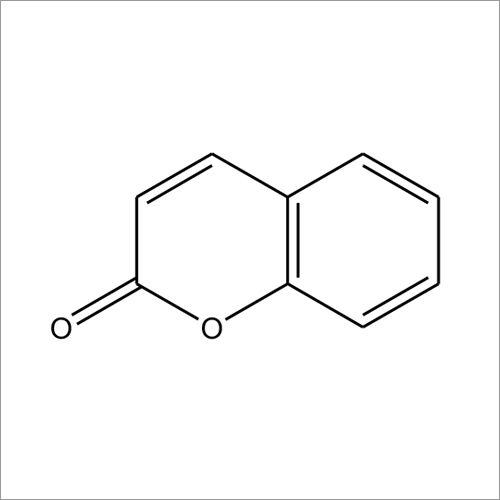
Warfarin – a coumarin – with brand name, Coumadin
Warfarin
This medication is used to treat blood clots and/or to prevent new clots from forming in your body.
Anticoagulant
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some of them occur naturally in blood-eating animals such as leeches and mosquitoes, where they help keep the bite area unclotted long enough for the animal to obtain some blood. As a class of medications, anticoagulants are used in therapy for thr…
What is coumarin used for in makeup?
Coumarin is super common in fragrances for women. But you’ll also find it in moisturizers, shampoos, cleansers, and serums. For cosmetics, you’ll see it in foundation, bronzer, lipstick, and eye shadow. The brands that use this ingredient are HUGE and people love the products too.
What is lymphedema and how does coumarin help?
Lymphedema is a condition characterized by the swelling of your arms or legs due to the buildup of lymph fluid under the skin. ( 7) Coumarin may also increase levels of antithrombin, an important protein that helps regulate blood clotting.
What is warfarin (coumarin)?
Warfarin – a coumarin – with brand name, Coumadin, is a prescription drug used as an anticoagulant to inhibit formation of blood clots, and so is a therapy for deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. It may be used to prevent recurrent blood clot formation from atrial fibrillation, thrombotic stroke, and transient ischemic attacks.
What are the uses of Coumadin?
Coumadin is used to treat or prevent blood clots in veins or arteries, which can reduce the risk of stroke, heart attack, or other serious conditions. Coumadin may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide.

Is coumarin toxic to humans?
The mechanism of coumarin-induced tumour formation in rodents is associated with metabolism-mediated, toxicity and it is concluded that exposure to coumarin from food and/or cosmetic products poses no health risk to humans.
What foods are high in coumarin?
Coumarin is a naturally occurring sweet-smelling compound found in many plants, including cinnamon, tonka beans, and sweet clover. High amounts of coumarin can be found in cassia cinnamon (also known as true cinnamon), whereas the Ceylon variety typically contains only traces.
What effect does coumarin have on the body?
Coumarins exhibited antitumor activities at different stages of cancer formation through various mechanisms, such as blocking cell cycle, inducing cell apoptosis, modulating estrogen receptor, or inhibiting the DNA-associated enzymes, such as topoisomerase (Emami and Dadashpour, 2015).
Is coumarin a blood thinner?
Warfarin – a coumarin – with brand name, Coumadin, is a prescription drug used as an anticoagulant to inhibit formation of blood clots, and so is a therapy for deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
Why is coumarin banned in US?
The tonka bean's distinct flavor is thanks to coumarin, a chemical compound that has been banned in the United States since 1954 because it can cause liver problems in high concentrations.
Why coumarin is not healthy?
Animal studies have shown that eating too much coumarin, which is abundant in Cassia cinnamon, may increase the risk of certain cancers ( 3 ). For example, studies in rodents have found that eating too much coumarin can cause cancerous tumors to develop in the lungs, liver, and kidneys (8, 9, 10 ).
Does coumarin cause hair loss?
