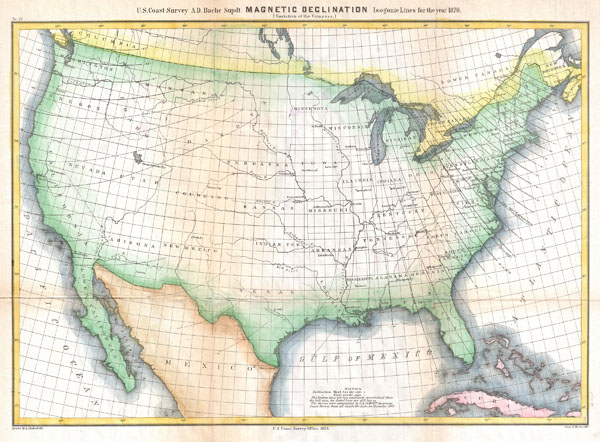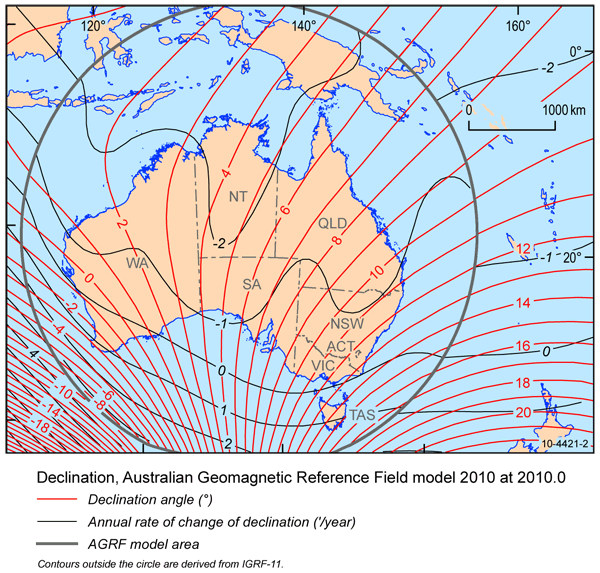
Magnetic Declination Magnetic declination (sometimes called magnetic variation) is the angle between magnetic north and true north. Declination is positive when this angle is east of true north and negative when it is west.
How do you calculate declination?
How do you find declination angle? The following equation can be used to calculate the declination angle: δ=−23.45°×cos (360/365× (d+10)) where the d is the number of days since the start of the year The declination angle equals zero at the equinoxes (March 22 and September 22), positive during the summer in northern hemisphere and ...
Can magnetic field create current?
When a conductor is placed in a changing magnetic field, the electrons in the conductor move, generating an electric current. Magnets produce such magnetic fields and can be used in various configurations to generate electricity.
What is the effect of magnetic declination?
These moving magnetic poles continually effect navigation. It's more serious for airplanes and ships, but even for hikers and backpackers, it causes problems. Using a 10 or 15 year old map is a bad idea since the declinations are no longer accurate.
How often does magnetic declination changes?
The secular variation of the magnetic field causes declination to change with time. Changes in declination can be quite large. At Yellowknife, NWT, for example, the declination is changing by more than one degree every three years. On the other hand, at Ottawa, the yearly change in declination is almost zero.

What is the current magnetic variation UK 2022?
5º over 5 years. It continued to decrease to zero degrees at Greenwich in 2019 and has now headed West by about 0. 5º. There are a couple of degrees variation between the most easterly and westerly points of the UK.
What is the current compass declination?
Answer: -4.82° (-5°49')
What is meant by magnetic declination?
At most places on the Earth's surface, the compass doesn't point exactly toward geographic north. The deviation of the compass from true north is an angle called "declination" (or "magnetic declination").
What is current magnetic variation?
Magnetic declination, or magnetic variation, is the angle on the horizontal plane between magnetic north (the direction the north end of a magnetized compass needle points, corresponding to the direction of the Earth's magnetic field lines) and true north (the direction along a meridian towards the geographic North ...
Do I add or subtract magnetic declination?
Whenever you transfer a magnetic bearing taken in the field to your map, you add the magnetic declination to get the true bearing. (Note that a west declination is, in essence, subtracted because you are adding a negative number.)
Why do we calculate magnetic declination?
We need to calibrate our compass so that it compensates for the angle between magnetic and geographic north, referred to as declination. This allows us to use the compass needle, which points at magnetic north, to navigate along a path referenced to true north.
How many degrees off is true north?
0 degreesAn azimuth value of 0 degrees signifies true north, pointing directly towards the geographical North Pole. Similarly, 180 degrees is the direction from the selected location to the geographic South Pole.
How do you calculate declination?
