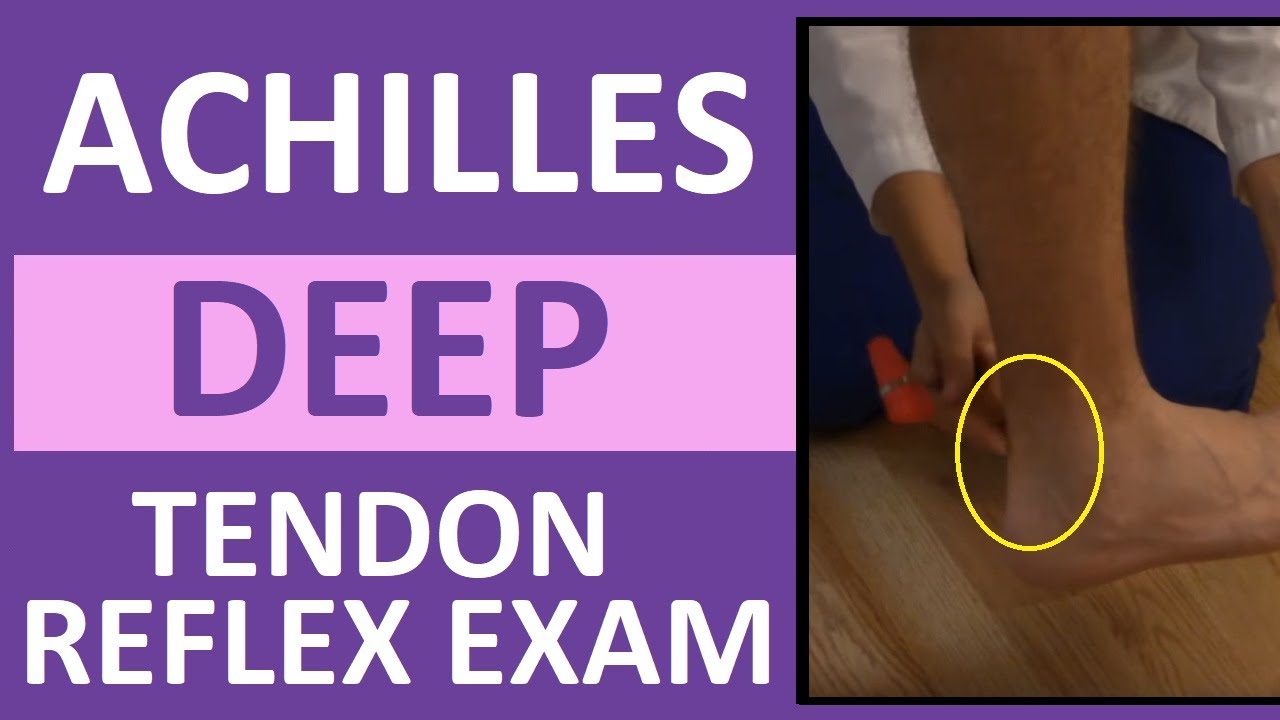
How to assess deep tendon reflexes?
Technique:
- In a supine patient, place the knee and hip in a partially flexed position by placing one hand beneath the knee to stretch the tendon while ensuring the limb is ...
- In a sitting patient, have the legs dangling with the heels resting on the floor. ...
- Palpate the patellar ligament
- Tap the tendon with the broad end of the Taylor hammer
What do deep tendon reflexes indicate?
What do deep tendon reflexes indicate? Deep tendon reflex also usually refers to this sense. A deep tendon reflex is often associated with muscle stretching. Tendon reflex tests are used to determine the integrity of the spinal cord and peripheral nervous system, and they can be used to determine the presence of a neuromuscular disease.
What is decreased deep tendon reflexes?
What does decreased deep tendon reflexes mean? Unilateral absence of a deep tendon reflex implies disease at the peripheral nerve or root level. Diffuse reduction or absence of deep tendon reflexes suggests a more generalized process affecting the peripheral nerve, seen frequently in peripheral neuropathies secondary to diabetes, alcohol abuse, or inflammation.
What are hyperactive deep tendon reflexes?
