Types of Experimental Designs
- Pre-experimental Research Design. The simplest form of experimental research design in Statistics is the pre-experimental research design.
- True-experimental Research Design. ...
- Quasi-Experimental Design. ...
- Randomized Block Design. ...
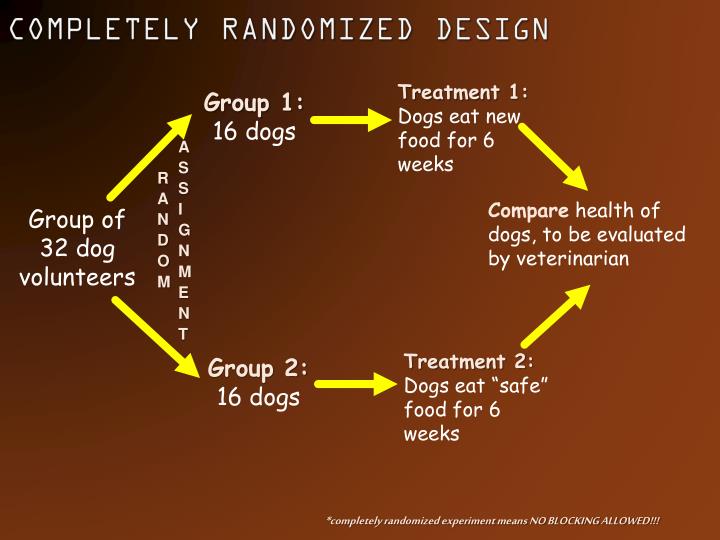
- Completely Randomized Design. ...
What is an example of a true experimental design?
Here are a few characteristics of experimental research:
- Dependent variables are manipulated or treated while independent variables are exerted on dependent variables as an experimental treatment. ...
- Researchers deliberately operate independent variables on the subject of the experiment. ...
- Once a variable is manipulated, researchers observe the effect an independent variable has on a dependent variable. ...
What are the four principles of experimental design?
Basic Principles of Experimental Design
- Randomization Randomization is the cornerstone underlying the use of statistical methods in experimental designs . ...
- Replication By replication, we mean that repetition of the basic experiments. ...
- Local Control It has been observed that all extraneous source of variation is not removed by randomization and replication, i.e. ...
How to design a statistical experiment?
- In addition to measurement error (explained above), other sources of error, or unexplained variation, can obscure the results. ...
- Uncontrollable factors that induce variation under normal operating conditions are referred to as " Noise Factors ". ...
- Correlation can often be confused with causation. ...
How do you set up an experiment?
- Have an Idea: “The most important thing is coming up with an idea: A really important question that is novel. ...
- Develop your Hypothesis: “Then, determine what the main hypothesis is: so either it works or it doesn’t.” What is your gut feeling about the question at hand? ...
- Define Change: “Figure out how to tell that difference. ...
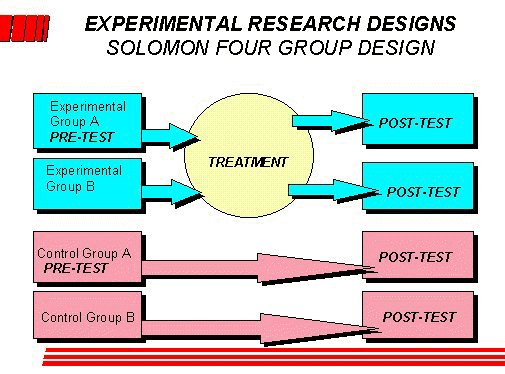
What is design of experiment also called?
Design of experiments, referred to as DOE, is a systematic approach to understanding how process and product parameters affect response variables such as processability, physical properties, or product performance.
What is the design of an experimental study?
Experimental design is the process of carrying out research in an objective and controlled fashion so that precision is maximized and specific conclusions can be drawn regarding a hypothesis statement. Generally, the purpose is to establish the effect that a factor or independent variable has on a dependent variable.
What is design of experiments used for?
Using Design of Experiments (DOE) techniques, you can determine the individual and interactive effects of various factors that can influence the output results of your measurements. You can also use DOE to gain knowledge and estimate the best operating conditions of a system, process or product.
What is an experiment definition and design?
