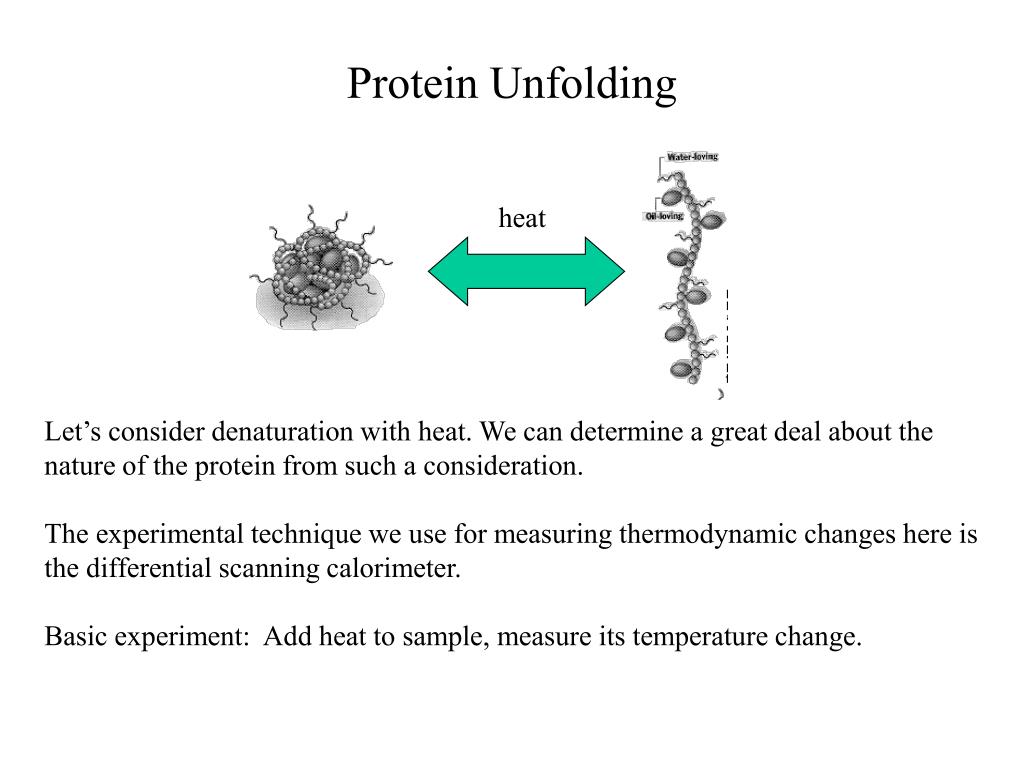
Can the process of denaturation be reversed?
Reversing Denaturation It is often possible to reverse denaturation because the primary structure of the polypeptide, the covalent bonds holding the amino acids in their correct sequence, is intact. However, denaturation can be irreversible in extreme situations, like frying an egg.
What is denaturing and what causes it to occur?
What conditions denature proteins quizlet?
- Denaturation. refers to the physical changes that take place in protein exposed to abnormal conditions in the environment.
- Heat/Temperature. Disrupts H-bonds and hydrophobic interactions between non-polar reactions. …
- Acid/Bases. …
- Organic Compounds. …
- Heavy Metal Ions. …
- Agitation.
Is denaturation an irreversible process?
Under these pH conditions the temperature denaturation is irreversible and coupled to aggregation and precipitation. This process is often seen by the appearance of an exothermic heat effect immediately following the endothermic denaturation peak.
What is Protein denaturing and why is it bad?
- For proteins to be utilized by the body, they need to be metabolized, or broken down to amino acids.
- We have enzymes or proteases to break down protein molecules into amino acid residues that are further utilized by the human body.
- When partially digested food reach the gut, the acidic environment is already going to have an impact on the struc
1. What is the process to turn egg whites from clear to white?
Objects like eggs change colour when exposed to heat or high temperature. The protein structure conforms to the most important component of a livin...
2. Name the factors that cause denaturation of proteins?
Various reasons cause the denaturation of protein. Some of them are an increased temperature that ruptures the protein molecules' structure, change...
