What is the difference between CSF and CSF count?
CSF is a clear fluid that is in the space around the spinal cord and brain. CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) is a clear fluid that circulates in the space surrounding the spinal cord and brain. A CSF cell count is a test to measure the number of red and white blood cells that are in CSF.
What does CSF stand for in anatomy?
What does CSF mean? CSF means cerebrospinal fluid. It is a clear, colorless fluid that is found only in the subarachnoid spaces that surrounds the brain and spine, and brain ventricles. Where is CSF absorbed? Reabsorption of cerebrospinal fluid into the bloodstream happens in structures located in the outer layer of the meninges.
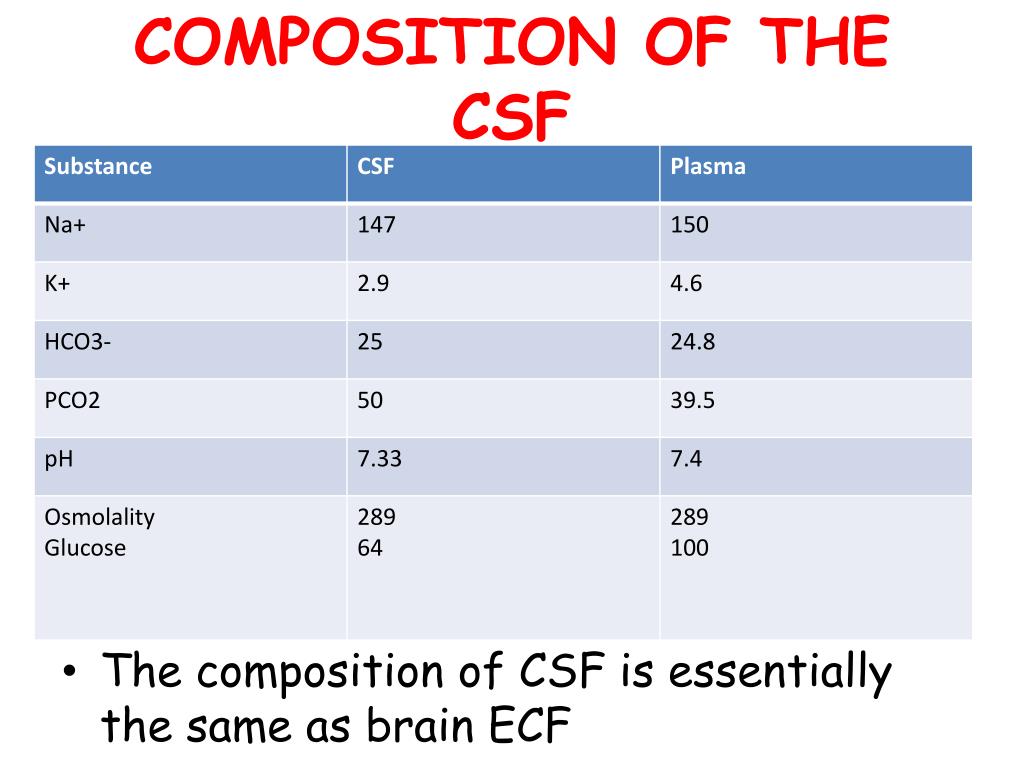
What is the composition of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
The composition of CSF is normally very consistent, except in cases of disease. Most cerebrospinal fluid is found in the subarachnoid spaces. The total volume of CSF in an adult is about 150 ml, but as much as 500 ml is produced daily as this fluid is constantly being used and cycled.
Where is the CSF located in the brain?
The CSF occupies the subarachnoid space (between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater) and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord. It fills the ventricles of the brain, cisterns, and sulci, as well as the central canal of the spinal cord.

What Are The Symptoms of CSF Leak?
Patients typically complain of clear, watery drainage usually from only one side of the nose or one ear. Drainage can increase with tilting the hea...
How Are CSF Leaks Diagnosed?