Common anticoagulants (blood thinners) that cause hair loss are: warfarin, coumarin, and heparin. A gout medication that may cause hair loss is: allopurinol (Zyloprim). It has already been noted that vitamin A in excessive doses over a period of time can cause hair loss.
What does cinnamon do to a female body?
It's filled with antioxidants and offers several health benefits, including reduced inflammation and blood sugar levels, improved heart health, and perhaps even weight loss. Cinnamon tea may also fight off infections and reduce PMS and menstrual cramps.
Is coumarin in all cinnamon?
Cassia cinnamon contains up to 1% coumarin, whereas true cinnamon contains only a trace, about 0.004% [1–3]. Due to the high cost of true cinnamon, cassia cinnamon is often used in the food industry, although in some countries, substitution of cassia for true cinnamon is prohibited.
What foods thicken your blood?
Leafy Greens The highest sources include parsley, kale and Swiss chard. One cup of raw parsley contains 984 micrograms of vitamin K; a cup of raw kale contains 472 micrograms; and 1 cup of raw Swiss chard contains 299 micrograms.
Is turmeric a blood thinner?
Yes, turmeric is a blood thinner. Though the researchers had found no published reports of patients bleeding from taking turmeric, it could increase the risk, especially if paired with another anticoagulating drug. They concluded that patients should “avoid concomitant use.”
How much coumarin is in green tea?
Application of the stable isotope dilution assay for the quantification of coumarin revealed that its levels in these Japanese green tea products ranged from 0.26 to 0.88 μg/g of green tea product, whereas concentrations were generally below 0.2 μg/g in common green tea products.
Why are tonka beans illegal in the US?
Tonka beans—an ingredient that people have used for centuries to add a vanilla-almond note to cakes, custards, ice creams, and even chicken—have been illegal since 1954 because they contain coumarin, a chemical compound found in cinnamon.
Are eggs high in choline?
Choline and Healthful Diets Fish, beef, poultry, eggs, and some beans and nuts are rich sources of choline.
Which food is highest in choline?
Choline is found in a variety of foods. The richest sources are meat, fish, poultry, dairy, and eggs.
How do you dissolve coumarin?
Coumarin hydrazine is soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, DMSO, and dimethyl formamide (DMF), which should be purged with an inert gas. The solubility of coumarin hydrazine in these solvents is approximately 1, 10, and 14 mg/ml, respectively. Coumarin hydrazine is sparingly soluble in aqueous buffers.
What is coumarin anticoagulant?
The coumarin anticoagulants were developed after 3,3′-methylbis- (4-hydroxycoumarin) was identified as the active principle in spoiled sweet clover responsible for the hemorrhages and prolonged clotting times of animals consuming that feedstuff. Compounds in this family block the thiol-dependent, redox recycling of the vitamin by inhibiting VKQR. This reduces carboxylation of the Gla protein precursors, including those involved in clotting.31 Several substituted 4-hydroxycoumarins have been widely used in anticoagulant therapy in clinical medicine, and rodenticides (effective by causing fatal hemorrhaging). The most widely used has been warfarin (3- [a-acetonylbenzyl]-4-hydroxycoumarin)32, an analog of the naturally occurring hemorrhagic factor dicumarol, and its sodium salt 33.
What is coumarin made of?
Coumarins are phenolic substances composed of fused benzene and α-pyrone rings. At least 1300 different coumarins have been identified. Coumarins have antithrombotic, antiinflammatory, and vasodilatory activities. Warfarin is the most popular one and it is used as an oral coagulant and rodenticide.
How does coumarin affect thiourea?
