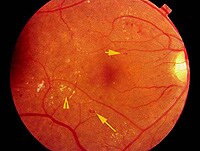
Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) is an accumulation of fluid in the macula part of the retina that controls our most detailed vision abilities—due to leaking blood vessels. In order to develop DME, you must first have diabetic retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy is a disease that damages the blood vessels in the retina, resulting in vision impairment.
Is macular degeneration linked to diabetes?
Macular Gegeneration and Diabetes. Diabetes and the eyes are closely related. Those who have diabetes have to regularly screen their eyes in order to make sure they don’t start to suffer from a range of diabetes-related conditions. One of these conditions is macular degeneration.
Is edema symptom of diabetes?
Two kinds of edema are associated with diabetes: peripheral edema and diabetic macular edema. Peripheral edema is swelling in your lower legs, ankles, or feet. It can result from having type 2 diabetes.
What does macular edema stand for?
The macula is the area in the very middle of your retina that is responsible for your central, detailed vision. Edema means swelling from an accumulation of fluid. When a person develops macular edema, fluid builds up within the retina and causes the macula to swell and thicken. This is macular edema or “ME”.
What is treatment for diabetic?
Treatment typically includes diet control, exercise, home blood glucose testing, and in some cases, oral medication and/or insulin. Approximately 40% of people with type 2 diabetes require insulin injections.
What are symptoms of diabetic macular edema?
Blurry vision and vision that gets worse over time are the main symptoms of macular edema. You may also notice that: Objects look wavy, especially when you look straight ahead. Objects look like they're different sizes if you look out of 1 eye and then the other.
Can diabetic macular edema be cured?
Diabetic macular edema is a complication of diabetes that can cause blindness. There is no cure for diabetic macular edema, but treatment can help slow progression of the condition and prevent blindness.
Why does diabetes cause macular edema?
High blood sugar weakens the blood vessels in your eyes. That can make them leak or grow out of control in your retina, the light-sensitive area at the back of your eye. This is called diabetic retinopathy. When fluid seeps into your retina, it can cause diabetic macular edema.
What is the difference between diabetic macular edema and diabetic retinopathy?
Diabetic macular edema is the leading cause of decreased vision from diabetic retinopathy. This decreased vision is caused by an increase in extracellular fluid within the retina distorting the retinal architecture and frequently taking on a pattern of cystoid macular edema.
How serious is diabetic macular edema?
Sometimes, tiny bulges (microaneurysms) protrude from the vessel walls, leaking or oozing fluid and blood into the retina. This fluid can cause swelling (edema) in the central part of the retina (macula). This is a serious eye complication called diabetic macular edema that can cause vision problems or blindness.
Can you go blind from macular edema?
If left untreated, macular edema can cause severe vision loss and even blindness.
How do you get macular edema?
WHAT CAUSES MACULAR EDEMA?Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Uveitis.Retinal Vein Occlusion.Blockage in the small veins of the retina.Side effects of certain medications.Certain genetic disorders, such as retinoschisis or retinitis pigmentosa.
What medications cause macular edema?
Various agents can cause cystoid macular edema including topical epinephrine, nicotinic acid, topical prostaglandin analogs (e.g., latanoprost), antimicrotubule agents (paclitaxel, docetaxel), fingolimod, imatinib, glitazones (rosiglitazone, pioglitazone), and trastuzumab.
How do you get rid of macular edema naturally?
What Are Some Natural or Home Remedies to Treat AMD?Avoid beta carotene.Eat more vegetables, especially leafy greens.Reduce sugar intake significantly.Consume more omega-3 fatty acid foods, like fish.Eat more fruit, especially high-fiber fruit.
What does vision look like with macular edema?
Macular edema causes painless blurring of central vision in one or both eyes. In some cases, the eye may be red or sensitive to light. The symptoms may fluctuate over time. Macular edema does not cause transient loss of vision, double vision, or eye irritation.
Is diabetic macular edema the same as macular degeneration?
Similar to wet macular degeneration, diabetic macular edema is primarily a retinal vascular disease. However, whereas wet macular degeneration is characterized by abnormal new blood vessel growth, diabetic macular edema is primarily caused by damage to existing retinal blood vessels.
Can macular edema be caused by stress?
Macular edema, which is a condition affecting the eyes, is commonly linked to mental stress. It is surprising to note that people who live a stressful hectic lifestyle are more prone to develop macular edema. Stress is both consequence and cause of vision loss.
Can vision be restored after macular edema?
Frank Siringo, M.D., O.D., chief of vitreoretinal diseases and surgery at Omni Eye Specialists in Denver, explains how vision loss can be reversed in diabetic macular edema. In fact, about two-thirds of patients can have their vision restored.
How long does it take to cure macular edema?
The macular edema may take up to four months to go away. If the swelling does not go away after that time or it comes back later, the laser treatment can be repeated.
Can you drive with diabetic macular edema?
Diabetic macular edema, a major cause of vision impairment, can have a substantial impact on the decision to drive as well as perception of difficulty with driving.
How do diabetics reduce eye swelling?
Your doctor may treat your eyes with anti-VEGF medicine, such as aflibercept, bevacizumab, or ranibizumab. These medicines block the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the eye. Anti-VEGF medicines can also stop fluid leaks, which can help treat diabetic macular edema.
What is the complication of diabetic macular edema?
People with type 1 or type 2 diabetes can develop DME. DME occurs when excess fluid starts to build up in the macula of the eye. The macula allows us to focus and see fine details. It’s located in the center of the retina, the lining at the back of the eye that’s full of blood vessels.
