Cost variance is the difference of earned value and actual cost. Schedule variance is the difference of earned value and planned value. If cost variance is negative then the project is over budget. If schedule variance is negative then the project is behind schedule. If the cost variance is positive then the project is under budget.
How do you calculate a schedule variance?
Tips for calculating schedule variance
- Use the formula when planning your project. You can predict the potential schedule variance week by week for your project by identifying successes or setbacks that would alter the planned ...
- Propose a method for checking project quality. ...
- Double-check your schedule variance calculations. ...
How do you calculate cost variance (CV)?
Cost Variance is expressed as the difference of the actual cost from earned value. Cost Variance = Earned Value – Actual Cost. CV = EV – AC. From the above formula, we can infer that: If CV > 0 (zero), You are under budget. If CV < 0 (zero), You are over budget. If CV = 0 (zero), You are on budget.
What is the meaning of cost variance?
What is a Cost Variance? A cost variance is the difference between the cost actually incurred and the budgeted or planned amount of cost that should have been incurred.
How to calculate a cost variance (CV)?
Cost Variance (CV) is a very important factor to measure project performance. CV indicates how much over - or under-budget the project is. CV can be calculated using the following formula: Cost Variance (CV) = Earned Value (EV) − Actual Cost (AC) OR. Cost Variance (CV) = BCWP − ACWP. The formula mentioned above gives the variance in terms ...
What is cost variance?
What is schedule variance?
Why is schedule variance important?
What does it mean when you are behind schedule?
How to calculate schedule variance?
What are the elements of earned value management?
Can management reserve be added to cost baseline?
See 2 more

What is schedule variance?
What is Schedule Variance in Project Management? Schedule variance is an indicator of whether a project schedule is ahead or behind. It is typically used within earned value management (EVM) to provide a progress update for project managers at the point of analysis.
What is cost variance?
The cost variance is defined as the 'difference between earned value and actual costs. (CV = EV – AC)' (PMI, 2004, p. 357) Sometimes this formula is expressed as the difference between budgeted cost of work performed and actual cost work performed. If the variance is equal to 0, the project is on budget.
What is CPI and SPI?
The Cost Performance Index (CPI) is defined as the ratio of Earned Value to Actual Cost, while the Schedule Performance Index (SPI) is defined as the ratio of cumulative Earned Value to cumulative Planned Value (PMI, 2000). Both CPI and SPI are traditionally defined in terms of the cumulative values.
What is SV and CV?
- Cost Variance (CV): The CV is the difference between the earned value of the work performed and the executed budget (Actual Cost). CV= EV-AC. - Schedule Variance (SV): The SV is the difference between the earned value of the work performed and the planned value of the work scheduled. SV= EV-PV.
What are the two types of variance?
When effect of variance is concerned, there are two types of variances:When actual results are better than expected results given variance is described as favorable variance. ... When actual results are worse than expected results given variance is described as adverse variance, or unfavourable variance.
Why is cost variance important?
Cost variance is important because it allows you to track the financial progression of your project. It is an indicator of how well you monitor and mitigate potential risks and how well you analyze data related to the project.
How is SPI calculated?
The SPI calculation easily displays how close the work is to progressing within the original schedule estimate. Using the formula SPI = EV / PV, the project manager will have a value of less than 1 (project behind schedule), of 1 (project on schedule), or greater than 1 (project ahead of schedule).
What is CPI schedule?
The Cost and Schedule Performance Indexes (CPI and SPI) are powerful metrics a project manager can use to monitor cost and schedule performance. CPI is calculated by dividing Earned Value by Actual Cost. CPI is an indicator of how efficiently project resources are performing relative to the project budget.
What does SPI less than 1 mean?
is behind scheduleSPI = EV / PV If the SPI calculation yields a value that is: Greater than 1: The project is ahead of schedule. Less than 1: The project is behind schedule. Equal to 1: The project is on schedule.
What is cost variance CV and schedule variance SV?
Cost variance is the difference of earned value and actual cost. Schedule variance is the difference of earned value and planned value. CV = EV - AC. SV = EV - PV. If cost variance is negative then the project is over budget.