Revised on April 12, 2022. Experiments are used to study causal relationships. You manipulate one or more independent variables and measure their effect on one or more dependent variables. Experimental design means creating a set of procedures to systematically test a hypothesis.
What is experimental design example?
For example, you might be testing a new depression medication: one group receives the actual medication and the other receives a placebo. Participants can only be a member of one of the groups (either the treatment or placebo group). A new group is created for every treatment.
What are the 4 types of experimental design?
While this type of research falls under the broad umbrella of experimentation, there are some nuances in different research design. Four major design types with relevance to user research are experimental, quasi-experimental, correlational and single subject.
What is the principle of DOE?
Design of experiments (DOE) is a systematic, rigorous approach to engineering problem-solving that applies principles and techniques at the data collection stage so as to ensure the generation of valid, defensible, and supportable engineering conclusions.
What are the 3 types of experimental design?
The types of experimental research design are determined by the way the researcher assigns subjects to different conditions and groups. They are of 3 types, namely; pre-experimental, quasi-experimental, and true experimental research.
What are the 3 types of experimental design?
There are three primary types of experimental design:Pre-experimental research design.True experimental research design.Quasi-experimental research design.
What are the 3 components of experimental research designs?
Several kinds of experimental designs exist. In general, designs that are true experiments contain three key features: independent and dependent variables, pretesting and posttesting, and experimental and control groups. In a true experiment, the effect of an intervention is tested by comparing two groups.
What are the main components of an experimental design?
What are the components of experimental design? The components of experimental design are control, independent variable and dependent variable, constant variables, random assignment and manipulation. These are the components that also help you define if the experiment is valid.
What are the three basic principles of experimental design?
Three main pillars of experimental design are randomization, replication, and blocking, and we will flesh out their effects on the subsequent analysis as well as their implementation in an experimental design.
What is the purpose of design of experiments?
Design of experiments (DOE) is a systematic, efficient method that enables scientists and engineers to study the relationship between multiple input variables (aka factors) and key output variables (aka responses). It is a structured approach for collecting data and making discoveries.
What is the purpose of factor analysis?
To determine whether a factor, or a collection of factors, has an effect on the response. To determine whether factors interact in their effect on the response. To model the behavior of the response as a function of the factors. To optimize the response.
How to do a trial and error?
1. Conduct a trial at starting values for the two variables and record the yield: 2. Adjust one or both values based on our results: 3. Repeat Step 2 until we think we've found the best set of values: As you can tell, the cons of trial-and-error are:
Why is DOE more effective?
DOE requires fewer trials. DOE is more effective in finding the best settings to maximize yield. DOE enables us to derive a statistical model to predict results as a function of the two factors and their combined effect. Learn More about different types of DOE.
What is experimental design?
Experimental design is the branch of statistics that deals with the design and analysis of experiments. The methods of experimental design are widely used in the fields of agriculture, medicine, biology, marketing research, and industrial production. In an experimental study, variables of interest are identified.
What is the statistical procedure used to analyze data from an experimental study?
A computational procedure frequently used to analyze the data from an experimental study employs a statistical procedure known as the analysis of variance. For a single-factor experiment, this procedure uses a hypothesis test concerning equality of treatment means to determine if the factor has a statistically significant effect on the response variable. For experimental designs involving multiple factors, a test for the significance of each individual factor as well as interaction effects caused by one or more factors acting jointly can be made. Further discussion of the analysis of variance procedure is contained in the subsequent section.
What is regression analysis?
Regression analysis involves identifying the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables . A model of the relationship is hypothesized, and estimates of the parameter values are used to develop an estimated regression equation. Various tests are then employed to determine if the model is satisfactory. If the model is deemed satisfactory, the estimated regression equation can be used to predict the value of the dependent variable given values for the independent variables.
Why do we use hypothesis tests in regression?
In a regression study, hypothesis tests are usually conducted to assess the statistical significance of the overall relationship represented by the regression model and to test for the statistical significance of the individual parameters.
What is factorial design?
The term factorial is used to indicate that all possible combinations of the factors are considered. For instance, if there are two factors with a levels for factor 1 and b levels for factor 2, the experiment will involve collecting data on ab treatment combinations. The factorial design can be extended to experiments involving more ...
How to find the mean square due to regression?