Interaction studies between coumarin and thiourea in their effect on germination and also between each of them and other substances were carried out. From a study of the interaction between coumarin and thiourea it appeared that coumarin, in essence, makes seeds more sensitive to thiourea, i.e. the maximum stimulatory effect on germination becomes evident at lower thiourea concentrations. Higher thiourea concentrations, which in the absence of coumarin caused a maximum effect, are much less effective in the presence of coumarin ( Table 6.4 ). Coumarin and thiourea interact not only in their effect on germination but also in the subsequent growth of the seedlings. The similarity between thiourea and light in stimulating germination is further reflected by the fact that coumarin makes seeds more sensitive to both agents ( Mayer and Poljakoff-Mayber, 1961 ). An additional interaction is that between coumarin and gibberellic acid. The latter can reverse the inhibitory action of coumarin in germination. Cycocel (2-chloroethyl-trimethyl ammonium chloride) can also reverse the germination inhibition induced by coumarin. This compound also reverses the inhibition of germination by IAA ( Khan and Tolbert, 1966 ). These results point to a possible action of coumarin on the balance of growth regulators in the seed.
How is Coumarin derived from cinnamic acid?
The coumarin structure is derived from cinnamic acid via ortho-hydroxylation, trans-cis isomerization of the side-chain double bond and lactonization as shown in Fig. 9.16. The trans form is stable and could not cyclize. The cis form is very unstable, therefore, will tend to go to the trans configuration. Glucose is a leaving group which assists in the cis-trans transformation. A specific enzyme found in Melilotus alba (Leguminosae) specifically hydrolyzes the cisglucoside (beta-glucosidase). The most widely available coumarins in nature are umbelliferone, esculetin, and scopoletin. The biosynthesis pathway of coumarins showed that all coumarins derivative oxygenated at position seven ( Jain and Joshi, 2012 ).
How does Coumarin affect the respiratory system?
Coumarin may act by affecting respiratory metabolism both directly, by interfering at the phosphorylation stage, and indirectly, by affecting the availability of phosphate. It may act by preventing the formation of certain enzyme systems possibly because it prevents their liberation from some bound form. Finally, it may interfere with the formation and destruction of endogenous substances regulating germination.
What is the most commonly used medication for stroke?
The most widely used has been warfarin (3- [a-acetonylbenzyl]-4-hydroxycoumarin)32, an analog of the naturally occurring hemorrhagic factor dicumarol, and its sodium salt 33. Warfarin therapy has been important in preventing strokes; the drug is prescribed for a million patients each year in the United States alone.
Where can coumarins be found?
Coumarins can also be found in many plants. Twenty-seven compounds of 4-anilino-coumarins with 3- (4-methoxyphenyl) group and nine compounds with 3-trifluoroacetylgroup (Fig. 2.18) were synthesized and their antiproliferative activity against a panel of different cancer cells (MCF-7, HepG2, HCT116, and Panc-1) was tested ( Luo et al., 2017 ). Among the different substituents at C-3 position of coumarin scaffold, 3-trifluroacetyl group seems to be the best since coumarins with this group showed the most promising results with one compound, 18a ( Fig. 2.18) displaying the best IC 50 values in MCF-7, HepG2, HCT116, and Panc-1 cells (IC 50 = 16.57, 5.45, 4.42, and 5.16 μM, respectively). Further analysis of this compound in MCF-7 cells demonstrated that its cytotoxicity was exerted by cell cycle arrest at G 2 /M phase and apoptosis ( Luo et al., 2017 ).
What are the derivatives of coumarin?
Some naturally occurring coumarin derivatives include umbelliferone (7-hydroxycoumarin), aesculetin (6,7-dihydroxycoumarin), herniarin (7-methoxycoumarin), psoralen and imperatorin . 4-Phenylcoumarin is the backbone of the neoflavones, a type of neoflavonoids.
What are the compounds in coumarin?
Compounds derived from coumarin are also called coumarins or coumarinoids; this family includes: 1 brodifacoum 2 bromadiolone 3 difenacoum 4 auraptene 5 ensaculin 6 phenprocoumon (Marcoumar) 7 PSB-SB-487 8 PSB-SB-1202 9 Scopoletin can be isolated from the bark of Shorea pinanga 10 warfarin (Coumadin)
What are compounds derived from coumarins called?