What is the formula for SV?
To calculate SV, subtract your project's planned value (PV) from its earned value (EV): SV = EV – PV. You will also need to know the value of your project's planned budget at completion (BAC). If your SV is positive, your project is ahead of schedule.
How is CV cost variance calculated?
Cost Variance (CV) Cost Variance can be calculated using the following formulas: Cost Variance (CV) = Earned Value (EV) – Actual Cost (AC) Cost Variance (CV) = BCWP – ACWP.
What does cost variance measure?
Cost variance (CV), also known as budget variance, is the difference between the actual cost and the budgeted cost, or what you expected to spend versus what you actually spent. This formula helps project managers figure out if they are over or under budget.
How do you interpret cost variance?
Cost Variance indicates how much over or under budget the project is in terms of percentage.Positive = indicates how much under budget the project.Negative = indicates how much over budget the project.
How do I calculate price variance?
Price variance is calculated by the following formula: Vmp = (Actual unit cost - Standard unit cost) * Actual Quantity Purchased. or. Vmp = (Actual Quantity Purchased * Actual Unit Cost) - (Actual Quantity Purchased * Standard Unit Cost).
What's cost variance analysis?
Cost variance analysis is a control system that is designed to detect and correct variances from expected levels. It is comprised of the following steps: Calculate the difference between an incurred cost and an expected cost. Investigate the reasons for the difference. Report this information to management.
What Is Cost Variance?
Cost Variance (CV) is an indicator of the difference between earned value and actual costs in a project. It is a measure of the variance analysis t...
What Is Point-in-time / Period-by-Period Cost Variance?
This is the simplest type of cost variance: It basically refers to the difference between actual cost and earned value within one period. Thereby,...
What Is Cumulative Cost Variance?
The cumulative CV is a measure for the cumulative difference of the cumulative earned value and actual cost figures of several, usually consecutive...
What Is Variance at Completion (VAC)?
The variance at completion is the cumulative cost variance at the end of the project. The calculation parameters are the budget at completion (BAC)...
How Is Cost Variance Calculated?
The basic formula for calculating the cost variance is: CV = EV – AC, where: EV = Earned value; AC = Actual cost. Earned value (EV) refers to the p...
How Is the Period-by-Period Cost Variance Calculated?
The period-by-period or point-in-time cost variance is calculated by using the basic formula with input parameters that refer to a single period: C...
How Is the Cumulative Cost Variance Calculated?
The cumulative cost variance uses the basic formula with cumulative input parameters over several periods: CV(cumulative) = EV(cumulative) – AC(cum...
What Is the Meaning of the Calculated Cost Variance Values?
The value of a calculated cost variance falls into one of the following 3 value ranges. Each of them has a different meaning: a negative cost varia...
Cost Variance and Schedule Variance Formula in Earned Value Management ...
Cost Variance and Schedule Variance Formula. Earned Value Management Variance Formula leverage the Earned Value Management Fundamental Formula (BAC, AC, PV, and EV) to determine the variances pertaining to project cost and schedule.
What Is Schedule Variance (SV)? Definition, Formula, Example ...
When you are in the process of controlling the schedule of your project, or when you are preparing for your PMP exam, you will likely make use of the Schedule Variance (SV) at some point. This is one of the key indicators of the variance analysis which is part of the earned value management of a project.. In this article, we are sharing the definition, formula and types of schedule variance ...
Why Should You Know the Difference between Cost Variance and Schedule Variance?
Knowing the difference between cost variance and schedule variance will help you in how you plan out your time and budget for your projects or business. Are you on schedule in finishing your target? Were you able to stick to a planned budget or have already exceeded it?
Cost Variance, Defined
In reality, a lot of things can happen when handling a business project. It is possible that you can find yourself incurring more costs than what you have budgeted. This is where cost variance will play a crucial role.
Project Managers Tip
An important tip is for project managers to give some leeway in budget planning, no matter how sound the budgeting is. Some factors can be hard to control such as spikes or shortages in supply pricing, fluctuations in currency changes, and costs in labor.
Download the Agency Profitability Toolkit!
Get the same templates & guides we use with consulting clients to get them results fast.