The mean square due to regression, denoted MSR, is computed by dividing SSR by a number referred to as its degrees of freedom; in a similar manner, the mean square due to error, MSE, is computed by dividing SSE by its degrees of freedom.
What is the independent variable in an agricultural experiment?
The independent variable is the one that you plan to change. In this sample case, the independent variable is the treatment with the new fertilizer. The dependent variable is whatever you plan to measure after the treatment. In this case, the dependent variable is the amount of soybeans per square meter. Most real-life studies also have extraneous variables that impact the results of the experiment. Extraneous variables in an agricultural study may include the amount of rain, sunshine, or insect populations.
What are extraneous variables in agriculture?
Extraneous variables in an agricultural study may include the amount of rain, sunshine, or insect populations. There are often variables that you don't even know about. A confounding variable is an extraneous variable that varies across the independent variable.
What is statistical experiment?
Statistical experiments are designed to compare the outcomes of applying one or more treatments to experimental units, then comparing the results to a control group that does not receive a treatment. Designing a statistical experiment starts with identifying the question (s) you want to answer.
What does a farmer want to test?
A farmer wants to test a new type of fertilizer to see if it improves her soybean crop yield. She will plant two sections of a field (experimental units). The farmer will apply fertilizer to one (treatment) and leave the other to grow under normal conditions (control).
What is observational study?
Observational studies observe and measure specific characteristics without modifying the subjects under study. In contrast, a statistical experiment applies a treatment to the subjects to see if a causal relationship exists.
What to do after analyzing data?
After analyzing the data, you can start to make conclusions about the experiment. Before drawing conclusions, it is important to identify any assumptions that you made during the experiment. In the sample case, we had one very simple assumption.
Can bias slip into an experiment?
Bias can slip into an experiment at any stage, so you must plan to prevent bias as much as possible. Most experiments will have an element of bias present. Even well-received published studies have a degree of bias, but these studies are designed to minimize bias and identify any bias that does occur.
What is single blind experiment?
A single-blind experiment is when the subjects are unaware of which treatment they are receiving, but the investigator measuring the responses knows what treatments are going to which subject. In other words, the researcher knows which individual gets the placebo and which ones receive the experimental treatment.
What is block design in research?
A block design is a research method that places subjects into groups of similar experimental units or conditions, like age or gender, and then assign subjects to control and treatment groups using probability, as shown below.
What is the term for when two explanatory variables are both associated with a response variable and also associated with each
Lurking variables. Blinding. Confounding happens when two explanatory variables are both associated with a response variable and also associated with each other, causing the investigator not to be able to identify their effects and the response variable separately.
What is the design of experiments?
The design of experiments ( DOE, DOX, or experimental design) is the design of any task that aims to describe and explain the variation of information under conditions that are hypothesized to reflect the variation. The term is generally associated with experiments in which the design introduces conditions that directly affect the variation, ...
What is the purpose of a properly designed experiment?
Correctly designed experiments advance knowledge in the natural and social sciences and engineering . Other applications include marketing and policy making. The study of the design of experiments is an important topic in metascience .
What happens when a double blind study is used?
When a double-blind design is used, participants are randomly assigned to experimental groups but the researcher is unaware of what participants belong to which group. Therefore, the researcher can not affect the participants' response to the intervention.
What is factorial experiment?
Factorial experiments. Use of factorial experiments instead of the one-factor-at-a-time method. These are efficient at evaluating the effects and possible interactions of several factors (independent variables).
How is the independent variable manipulated?
In the pure experimental design, the independent (predictor) variable is manipulated by the researcher – that is – every participant of the research is chosen randomly from the population, and each participant chosen is assigned randomly to conditions of the independent variable. Only when this is done is it possible to certify with high probability that the reason for the differences in the outcome variables are caused by the different conditions. Therefore, researchers should choose the experimental design over other design types whenever possible. However, the nature of the independent variable does not always allow for manipulation. In those cases, researchers must be aware of not certifying about causal attribution when their design doesn't allow for it. For example, in observational designs, participants are not assigned randomly to conditions, and so if there are differences found in outcome variables between conditions, it is likely that there is something other than the differences between the conditions that causes the differences in outcomes, that is – a third variable. The same goes for studies with correlational design. (Adér & Mellenbergh, 2008).