The following equation can be used to calculate the declination angle: δ=−23.45°×cos(360/365×(d+10)) where the d is the number of days since the start of the year The declination angle equals zero at the equinoxes (March 22 and September 22), positive during the summer in northern hemisphere and negative during winter ...
How do you find declination?
The degrees of declination for an area are usually located on the bottom margin of the map near the north arrow, or they can be located using a declination chart.
What is the difference between magnetic variation and declination?
The terms variation and declination refer to the same feature. On a map refer to it as declination. On a chart refer to it as variation. Magnetic declination, also called variation, is the difference between true north and magnetic north.
What is negative declination?
When located east of the 0° line, the declination is west (or negative). To translate the difference between the geographic and magnetic meridian, the angle of declination must be subtracted from the magnetic north reading.
What causes declination?
Magnetic declination is caused by the complex shape of the Earth's magnetic field. Magnetic declination refers to the use of a compass with its needle pointing north for navigation.
What is my true north declination?
Remove the compass from the map. With the compass in your hand, turn your whole body until the compass needle points to the magnetic declination of +12°. At this point, you have aligned your compass, which means the north marking on the compass is pointing at true north.
How many degrees off is true north?
0 degreesAn azimuth value of 0 degrees signifies true north, pointing directly towards the geographical North Pole. Similarly, 180 degrees is the direction from the selected location to the geographic South Pole.
What is the declination in Los Angeles?
The magnetic declination in Los Angeles is 13 degrees east. New York City is 13 degrees west. If you are lucky enough to be lost just west of the Mississippi River on the agonic line where the declination is zero, then magnetic north and true north are the same, so your compass reads true north.
What is the declination of Dallas Texas?
Answer: +2.82° (3°49')
Common Questions
You can compute the true bearing from a magnetic bearing by adding the magnetic declination to the magnetic bearing. This works as long as you follow the convention that degrees west are negative (i.e. a magnetic declination of 10-degrees west is -10 and bearing of 45-degrees west is -45).
Access Tools
This map displays historical isogonic lines and magnetic poles calculated for the years 1590–2025.
What is the declination of the magnetic field in the Arctic?
In the Arctic, the magnetic declination is largely a result of that distance. For example, a compass positioned between the magnetic and the geographical North Pole will point due south, towards the magnetic pole and away from the geographical pole, amounting to a magnetic declination of around 180°.
Which cities have a magnetic declination of 0?
Cities like New Orleans and Minneapolis are situated very close to an agonic line, meaning that the magnetic declination is close to 0, so a compass actually shows true north there. The same is true for Paris, France. In general, western Europe has a comparatively small declination, which ranges from -1 to 4 degrees.
What is the declination of the compass?
In locations on the east coast, the magnetic declination is about 10–13 degrees west. Cities like New Orleans and Minneapolis are situated very close ...
How many degrees is the declination of the North Pole?
However, the actual declination at that longitude is between 10 and 20 degrees on the equator. In practice, following a compass to the magnetic North Pole will get you there – but not via the shortest route.
Why is the magnetic declination on the meridian south of the magnetic North Pole 0?
Without these variations, the magnetic declination on the meridian south of the magnetic North Pole would be 0 because both the magnetic and the geographical poles are due north. However, the actual declination at that longitude is between 10 and 20 degrees on the equator.
What is the difference between a western and eastern declination?
A western declination is usually stated as a negative value while an eastern declination is represented by a positive value. For example, in Florida, magnetic north currently lies around 5 degrees west of true north, so the Sunshine State has a magnetic declination of -5°. Trying to figure out a compass heading for the true-north directions shown ...
How to convert a north heading to a compass?
To convert this true north heading to a compass heading, you have to subtract 11° from 44°, so the sunrise occurs at 33° on your compass. Example for locations with negative (western) declination: In New York, the sunrise on July 1 is at 58° each year. New York has a declination of roughly -13°.
What is the declination of the magnetic field?from ngdc.noaa.gov
Magnetic declination, sometimes called magnetic variation, is the angle between magnetic north and true north. Declination is positive east of true north and negative when west. Magnetic declination changes over time and with location. As the compass points with local magnetic fields, declination value is needed to obtain true north.. more
How to measure magnetic declination?from en.wikipedia.org
The magnetic declination at any particular place can be measured directly by reference to the celestial poles —the points in the heavens around which the stars appear to revolve, which mark the direction of true north and true south. The instrument used to perform this measurement is known as a declinometer .