Schedule Variance, Defined
Everyone loves a tight and well-planned schedule. One needs to recognize that for every delay, there is an undesirable effect.
Schedule Variance, Illustrated
To illustrate how to schedule variance analysis is done, below is a sample scenario. To help simplify it, let’s break it down into steps.
The Bottom Line
Simply put, in knowing cost and schedule variance, you will have the power to run your business through two lenses: One that looks at the costs you have incurred while working on a project, and one that looks at the time allotted to working towards that goal or cause.
What is cost variance?
It provides you with information on whether you are over or under budget, in dollar terms. Cost Variance is a measure of the cost performance of a project.
What is schedule variance?
Schedule Variance (SV) and Cost Variance (CV) are two essential parameters in Earned Value Management. They help you analyze the project’s progress, i.e., how you are performing in terms of schedule and cost.
Why is schedule variance important?
Schedule Variance helps to understand if you are behind or ahead of schedule. Cost Variance helps determine if you are under or over budget. Variance analysis is the key to the success of any project, which is finished on time and within the approved budget.
What does it mean when you are behind schedule?
You are behind schedule if the Schedule Variance is negative.
How to calculate schedule variance?
You can calculate Schedule Variance by subtracting Planned Value from Earned Value.
What are the elements of earned value management?
You will get this information with the help of Earned Value Management. Earned Value Management has three basic elements: Earned Value, Planned Value, and Actual Cost.
Can management reserve be added to cost baseline?
I think management reserve will not be added to the cost baseline like contingency reserve unless it goes through change control process.
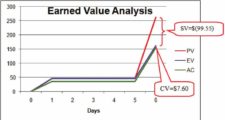
What does it mean when the cost variance is negative?
Since the Cost Variance is negative, this means the project is over-budget and Schedule Variance is negative, the project is behind schedule.
What does SV mean in a CV?
If CV is negative, the task is over budget. If CV is zero, the task is on budget. If CV is positive, the task is under budget. Schedule Variance (SV): Schedule variance is basically used to indicate whether a project is running ahead or behind. It is the difference of Budgeted Cost of Work Performed (BCWP) and Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled (BCWS).
What Is the Meaning of the Calculated Cost Variance Values?
The value of a calculated cost variance falls into one of the following 3 value ranges. Each of them has a different meaning:
How to calculate cumulative cost variance?
If you need to determine the cumulative cost variance, fill in the cumulative earned value and cumulative actual cost (make sure that both values relate to the same scope of periods). For a single period, populate AC and EV with the values for that particular period.
What does negative cumulative cost variance mean?
Again, the negative cumulative cost variance indicates a cost overrun after the first 3 months of the project.
What is variance at completion?
The variance at completion is the cumulative cost variance at the end of the project. The calculation parameters are the budget at completion (BAC) and the actual or estimated cost at completion (EAC). The VAC is often used as a measure of the forecasting techniques – you will find more details in this article on the estimate at completion (EAC).
What is the cumulative cost variance of the 1st to the 4th month?
In other words, the cumulative cost variance of the 1 st to the 4 th month is the difference between the sum of EV (1)+ EV (2)+EV (3)+EV (4) and the sum of AC (1)+AC (2)+AC (3)+AC (4).
Is cost variance positive or negative?
The cost variance is positive as the earned value exceeds the actual cost.
Is the difference between earned value and actual cost in this example insignificant?
This difference between earned value and actual cost in this example is actually not insignificant. Calculating the cost-performance index and determining the to-complete performance index can help analyze this result and assess its impact on the overall project.
What is cost variance?
Cost variance is the difference between the amount you budget for a project and the actual amount you spend completing the project. The technical definition is the difference between the Budgeted Cost of Work Performed (BCWP) and the Actual Cost of Work Performed (ACWP). It's a way to show how an expense line item, project or any budget is performing financially. Many industries use cost variance in a variety of ways, from reports to forecasts, depending on what they're trying to achieve. Here are some example of cost variance in relation to specific costs:
Why is cost variance important?
