Critical Value
| 1. | What is Critical Value? |
| 2. | Critical Value Formula |
| 3. | T Critical Value |
| 4. | Z Critical Value |
| 5. | F Critical Value |
What does the critical value z a denote?
What does the Z critical value mean? A critical value of z (Z-score) is used when the sampling distribution is normal, or close to normal. …. While the z-score can also be used to calculate probability for unknown standard deviations and small samples, many statisticians prefer to use the t distribution to calculate these probabilities.
What is the minimum value for Z?
Geometrically, it is the sum of the distances from z to 0 and to 1. The minimum clearly occurs when z lies on the segment [0, 1] and its value is 1. Equivalently, you can say “by the triangle inequality, |z|+|z-1| = |z|+|1-z| ≥ |z + (1-z)| = 1, and that value is actually attained whenever 0<z<1.”
How to calculate critical value.?
To calculate critical values, you must first understand the distribution of your test statistic under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true. The critical values are the points on the distribution that have the same possibility as your test statistic and are equal to the significance level.
How do you find critical values?
To find the critical value for an f test the steps are as follows:
- Find the alpha level.
- Determine the degrees of freedom for both samples by subtracting 1 from each sample size.
- Find the corresponding value from a one-tailed or two-tailed f distribution at the given alpha level.
- This will give the critical value.

How do you find the critical z value?
The level of significance which is selected in Step 1 (e.g., α =0.05) dictates the critical value. For example, in an upper tailed Z test, if α =0.05 then the critical value is Z=1.645....Upper-Tailed TestαZ0.051.6450.0251.9600.0102.3264 more rows•Nov 6, 2017
What is the 95% critical z value?
1.96For a 95% confidence interval Zcritical = 1.96.
What do you mean by critical value?
A critical value is the value of the test statistic which defines the upper and lower bounds of a confidence interval, or which defines the threshold of statistical significance in a statistical test.
What is Z for 94% confidence?
at 94% confidence level, the Z is Alpha equals 1 -94%, which equals 1 -0.94, which gives us 0.06.
Why is 1.96 the z-score?
A key idea here is that the values in the middle of the normal distribution (z-scores like 0.19 or -1.2, for example), represent the expected outcome....Confidence Levels.z-score (Standard Deviations)p-value (Probability)Confidence level< -1.96 or > +1.96< 0.0595%< -2.58 or > +2.58< 0.0199%1 more row
Is critical value the same as Z score?
Express critical value as a Z-score for large data sets For population sizes larger than 40 samples in a set, you can express the critical value as a Z-score. The Z-score should have a cumulative probability that is equal to the critical probability.
Why is 0.05 the critical value?
Critical values for a test of hypothesis depend upon a test statistic, which is specific to the type of test, and the significance level, \alpha, which defines the sensitivity of the test. A value of \alpha = 0.05 implies that the null hypothesis is rejected 5 % of the time when it is in fact true.
Why do we use critical values?
A critical value defines regions in the sampling distribution of a test statistic. These values play a role in both hypothesis tests and confidence intervals. In hypothesis tests, critical values determine whether the results are statistically significant.
How do you calculate 95 Z interval?
where the value of z is appropriate for the confidence level. For a 95% confidence interval, we use z=1.96, while for a 90% confidence interval, for example, we use z=1.64.
Why is Z 1.96 at 95 confidence?
The value of 1.96 is based on the fact that 95% of the area of a normal distribution is within 1.96 standard deviations of the mean; 12 is the standard error of the mean.
What is critical value in statistics?
In testing statistics, a critical value is a factor that determines the margin of error in a distribution graph. According to Statistics How To, a site headed by math educator Stephanie Glen, if the absolute value of a test statistic is greater than the critical value, then there is statistical significance that rejects an accepted hypothesis.
What is a hypothesis test?
Hypothesis tests check if your data was taken from a sample population that adheres to a hypothesized probability distribution. It is characterized by a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis.
How long do CFL bulbs last?
A factory produces CFL light bulbs. The owner says that CFL bulbs from their factory lasts for 160 days. Quality specialists randomly chose 20 bulbs for testing, which lasted for an average of 150 days, with a standard deviation of 40 days. If the CFL bulbs really last for 160 days , what is the probability that 20 random CFL bulbs would have an average life that’s less than 150 days?
How to find margin of error?
Margin of error = Critical value x Standard deviation of the statistic
What does null hypothesis mean?
The value of a null hypothesis implies that no statistical significance exists in a set of given observations. It is assumed to be true unless statistical evidence from an alternative hypothesis invalidates it.
What does critical value mean in a distribution graph?
Critical values divide a distribution graph into sections which indicate ‘rejection regions. ’. Basically, if a test value falls within a rejection region, it means an accepted hypothesis (referred to as a null hypothesis) must be rejected. And if the test value falls within the accepted range, the null hypothesis cannot be rejected.
Why is hypothesis testing important?
Moreover, hypothesis testing is crucial for the scientific and medical community because it is imperative for the advancement of theories and ideas. If you’ve come across research that studies behavior, then the study likely used hypothesis testing and sampling in populations.
What is the critical probability of 0.025?
1 - (0.05 / 2) = 1 - (0.025) = 0.975 is the critical probability (p*). In this case, the critical
What is cumulative probability?
probability. The cumulative probability is the likelihood that a random variable will be
How to calculate a conducted test?
conducted test. It can be calculating by dividing two mean squares. Mostly, it is used in
Why is critical value important in statistics?
In statistics, the critical value is vital for correctly reflecting a variety of features. In. addition to validity and accuracy, the critical value can be useful for disproving. hypotheses when they are tested. Understanding critical value and how to calculate it is.