3. How is the process of denaturation of proteins important to human beings?
The process of denaturation is extremely important to live beings. When we ingest food, and it goes to our stomach, the acids present over there, t...
What is denaturation in biology?
Note 2: Denaturation can occur when proteins and nucleic acids are subjected to elevated temperature or to extremes of pH, or to nonphysiological concentrations of salt, organic solvents, urea, or other chemical agents.
Which method of denaturation provides faster denaturation?
Studies comparing different denaturation methods such as heating, beads mill of different bead sizes, probe sonification, and chemical denaturation show that chemical denaturation can provide quicker denaturation compared to the other physical denaturation methods described.
How are nucleic acids synthesized?
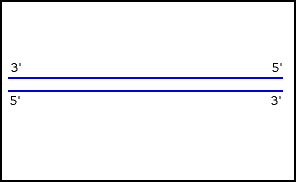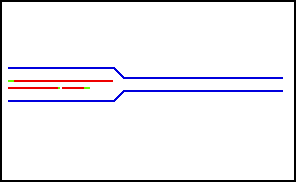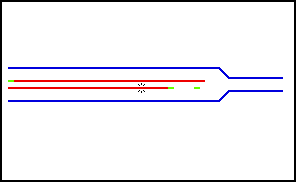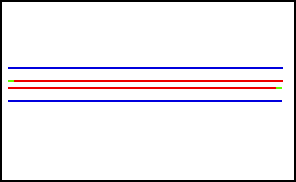
Nucleic acids (including RNA and DNA) are nucleotide polymers synthesized by polymerase enzymes during either transcription or DNA replication . Following 5'-3' synthesis of the backbone, individual nitrogenous bases are capable of interacting with one another via hydrogen bonding, thus allowing for the formation of higher-order structures. Nucleic acid denaturation occurs when hydrogen bonding between nucleotides is disrupted, and results in the separation of previously annealed strands. For example, denaturation of DNA due to high temperatures results in the disruption of Watson and Crick base pairs and the separation of the double stranded helix into two single strands. Nucleic acid strands are capable of re-annealling when " normal " conditions are restored, but if restoration occurs too quickly, the nucleic acid strands may re-anneal imperfectly resulting in the improper pairing of bases.
What happens to albumin in eggs?
(Top) The protein albumin in the egg white undergoes denaturation and loss of solubility when the egg is cooked. (Bottom) Paperclips provide a visual analogy to help with the conceptualization of the denaturation process.
What is the effect of temperature on enzyme activity?
Denaturation (biochemistry) The effects of temperature on enzyme activity. Top - increasing temperature increases the rate of reaction ( Q10 coefficient ). Middle - the fraction of folded and functional enzyme decreases above its denaturation temperature. Bottom - consequently, an enzyme's optimal rate of reaction is at an intermediate temperature.
What are the characteristics of denatured proteins?
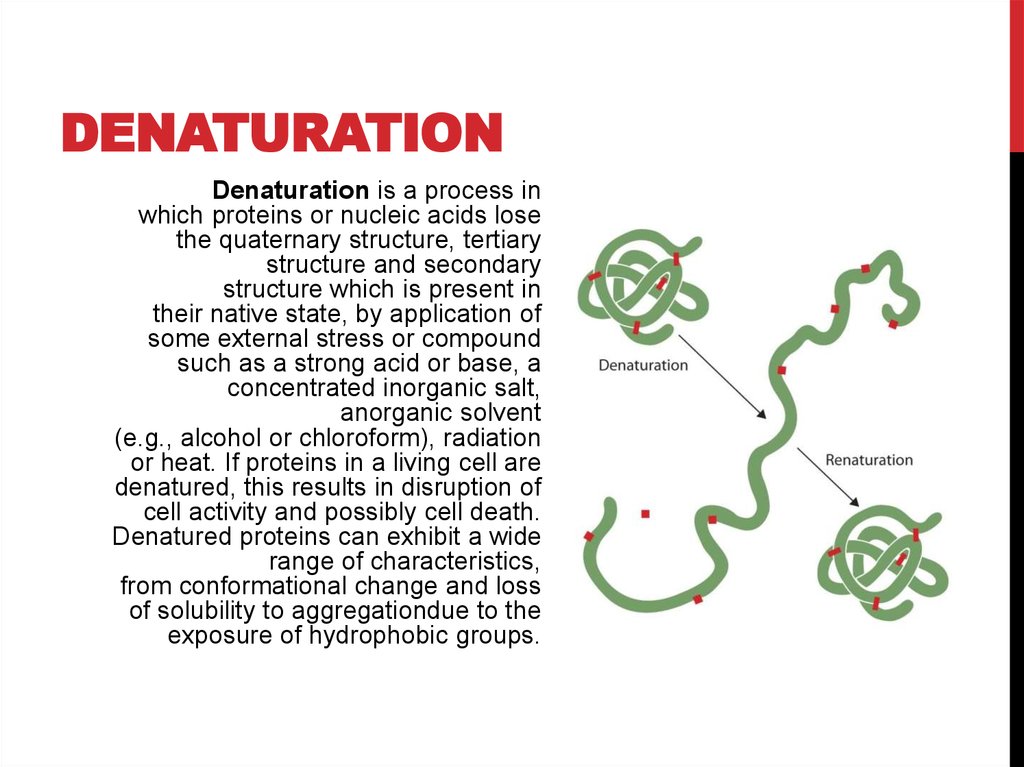
Denatured proteins can exhibit a wide range of characteristics, from conformational change and loss of solubility to aggregation due to the exposure of hydrophobic groups. Denatured proteins lose their 3D structure and therefore cannot function.
Why do amino acids denaturate?
Protein denaturation due to pH. Denaturation can also be caused by changes in the pH which can affect the chemistry of the amino acids and their residues. The ionizable groups in amino acids are able to become ionized when changes in pH occur. A pH change to more acidic or more basic conditions can induce unfolding.
Why is denaturation important?
When we ingest food, and it goes to our stomach, the acids present over there, that is, HCL breaks down the protein molecule components so that the body can easily consume the nutrition. Without breaking the secondary and tertiary protein structure, facilitate the working ability of pepsin enzymes to convert it into peptides. Thus, digestion would not have been properly possible without denaturation of proteins.
What causes denaturation of proteins?
Causes of Denaturation of Proteins 1 Temperature maintains stability to a great extent. The heat can disrupt hydrogen bonds and non-polar hydrophobic interactions. When heat is applied, it causes the molecules to vibrate, and it increases the kinetic energy, which disrupts the molecular structure. 2 Due to certain changes in the pH level, temperature, and chemical structure, the hydrogen bonds are disrupted, which results in the unfolding of globular proteins and uncoiling of the helix structure. Thus, the denaturation of proteins takes place, and the secondary and the tertiary structures are destroyed. Heavy salts disrupt the protein molecule structure in the same manner as the salts and the bases. 3 Denaturation breaks the covalent bonds and disrupts the amino acid chains. For instance, alcohol of a very high concentration can disrupt the hydrogen bonding in amide groups in the secondary or tertiary protein structure in various amino acid combinations.
How does denaturation affect protein?
Heavy salts disrupt the protein molecule structure in the same manner as the salts and the bases. Denaturation breaks the covalent bonds and disrupts the amino acid chains. For instance, alcohol of a very high concentration can disrupt the hydrogen bonding in amide groups in the secondary or tertiary protein structure in various amino acid ...
What is the process of breaking down the bonds that make up a protein?
Denaturation of protein is a process that breaks down the strong links or bonds that makes up the protein molecules. Protein molecules in their native or natural form have strong bonds and a highly ordered and stable structure.
What happens to the hydrogen bonds in a protein?
Due to certain changes in the pH level, temperature, and chemical structure, the hydrogen bonds are disrupted, which results in the unfolding of globular proteins and uncoiling of the helix structure. Thus, the denaturation of proteins takes place, and the secondary and the tertiary structures are destroyed.
Why do proteins denaturate?
Various reasons cause denaturation of protein. Some of them are an increased temperature that ruptures the protein molecules' structure, changes in pH level, adding of heavy metal salts, acids, bases, protonation of amino acid residues, and exposure to UV light and radiation.
Can denaturation be reversed?
