Depressive neurosis: This consists of ongoing and profound sadness, often coupled with losing interest in activities that once provided pleasure. Obsessive-compulsive neurosis: This condition involves repeating intrusive thoughts, behaviors, or mental acts.
Full Answer
What are examples of neurosis?
- anxiety
- depression
- emotional volatility
Is depression a neurosis, psychosis, or personality disorder?
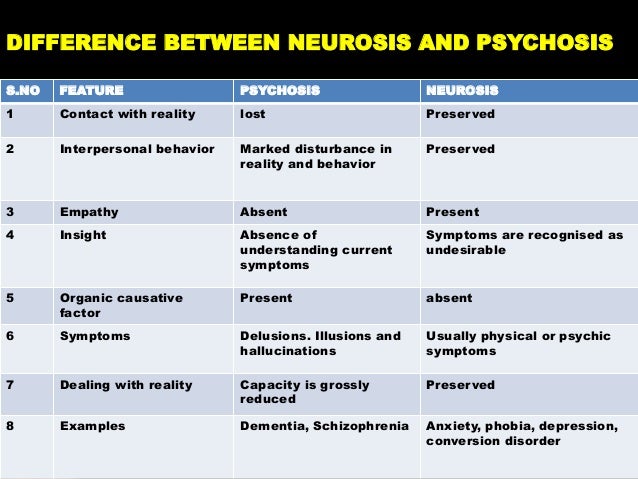
Psychotic disorders, such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, can cause delusions, hallucinations, and other symptoms of psychosis. Non-psychotic disorders, which used to be called neuroses, include depressive disorders and anxiety disorders like phobias, panic attacks, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
What does neurotic depression mean?
Neurotic depression, then, is the addition of depressive symptoms such as depressed mood, decreased pleasure in activities that used to be pleasurable, sleep difficulties, and others, to a neurotic disorder.
Is BPD psychosis or neurosis?
Today, the term “ neurosis” isn't used as a diagnosis, and BPD is not considered a disorder falling under the category of psychosis. BPD officially became a personality disorder in 1980 in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders III (DSM III).

What is the another name of the depressive neurosis?
In the past, persistent depressive disorder had several other names: dysthymia, depressive neurosis, neurotic depression, depressive personality disorder, and persistent anxiety depression.
What is meant by neurotic depression?
A neurotic depression is a depression in an emotionally unstable person. Secondary depressions to major personality disorders, neuroses, and drug use disorders fit the above definition.
What is the cause of neurotic depression?
This form of depression relies heavily on the presence of maladaptive processing and general life chaos, which may be the result of a comorbid diagnosis such as a personality disorder or a substance use disorder.
Is depression a form of neurosis?
Depression, when neither excessively severe nor prolonged, is regarded as a neurosis.
What is the most common cause of neurosis?
Overwork, insufficient rest, and an inability to relax all contribute to the development of neurosis. Neurotic diseases are caused by a disruption in the metabolism of neurotransmitters, hormones, vitamins, and other biologically active chemicals necessary for the regular functioning of the central nervous system.
What are the symptoms of neurosis?
SymptomsAnxiety and apprehension.Excessive worry and guilt.Tendency toward more negative emotions and reactions.Irritability and anger.Low self-esteem and self-consciousness.Poor response to stressors.An interpretation of everyday situations as threatening.Depression.More items...•
How does a neurosis begin?
Caused by an unpleasant experience: According to Sigmund Freud (1856-1939), a famous Austrian neurologist who founded the discipline of psychoanalysis, neurosis is a coping strategy caused by unsuccessfully repressed emotions from past experiences. These emotions overwhelm or interfere with current experience.
What does a neurotic person act like?
The Meaning of “Neurotic” Neuroticism is defined by a propensity toward anxiety, negativity, and self-doubt. It is often experienced by constantly rehashing worst–case scenarios in your head, and can be linked to a high level of guilt, worry, fear, and depression.
What is an example of a neurosis?
Common behavior: You worry about finishing a big project at work on time. Neurotic behavior: You fixate on the deadline and moan, “I'll never get this done!” even though it's not due for months and you have little other work to do. Common behavior: You like to get to the airport 2 hours before every flight.
How do you fix neurosis?
