What is expected in recovering from a traumatic brain injury?
What to Expect During Brain Injury Recovery To maximize recovery outcomes, individuals should participate in rehabilitative therapies such as physical, occupational, and speech therapy as early as possible. Generally, the most recovery is seen within the first 6 months after brain injury.
What are the stages of brain injury recovery?
What are the 10 Recovery Stages After a Brain Injury?
- Coma. A coma allows the brain to heal; uninterrupted. ...
- Vegetative state. Comas and a vegetative state are not the same as they are different states of consciousness. ...
- Minimally Conscious. Patients may come in and out of consciousness when they are in this stage. ...
- Post-Traumatic Amnesia. ...
- Inappropriate Behaviors. ...
- Confusion. ...
- Automatic and Appropriate. ...
- Purposeful. ...
What are coup and contrecoup brain injuries?
The terms coup and contrecoup are French for “blow” and “counterblow.” Therefore, a coup-contrecoup injury actually refers to two separate brain injuries sustained during the same incident. A coup injury refers to the brain damage that occurs directly under the point of impact.
What are some examples of traumatic brain injuries?
What are some examples of traumatic brain injuries?
- Intracranial Hemotomas. Intracranial hematomas are the rupture of a blood vessel leading to the collection of blood in brain tissues or empty spaces. ...
- Skull Fractures. ...
- Contusions/Coup-Countrecoup. ...
- Diffuse Axonal Injury (DAI)

What are 5 CTE symptoms?
The symptoms of CTE include memory loss, confusion, impaired judgment, impulse control problems, aggression, depression, anxiety, suicidality, parkinsonism, and, eventually, progressive dementia. These symptoms often begin years or even decades after the last brain trauma or end of active athletic involvement.
What does CTE do to the brain?
In brains with CTE , researchers have found that there is a buildup of a protein called tau around the blood vessels. Tau buildup in CTE is different from accumulations of tau found in Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia. CTE is thought to cause areas of the brain to waste away (atrophy).
What is CTE life expectancy?
Some researchers believe the severity of the disease might correlate with the length of time a person spend participating in the sport. Unfortunately, a 2009 analysis of 51 people who experience CTE found the average lifespan of those with the disease is just 51 years.
Can CTE be treated?
There is no cure or treatment for CTE, but certain medicines may be used to temporarily treat the cognitive (memory and thinking) and behavioral symptoms. Consult your doctor before taking any prescription or over-the-counter medication.
At what age does CTE start?
Research suggests that people with CTE often begin to have symptoms years or even decades after the last brain injury or end of active participation in contact sports, although this can vary from person to person. Symptoms may start between the ages of 40 and 60 years old.
What are the 4 stages of CTE?
Going through the Stages of CTEStage I. This first stage is most commonly marked by headaches, and loss of attention and concentration. ... Stage II. Depression, moods swings, headache, and short-term memory loss top the list of most frequently experienced symptoms in Stage II. ... Stage III. ... Stage IV.
Does CTE show up on MRI?
While chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) cannot yet be diagnosed during life, a new study provides the best evidence to date that a commonly used brain imaging technique, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), may expedite the ability to diagnose CTE with confidence in the living.
Does CTE get worse with age?
The study's findings suggest that CTE begins as focal cortical lesions that evolve into a progressive neurodegeneration, and the disease worsens with age even in the absence of additional exposure to head trauma.
What causes death in CTE?
In CTE, a protein called tau misfolds and malfunctions, causes other proteins to misfold, and sets off a chain reaction where this malfunctioning tau slowly spreads throughout the brain, killing brain cells.
Can you live a normal life with CTE?
What is the outlook for people with chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE)? Many people who show signs of CTE live healthy and fulfilling lives. Regular exercise and good nutrition can help manage symptoms, including pain and stress. People can use many strategies to deal with behavioral symptoms associated with CTE.
What is it like living with CTE?
Symptoms of CTE include emotional instability, depression and memory loss. Doctors said the brain damage is more common than previously thought, and more work should be done to detect and treat it in its earliest stages. The NFL said it has pledged $200 million for research in the prevention and treatment of CTE.
What part of the body does CTE impact?
CTE usually begins gradually several years after receiving repetitive blows to the head or repeated concussions. The symptoms affect the functioning of the brain and eventually lead to dementia.
What part of the brain is affected by CTE?
The neuropathology of CTE is characterized by a focal perivascular deposits of p‐tau in the neocortex that appear to spread to affect the superficial layers of adjacent cortex, and eventually, the medial temporal lobe, diencephalon and brainstem in susceptible individuals.
Does CTE get worse over time?