What are hyperactive deep tendon reflexes? Dr. David Rosenfeld answered Pain Management 27 years experience See below: A DTR is a brisk contraction of a muscle in response to a sudden stretch induced by a sharp tap by a finger or rubber hammer on the tendon of insertio... Read More 5.4k views Answered >2 years ago Thank 1 thank
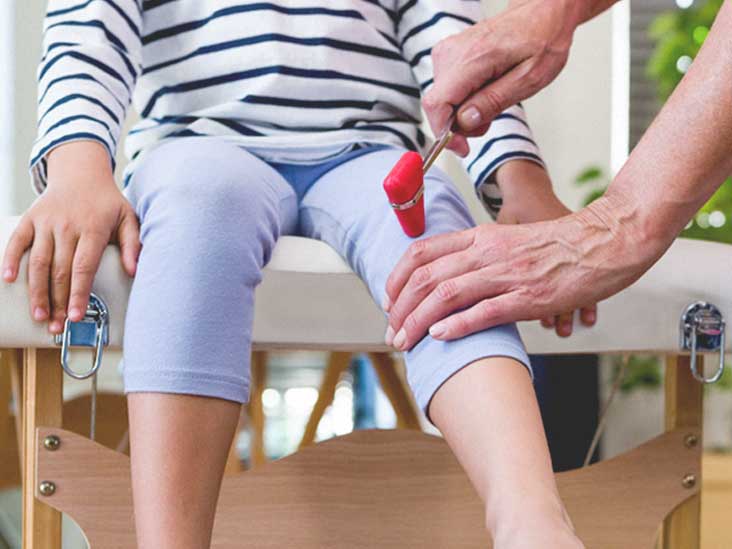

How does a deep tendon reflex work?
The DTR is a monosynaptic reflex arc. It is monosynaptic because only two neurons are involved: a sensory and a motor neuron, with a single synapse. After the examiner taps the muscle's tendon, the muscle fibers' stretch is detected at the muscle spindle located within the muscle fibers.
What is a deep tendon reflex assessment?
0:239:04Deep Tendon Reflex Examination for Nursing Head to Toe Assessment of ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe bicep the triceps the brachioradialis. The patellar and the Achilles. And in order to do thisMoreThe bicep the triceps the brachioradialis. The patellar and the Achilles. And in order to do this you will need a reflex hammer and this is what a common reflex hammer looks like. So you may be asking
What are deep tendon reflexes examples?
2:476:48Deep Tendon Reflexes (Stanford Medicine 25) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWe're going to do the brachioradialis reflex. It's important to tap on the tendon. And not theMoreWe're going to do the brachioradialis reflex. It's important to tap on the tendon. And not the muscle. And to look at the muscle for contraction. Rather than looking for the movement. So even though
What does it mean if deep tendon reflexes are absent?
If your doctor taps on a tendon and there isn't a reflexive movement in the muscle, it's a sign of a health issue. Usually, absent reflexes are caused by an issue with the nerves in the tendon and muscle. You may have other muscle symptoms along with areflexia, like weakness, twitching, or atrophy.
Why are deep tendon reflexes important?
Tendon reflexes are important because they provide an objective sign indicating abnormality and some indication as to the level of the abnormality. Reflexes can be graded as absent, obtainable with reinforcement (see below), reduced, normal, increased and increased with clonus.
How does the nurse assess deep tendon reflexes?
To perform deep reflex tendon testing, place the patient in a seated position. Use a reflex hammer in a quick striking motion by the wrist on various tendons to produce an involuntary response.
What are the 4 types of reflexes?
We have different types of reflexes in the body. Four key examples are the stretch reflex, the flexor reflex, the crossed-extensor reflex, and the Golgi tendon reflex.
What causes loss of deep tendon reflexes?
Peripheral neuropathy is today the most common cause of absent reflexes. The causes include diseases such as diabetes, alcoholism, amyloidosis, uremia; vitamin deficiencies such as pellagra, beriberi, pernicious anemia; remote cancer; toxins including lead, arsenic, isoniazid, vincristine, diphenylhydantoin.
What does it mean if you don't have a reflex in your knee?
What does it mean if I don't have a knee-jerk reflex? If your knee doesn't kick out when the patellar tendon is tapped, it's called Westphal's sign. The lack of a reaction is usually a sign of neurological problems specifically related to the peripheral nervous system.
Why do doctors hammer your knee?
The reflex that the doctor checks by tapping your knee is called the patellar, or knee-jerk, reflex. It is also known as a deep tendon reflex (DTR) because the doctor is actually tapping on a tendon called the patellar (say: puh-TEL-ur) tendon.
What are deep tendon reflexes and how are they graded?
By convention the deep tendon reflexes are graded as follows: 0 = no response; always abnormal. 1+ = a slight but definitely present response; may or may not be normal. 2+ = a brisk response; normal.
