
Definition of Demand
- 1) Demand is a relative concept.
- 2) Demand is essentially expressed with reference to time and price. Types of Demand in Economics 1) Direct demand It is the demand by the consumer for goods that satisfy their wants directly. They serve direct consumption needs of the consumers. Thus, it is the demand for consumer goods. For example, demand for cloth, sugar, etc. 2) Indirect demand ...
What are the different types of demand?
Types of demand
- Joint demand. Joint demand is the demand for complementary products and services. ...
- Composite demand. Composite demand happens when there are multiple uses for a single product. ...
- Short-run and long-run demand. ...
- Price demand. ...
- Income demand. ...
- Competitive demand. ...
- Direct and derived demand. ...
What are the different types of demand patterns?
Types of Demand in Marketing | 8 Types of demands with examples
- NEGATIVE DEMAND. The first type of demand is Negative demand. ...
- UNWHOLESOME DEMAND. The second type of demand in economics is unwholesome demand. ...
- NON-EXISTING DEMAND. The third type of demand in economics is known- existing demand. ...
- LATENT DEMAND. ...
- DECLINING DEMAND. ...
- IRREGULAR DEMAND. ...
- FULL DEMAND. ...
- OVERFULL DEMAND. ...
What are the types of demand function?
What are the types of demand function?
- Negative demand- Consumers dislike the product and may even pay a price to avoid it. (Hospitals, Life Insurance)
- Nonexistent demand – Consumers may be unaware or uninterested in the product. (Pager, Typewriter)
- Latent demand – Consumers may share a strong need that cannot be satisfied by an existing product. ...
What are the difference types of demand in economics?
- i. Individual and Market Demand: Refers to the classification of demand of a product based on the number of consumers in the market. ...
- ii. Organization and Industry Demand: Refers to the classification of demand on the basis of market. ...
- iii. ...
- iv. ...
- v. ...
What is demand in economics?
Demand refers to the willingness or effective desire of individuals to buy a product supported by their purchasing power. In economics, Demand is generally classified based on various factors, such as the number of consumers for a given product, the nature of products, the utility of products, and the interdependence of different demands.
What is individual demand?
In dividual demand refers to the quantity of a commodity or service demanded by an individual consumer at a given price at a given time period. For example, the quantity of sugar that an individual or household purchases in ...
What is the difference between market demand and individual demand?
On the other hand, Market demand is the aggregate of individual demands of all the consumers of a product over a period of time at a specific price while other factors are constant.
What is price demand?
Price Demand is a demand for different quantities of a product or service that consumers intend to purchase at a given price and time period a ssuming other factors, such as prices of the related goods, level of income of consumers, and consumer preferences, remain unchanged.
What happens when the price of one commodity rises?
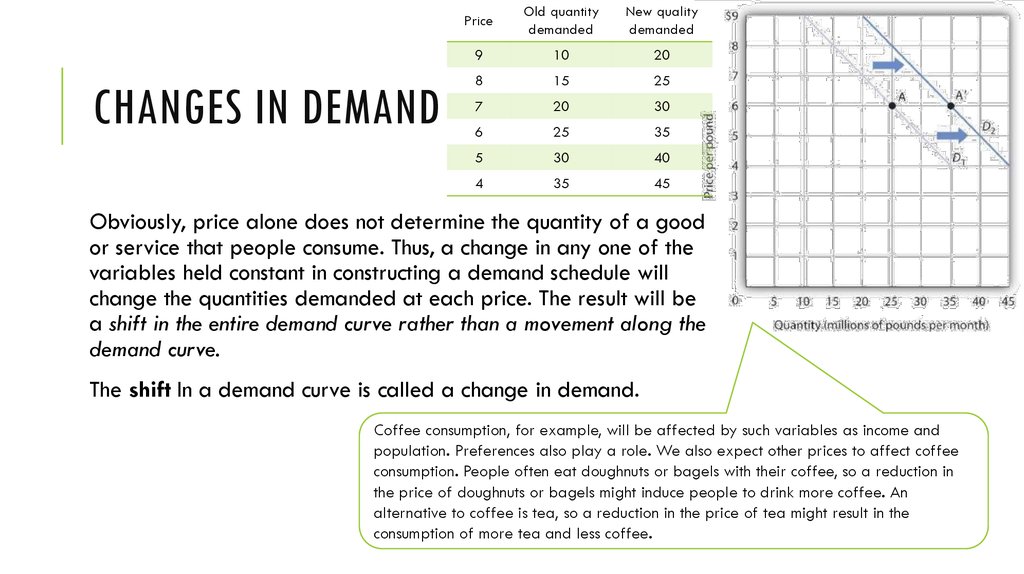
However, in the case of joint demand, rise in the price of one commodity results in the fall of demand for the other commodity. In the above example, an increase in the price of cars will cause a fall in the demand of not only of cars but also of petrol.
What are some examples of commodities?
For example, car and petrol, bread and butter, pen and refill, etc. are commodities that are used jointly and are demanded together. The demand for such commodities changes proportionately. For example, a rise in the demand for cars results in a proportionate rise in the demand for petrol.
What is geektonight team?