Some effective methods of coping with neurotic thoughts and feelings include:Reappraisal: Challenge Your Thinking. ... Mindfulness: Pay Attention to the Present Moment. ... Opposite Action: Do the Opposite of What You Feel. ... Problem-Solving: Focus on the Problem, Not the Emotion. ... Strengthen Relationships: Connect With Others.
Is neurosis a mental illness?
Neurosis refers to a class of functional mental disorder involving distress but not delusions or hallucinations, where behavior is not outside socially acceptable norms. It is also known as psychoneurosis or neurotic disorder.
What does neurotic mean in simple terms?
Neuroticism is defined by a propensity toward anxiety, negativity, and self-doubt. It is often experienced by constantly rehashing worst–case scenarios in your head, and can be linked to a high level of guilt, worry, fear, and depression.
What It Means to Be neurotic?
Neuroticism is the trait disposition to experience negative affects, including anger, anxiety, self‐consciousness, irritability, emotional instability, and depression1.
What does it mean to be called neurotic?
Neurotic means you're afflicted by neurosis, a word that has been in use since the 1700s to describe mental, emotional, or physical reactions that are drastic and irrational. At its root, a neurotic behavior is an automatic, unconscious effort to manage deep anxiety.
What is neurotic in simple words?
The adjective neurotic refers to someone who shows signs of mental disturbance but does not indicate complete psychosis. Neurotic comes from neuro-, from a Greek word for "nerve." It can also describe someone with neurotic behaviors, so you can think of a neurotic as someone who has a particularly bad case of nerves.
What Is Neurotic Depression?
Neurotic depression is a type of depression distinguished by depressive symptoms in someone who is emotionally unstable. Neurotic depression presents as depression, but with the added discomfort of a ruminative loop of negative and anxious thoughts.
Signs of Neurotic Depression
In general, the signs that someone is dealing with neurotic depression include a blended presentation of depressive and neurotic behaviors. 3,5,6 However, neurotic depression holds similarities and differences from non-neurotic depression, also known as melancholic depression.
Symptoms of Neurotic depression
Neurotic depression involves a ruminative loop that can paralyze individuals and inhibit their ability to utilize coping skills and solution-focused thought processes. Long-term experiences with anxiety are connected to depression and can yield neurotic symptoms. 5
Getting Treatment for Neurotic Depression
Treatment specific to neurotic depression consists of clinical therapy, holistic intervention, and medication management. Presumably, due to the deterrence from the neurotic depression diagnosis, there is more research on treatment that dates prior to its omission.
Final Thoughts
Depression is a common mental health condition characterized by a group of symptoms that include general unhappiness, hopelessness, low energy, apathy, and fatigue.
Additional Resources
Education is just the first step on our path to improved mental health and emotional wellness. To help our readers take the next step in their journey, Choosing Therapy has partnered with leaders in mental health and wellness. Choosing Therapy may be compensated for referrals by the companies mentioned below.
For Further Reading
Choosing Therapy strives to provide our readers with mental health content that is accurate and actionable. We have high standards for what can be cited within our articles.
What is neurosis?
Before explaining what depressive neurosis consists of, let's define what neurosis is. Neurosis It is a concept that was originally introduced by the Scottish physician William Cullen, in the year 1769.
Depressive neurosis: what is it?
Depressive neurosis (also called neurotic depression) is a term that was previously used in psychiatry to designate those depressions whose origin was explained by an intrapsychic conflict. The origin of the description of this picture is psychoanalytic.
Symptoms
Typical symptoms of depressive neurosis, beyond those already listed, are:
1. Depressed mood
It consists of the main symptom of depressive neurosis, as well as that of depression.
3. Slowed cognitive processes
Mainly, speech and thinking are slowed. In addition, there is an added difficulty to concentrate.
4. Apathy
Apathy is a general state of disinterest, coupled with a lack of motivation to do things. In patients with depressive neurosis, in addition, there is also a decrease in productivity in all senses.
5. Abulia
Apathy is the lack of will, or energy, when doing things or moving. Thus, the individual with depressive neurosis does not usually feel like doing "nothing", it is very difficult for him to start or do something, such as getting up in the morning, avoiding social activities, etc.
What is the name of the disorder that causes agitation?
agitated depression major depressive disorder characterized by signs and symptoms of agitation, such as restlessness, racing thoughts, pacing, hand-wringing, sighing, or moaning. congenital chondrosternal depression a congenital, deep, funnel-shaped depression in the anterior chest wall.
What are the feelings of a depressed patient?
