be sorted out from the current record balance, the organization’s underlying balance sheet, or the balance of the earlier year.
When should you include completed goods made in the warehouse?
You should include the completed goods made in the warehouse toward the start of the period with the production cost of the current time frame , afterward lower the completed products staying in the warehouse toward the finish of the period. Here is the equation:
What is Cost of Goods Sold?
In short, cost of goods sold is how much it costs your business to sell inventory over a given period of time. This could be monthly, quarterly, or yearly. You could calculate COGS every month, and also do a quarterly review to make sure everything lines up. Other businesses may only do this quarterly.
Why is it important to keep track of cost of goods sold?
Keeping track of cost of goods sold is essential for tax purposes and profit margins. It is also important for steering your business down the right path in the future. Nothing is static in business.
How does perpetual inventory work?
A perpetual inventory system requires you to make stock adjustments for each sale. That means you can calculate COGS for each sale. Doing this manually is way more labor-intensive but gives you more information and accuracy. Once you have your COGS value, you can use it to work out your gross profit.
What is a COGS?
In any case, the basic principles stay the same. COGS is a method of giving a real-world valuation to your inventory. It’s a must-know for proper inventory management.
How much does it cost to make 30 candles?
As the first batch is running low you manufacture a further 30. But your supplier costs have gone up and it now costs $3 to make one candle.
What is SG&A in accounting?
SG&A (Sales, General, and Admin costs), including rent, utilities, and e-commerce fees; and
Is inventory valuation correct?
Many large manufacturers regard this as the “theoretically correct” inventory valuation method. It asserts that the first materials and stock to come into inventory, will be the first out when sold.
What Does Cost of Goods Sold Tell You, and Why is it Important?
Subtracting COGS from revenue gives gross profit, which reveals the core essence of business viability: What are my costs to make a product, and how much do I sell it for?
What is Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)?
If revenue represents the total sales of a company’s products and services, then COGS is the accumulated cost of creating or acquiring those products.
How to calculate COGS?
Diving a level deeper into the COGS formula requires five steps. Typically, these are tackled by accounting and tax experts, often with the help of powerful software. But these four steps are something all managers should have an appreciation for: 1 Identify the beginning inventory of raw materials, then work in process and finished goods, based on the prior year’s ending inventory amounts. 2 Determine the cost of purchases of raw materials that were made during the period, taking into account freight in, trade and cash discounts. 3 Determine the ending inventory balance. Typically, it’s based on physical cycle counts and is done in accordance with the company’s inventory-valuation method of choice. 4 Ensure that any other direct costs of production are included in the valuation of inventory.
What is the meaning of COGS in accounting?
The higher a company’s COGS, the lower its gross profit. So, COGS is an important concept to grasp. COGS, sometimes called “cost of sales,” is reported on a company’s income statement, right beneath the revenue line.
Why is a COGS calculation wrong?
Because a COGS calculation has so many moving parts, it can be prone to errors and subject to manipulation. An incorrect COGS calculation can obscure the true results of a business’ operations. It can also result in misstated net income and tax liability.
How many steps are required to calculate COGS?
Diving a level deeper into the COGS formula requires five steps. Typically, these are tackled by accounting and tax experts, often with the help of powerful software. But these four steps are something all managers should have an appreciation for:
What is a cog?
Most importantly, COGS is a key component of determining two critical business metrics: a company’s gross profit and its gross margin. Gross profit is obtained by subtracting COGS from revenue, while gross margin is gross profit divided by revenue. The higher a company’s COGS, the lower its gross profit. So, COGS is an important concept to grasp. ...
What are the costs of goods sold?
The items that make up costs of goods sold include: 1 Cost of items intended for resale 2 Cost of raw materials 3 Cost of parts used to make a product 4 Direct labor costs 5 Supplies used in either making or selling the product 6 Overhead costs, like utilities for the manufacturing site 7 Shipping or freight in costs 8 Indirect costs, like distribution or sales force costs 9 Container costs
What are the items that make up the cost of goods sold?
The items that make up costs of goods sold include: Cost of items intended for resale. Cost of raw materials. Cost of parts used to make a product. Direct labor costs. Supplies used in either making or selling the product. Overhead costs, like utilities for the manufacturing site. Shipping or freight in costs.
How to find cost of goods sold?
To do this, a business needs to figure out the value of its inventory at the beginning and end of every tax year. Its end of year value is subtracted from its beginning of year value to find cost of goods sold. The below section deals with calculating cost of goods sold.
What is the value of the business's inventory subtracted from?
Finally, the value of the business’s inventory is subtracted from beginning value and costs. This will provide the e-commerce site the exact cost of goods sold for its business, according to The Balance.
What is sales revenue minus cost of goods sold?