Your doctor will perform a history and physical exam. Often, the doctor will examine the nose with an endoscope. Your physician may also ask you to...
What Is The Treatment For A CSF Leak?
Treatment can be either medical or surgical. Conservative treatment is usually recommended first in cases of spontaneous CSF leak or head trauma. T...
What is the CSF?
Cerebrospinal fluid, the full name for CSF, is a sterile, clear, colorless fluid from filtrate of the blood containing ions: sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), chlorine (Cl-), and calcium (Ca++); protein; glucose; and other nutrients. It cushions, protects, nourishes, and detoxifies the brain.
What is CSF in the brain?
That's what the inside of your skull is like. But what's this fluid inside your skull? Cerebrospinal fluid, or CSF, is clear, colorless, and filtered from the blood by cells in the ventricles (fluid spaces).
What happens when CSF pressure rises?
When CSF pressure rises, the brain is compressed and the fluid must be removed. Often a device called a shunt is placed for this purpose. A number of diseases can be diagnosed by analysis of CSF, obtained by a lumbar puncture or spinal tap.
What is hydrocephalus in CSF?
Hydrocephalus is an abnormality of CSF volume. When absorption sites are blocked, absorption is slowed but production remains constant. This is communicating hydrocephalus and can occur when proteins or cells have caused a blockage (head trauma, bleeding in the brain, infection, or inflammation).
How is CSF pressure measured?
CSF pressure is measured by lumbar puncture (LP) or spinal tap. The skin is anesthetized and a thin needle is introduced below the end of the spinal cord, allowing removal of CSF without damaging the spinal cord. Elevated pressure usually indicates swelling, infection, or mass (tumor or clot).
What is the normal CSF protein?
Normal CSF glucose is usually 2/3 of blood glucose. Normal CSF protein is 15-60 mg/100 ml and contains no red blood cells (RBC) or clotting factors and only 0-3 white blood cells (or WBC). CSF is in a closed system, so pressure is an important component of analysis.
Where does CSF come from?
Cerebrospinal fluid, or CSF, is clear, colorless, and filtered from the blood by cells in the ventricles (fluid spaces). The body produces 500 ml/day, but reabsorption is slower, so only 100-150 ml is found circulating around the brain and spine. CSF flows from the ventricles to the subarachnoid space, which is a space between ...
What is a CSF cell count?
CSF cell count. Share. A CSF cell count is a test to measure the number of red and white blood cells that are in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF is a clear fluid that is in the space around the spinal cord and brain.
Why is CSF count important?
Why the Test is Performed. The CSF cell count may help detect: Meningitis and infection of the brain or spinal cord. Tumor, abscess, or area of tissue death (infarct) Inflammation.
What is the most common way to collect CSF?
A lumbar puncture (spinal tap) is the most common way to collect this sample. Rarely, other methods are used for collecting CSF such as:
What is CSF used for?
How is it used? Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis may be used to help diagnose a wide variety of diseases and conditions affecting the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system).
What is CSF testing?
What is being tested? Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, watery liquid that flows around the brain and spinal cord, surrounding and protecting them. A CSF analysis is a group of tests that evaluate substances in CSF in order to diagnose conditions affecting the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system).
Why is CSF testing important?
Because CSF surrounds the brain and spinal cord, testing a sample of CSF can be very valuable in diagnosing a variety of conditions affecting the central nervous system.
Why is CSF protein small?
CSF protein – only a small amount is normally present in CSF because proteins are large molecules and do not cross the blood/brain barrier easily. Decreases in CSF protein are not generally considered significant. Increases in protein are most commonly seen with:
How many ounces of CSF are produced in a day?
About 17 ounces (500 mL) are produced each day. This rate of production means that all of the CSF is replaced every few hours. A protective blood-brain barrier separates the brain from the bloodstream and regulates the distribution of substances between the blood and the CSF.
How is CSF produced?