What does sample size minus one mean?
The sample size minus one equals the degree of freedom (df). This implies that dividing
What is confidence level?
The confidence level shows the likelihood that a statistical parameter is also true for the
What is critical value?
Z critical values are the standard scores that may be calculated from a data collection.
What is standard deviation in statistics?
The standard deviation is the average amount of variability in your data set. It tells you, on average, how far each score lies from the mean.
What is critical value in statistics?
A critical value is the value of the test statistic which defines the upper and lower bounds of a confidence interval, or which defines the threshold of statistical significance in a statistical test.
What is statistical significance?
Statistical significance is a term used by researchers to state that it is unlikely their observations could have occurred under the null hypothesis of a statistical test. Significance is usually denoted by a p -value, or probability value.
How many values are within 1 standard deviation of the mean?
Around 68% of values are within 1 standard deviation of the mean.
What is the alpha value of a statistical test?
The alpha value, or the threshold for statistical significance, is arbitrary – which value you use depends on your field of study. In most cases, researchers use an alpha of 0.05, which means that there is a less than 5% chance that the data being tested could have occurred under the null hypothesis.
What are the two types of estimates of a population?
Using descriptive and inferential statistics, you can make two types of estimates about the population: point estimates and interval estimates. A point estimate is a single value estimate of a parameter. For instance, a sample mean is a point estimate of a population mean.
Why is homogeneity important in statistical analysis?
This is an important assumption of parametric statistical tests because they are sensitive to any dissimilarities. Uneven variances in samples result in biased and skewed test results.
What is a critical value?
In hypothesis testing, critical values are one of the two approaches which allow you to decide whether to retain or reject the null hypothesis. The other approach is to calculate the p-value.
How to calculate critical values?
The formulae for the critical values involve the quantile function, Q, which is the inverse of the cumulative distribution function ( cdf) for the test statistic distribution (calculated under the assumption that H₀ holds!): Q = cdf -1
What does Q F,D1,D2 stand for?
In the formulae below, Q F,d1,d2 stands for the quantile function of the F-distribution with (d 1, d 2) degrees of freedom:
What is the alternative hypothesis?
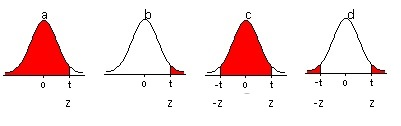
The alternative hypothesis determines what "at least as extreme" means. In particular, if the test is one-sided, then there will be just one critical value, if it is two-sided, then there will be two of them: one to the left and the other to the right of the median value of the distribution.
What is the ANOVA test?
ANOVA: tests the equality of means in three or more groups that come from normally distributed populations with equal variances. There are (k - 1, n - k) degrees of freedom, where k is the number of groups, and n is the total sample size (across every group).
When to use chi squared?
Use the χ² (chi-square) option when performing a test in which the test statistic follows the χ²-distribution . You need to determine the number of degrees of freedom of the χ²-distribution of your test statistic - below we list them for the most commonly used χ²-tests.
When to use t-student?
Use the t-Student option if your test statistic follows the t-Student distribution. This distribution is similar to N (0,1), but its tails are fatter - the exact shape depends on the number of degrees of freedom. If this number is large (>30), which generically happens for large samples, then the t-Student distribution is practically indistinguishable from N (0,1).

Hypothesis Testing and The Distribution Curve
Finding The Critical Value
- The standard equation for the probability of a critical value is: p = 1 – α/2 Where p is the probability and alpha(α)represents the significance or confidence level. This establishes how far off a researcher will draw the line from the null hypothesis. The alpha functions as the alternative hypothesis. It signifies the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true. For instanc…
Z Score Or T Score: Which Should You use?
- Typically, when a sample size is big (more than 40) using z or t statistics is fine. However, while both methods compute similar results, most beginner’s textbooks on statistics use the z score. When a sample size is small and the standard deviation of a population is unknown, the t score is used. The t score is a probability distribution that allows statisticians to perform analyses on sp…
Calculating Z Score
- The critical value of a z score can be used to determine the margin of error, as shown in the equations below: 1. Margin of error = Critical value x Standard deviation of the statistic 2. Margin of error = Critical value x Standard error of the statistic The z score, also known as the standard normal probability score, signifies how many standard deviations a statistical element is from th…
Calculating T Score
- On the other hand, here’s the standard formula for the t score: t = [ x – μ ] / [ s / sqrt( n ) ] Where, 1. x is the sample mean 2. μ is the population mean 3. s is the sample’s standard deviation 4. n is the sample size Then, we account for the degrees of freedom (df) which is the sample size minus 1. df = n – 1 T distribution, also known as the student’s distribution, is associated with a unique cu…
Why Is Determining Critical Value Important?
- Researchers often work with a sample population, which is a small percentage when they gather statistics. Working with sample populations does not guarantee that it reflects the actual population’s results. To test if the data is representative of the actual population, researchers conduct hypothesis testing which make use of critical values.
What Are Real-World Uses For It?
- Validating statistical knowledge is important in the study of a wide range of fields. This includes research in social sciences such as economics, psychology, sociology, political science, and anthropology. For one, it keeps quality managementin check. This includes product testing in companies and analyzing test scores in educational institutions. Moreover, hypothesis testing i…
The Bottom Line
- Finding critical values are important for testing statistical data. It’s one of the main factors in hypothesis testing, which can validate or disprove commonly accepted information. Proper analysis and testing of statistics help guide the public, which corrects misleading or dated information. Hypothesis testing is useful in a wide range of disciplines, such as medicine, sociol…