Sales revenue minus cost of goods sold is a business’s gross profit. Cost of goods sold is considered an expense in accounting and it can be found on a financial report called an income statement. There are two way to calculate COGS, according to Accounting Coach. In this article, we’ll cover:
What is the beginning inventory?
The beginning inventory is the value of inventory at the beginning of the year, which is actually the end of the previous year. Cost of goods is the cost of any items bought or made over the course of the year. Ending inventory is the value of inventory at the end of the year. This formula shows the cost of products produced and sold over the year, ...
How is cost of goods made or bought adjusted?
Cost of goods made or bought is adjusted according to change in inventory. For example, if 500 units are made or bought but inventory rises by 50 units, then the cost of 450 units is cost of goods sold. If inventory decreases by 50 units, the cost of 550 units is cost of goods sold.
What is Cost of Goods Sold?from manufacturing-software-blog.mrpeasy.com
Cost of Goods Sold, also known as Cost of Sales, is a key metric in determining a company’s Gross Profit and Gross Margin. It measures only the direct costs associated with the production of goods within a manufacturing company. For accounting purposes, Cost of Goods Sold is listed under “current assets” on a balance sheet. Current assets are goods expected to be converted to cash within one year and include cash, accounts receivable, stock inventory, work in progress inventory and other liquid assets.
How Do You Calculate Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)?from investopedia.com
Cost of goods sold (COGS) is calculated by adding up the various direct costs required to generate a company’s revenues. Importantly, COGS is based only on the costs that are directly utilized in producing that revenue, such as the company’s inventory or labor costs that can be attributed to specific sales. By contrast, fixed costs such as managerial salaries, rent, and utilities are not included in COGS. Inventory is a particularly important component of COGS, and accounting rules permit several different approaches for how to include it in the calculation.
How to calculate COGM?from manufacturing-software-blog.mrpeasy.com
Using the beginning Work in Process (WIP) inventory, subtract the ending WIP inventory value and add to the Total Manufacturing Costs in step 2. This is the Cost of Goods Manufactured (COGM).
What is the beginning inventory?from investopedia.com
Inventory that is sold appears in the income statement under the COGS account. The beginning inventory for the year is the inventory left over from the previous year—that is, the merchandise that was not sold in the previous year. Any additional productions or purchases made by a manufacturing or retail company are added to the beginning inventory. At the end of the year, the products that were not sold are subtracted from the sum of beginning inventory and additional purchases. The final number derived from the calculation is the cost of goods sold for the year.
Why do manufacturers need raw materials?from wikiaccounting.com
Essentially, raw materials are the principal necessity for determining the expense of goods sold. Manufacturers are responsible for deciding the number of raw materials that will be utilized to make a thing.
Why is accurate inventory counting important?from manufacturing-software-blog.mrpeasy.com
Having accurate inventory counting and adhering to a strict COGS calculation can help determine which products may be too low, or too high, and allows a company to set appropriate pricing.
What are some examples of pure service companies?from investopedia.com
Examples of pure service companies include accounting firms, law offices, real estate appraisers, business consultants, professional dancers, etc. Even though all of these industries have business expenses and normally spend money to provide their services, they do not list COGS. Instead, they have what is called "cost of services," which does not count towards a COGS deduction.
Merchandising COGS
Because a merchandising business buys products from manufacturers and resells them, they only have one type of inventory to keep track of – which makes calculating COGS fairly easy.
Manufacturing COGS
First off, calculating manufacturing COGS will not be as simplistic as for merchandising COGS. The reason for that is that a manufacturing company does not only have one type of inventory, they have three:
How to calculate Manufacturing COGS
Direct material cost = Beginning raw materials + Purchases – Ending raw materials

Introduction
- Cost of goods sold is defined as the complete cost legitimately brought about by a company to sell products and services. During the manufacturing process, the expense of goods sold is otherwise called the cost of goods manufactured. The calculations for COGS are led to decide the measure of production costs that will be acquired by the organizatio...
The Factors Involved in The Calculation of Cogs
- To have the exact COGS calculation, it is essential to know the three important parts which are: 1. Starting inventory costs (towards the start of the year) The starting inventory expenses are the whole, the inventory expenses toward the start of the period or the current monetary year. The equalization of the starting inventory expenses can be sorted out from the current record balanc…
Instructions For Calculating Cogs
- The COGS computation strategy in manufacturing companies is somewhat dissimilar to that of in-service and retail organizations. Here are the means to determine it:
Conclusion
- Computing COGS by the manual way is quite a headache because typically, it requires a ton of documents to record every part. Separate paper records or spreadsheets regularly get lost or even harmed. What’s more, the manual calculation of COGS is additionally inclined to mistakes. The calculation of COGS can be made significantly less complex and simpler with the assistanc…