These are a lack of desire for socializing or physical activity, feelings of worthlessness and loss of self esteem, and thoughts of self-injury or destruction. In planning the care of the depressed patient, one must always consider these feelings and strive for some understanding of the reasons for the patient's behavior. Only by gradually gaining their attention and pointing out encouraging signs of progress can they be helped in their early attempts to return to reality and socialize with others.
What is the best treatment for depression?
Treatment of profound and chronic depression is often very difficult, requiring in most cases intensive psychotherapy to help the patient understand the underlying cause of the depression. antidepressantdrugs such as imipraminehydrochloride (Tofranil) and amitriptyline(Elavil)are often used in the treatment of profound depression. They are not true stimulants of the central nervous system, but they do block the reuptake of neurotransmitter substances, which may potentiate the action of norepinephrine and serotonin. monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitorsare also used. When antidepressants fail, a different technique such as electroconvulsive therapymay be used in conjunction with the psychotherapy.
How long does postpartum depression last?
postpartum depressionmoderate to severe depression beginning slowly and sometimes undetectably during the second to third week post partum, increasing steadily for weeks to months and usually resolving spontaneously within a year. Somatic complaints such as fatigue are common. It is intermediate in severity between the mood fluctuations experienced by the majority of new mothers and frank postpartum psychosis.
What is the relationship between depression and anger?
Depression is closely associated with a lack of confidence and self-esteem and with an inability to express strong feelings. Repressed anger is thought to be a powerful contributor to depression. The person feels inadequate to cope with the situations that arise in everyday life and so feels insecure.
Why is constant vigilance important?
Constant vigilance must be maintained to prevent the profoundly depressed patient from injuring himself or committing suicide. Self-destructive behavior is a manifestation of the patient's feeling of worthlessness and loss of self esteem. An awareness of the potential dangers in such a situation should help the provider plan and provide a safe and congenial atmosphere, remaining alert to the early signs of a patient's intention to harm or destroy himself. In most cases suicide is most likely to occur when the patient is recovering from severe depression.
How to help a patient who is depressed?
When patients are depressed, they are likely to isolate themselves and avoid social contact even with those who are trying to help them. Since loss of contact with others contributes to depression, members of the health care team should persist in attempts to talk with these patients, by asking them questions, and actively listening when they attempt to express their feelings. One should be especially careful to avoid being judgmental when the patient does express despair, anger, hostility, or some negative feeling. Above all, it is important not to be condescending or to respond to statements with a meaningless cliché such as “Don't worry,” or “I'm sure everything will turn out okay.” These responses convey a lack of empathy with the patient's suffering and are an unrealistic approach to a problem that is very real.
What is neurotic depression?
A neurotic depression is a depression in an emotionally unstable person. Secondary depressions to major personality disorders, neuroses, and drug use disorders fit the above definition. Likewise, primary depressions with a family history of alcohol (depression spectrum disease) are characterized by a long history of stormy life problems and, ...
What is secondary depression?
Secondary depressions to major personality disorders, neuroses, and drug use disorders fit the above definition. Likewise, primary depressions with a family history of alcohol (depression spectrum disease) are characterized by …. A neurotic depression is a depression in an emotionally unstable person. Secondary depressions to major personality ...
Do neurotic depressives have memory problems?
The neurotic depressives were younger and the neurotic patients had made more previous suicide attempts. They were less likely to show memory deficits or delusions and less likely to show symptom criteria of melancholia. They were more likely to have suicide thoughts at index.
Content
The depressive neurosis it is a psychopathological disorder characterized by the presence of a constantly sad mood; it can be considered as a mild and permanent case of depression.
Characteristics of depressive neurosis
Depressive neurosis is a mood disorder that is defined by seven main and stable characteristics. These are:
Symptoms
Depressive neurosis is characterized by the typical triad of symptoms: decreased vitality, depressed mood, and slowed thinking and speech.
Clinic
Depressive neurosis causes an abnormally low mood and a general feeling of weakness. These typical symptoms of psychopathology are usually accompanied by other somatic manifestations.
Causes according to psychoanalysis
According to the psychoanalytic currents, which were the ones who coined the depressive neurosis disorder, this psychopathology is caused by the psychogenic condition of the individual. In this sense, the appearance of depressive neurosis is related to traumatic circumstances or external unpleasant experiences.