What do deep tendon reflexes assess quizlet?
A reflex is a motor response to a sensory stimulation that is used in an assessment to observe the integrity of the nervous system. They elicit a muscle contraction when the muscle's tenon is stimulated.
What do abnormal reflexes indicate?
Different types of reflexes can be signs of serious disorders related to the nervous system. Spinal cord injuries are most likely to cause these unusual reflexes, but other disorders that can result in abnormal reflexes include brain tumors, brain trauma, stroke, meningitis, or spinal cord injuries.
What are the 4 types of reflexes?
We have different types of reflexes in the body. Four key examples are the stretch reflex, the flexor reflex, the crossed-extensor reflex, and the Golgi tendon reflex.
What is the DTR in neurology?
The DTR is used to assess the integrity of the motor system. They also provide information on the condition of upper and lower motor neurons. The DTR depends on the integrity of both the upper motor neuron and the lower motor neuron. If a patient has an injury or a disease involving a lower motor neuron (nerve roots or peripheral nerves), a decrease or loss of the reflex will be noted. If the lesion or injury involves the upper motor neuron (brain, brainstem, or spinal cord), an increased reflex will be present. In severe chronic cases, usually associated with spasticity, clonus can be seen. It is common in stroke, spinal cord injury, cerebral palsy, and multiple sclerosis.[20] It can also occur after ingesting a large amount of serotonergic drugs.
What is a DTR test?
The deep tendon reflex (DTR) examination is part of the neurologic exam. They were first described by Wilhelm Heinrich Erb and Carl Friedrich Otto Westphal more than a century ago.[1] Their use continues to this day. The presence of hyporeflexia or hyperreflexia may indicate an underlying disease. Proper technique and interpretation of results are crucial to help in the diagnosis of many upper and lower motor neuron pathologic processes such as multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, spinal cord injuries, spinal muscular atrophies, among others. They are sometimes referred to as muscle stretch reflexes.
What reflex is used in neurological examination?
Applying the extensor digitorum reflex to neurological examination.
How to perform patellar reflex?
For the tricep reflex, the patient's arm should be held and suspended by the examiner at 90 degrees. Gravitational force is usually sufficient. The patellar reflex is performed with the patient sitting and legs hanging free over the chair's edge. If no visible response occurs, the examiner places his hand over the patient's ipsilateral quadriceps muscle and tries to feel a contraction; the Jendrassik maneuver helps elicit this reflex. The same position is used for the ankle reflex. Tapping the Achilles tendon will elicit a response.
What causes an absent reflex in the ankle?
If the reflex is absent, other findings are usually present secondary to the lower motor neuron disease. They include muscle atrophy, weakness, and sometimes fasciculations. If it is an isolated reflex deficit, it is most commonly the result of a root lesion, a peripheral nerve injury or entrapment, or a mononeuropathy.[21] If several reflexes are involved, peripheral neuropathy is the probable etiology. Bilateral absent ankle jerk usually indicates a peripheral neuropathy, but a cauda equina syndrome can also produce it. [21]
What causes reflexes to decrease?
Decreased reflexes present in lower motor neuron lesions, including nerve root lesions with radiculopathy and peripheral nerve lesions. Diabetes and hypothyroidism slow down the response of the DTR. If absent when initially tested, the response can be elicited with repetitive tapping of the tendon; however, this maneuver sometimes causes extinguishment of the reflex. Muscle disease may cause the reflex to become diminished as the muscle fiber can not respond adequately. A patient with a spinal cord injury presenting spinal shock can have hyporeflexia. Cerebellar disease can also produce hyporeflexia. If the reflexes decrease bilaterally, it is often a normal finding.
What is the role of stretch reflex?
[14][18] It probably plays an important role in maintaining muscle tone and upright posture. The cerebral cortex and possible brainstem nuclei produce influence in the muscle spindle through the gamma motor neurons. [13][15][17][19] Dorsal spinocerebellar tracts carry the information from the spinal cord to the cerebellum.
What is reflex exam?
Reflex Exam (Deep Tendon Reflexes) The reflex exam is fundamental to the neurological exam and important to locating upper versus lower motor neuron lesions. There are five deep tendon reflexes and a number of superficial and visceral reflexes covered here.
What does significant if asymmetric mean?
Significant if asymmetric–usually signifies a UMN lesion on the absent side.
Is grading reflexes useful?