What is the magnetic azimuth of a runway?from en.wikipedia.org
Runways are designated by a number between 01 and 36, which is generally one tenth of the magnetic azimuth of the runway's heading: a runway numbered 09 points east (90°), runway 18 is south (180°), runway 27 points west (270°) and runway 36 points to the north (360° rather than 0°). However, due to magnetic declination, changes in runway designators have to occur at times to keep their designation in line with the runway's magnetic heading. An exception is made for runways within the Northern Domestic Airspace of Canada; these are numbered relative to true north because proximity to the magnetic North Pole makes the magnetic declination large and changes in it happen at a high pace.
What is magnetic deviation?from en.wikipedia.org
Magnetic deviation is the angle from a given magnetic bearing to the related bearing mark of the compass. Deviation is positive if a compass bearing mark (e.g., compass north) is right of the related magnetic bearing (e.g., magnetic north) and vice versa. For example, if the boat is aligned to magnetic north and the compass' north mark points 3° more east, deviation is +3°. Deviation varies for every compass in the same location and depends on such factors as the magnetic field of the vessel, wristwatches, etc. The value also varies depending on the orientation of the boat. Magnets and/or iron masses can correct for deviation, so that a particular compass accurately displays magnetic bearings. More commonly, however, a correction card lists errors for the compass, which can then be compensated for arithmetically. Deviation must be added to compass bearing to obtain magnetic bearing.
What is magnetic north?from en.wikipedia.org
A magnetic compass points to magnetic north, not geographic north. Compasses of the style commonly used for hiking include a declination adjustment in the form of a bezel which swivels relative to the base plate. To establish a declination the bezel is rotated until the desired number of degrees plus or minus lie between the bezel's designation N (for North) and the direction indicated by the magnetic end of the needle (usually painted red). This allows the user to establish a true bearing for travel or orientation by aligning the embossed red indicator arrow on the base plate with a landmark or heading on a map. A compass thus adjusted can be said to be reading “true north” instead of magnetic north (as long as it remains within an area on the same isogonic line).
How to compensate for magnetic declination when reading a compass?from en.wikipedia.org
In this example, the declination is 14°E (+14°), so the compass card points to a "north" 14 degrees to the East of true North. To obtain a true bearing, add 14 degrees to the bearing shown by the compass.
How to determine the north celestial pole?from en.wikipedia.org
In the northern hemisphere, declination can therefore be approximately determined as the difference between the magnetic bearing and a visual bearing on Polaris . Polaris currently traces a circle 0.73° in radius around the north celestial pole, so this technique is accurate to within a degree. At high latitudes a plumb-bob is helpful to sight Polaris against a reference object close to the horizon, from which its bearing can be taken.
How to compensate for magnetic declination when reading a compass?from en.wikipedia.org
In this example, the declination is 14°E (+14°), so the compass card points to a "north" 14 degrees to the East of true North. To obtain a true bearing, add 14 degrees to the bearing shown by the compass.
What is magnetic deviation?from en.wikipedia.org
Magnetic deviation is the angle from a given magnetic bearing to the related bearing mark of the compass. Deviation is positive if a compass bearing mark (e.g., compass north) is right of the related magnetic bearing (e.g., magnetic north) and vice versa. For example, if the boat is aligned to magnetic north and the compass' north mark points 3° more east, deviation is +3°. Deviation varies for every compass in the same location and depends on such factors as the magnetic field of the vessel, wristwatches, etc. The value also varies depending on the orientation of the boat. Magnets and/or iron masses can correct for deviation, so that a particular compass accurately displays magnetic bearings. More commonly, however, a correction card lists errors for the compass, which can then be compensated for arithmetically. Deviation must be added to compass bearing to obtain magnetic bearing.
What is magnetic north - and why is it different to true north?from rmg.co.uk
True north is a fixed point on the globe. Magnetic north is quite different.
How are compasses used to navigate?from rmg.co.uk
For navigators at sea, one of the most important things is to find your direction. In the open ocean, there are no landmarks or signposts to help navigate, so you have to know which way you are heading.
Do ships still use compasses today?from rmg.co.uk
Right now, ships navigate using GPS and a highly sophisticated system of satellites that are constantly monitoring the journeys of ships across the ocean.
What is the magnetic azimuth of a runway?from en.wikipedia.org
Runways are designated by a number between 01 and 36, which is generally one tenth of the magnetic azimuth of the runway's heading: a runway numbered 09 points east (90°), runway 18 is south (180°), runway 27 points west (270°) and runway 36 points to the north (360° rather than 0°). However, due to magnetic declination, changes in runway designators have to occur at times to keep their designation in line with the runway's magnetic heading. An exception is made for runways within the Northern Domestic Airspace of Canada; these are numbered relative to true north because proximity to the magnetic North Pole makes the magnetic declination large and changes in it happen at a high pace.
What are isogonic lines?from en.wikipedia.org
Isogonic lines are lines on the Earth's surface along which the declination has the same constant value, and lines along which the declination is zero are called agonic lines. The lowercase Greek letter δ (delta) is frequently used as the symbol for magnetic declination.