Compounds derived from coumarin are also called coumarins or coumarinoids; this family includes:
What is the name of the drug that is used to treat pulmonary embolism?
Warfarin – a coumarin – with brand name, Coumadin, is a prescription drug used as an anticoagulant to inhibit formation of blood clots, and so is a therapy for deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. It may be used to prevent recurrent blood clot formation from atrial fibrillation, thrombotic stroke, and transient ischemic attacks.
How is coumarin biosynthesis done?
The biosynthesis of coumarin in plants is via hydroxylation, glycolysis, and cyclization of cinnamic acid. In humans, the enzyme encoded by the gene UGT1A8 has glucuronidase activity with many substrates, including coumarins.
How is coumarin prepared?
Coumarin can be prepared by a number of name reactions, with the Perkin reaction between salicylaldehyde and acetic anhydride being a popular example. The Pechmann condensation provides another route to coumarin and its derivatives, as does the Kostanecki acylation, which can also be used to produce chromones .
Why was Coumarin banned?
Coumarin was banned as a food additive in the United States in 1954, largely because of the hepatotoxicity results in rodents.
What is Coumarin used for?
Coumarin's production and use as a fragrance ingredient in soaps, detergents, lotions, perfumes, tobacco, household products and as a pharmaceutical flavoring may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams. Coumarin is a naturally occurring compound found in a large number of plants belonging to many different families, including lavender oil, woodruff (Asperula species), and sweet clover (Melilotus). If released to air, a vapor pressure of 9.8X10-4 mm Hg at 25 °C indicates coumarin will exist in both the vapor and particulate phases in the ambient atmosphere. Vapor-phase coumarin will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 29 hrs. Particulate-phase coumarin will be removed from the atmosphere by wet and dry deposition. Direct photlyisis may be an important environmental fate process based on a 59.2% mineralization to CO2 when exposed to UV radiation >290 nm for 17 hr. If released to soil, coumarin is expected to have high mobility based upon an estimated Koc of 140. Biodegradation in soil may be an important environmental fate process based on 100% degradation after 2 weeks incubation in a mixed inoculum obtained from freshwater, soil, and sludge. Volatilization from moist soil surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon a Henry's Law constant of 9.9X10-8 atm-cu m/mole. If released into water, coumarin is not expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the estimated Koc. Volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process based upon this compound's Henry's Law constant. A BCF of <10 suggests bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. The lactone is easily hydrolyzed by alkalies to the corresponding salts of coumarinic acid or o-hydroxy-cis-cinnamic acid; hoever, no data are available concerning the hydrolysis of coumarin under environmental conditions. Occupational exposure to coumarin may occur through inhalation and dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where coumarin is produced or used. Monitoring data indicate that the general population may be exposed to coumarin via inhalation and dermal contact and ingestion of fresh fruits containing coumarin. (SRC)
What is the koc of coumarin?
The Koc of coumarin is estimated as 140 (SRC), using a log Kow of 1.39 (1) and a regression-derived equation (2). According to a classification scheme (3), this estimated Koc value suggests that coumarin is expected to have high mobility in soil.
What is the Henry's law constant for Coumarin?
The Henry's Law constant for coumarin is 9.9X10-8 atm-cu m/mole (SRC), derived from its vapor pressure, 9.8X10-4 mm Hg (1), and water solubility, 1,900 mg/l (2). This Henry's Law constant indicates that coumarin is expected to be essentially nonvolatile from water surfaces (3). Coumarin is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces (SRC) based upon its vapor pressure (1).
How long did pregnant mice eat coumarin?
Groups of three male and three female Orsborne-Mendel rats were fed coumarin in the diet for four weeks.
How much coumarin is excreted in rabbit urine?
Within 4 days rats excreted 47% of the label in the urine and 39% in the feces, whereas rabbits excreted 92% in the urine and negligible amount in the feces.