CTE, however, is totally different. Instead of a single injury, it's a degenerative neurological condition, meaning that it gets worse over time, Manning said. The only common threads in these cases are that they involve brain damage and are commonly seen in contact sports like boxing and U.S. football.
Can CTE be reversed?
While CTE is neurodegenerative disease and there isn't a cure, the symptoms often associated with the condition – like depression or anxiety– can be treated. Nowinski urges those that believe they have symptoms to see their doctor because the situation isn't hopeless.
Is CTE reversible?
It's not reversible or curable. Mez says there can be no therapies to treat CTE until it can be diagnosed in living patients. However, some of the symptoms can be treated. For example, behavioral therapies can help treat mood changes.
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy Explained
The condition known as chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) was formerly believed to exist primarily among boxers, and was referred to as dementi...
Symptoms of Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy
The symptoms of CTE can be debilitating and may have life-changing effects for both the individual and for his or her family. Some of the most comm...
Diagnosing Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy
Brain Injury Research Institute doctors Bennet I. Omalu, M.D. and Julian Bailes, M.D. were the first to diagnose CTE in a professional football pla...
What are the symptoms of CTE?
Some of the most common include loss of memory, difficulty controlling impulsive or erratic behavior, impaired judgment, behavioral disturbances including aggression and depression, difficult with balance, and a gradual onset of dementia. An individual with CTE may mistakenly ascribe the symptoms to the normal process of aging, or might receive a wrong diagnosis due to the fact that many of the symptoms are similar to other conditions such as Alzheimer's or Parkinson's disease. CTE has been diagnosed in several notable cases which received widespread media attention, including the suicide deaths of NFL player Junior Seau, and professional wrestler Chris Benoit who committed suicide after murdering his wife and son.
What is CTE in boxing?
The condition known as chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) was formerly believed to exist primarily among boxers, and was referred to as dementia pugilistica. It is a progressive degenerative disease which afflicts the brain of people who have suffered repeated concussions and traumatic brain injuries, such as athletes who take part in contact ...
How many boxers have brain injuries?
87% of professional boxers have sustained a brain injury. 5% of soccer players sustain brain injuries as a result of their sport. 1.5 million Americans suffer from traumatic brain injuries. Traumatic brain injuries cause 1.5 times more deaths than AIDS.
What is the effect of tau protein on CTE?
Another aspect of CTE is that some areas of the brain experience an accumulation of tau protein, a substance which serves to stabilize cellular structure in the neurons but which may become defective and subsequently may cause major interference with the function of the neurons.
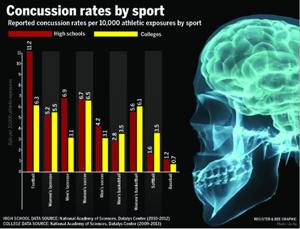
How many athletes sustain concussions yearly?
10% of all contact sport athletes sustain concussions yearly.
Where does the term "encephalopathy" come from?
The term encephalopathy derives from Ancient Greek en - "in," kephale "head," and patheia "suffering.". Chronic traumatic encephalopathy is a condition of brain damage which persists over a period of years or decades and which is the result of traumatic impacts to the cranium.
What are the most common sports that cause concussions?
Among children and youth ages 5-18 years old, the five leading sports or recreational activities which account for concussions include: bicycling, football, basketball, playground activities, and soccer. 10% of all contact sport athletes sustain concussions yearly.
How is CTE diagnosed?
CTE is only diagnosed definitively by studying brain tissue after death. Investigators are working to identify methods and biomarkers that would allow health care professionals to diagnose CTE In living subjects.
What is CTE in sports?
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy, or CTE, is a progressive degenerative disease affecting people who have suffered repeated concussions and traumatic brain injuries, that may occur in some athletes and others who have been exposed to concussions and repetitive head impacts.
What are the differences between CTE and Alzheimer's?
While both Alzheimer’s disease and CTE may present with similar symptoms, significant differences do exist between the two. Alzheimer’s disease typically presents with memory complaints and problems, whereas the initial symptoms of CTE are often problems with impaired judgement and reasoning, impulse control and aggression.
What are the symptoms of chronic trauma?
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy typically presents with several of the same symptoms seen in those who suffer from other kinds of dementia, including memory loss, aggression, confusion depression, impaired judgement, difficulty controlling impulses, erratic behavior, suicidal tendencies, anxiety, trouble sleeping, dizziness and trouble balancing.
Can a brain injury cause CTE?
Not everyone who has a brain injury or who has been exposed to repetitive head impacts develops CTE. In fact, at this time, research has not yet revealed how many or which individuals exposed to repetitive injuries will develop this condition.