Geektonight is a vision to provide free and easy education to anyone on the Internet who wants to learn and grow in their career. We are working towards bringing the entire study routine of students on the Internet.
What is Demand in Economics?
Demand in Economics is an economic principle can be defined as the quantity of a product that a consumer desires to purchase goods and services at a specific price and time.
How does price demand relate to price?
Price demand is inversely proportional to the price of a commodity or service. As the price of a commodity or service rises, its demand falls and vice versa.
What factors influence the demand for a product?
Factors such as the price of the product, the standard of living of people and change in customers’ preferences influence the demand. The demand for a product in the market is governed by the Laws of Economics
How does credit policy affect demand?
Credit policy: The credit policy of suppliers or banks also affects the demand for a commodity. Size and composition of the population: An increase in the size of a population increases the demand for commodities as the number of consumers would increase.
What is demand in terms of a time period?
Demand is always referred in terms of a time period and bears no meaning if it is not expressed in relation to a time period. For example, a garment manufacturer has a demand for 200 metres of cloth in a month or 2400 metres of cloth in a year. A statement referring to demand for a commodity or service must include the following three key factors: ...
Why is demand important?
Demand is considered the basis of the entire process of economic development, hence demand plays an important role in the economic, social and political fields. The importance of demand are: Importance in Consumption. Advantageous to producers.
What is the demand for anything at a given price?
According to Benham “ The demand for anything at a given price, is the amount of it which will be bought per unit of time at that price. ”
Why is latent demand not realized?
Latent demand has not been active, cannot be observed, or has not been realized. It appeared for several reasons. First, consumers want a product, but they don’t have the money to buy it. Thus, their wishes are not realized. Or they have hidden and undisclosed desires. It requires marketers to dig deep through marketing research.
How to calculate current demand?
We can calculate it by multiplying the total number of buyers by the average quantity or value purchased from each buyer.
Why do consumers choose their brands over competing brands?
Promotion to create secondary demand leads to brand competition. Companies compete with each other to highlight their respective brands and try to create preferences . Thus, consumers choose their brands over competing brands.
What is demand in economics?
This article will discuss the types of demand. What is a demand? Economists define it as the willingness and ability of consumers to buy goods at any given price. Willingness means we want things. Ability means we have the money (resources) to buy.
How many units of a product is needed at $10?
For example, at the current price of $10, the consumer is willing to buy 10 units of the product. If there are 3,000 consumers in the market, the current demand is 30,000 units. If the price changes, the volume will also change.
How does our desire to buy goods lead to demand?
In other words, our desire to buy goods leads to demand if it is backed by the ability to buy. And, if we have enough money, it will lead to demand if we spend it on the things we want.
Why is a product not available?
Second, consumers want a product. However, the product is not available because it has not been produced or is under-produced. Thus, the product is not available in their vicinity.
Demand
Demand refers to the willingness or effective desire of individuals to buy a product supported by their purchasing power. Here effective desire is the quantity of a commodity or service that is purchased at a given time period at a given price from the market.
Types of Demand
It is a demand for different quantities of a commodity or service that consumers intend to purchase at a given price and time period assuming other factors, such as prices of the related goods, level of income of consumers, and consumer preferences, remain unchanged.
Factors Affecting Demand
There is an inverse or we can say negative relationship between the price of a product and the amount of that product consumers are willing and able to buy.
General FAQ
Demand refers to the willingness or effective desire of individuals to buy a product supported by their purchasing power. Here effective desire is the quantity of a commodity or service that is purchased at a given time period at a given price from the market.
What is the difference between negative demand and unwholesome demand?
They both have almost same elements except there is a single difference between the two which is in negative demand, a consumer doesn’t feel the urge or requirement to buy the product but in unwholesome demand consumer badly wants the product but shouldn’t desire or take the decision to buy it.
What are the types of demand?
Types of demand also called classification of demand. There are 8 types of demand or classification of demand. 8 Types of demands in Marketing are Negative Demand, Unwholesome demand, Non-Existing demands, Latent Demand, Declining demand, Irregular demand, Full demand, Overfull demand. Full Detail in Blog.
Why is demand negative?
The product is good in quality, affordability and many other things but its demand is going negative because the customer doesn’t need it. In such cases, it is very difficult for the marketer to sell the product to its customers.
What does declining demand mean?
Declining demand as the name suggests means the demand for the product whose demand is declining with time. It depends on product to product. It may be due to a new invention in that particular product field, bad brand marketing or decreasing the quality of the product. There are various products like technological products in which the coming ...
What is the second type of demand?
The second type of demand in economics is unwholesome demand. If negative demand is the head, Unwholesome demand is the tail. Another face of negative demand is unwholesome demand.
What does it mean when a company keeps producing a certain product thinking that there is the demand for the product in?
It means if a company keeps producing a certain product thinking that there is the demand for the product in the market , it will end up suffering huge losses because people will not purchase their product which results in losing both market share and reputation of the brand.
Why is brand equity affected by demand?
The brand equity of the company is highly affected in this type of demand due to which sometimes companies use De- marketing techniques to decrease the demand for their product so that the sales can match the demand.