Cost variance is important because it allows you to track the financial progression of your project. It is an indicator of how well you monitor and mitigate potential risks and how well you analyze data related to the project. You can also evaluate your cost variance to make comparisons between the budget and actual cost throughout a project your team completes, giving you the opportunity to make improvements to your budget approaches that align with your goals. Another helpful aspect is that you can use historical data from similar projects to create a more accurate projection for the budget.
What is a negative cost variance?
Cost variances are negative, positive or zero. A negative cost variance happens when you overspend and go above your budget. A positive cost variance happens when you underspend and stay below your budget. A zero cost variance is when the amount you spend matches your budget exactly. Negative cost variances can indicate a business is overspending and whether the business has enough excess funds to cover its overspending. Positive cost variance can indicate both effective and unsuccessful activities, and zero cost variances are ideal.
Why do project managers use variance?
Project managers often use cost variance to track where their actual costs stand compared to their budget. They use cost variance to make financial adjustments throughout the duration of the project. Cost accountants also use cost variance to track, investigate and report the reasons for a variance. They often give these reports to management along with suggestions for future changes to reduce or increase the size of the variance in the future.
Why do direct product costs change?
Direct product costs: Direct product costs can change unexpectedly due to product damage, delays in handling, an industry shortage of an item or an increase in shipping fees.
What is cost variance?
Cost Variance (CV): This is the completed work cost when compared to the planned cost. Cost Variance is computed by calculating the difference between the earned value and the actual cost, i.e. EV – AC. As you can deduce from the formula, Cost Variance will be negative for projects that are over-budget. Monitoring project cost variance is critical to ensuring the project is delivered on budget. Using realistic project estimations is a good start to ensuring there isn’t significant cost variance.
What is schedule variance?
Schedule Variance (SV): This is the completed work when compared to the planned schedule. Schedule Variance is computed by calculating the difference between the earned value and the planned value, i.e. EV – PV. A positive Schedule Variance tells you that the project is ahead of schedule, while a negative Schedule Variance tells you the project is behind schedule. Monitoring Schedule Variance is critical to delivering the project on-time.
What does negative cost variance mean?
Interpretation: Since the Project Cost Variance is negative, this means the project is over-budget. Since Schedule Variance is negative, the project is behind schedule. This example project is in major trouble and corrective action needs to be taken to get it back on track. Earned Value Management cost variance and schedule variance will help you identify a project in trouble. To fix the problem areas is a different ball game. You will need to use effective risk management. In this case, the project schedule variance can be controlled by using the critical path method.
Is schedule variance positive?
Since Schedule Variance is positive, the project is ahead of schedule. However, this has come at a cost of going over-budget. If work is continued at this rate, the project will be delivered ahead of schedule and over-budget. Therefore, corrective action should be taken in terms of cost.
What is cost variance?
It provides you with information on whether you are over or under budget, in dollar terms. Cost Variance is a measure of the cost performance of a project.
What is schedule variance?
Schedule Variance (SV) and Cost Variance (CV) are two essential parameters in Earned Value Management. They help you analyze the project’s progress, i.e., how you are performing in terms of schedule and cost.
Why is schedule variance important?
Schedule Variance helps to understand if you are behind or ahead of schedule. Cost Variance helps determine if you are under or over budget. Variance analysis is the key to the success of any project, which is finished on time and within the approved budget.
What does it mean when you are behind schedule?
You are behind schedule if the Schedule Variance is negative.
How to calculate schedule variance?
You can calculate Schedule Variance by subtracting Planned Value from Earned Value.
What are the elements of earned value management?
You will get this information with the help of Earned Value Management. Earned Value Management has three basic elements: Earned Value, Planned Value, and Actual Cost.
Can management reserve be added to cost baseline?
I think management reserve will not be added to the cost baseline like contingency reserve unless it goes through change control process.

Why Should You Know The Difference Between Cost Variance and Schedule Variance?
Cost Variance, Defined
Project Managers Tip
Cost Variance, Exemplified
Schedule Variance, Defined
Schedule Variance, Illustrated
The Bottom Line
- Simply put, in knowing cost and schedule variance, you will have the power to run your business through two lenses: One that looks at the costs you have incurred while working on a project, and one that looks at the time allotted to working towards that goal or cause.