What is CYP2A6?
These results indicate that CYP2A6 is largely or entirely responsible for catalyzing the 7-hydroxylation of coumarin in human liver, microsomes. Treatment of monkeys with phenobarbitalor dexamethasoneincreased coumarin 7-hydroxylase activity, whereas treatment with beta-naphthoflavonecaused a slight decr.
Is Coumarin a fragrance?
Coumarin's production and use as a fragrance ingredient in soaps, detergents, lotions, perfumes, tobacco, household products(1) and as a pharmaceutical flavoring(2) may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams(SRC).
What is Coumarin?
It’s thought to serve as a chemical defense in plants to protect them against predators. It naturally has a sweet, nutty, vanilla scent. However, when it’s diluted it is often compared to smelling like freshly-mown hay.
What Products Use Coumarin?
Coumarin is super common in fragrances for women. But you’ll also find it in moisturizers, shampoos, cleansers, and serums. For cosmetics, you’ll see it in foundation, bronzer, lipstick, and eye shadow.
Is Coumarin safe for pregnant women?
Many have also warned that products with this ingredient aren’t safe for children or pregnant women. Coumarin is also listed as one of 26 ingredients that is known to cause allergies in perfume by ...
Can coumarin cause problems?
This goes back to the concentration levels of the ingredient. Any product that uses trace amounts of coumarin may not cause you any trouble, but it’s important to keep an eye on any item with coumarin lists as an ingredient.
Is it safe to use coumarin topically?
With all the concerns and risks of consuming coumarin, you might be wondering if it’s safe to use topically. Since this ingredient absorbs directly into the skin, it does pose a risk. However, the concentration of this ingredient is what is important to understand. If the coumarin concentration is high enough, there may be risk liver damage and/or ...
Is Coumarin Vegan?
Yes, coumarin occurs naturally in plants. This compound can be sourced from plant-based ingredients, so there isn’t a concern to those adverse to animal-based products. However, if you are averse to allergies liver risks, you still might want to avoid this particular ingredient.
How many servings of coumarin are safe?
Thus as long as you’re not undergoing daily “cinnamon challenges”, you’re quite safe to enjoy your coumarin flavored special desserts, just not 2400 servings on any given day.
Is coumarin poisonous to humans?
Coumarin, or is 1,2-benzopyrone, occurs naturally in tonka beans and cinnamon, but can also be found in trace amounts in bison grass, green tea, carrots, and even some beers. Poisoning by coumarin is extremely rare and has only occurred in clinical settings, where high doses of the chemical were medically administered as treatments for lymphedema and some cancers. Recently researchers found that subgroups of humans might be more susceptible to the hepatotoxic effects of the chemical, but the mechanism for why this might be is unknown. Even with an added risk, heavy consumers of the compound barely reach levels of threatening exposure. Accordingly, the FDA ban on this substance has been highly criticized since it is very unlikely that anyone could be exposed to enough coumarin from tonka beans to cause liver damage. It has been estimated that every day we consume about 0.06mg/kg of the substance daily through our diet and cosmetics. This falls safely under the 2004 tolerable daily food intake (TDI) set by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) at 0.1mg/kg daily. For a fully grown adult to research this threshold, they would need to consume about 2400 plates of tonka bean flavoured desserts, in which case liver damage would probably not be their major concern.
Is coumarin illegal in Canada?
In Canada, directly adding coumarin to food is illegal, but consuming it through other spices, like tonka beans, is not. One of the most common ways that coumarin makes its way into our diets is actually through cinnamon, an extremely popular spice, second only to black pepper.
What is Coumadin?
Coumadin (warfarin) is an anticoagulant (blood thinner). Warfarin reduces the formation of blood clots.
How should I take Coumadin?
Take Coumadin exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Follow all directions on your prescription label. Your doctor may occasionally change your dose. Do not take warfarin in larger or smaller amounts or for longer than your doctor tells you to.