How many head traumas does CTE have?
It is not known how many head traumas, or exactly what kinds, it takes for CTE to develop.
How to deal with CTE symptoms?
People can use many strategies to deal with behavioral symptoms associated with CTE. These include the following: Establish a daily routine.
What is CTE in sports?
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is generally thought of as a progressive (gradually increasing) degenerative (worsening) brain condition that is linked to repeated blows to the head over a long period of time. The condition has been found in athletes who take part in contact sports, military personnel exposed to repetitive blast injuries, ...
How long does it take for CTE symptoms to show?
Symptoms of CTE may not appear until many years after a person experiences the brain trauma. Some of the symptoms are similar to those of other degenerative brain conditions, like Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Symptoms of CTE can include: Headaches. Memory loss.
How to treat CTE after death?
Because CTE can only be diagnosed after the person has died, treatment can be challenging. Treatment for people who have symptoms of CTE include: Behavioral therapy to deal with mood swings. Pain management therapy, including medicines, massage and acupuncture, to relieve discomfort.
How to reduce CTE risk?
You can lessen your risk of CTE by reducing the number of times you take a hit to the head. Taking proper care of brain trauma when it occurs can also help prevent the condition. For athletes, this means coming out of the game after a head injury, resting, and following “return to play” guidelines.
What happens when you lose tau?
The loss of these cells can interfere with healthy brain function, causing neurological changes that include memory loss, depression, aggressiveness, and balance and movement problems.
What is CTE?
According to the Boston University CTE Center, Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) is a degenerative brain disease found in athletes, military veterans, and others with a history of repetitive brain trauma. Most of what we have learned about CTE has come from the research of Dr. Ann McKee, director of the VA-BU-CLF Brain Bank. In CTE, a protein called tau misfolds and malfunctions, causes other proteins to misfold, and sets off a chain reaction where this malfunctioning tau slowly spreads throughout the brain, killing brain cells. CTE has been seen in people as young as 17, but symptoms do not generally begin appearing until years after the onset of head impacts.
How does CTE happen?
The best available evidence tells us that CTE is caused by repetitive hits to the head sustained over a period of years. This doesn’t mean a handful of concussions; most people diagnosed with CTE suffered hundreds or thousands of head impacts over the course of many years playing contact sports or serving in the military.
Who is most at risk for CTE?
Every person diagnosed with CTE has one thing in common: a history of repetitive hits to the head. CTE is most frequently found in contact sport athletes and military veterans. CTE has been found in individuals whose primary exposure to head impacts was through tackle football (500+ cases confirmed at the VA-BU-CLF Brain Bank), the military (50+ cases), hockey (30+ cases), boxing (20+ cases, 50+ globally), rugby (10+ cases), soccer (5+ cases, 20+ globally), pro wrestling (5+ cases), and, in fewer than three cases each, baseball, basketball, intimate partner violence, and individuals with developmental disorders who engaged in head banging behaviors.
How is CTE diagnosed?
Currently, CTE can only be diagnosed after death through brain tissue analysis. Doctors with a specialty in brain diseases slice brain tissue and use special chemicals to make the abnormal tau protein visible. They then systematically search areas of the brain for tau in the unique pattern specific to CTE. The process can take several months to complete, and the analysis is not typically performed as a part of a normal autopsy. In fact, until recently there were relatively few doctors who knew how to diagnose CTE.
When was CTE first discovered?
CTE was first described in 1928, when Dr. Harrison Martland described a group of boxers as having “punch drunk syndrome.” Over the next 75 years, several researchers reported similar findings in boxers and other victims of brain trauma, but fewer than 50 cases were confirmed. In 2005, a pathologist named Bennet Omalu published the first evidence of CTE in an American football player: former Pittsburgh Steeler Mike Webster. The publication caught the attention of CLF co-founder Dr. Chris Nowinski, who envisioned the world’s first athlete brain bank. Nowinski began reaching out to the families of NFL players and other athletes who had recently passed away to arrange brain donation. He and Dr. Robert Cantu soon founded the Concussion Legacy Foundation and partnered with Boston University and the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs to form the VA-BU-CLF Brain Bank, led by Dr. Ann McKee. The Brain Bank has revolutionized how we understand the disease, with more than 1,000 brains donated, about two-thirds of which have been found to have CTE.
How long does it take to get CTE?
The process can take several months to complete, and the analysis is not typically performed as a part of a normal autopsy. In fact, until recently there were relatively few doctors who knew how to diagnose CTE.
When do symptoms of CTE appear?
Among individuals diagnosed with CTE, some report mood and behavior symptoms that can appear as early as the patient’s 20s. Common changes seen include: