What is dense collagenous connective tissue? Dense connective tissue, also called dense fibrous tissue, is a type of connective tissue with fibers as its main matrix element. The fibers are mainly composed of type I collagen.
What is dense regular?
Apr 25, 2020 · Dense connective tissue, also called dense fibrous tissue, is a type of connective tissue with fibers as its main matrix element. The fibers are mainly composed of type I …
What is the most abundant cells in dense connective?
Mar 16, 2022 · Dense connective tissue, is one of the types of connective tissue also referred to as dense fibrous tissue due to relative abundance of the collagen fibers. It also contains …
What is the structure of dense regular tissue?
Dense connective tissue, also called dense fibrous tissue, is a type of connective tissue with fibers as its main matrix element. The fibers are mainly composed of type I collagen. Dense …
Where is dense regular tissue found?
Dense connective tissue is often seen as the capsules enclosing organs and, in particular, tubular structures, but is most strikingly characterized in its appearance as tendons and ligaments. …

What is an example of dense collagenous connective tissue?
What is the function of dense collagenous connective tissue?
Where is dense collagenous connective tissue?
In this type of tissue, the collagen fibres are densely packed, and arranged in parallel. This type of tissue is found in ligaments (which link bone to bone at joints) and tendons (connections between bones or cartilage and muscle).
What are the 3 types of dense connective tissue?
What is dense connective?
What is loose and dense connective tissue?
What is the difference between loose connective tissue CT and dense connective tissue?
How is the dense regular connective tissue describe?
Is dense connective tissue solid or liquid?
What are the two types of dense connective tissue?
- dense regular connective tissue – found in tendons and ligaments.
- dense irregular connective tissue – found in lower layers of the skin (dermis) and in the protective white layer of the eyeball.
What is loose tissue?
Which connective tissue is dense regular type?
What is dense connective tissue?
Dense connective tissue is often seen as the capsules enclosing organs and, in particular, tubular structures, but is most strikingly characterized in its appearance as tendons and ligaments.
What is the term for dense connective tissue that connects bone to bone and provides stabilization to a joint?
Ligament Pathology. Ligaments are dense connective tissue that connect bone to bone and provide stabilization to a joint. Though ligaments are functionally different from tendons as they connect bone to bone, they are structurally similar.
Which direction do collagenic fibers and fibroblasts go?
These are basically dense masses of collagenic fibers and fibroblasts arranged in an orderly manner, with the cells and fibers being oriented in the same direction (i.e. parallel to the long axis of the tendon).
What is the difference between collagen and elastic fibers?
The collagenous types are far more abundant and are called fibrous or ‘white’ CT. Elastic fibres , on the other hand, appear yellow in unstained tissues and are commonly referred to as ‘yellow’ CT (e.g. the yellow ligaments of the spine).
What is the yellow part of the spine called?
Elastic fibres, on the other hand, appear yellow in unstained tissues and are commonly referred to as ‘yellow’ CT (e.g. the yellow ligaments of the spine). Fibroblasts are the only cells visible and are arranged in rows between the fibres. Their function is to create the collagen fibres of the tissue.
What is the function of dense CT?
Their function is to create the collagen fibres of the tissue. The main roles of dense CT are to transmit forces over a distance and to connect different organs/muscles. Collagen fibres are disposed along the direction of mechanical loads present in that specific tissue.
What is a dense CT?
Dense, regular CT is a white, flexible tissue that contains tightly packed bundles of collagen fibres. All of these fibres run in one direction and are arranged parallel to the direction of forces exerted on the particular body part where the tissue is located.
What is dense connective tissue?
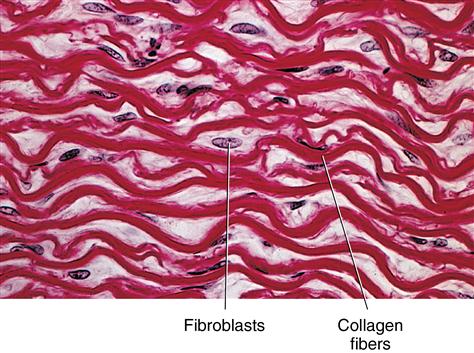
Anatomical terms of microanatomy. Dense connective tissue, also called dense fibrous tissue, is a type of connective tissue with fibers as its main matrix element. The fibers are mainly composed of type I collagen. Crowded between the collagen fibers are rows of fibroblasts, fiber-forming cells, that generate the fibers.
What is the dense connective tissue that connects bones to bones?
Dense connective tissue forms strong, rope-like structures such as tendons and ligaments. Tendons attach skeletal muscles to bones; ligaments connect bones to bones at joints.
Which type of connective tissue attaches skeletal muscles to bones?
Tendons attach skeletal muscles to bones; ligaments connect bones to bones at joints. Ligaments are more stretchy and contain more elastic fibers than tendons. Dense connective tissue also make up the lower layers of the skin (dermis), where it is arranged in sheets.
What is Dense Connective Tissue?
Connective tissues are found throughout the body and are incredibly diverse in appearance and function. However, the structural components of connective tissues are consistent. All connective tissues contain specialized cells, extracellular protein fibers, and ground substance.
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Protein fibers in dense regular connective tissue run in tightly packed, parallel bundles. Fibers are often wavy in appearance. The specialized cells in this tissue type are called fibroblasts. They are often more darkly stained in histological slides and diagrams, they are scattered in between the parallel fibers.
Structure of Dense Regular Connective Tissue
The identifiable components of dense regular connective tissues are fibroblasts and protein fibers. Because of the dense, regular arrangement of the fibers, the ground substance is rarely visible on histological slides and diagrams. There are far more fibers than fibroblasts present in dense regular connective tissue.
Why is dense regular connective tissue important?
Dense regular connective tissue is an extremely important type of connective tissue that provides the structures that they bind and/or encase a great deal of protection because they are strong yet flexible.
What type of fiber is found in dense connective tissue?
Elastin fibers are the other type of fiber found in dense regular connective tissue. They are much thinner than collagen fibers, and they allow a higher degree of stretch than collagen alone. Elastin fibers work like elastic bands.
What is connective tissue?
Connective tissues aren't, as the name suggests, merely just tissues that connect tissues or organs to one another; they are also responsible for anchoring, separating, and encasing other tissues and organs within the body. Within the category of connective tissue there are six types: Here, we are going to explore one of ...
Why do fibroblasts have flat nuclei?
They appear as having long flat nuclei because they are literally squished between the many layers of densely packed fibers.
What is collagen fiber?
Collagen fibers are very thick wide fibers that provide the tissue with a high degree of stretch (due to the undulating pattern of fibers that can stretch straight) and a very high level of tensile strength, meaning that they can resist tearing when the fibers are pulled on length-wise.
Is elastin fiber the same as collagen?
They are much thinner than collagen fibers, and they allow a higher degree of stretch than collagen alone. Elastin fibers work like elastic bands. The tissue can actually be stretched to 150% of its original length and still bounce back to its original shape, just like a rubber band.
How much of the tissue can be stretched?
The tissue can actually be stretched to 150% of its original length and still bounce back to its original shape, just like a rubber band. The proportions of these two fibers vary based on the elastic needs of the location where dense regular connective tissue is found.