We are not big believers in grading reflexes ( grading muscle power is much more useful). Nevertheless, if you need something beyond “absent,” “present,” “brisk,” or “hyperactive” then use below. If you have a hyperactive reflex don’t forget to look for clonus.
Can you evaluate reflexes?
Reflexes are useful for the general internist to perform, but you can’t evaluate them if …. You don’t have a hammer. You don’t use proper technique, in which case the reflex will appear to be absent when it is present. If you don’t know what abnormalities to expect and what they mean.
Can you add videos to your watch history?
Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations. To avoid this, cancel and sign in to YouTube on your computer.
What neuron innervates the Golgi tendon?
In a normal person, when a muscle tendon is tapped briskly, the muscle immediately contracts due to a two-neuron reflex arc involving the spinal or brainstem segment that innervates the muscle. The afferent neuron whose cell body lies in a dorsal root ganglion innervates the muscle or Golgi tendon organ associated with the muscles; the efferent neuron is an alpha motoneuron in the anterior horn of the cord. The cerebral cortex and a number of brainstem nuclei exert influence over the sensory input of the muscle spindles by means of the gamma motoneurons that are located in the anterior horn; these neurons supply a set of muscle fibers that control the length of the muscle spindle itself.
What happens when a tendon is tapped?
In a normal person, when a muscle tendon is tapped briskly, the muscle immediately contracts due to a two-neuron reflex arc involving the spinal or brainstem segment that innervates the muscle.
Which neuron innervates the muscle?
In a normal person, when a muscle tendon is tapped briskly, the muscle immediately contracts due to a two-neuron reflex arc involving the spinal or brainstem segment that innervates the muscle. The afferent neuron whose cell body lies in ...
What is the term for an absent or diminished response to tapping?
Hyporeflexiais an absent or diminished response to tapping. It usually indicates a disease that involves one or more of the components of the two-neuron reflex arc itself.
What does "1+" mean in math?
1+ = a slight but definitely present response; may or may not be normal. 2+ = a brisk response; normal. 3+ = a very brisk response; may or may not be normal. 4+ = a tap elicits a repeating reflex (clonus); always abnormal.
Which part of the brain controls the sensory input of the muscle spindles?
The cerebral cortex and a number of brainstem nuclei exert influence over the sensory input of the muscle spindles by means of the gamma motoneurons that are located in the anterior horn; these neurons supply a set of muscle fibers that control the length of the muscle spindle itself.
Is 1 + 3 + reflex normal?
Whether the 1 + and 3 + responses are normal depends on what they were previously, that is, the patient's reflex history; what the other reflexes are; and analysis of associated findings such as muscle tone, muscle strength, or other evidence of disease. Asymmetry of reflexes suggests abnormality.
What scale is used to grade reflexes?
Reflexes are graded based on amplitude. Various scales have been used to grade reflexes. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) Muscle Stretch Reflex Scale is frequently used and empirically supported[6]:
What is the term for deep tendon reflexes?
This article will focus on the “deep tendon reflexes” which are more appropriately named — and will be referred to herein — as muscle stretch reflexes (MSR).
Why are reflexes used in physical examination?
Several types of reflexes can be tested as part of a physical examination and these all reveal something about the status of the elements of the nervous system that contribute to their functioning . They have been used for over a century as part of a routine neurological examination due to their safety, low cost, predictive value, and ability to be performed rapidly, even without specialized equipment.
What are the different types of reflex hammers?
The most commonly used specialized reflex hammers are grouped into 3 types by the shape of the head: triangular/tomahawk shaped (Taylor), T-shaped (Tromner, Buck), or circular (Queen Square, Babinski). Each is effective at provoking reflexes, with the Taylor being possibly less favorable at eliciting more stubborn (hyporeflexia) reflexes. [2]
How to strike patellar tendon?
The technique may vary slightly depending on what type of tool is used or what reflex is being tested, for instance, circular hammers can be "dropped" passively through an arc using gravity to strike the patellar tendon, but when striking the biceps tendon are generally swung like a drumstick. In any case, the tendon’s axis is generally struck perpendicular to the plane of the hammer (if the hammer has a flat edge), meaning if you are striking the vertically oriented patellar tendon in a seated patient the rim of the tool will generally be horizontal and parallel to the floor. A stethoscope should be held 1 inch from the stem, on the tubing, and swung in a short arc.[3] If a patient is hyperreflexic, a clinician’s finger may be all that is needed because the forces needed are so slight. With any tool, a finger can be placed on the tendon to help guide the clinician's blow to the correct location, to help feel the contraction, and to reduce discomfort for the patient by cushioning the blow. This is most commonly done when eliciting the biceps reflex.