CSF is formed and secreted by the choroid plexus, a special tissue that has many blood vessels and that lines the small cavities or chambers (ventricles) in the brain. It is continually produced, circulated, and then absorbed into the blood. About 17 ounces (500 mL) are produced each day.
When is CSF analysis ordered?
CSF analysis may be ordered when a health practitioner suspects that a person has a condition or disease involving their central nervous system. A person's medical history may prompt the request for CSF analysis. It may be ordered when someone has suffered trauma to the brain or spinal cord, has been diagnosed with cancer that may have spread into the central nervous system, or has signs or symptoms suggestive of central nervous system involvement.
Where is CSF manufactured?
CSF is manufactured continuously in areas of the brain called ventricles and is absorbed by the bloodstream. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services.
How rare are CSF leaks?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks are a rare event. Researchers estimate that they occur in about 5 in every 100,000 people. However, they also believe that this is an underestimate and that the true number of people affected remains unknown. They are mostly found in people in their 30s and 40s.
What is the best treatment for spinal CSF leaks?
Spinal CSF leaks. After conservative treatments have been tried, an epidural blood patch is the most common treatment for spinal CSF leaks. In this procedure, your own blood is injected into the spinal canal. The blood clot that forms creates a seal to stop the leak.
What causes cerebrospinal fluid to leak?
The following are other possible common causes: Head trauma or spine injury. Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) History of epidurals or spinal catheters. Certain head and spine surgeries.
What is the process of leaking cerebrospinal fluid?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak occurs when CSF escapes through a small tear or hole in the outermost layer of connective tissue (called the dura mater) that surrounds the brain and spinal cord and holds in the CSF. The tear or hole allows the CSF to leak out.
How to repair cranial CSF leak?
Repair of cranial CSF leaks depend on the size and the location of the leak. CSF leaks from your nose can usually be repaired using nasal endoscopy (using a camera and a thin long lens through your nostril). CSF leaks into your ear will usually need the use of a microscope.
What causes a headache when you lose CSF?
The tear or hole allows the CSF to leak out. The loss of CSF causes the previously cushioned brain to sag inside the skull, which results in a headache. Loss of fluid also causes a lowering of pressure within the skull, a condition called intracranial hypotension. CSF leaks can occur in the brain ...
Where is CSF found?
Cerebrospinal fluid ( CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates. It replaces the body fluid found outside the cells of all bilateral animals. The CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexuses of the ventricles of the brain, ...
What is the purpose of a CSF test?
Testing often includes observing the colour of the fluid, measuring CSF pressure , and counting and identifying white and red blood cells within the fluid; measuring protein and glucose levels; and culturing the fluid. The presence of red blood cells and xanthochromia may indicate subarachnoid hemorrhage; whereas central nervous system infections such as meningitis, may be indicated by elevated white blood cell levels. A CSF culture may yield the microorganism that has caused the infection, or PCR may be used to identify a viral cause. Investigations to the total type and nature of proteins reveal point to specific diseases, including multiple sclerosis, paraneoplastic syndromes, systemic lupus erythematosus, neurosarcoidosis, cerebral angiitis; and specific antibodies such as Aquaporin 4 may be tested for to assist in the diagnosis of autoimmune conditions. A lumbar puncture that drains CSF may also be used as part of treatment for some conditions, including idiopathic intracranial hypertension and normal pressure hydrocephalus.
How is CSF produced?
Firstly, a filtered form of plasma moves from fenestrated capillaries in the choroid plexus into an interstitial space , with movement guided by a difference in pressure between the blood in the capillaries and the interstitial fluid. This fluid then needs to pass through the epithelium cells lining the choroid plexus into the ventricles, an active process requiring the transport of sodium, potassium and chloride that draws water into CSF by creating osmotic pressure. Unlike blood passing from the capillaries into the choroid plexus, the epithelial cells lining the choroid plexus contain tight junctions between cells, which act to prevent most substances flowing freely into CSF. Cilia on the apical surfaces of the ependymal cells beat to help transport the CSF.