What is sequential analysis?
The use of a sequence of experiments, where the design of each may depend on the results of previous experiments, including the possible decision to stop experimenting, is within the scope of sequential analysis, a field that was pioneered by Abraham Wald in the context of sequential tests of statistical hypotheses. Herman Chernoff wrote an overview of optimal sequential designs, while adaptive designs have been surveyed by S. Zacks. One specific type of sequential design is the "two-armed bandit", generalized to the multi-armed bandit, on which early work was done by Herbert Robbins in 1952.
How to prevent false positives in research?
A good way to prevent biases potentially leading to false positives in the data collection phase is to use a double-blind design. When a double-blind design is used, participants are randomly assigned to experimental groups but the researcher is unaware of what participants belong to which group. Therefore, the researcher can not affect the participants' response to the intervention. Experimental designs with undisclosed degrees of freedom are a problem. This can lead to conscious or unconscious " p-hacking ": trying multiple things until you get the desired result. It typically involves the manipulation – perhaps unconsciously – of the process of statistical analysis and the degrees of freedom until they return a figure below the p<.05 level of statistical significance. So the design of the experiment should include a clear statement proposing the analyses to be undertaken. P-hacking can be prevented by preregistering researches, in which researchers have to send their data analysis plan to the journal they wish to publish their paper in before they even start their data collection, so no data manipulation is possible ( https://osf.io ). Another way to prevent this is taking the double-blind design to the data-analysis phase, where the data are sent to a data-analyst unrelated to the research who scrambles up the data so there is no way to know which participants belong to before they are potentially taken away as outliers.
Why are screeners used in experiments?
They’re typically used in initial stages of experimentation to narrow down the long list of potentially important factors and interactions to only a few important effects. Screening designs usually require fewer experimental runs than other designs. The experiments are small and efficient, involving many factors.
When to use mixture design?
Mixture designs are used when factors are interdependent, and when each component in a mixture is dependent upon the settings of other component settings. For example, in the case of stainless steel made up of Fe, Cu, Cr and Ni, the relative proportions of these components contribute to the properties of resulting steel.
What is sample size in factorial?
Trials are run at all possible combinations of factor settings. The sample size is the product of the numbers of levels of the factors. For example, a factorial experiment with a two-level factor, a three-level factor and a four-level factor has 2 x 3 x 4 = 24 runs.
Can a definitive screening design be used to solve ambiguity?
Unlike traditional screening designs, which usually require follow-up experimentation to resolve ambiguity if there’s any two-factor interaction, definitive screening design can reliably accomplish the task of screening even if there are a couple of second-order effects.
How are experimental fields divided?
The experimental field is divided into homogeneous parts equal to the number of replications. Each part is further divided into plots of equal size in such a way that the number of plots should form a square and each replication has equal plots in each direction (i.e., equal rows and columns). ii.
What is the name of the group of experiments that are divided into homogeneous groups equal to the number of replication
ADVERTISEMENTS: First the experimental field is divided into homogeneous groups equal to the number of replications. These homogeneous groups are known as blocks. Then each block is further divided into plots of similar shape and size equal to the number of treatments.
Why should the number of replications for different treatments be equal?
Normally, the number of replications for different treatments should be equal to get the estimates of treatment effects with same precision. The number of replication depends on the availability of experimental material and level of precision required.
How is randomization done?
Randomization: The randomization is done treatment wise with the help of random table. First random numbers equal to the number of plots are taken from the random table. From these random numbers each treatment is assigned numbers as per number of replications.
What is the name of the design that simultaneously controls the fertility variation in two directions?
Latin Square Design (LSD): The experimental design which simultaneously controls the fertility variation in two directions is called Latin square design (LSD). In other words, Latin square designs are adopted for eliminating the variation of two factors which are generally called rows and columns.
What is split plot design?
The experimental design in which experimental plots are split or divided into main plots, subplots and ultimate-plots is called split plot design (SPD). In this design several factors are studied simultaneously with different levels of precision. The factors are such that some of them require larger plots like irrigation, depth of ploughing and sowing dates, and others require smaller plots.
Which experimental design controls the fertility variation in one direction only?
The experimental design which controls the fertility variation in one direction only is known as randomized block design (RBD). Adoption of this design is useful when the variation between the blocks is significant.