How to measure magnetic declination?
The magnetic declination at any particular place can be measured directly by reference to the celestial poles —the points in the heavens around which the stars appear to revolve, which mark the direction of true north and true south. The instrument used to perform this measurement is known as a declinometer .
How often does the declination of a magnetic field change?
The magnetic declination in a given area may (most likely will) change slowly over time, possibly as little as 2–2.5 degrees every hundred years or so, depending upon how far from the magnetic poles it is. For a location closer to the pole like Ivujivik, the declination may change by 1 degree every three years.
How to determine the north celestial pole?
In the northern hemisphere, declination can therefore be approximately determined as the difference between the magnetic bearing and a visual bearing on Polaris . Polaris currently traces a circle 0.73° in radius around the north celestial pole, so this technique is accurate to within a degree. At high latitudes a plumb-bob is helpful to sight Polaris against a reference object close to the horizon, from which its bearing can be taken.
How often does the declination change?
For a location closer to the pole like Ivujivik, the declination may change by 1 degree every three years. This may be insignificant to most travellers, but can be important if using magnetic bearings from old charts or metes (directions) in old deeds for locating places with any precision.
What is the angle between the magnetic and geographic meridians at any place, expressed in degrees and minutes east or west?
This angle varies depending on position on the Earth's surface and changes over time . Somewhat more formally, Bowditch defines variation as “the angle between the magnetic and geographic meridians at any place, expressed in degrees and minutes east or west to indicate the direction of magnetic north from true north.
What is the difference between N g and N m?
N g is geographic or true north, N m is magnetic north, and δ is magnetic declination. Magnetic declination, or magnetic variation, is the angle on the horizontal plane between magnetic north (the direction the north end of a magnetized compass needle points, corresponding to the direction of the Earth's magnetic field lines) ...
Why are sectional charts based on true north and south?
Aviation sectional charts (maps) and databases used for air navigation are based on true north and south because the planetary rotational poles do not change location on the landscape anywhere near as much as do the magnetic poles. That said, low-tech ways of identifying true north or south include waiting for noon with a stick in the ground to judge the shortest shadow, or waiting for a clear night in order to consult a pole star. By contrast, with a low-tech magnetic compass, one can identify magnetic north or south at any time, hence the presence of a magnetic compass in every cockpit, even today in the GPS era. When onboard electronics fail, pilots can still rely on paper charts and Edwardian-era instruments such as a magnetic compass. There is still the need to convert magnetic to true, however. Sectional charts indicate by dashed magenta lines the number of degrees variation between true and magnetic at any local vicinity as of the printing of that chart. Since the true locations of the magnetic poles meander over time, occasionally quite dramatically, charts and databases are required to be updated at least twice each year. Another reason for frequent chart updates is construction (new tall radio towers, runway renovation, etc.).
How much does the declination of a magnetic field change over time?
The magnetic declination in a given area will change slowly over time, possibly as much as 2-25 degrees every hundred years or so, depending upon how far from the magnetic poles it is.
What is the angle between the magnetic north and the true north?
The direction in which the compass needle points is known as Magnetic North, and the angle between Magnetic North and the True North direction is called magnetic declination. Magnetic declination varies both from place to place, and with the passage of time.
Why are declination values constantly changing?
Unfortunately because of secular variation, declination values are constantly changing. When printed maps were the only way of getting this information, the declination values were somewhat out of date by the time the maps got to the general public. Another way would be to perform a prediction. This should be based on a world-wide empirical model ...
Is NDGC a good declination model?
This web page operated by the National Geophysical Data Center (NDGC) offers a pretty good value for declination. The model reflects a highly predictable rate of change, and will usually be more accurate than a map, and almost never less accurate.
Is declination positive or negative?
If the compass at your place is pointing counter-clockwise with respect to the True North, declination is negative or WEST. Negative declination ( WEST)
Where is the magnetic declination of North America?
In North America, magnetic declination varies from 30 degrees East in Alaska to 20 degrees West in Labrador, Maine. The degrees of declination for an area are usually located on the bottom margin of the map near the north arrow, or they can be located using a declination chart. 1.
How to correct for declination?
For Easterly Declination, subtract the declination from the true reading to obtain the magnetic reading. Magnetic = true - easterly declination. 2. For Westerly Declination, add the declination to the true reading to obtain the magnetic reading. Magnetic = true + westerly declination.
What is the magnetic reference for Earth?
The magnetic reference for Earth is north regardless of whether you are traveling north or south. Magnetic declination, or declination, is the difference between the true north reading from the map and the magnetic north reading from a compass.