How to test for bicep reflex?
This may require supporting the distal component of the joint (for instance, when testing the biceps reflex, the elbow will naturally hang limply at nearly 180 degrees of extension but can be supported to approximately 90 degrees while remaining fully relaxed by placing it on the patient’s thigh if seated, or by supporting it in a clinician’s arm). The infant’s heads should be positioned midline when assessing any reflex.
What does "reflex small" mean?
1: Reflex small, less than normal; includes a trace response or a response brought out only with reinforcement
What is reflex exam?
Reflex Exam (Deep Tendon Reflexes) The reflex exam is fundamental to the neurological exam and important to locating upper versus lower motor neuron lesions. There are five deep tendon reflexes and a number of superficial and visceral reflexes covered here.
What does significant if asymmetric mean?
Significant if asymmetric–usually signifies a UMN lesion on the absent side.
Is grading reflexes useful?
We are not big believers in grading reflexes ( grading muscle power is much more useful). Nevertheless, if you need something beyond “absent,” “present,” “brisk,” or “hyperactive” then use below. If you have a hyperactive reflex don’t forget to look for clonus.
Can you add videos to your watch history?
Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations. To avoid this, cancel and sign in to YouTube on your computer.
Where Do You Tap?
Once you realize the simplicity of deep reflexes, knowing all the possible places to find them is the next challenge. Although there are many locations to elicit the stretch reflex, this article focuses on common locations for assessing reflexes in high-risk obstetric patients. FIGURE 2, FIGURE 3, FIGURE 4, FIGURE 5, FIGURE 6, FIGURE 7 show tendon locations, associated muscle groups, limb positioning, and proper use of the reflex hammer.
How Do You Tap?
Once the tendon is located, six basic principles must be followed to correctly elicit a deep reflex response . Understanding these principles will help the nurse achieve accuracy and expertise.
How to do a patellar knee jerk reflex?
Accessibility coupled with easy palpation makes the patellar or knee jerk reflex the most commonly assessed lower extremity reflex. To elicit a response with the patient lying in bed, the nurse bends the patient’s knee slightly using his or her nondominant hand while using the other hand to palpate the tendon. Bending the knee gently stretches the tendon in preparation for the tap. Proper support of the limb will ensure good relaxation. The practitioner lightly taps the tendon with the broad edge of the reflex hammer (see Figure 4 ). Stimulation of the muscle from the patellar tendon causes the quadriceps muscle to contract and the leg extends. The quadriceps muscle is by far the largest muscle group of all the deep reflexes to be stimulated; therefore, the biggest response comes from this muscle.
Why are regional blocks important?
Because regional blocks disable the reflex arc’s ability to send a message to move the limb via the efferent pathway, it would be useful to determine if the reappearance of DTRs (after an epidural is discontinued) is a reliable indicator of ability to ambulate. Research would establish how much motor control returns when the patient still has hyporeflexia or has normoreflexia. At what point can the patient safely ambulate? How much motor control (as measured by tendon reflexes) should be required before attempting ambulation? Many times nurses have had to catch patients who fall when getting up for the first time after giving birth. Nurses should document the return of reflexes before discharging patients from the recovery area or before ambulation if an association exists between the presence of reflexes and returning motor control.
What is the difference between deep and superficial reflexes?
The difference between the two is not with the reflex arc, because both deep and superficial reflexes involve the action of the reflex arc. They differ in where the receptor organ, which initially starts the reflex arc, is embedded.
Why do spinal cord injuries have deep reflexes?
Because the reflex arc is a localized response involving the limb-spinal cord-limb arc , clients with spinal cord injuries still have deep reflexes. The signal generating from the muscle spindle runs up the lower extremity, jumps across one side of the spinal cord to the other, and races down the leg telling the muscle to contract. Unfortunately, because the cord is severed, there is no communication between the cerebral cortex and the spinal cord; neither voluntary muscle movement nor inhibitory signals reach the spinal cord. These patients typically exhibit hyperreflexia.
What is the structure of deep reflexes?
With deep reflexes, an internal structure (i.e., a tendon) stretches and stimulates the receptors in the muscle group. The aroused receptors initiate the reflex arc, causing the muscle to move. Deep reflexes include patellar, Achilles, plantar, triceps, and biceps reflexes.