Most of the denaturation process cannot be reversed. However, there is a certain exception in which the process could be reversed, called the renaturation of proteins. For instance, when milk is curdled, it turns into a semi-solid substance called curd due to the molecules' rapid movement and the increase in kinetic energy.
What is the Denaturation of Protein?
Proteins are complex molecules made of amino acids. They are present in all organisms and play a vital role in cellular functions and processes. Denaturation of proteins occurs when the secondary and tertiary structure of a protein is altered and the protein is no longer capable of performing its function.
The Structure of Proteins
Proteins are composed of very long strands of amino acids linked together by covalent peptide bonds. Once the strands are formed, they fold into a 3-D shaped protein. The shape of the 3-D protein is determined by the amino acid sequence. Hydrophobic elements do not mix with water. These elements of the protein get buried inside the 3-D shape.
What Happens When a Protein is Denatured?
Reactions that occur during denaturing are not strong enough to disrupt the peptide bonds found in the primary structure of a protein. Denaturing can, however, affect both the secondary and tertiary structure of a protein.
Denaturation in Action
Denaturation of proteins causes the protein structure to degrade and subsequently the protein loses its shape. As you read in the lesson, an egg is a great model for protein denaturation because the white is composed mostly of the protein albumin.
Protein Denaturation process
Proteins can be a large molecule that is found in the body and food having tiny materials called the amino acids.
Cause of denaturation of proteins
The shape of the protein cab be a good reason for having the protein denatured and is mostly for external causes.
Loss of function
Most of the biological substrates gets to lose all the biological activity when gets denatured.
Loss of activity for the use of heavy metalloids and the metals
By getting to target the proteins the heavy metals have been called to disrupt the use of the proteins activity that they carry on.
Reversibility and Irreversibility
In many cases, denaturation is reversible like the proteins can regain their native state when the denaturing influence is removed. This process can be called renaturation.
Denaturation of protein for change in pH
Denaturation is the legit method of getting to break the bond of the proteins so that they can be changed in its shape and form.
What is the purpose of detergents?
Detergents break the protein-protein, protein-lipid and lipid-lipid associations, denature proteins.
Is denaturation reversible?
In many cases, denaturation is reversible (the proteins can regain their native state when the denaturing influence is removed). This process is called renaturation. It could be complete or partial.
Overview
Denaturation is a process in which proteins or nucleic acids lose the quaternary structure, tertiary structure, and secondary structure which is present in their native state, by application of some external stress or compound such as a strong acid or base, a concentrated inorganic salt, an organic solvent (e.g., alcohol or chloroform), agitation and radiation or heat. If proteins in a living cell are denatured, this results in disruption of cell activity and possibly cell death. Protein denaturation i…
Common examples
When food is cooked, some of its proteins become denatured. This is why boiled eggs become hard and cooked meat becomes firm.
A classic example of denaturing in proteins comes from egg whites, which are typically largely egg albumins in water. Fresh from the eggs, egg whites are transparent and liquid. Cooking the thermally unstable whites turns them opaque, forming an interconnected solid mass. The same t…
Protein denaturation
Denatured proteins can exhibit a wide range of characteristics, from loss of solubility to protein aggregation.
Proteins or polypeptides are polymers of amino acids. A protein is created by ribosomes that "read" RNA that is encoded by codons in the gene and assemble the requisite amino acid combination from the genetic instruction, in a process known as translation. The newly created protein strand t…
Nucleic acid denaturation
Nucleic acids (including RNA and DNA) are nucleotide polymers synthesized by polymerase enzymes during either transcription or DNA replication. Following 5'-3' synthesis of the backbone, individual nitrogenous bases are capable of interacting with one another via hydrogen bonding, thus allowing for the formation of higher-order structures. Nucleic acid denaturation occurs when hydrogen bonding between nucleotides is disrupted, and results in the separation of previously annealed st…
Denaturants
Acidic protein denaturants include:
• Acetic acid
• Trichloroacetic acid 12% in water
• Sulfosalicylic acid
Bases work similarly to acids in denaturation. They include:
See also
• Denatured alcohol
• Equilibrium unfolding
• Fixation (histology)
• Protein folding
• Random coil
External links
• McGraw-Hill Online Learning Center — Animation: Protein Denaturation