Diagnosis
At present, the diagnosis of depressive neurosis has been evicted. This means that the term neurosis is no longer used to detect this mood alteration, however, it does not mean that the disorder does not exist.
Treatment
The current treatment of depressive neurosis is complex and controversial. Subjects with this alteration usually require medication, although it is not always satisfactory. The intervention of this psychopathology usually includes both psychotherapy and pharmacological treatment.
What are Neurosis Symptoms?
Neurosis is simply defined as "a poor ability to adapt to one's environment, an inability to change one's life patterns, and an inability to develop a richer, more complex, and more satisfying personality." There are numerous types of neurosis, including:
Why can't psychogenic neurosis be considered separately?
This reason cannot be considered separately from psychogenic neurosis because, in the end, it all comes down to impaired brain neuron function; however, what is the primary factor in pathological changes in nerve cells is considered to be the primary cause of neurotic disorder.
What is a disorder that is not deviated from social norms?
It is a type of functional mental disorder characterised by distress but not by delusions or hallucinations, and by behaviour that does not deviate from socially acceptable norms. It's also referred to as psychoneurosis or neurotic disorder.
What is neurotic tendencies?
Neurotic tendencies are common, manifesting as acute or chronic anxiety, depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder, phobia, or personality disorder. Horney's Theory: Karen Horney's final book, Neurosis and Human Growth, lays out a comprehensive theory of the origins and dynamics of neurosis. Neurosis, according to her theory, is a distorted way ...
Why do people have neurotic disorders?
The inability to adequately respond to external stimuli, which causes stress, is one of the psychogenic causes of neurotic disorders. The first reason for an inadequate reaction could be a low-stress tolerance, as well as high susceptibility to even those things that do not cause a pathological reaction from the psyche in stronger people. Dripping water from a faucet, for example, can cause severe irritability in some people, while others simply do not notice these sounds. As a result, the former has a much higher proclivity and risk of developing a neurosis. It is impossible to discuss the presence of such a person in psychopathology because it is a personality trait, a character caused by a hereditary, genetic or acquired (as a result of upbringing or social environment) factor.
What is the theory of neurosis?
Neurosis, according to her theory, is a distorted way of viewing the world and oneself that is determined by compulsive needs rather than a genuine interest in the world as it is . Horney proposes that neurosis is passed down to a child from his or her early environment and that this can happen in a variety of ways.
What are the symptoms of a somatic organ system?
The Symptoms of Various Organ Systems (vegetative, Somatic Symptoms) are an Unavoidable Component of the Clinical Picture of Neurosis: Increased heart rate, aching pain behind the sternum ("aching heart"), blood pressure fluctuations, and rhythm disturbances;
How to get rid of neurotic behavior?
Treatment. If you manage your anxiety and stress, it may help curb your neurotic behaviors. Self-treatment may work if your anxiety is mild and brief. Experts recommend that you: Exercise every day. Thirty minutes is best, but even a 15-minute walk can help you feel better. Talk to someone.
What is neurotic conduct?
Neurotic Conduct. The line that divides neurotic from normal is the intensity. Neurotic thoughts and behaviors by definition are so extreme that they interfere with your personal, professional, and romantic lives. What’s more, they tend to be your default response to even minor problems.
What is a neurotic personality?
A neurotic personality has little natural buffer against stress. You see everyday situations as far worse than they really are, and then blame yourself for your extreme pessimism and negativity. You might constantly feel:
What happens if your worry doesn't go away?
But what if your extreme worry doesn’t go away? Negative or obsessive thoughts can take over your mind to the point that it’s hard for you to handle everyday situations. That’s called neurotic behavior. It can -- but not always -- stem from a mental illness.
Why are neurotic people more likely to smoke?
People with neurotic personalities are more likely to smoke, abuse alcohol and other drugs, have eating disorders, lack social support, and divorce. At the same time, a healthy dose of neurotic tendencies can be useful.
What are the symptoms of a psychotic disorder?
Posttraumatic stress disorder. Panic disorder. Antisocial personality disorder. Neurotic personality or neurotic behaviors do not include delusions or hallucinations, which are symptoms of psychotic disorders where you lose touch with reality.
What is neuroticism?
Also called neuroticism, it’s a personality type, not a diagnosable medical problem. Experts call it one of the “Big Five” personality traits (the others are extroversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness, and openness to experience), a set of common characteristics that are found around the world most often.