What other drugs will affect Coumadin?
Many drugs (including some over-the-counter medicines and herbal products ) can affect your INR and may increase the risk of bleeding if you take them with Coumadin. Not all possible drug interactions are listed in this medication guide. It is very important to ask your doctor and pharmacist before you start or stop using any other medicine, especially:
How long do you have to stop taking Coumadin?
You may need to stop taking Coumadin 5 to 7 days before having any surgery, dental work, or a medical procedure. Call your doctor for instructions. Wear a medical alert tag or carry an ID card stating that you take warfarin. Any medical care provider who treats you should know that you are taking this medicine.
What tests are needed to determine if you are taking Coumadin?
You will need frequent "INR" or prothrombin time tests (to measure your blood-clotting time and determine your warfarin dose). You must remain under the care of a doctor while taking Coumadin.
How long does it take for a bleed to stop after stopping Coumadin?
Use extra care to prevent bleeding while shaving or brushing your teeth. You may still bleed more easily for several days after you stop taking Coumadin.
Does Warfarin cause bleeding?
Warfarin increases your risk of severe or fatal bleeding, especially if you have certain medical conditions, if you are 65 or older, or if you have had a stroke, or bleeding in your stomach or intestines. Seek emergency help if you have any bleeding that will not stop.
Overview
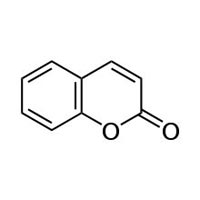
Coumarin or 2H-chromen-2-one is an aromatic organic chemical compound with formula C9H6O2. Its molecule can be described as a benzene molecule with two adjacent hydrogen atoms replaced by a lactone-like chain −(CH)=(CH)−(C=O)−O−, forming a second six-membered heterocycle that shares two carbons with the benzene ring. It can be placed in the benzopyrone chemica…
Etymology
Coumarin is derived from coumarou, the French word for the tonka bean. The word tonka for the tonka bean is taken from the Galibi (Carib) tongue spoken by natives of French Guiana (one source for the plant); it also appears in Old Tupi, another language of the same region, as the name of the tree. The old genus name, Coumarouna, was formed from another Tupi name for tree, kumarú.
History
Coumarin was first isolated from tonka beans in 1820 by A. Vogel of Munich, who initially mistook it for benzoic acid.
Also in 1820, Nicholas Jean Baptiste Gaston Guibourt (1790–1867) of France independently isolated coumarin, but he realized that it was not benzoic acid. In a subsequent essay he presented to the pharmacy section of the Académie Royale de Médecine, Guibourt named the ne…
Synthesis
Coumarin can be prepared by a number of name reactions, with the Perkin reaction between salicylaldehyde and acetic anhydride being a popular example. The Pechmann condensation provides another route to coumarin and its derivatives, as does the Kostanecki acylation, which can also be used to produce chromones.
Biosynthesis
From lactonization of ortho-hydroxylated cis-hydroxycinnamic acid.
Natural occurrence
Related compounds and derivatives
Coumarin and its derivatives are all considered phenylpropanoids.
Some naturally occurring coumarin derivatives include umbelliferone (7-hydroxycoumarin), aesculetin (6,7-dihydroxycoumarin), herniarin (7-methoxycoumarin), psoralen and imperatorin.
4-Phenylcoumarin is the backbone of the neoflavones, a type of neoflavonoids.
Coumarin pyrazole hybrids have been synthesized from hydrazones, carbazones and thiocarbaz…
Uses
Warfarin – a coumarin – with brand name, Coumadin, is a prescription drug used as an anticoagulant to inhibit formation of blood clots, and so is a therapy for deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. It may be used to prevent recurrent blood clot formation from atrial fibrillation, thrombotic stroke, and transient ischemic attacks.
Coumarins have shown some evidence of biological activity and have limited approval for few m…