What causes CSF to leak?
CSF can leak from the dura as a result of different causes such as physical trauma or a lumbar puncture, or from no known cause when it is termed a spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leak. It is usually associated with intracranial hypotension: low CSF pressure. It can cause headaches, made worse by standing, moving and coughing, as the low CSF pressure causes the brain to "sag" downwards and put pressure on its lower structures. If a leak is identified, a beta-2 transferrin test of the leaking fluid, when positive, is highly specific and sensitive for the detection for CSF leakage. Medical imaging such as CT scans and MRI scans can be used to investigate for a presumed CSF leak when no obvious leak is found but low CSF pressure is identified. Caffeine, given either orally or intravenously, often offers symptomatic relief. Treatment of an identified leak may include injection of a person's blood into the epidural space (an epidural blood patch ), spinal surgery, or fibrin glue.
How does CSF protect the brain?
Protection: CSF protects the brain tissue from injury when jolted or hit, by providing a fluid buffer that acts as a shock absorber from some forms of mechanical injury. Prevention of brain ischemia: The prevention of brain ischemia is aided by decreasing the amount of CSF in the limited space inside the skull.
How much cerebrospinal fluid is produced in the brain?
The brain produces roughly 500 mL of cerebrospinal fluid per day , at a rate of about 25 mL an hour. This transcellular fluid is constantly reabsorbed, so that only 125–150 mL is present at any one time. CSF volume is higher on a mL/kg basis in children compared to adults.
What test is used to detect a CSF leak?
If a leak is identified, a beta-2 transferrin test of the leaking fluid, when positive, is highly specific and sensitive for the detection for CSF leakage. Medical imaging such as CT scans and MRI scans can be used to investigate for a presumed CSF leak when no obvious leak is found but low CSF pressure is identified.
What is the CSF?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless plasma-like fluid that bathes the central nervous system (CNS). Cerebrospinal fluid circulates through a system of cavities found within the brain and spinal cord; ventricles, subarachnoid space of the brain and spinal cord and the central canal of the spinal cord. Most CSF is secreted by the specialized tissue called the choroid plexus, which is located within the lateral, third and fourth ventricles. The secretion of CSF equals its removal, so there is around 150-270 milliliters of cerebrospinal fluid within the CNS at all times.
What is the CSF fluid?
Thus, the CSF fluid is not simply an ultrafiltrate of blood but differs from it in terms of its electrolyte, glucose and protein content.
How does CSF exit the subarachnoid space?
The CSF exits the subarachnoid space by diffusing through the walls of arachnoid granulations. The arachnoid granulations provide a valvular mechanism for the flow of CSF, which allows the inflow of CSF into the bloodstream without permitting the backflow of blood into the CSF. Normally the pressure of the CSF is higher than that of the venous system, so CSF flows through the villi and granulations into the venous blood.
How much CSF is produced in a day?
Cerebrospinal fluid is constantly produced at a secretion rate of 0.2-0.7 ml/min, meaning that there is 600–700 ml of newly produced CSF per day. Since the total volume of CSF averages around 150-270 mL, this means that the entire volume of CSF is replaced around 4 times per day.
Which system does CSF exit?
There are three recognized routes through which CSF exits the subarachnoid space (SAS) to enter the cerebral venous system; arachnoid granulations, minute channels that pass through the cribriform plate of ethmoid bone, and the glymphatic system.
Where is the most CSF secreted?
Most CSF is secreted by the specialized tissue called the choroid plexus, which is located within the lateral, third and fourth ventricles. The secretion of CSF equals its removal, so there is around 150-270 milliliters of cerebrospinal fluid within the CNS at all times.
Where is CSF obtained?
CSF is also very useful for clinical diagnosis, and its samples are usually obtained from the subarachnoid space (SAS) by lumbar puncture. This article will discuss the anatomy and functions of the cerebrospinal fluid flow. Key facts about cerebrospinal fluid flow. Secretion.