Where is the DME located?
It’s located in the center of the retina, the lining at the back of the eye that’s full of blood vessels. When excess fluid builds up in the macula, it causes vision problems. DME generally develops over time. High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the retina.
What does an eye doctor do?
Your eye care doctor will determine the specific medication and frequency of treatment that’s right for you.
Can diabetes cause vision loss?
If you have diabetes, it’s important to see an eye care doctor every year so they can examine your eyes for any changes. If there’s any sign of retinopathy or DME, early treatment can prevent or restore vision loss.
Can high blood sugar cause retinopathy?
High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the retina. Damaged blood vessels can leak fluid, which causes swelling and other issues. This damage is called retinopathy. There are several treatment options for DME. It’s easiest to treat when diagnosed early and monitored regularly by an eye care doctor.
Is macular edema a manageable condition?
Diabetic macular edema (DME) is a manageable condition. Several effective treatment options are available. Maintaining eyesight or recovering lost sight is possible. Seeing your eye care doctor at least every year is an important step in taking care of your eyes and overall well-being.
What is macular edema?
Macular edema is the build-up of fluid in the macula, an area in the center of the retina. The retina is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye and the macula is the part of the retina responsible for sharp, straight-ahead vision. Fluid buildup causes the macula to swell and thicken, which distorts vision.
What are the symptoms of macular edema?
The primary symptom of macular edema is blurry or wavy vision near or in the center of your field of vision. Colors might also appear washed out or faded. Most people with macular edema will have symptoms that range from slightly blurry vision to noticeable vision loss. If only one eye is affected, you may not notice your vision is blurry until the condition is well-advanced.
How long does it take for macular edema to develop?
A small number of people who have cataract surgery (experts estimate only 1-3 percent) may develop macular edema within a few weeks after surgery.
What is the name of the area in the center of the eye that is affected by fluid buildup?
Macular edema is the build-up of fluid in the macula, an area in the center of the retina. The retina is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye and the macula is the part of the retina responsible for sharp, straight-ahead vision. Fluid buildup causes the macula to swell and thicken, which distorts vision.
How do you know if you have macular edema?
Most people with macular edema will have symptoms that range from slightly blurry vision to noticeable vision loss. If only one eye is affected, you may not notice your vision is blurry until the condition is well-advanced.
What happens if blood is blocked in the retina?
If it leaks into the macula, this produces macular edema. Leakage is worsened by the severity of the blockage, how many veins are involved, and the pressure inside them.
Is macular edema the same as diabetic edema?
Treatments for diabetic macular edema and macular edema caused by other conditions are often the same. However, some cases of macular edema may need additional treatments to address associated conditions.
What is the term for fluid in the macula?
Diabetic Macular Edema. Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) is an accumulation of fluid in the macula part of the retina that controls our most detailed vision abilities—due to leaking blood vessels. In order to develop DME, you must first have diabetic retinopathy.
What causes DME in diabetics?
Diabetic retinopathy is a disease that damages the blood vessels in the retina, resulting in vision impairment. Left untreated, these blood vessels begin to build up pressure in the eye and leak fluid, causing DME. DME usually takes on two forms:
Why do diabetics have diffuse DME?
Diffuse DME, which occurs because of widening/swelling retinal capillaries (very thin blood vessels). Diabetic Retinopathy and DME are common problems for diabetics. Roughly 8% of the U.S. population is diabetic, and about 28% of those diabetics have eye trouble because of it.
How to prevent diabetic retinopathy?
Sometimes, there is nothing you can do to prevent diabetic retinopathy or DME, but your best chance at avoiding them comes by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, exercising regularly, eating lots of vegetables and fruit, and visiting your eye doctor at least once a year to stay on top of your eye health.
What are the symptoms of DME?
Common symptoms of DME are blurry vision, floaters, double vision, and eventually blindness if it goes untreated.
How long does it take for a DME to heal?
DME Procedure Recovery. Normal recovery time after a DME procedure is 3-6 months. As the eye heals and the swelling in and around the macula subsides, you may experience sensitivity to light, irritation in the eye, and black spots in the center of your vision.
Signs and Symptoms of Diabetic Macular Edema
At first, you might not notice any symptoms of diabetic macular edema, noted an article published in July 2016 in the American Journal of Managed Care.
Causes and Risk Factors of Diabetic Macular Edema
Diabetic macular edema is essentially a result of another diabetes complication, called diabetic retinopathy.
How Is Diabetic Macular Edema Diagnosed?
To diagnose diabetic macular edema, your eye doctor will likely first perform a comprehensive vision exam. They will need to widen (dilate) your pupils to better see your retina and look for signs of damage, according to the American Academy of Ophthalmology.
Duration of Diabetic Macular Edema
Though many treatment options are available, diabetic macular edema is still considered a chronic condition that requires long-term follow-up care, according to an article published in October 2015 in Federal Practitioner.
Treatment and Medication Options for Diabetic Macular Edema
Treatments for diabetic macular edema will depend on your overall health, how severe the condition is, and other factors. It’s important to remember that habits like good blood sugar control and a healthy lifestyle are essential for a successful treatment outcome.
Complications of Diabetic Macular Edema
If diabetic macular edema isn’t treated, it can lead to irreversible damage of the macula, which can cause permanent vision loss, notes American Society of Retina Specialists.
Research and Statistics: Who Has Diabetic Macular Edema?
According to the National Eye Institute, about 750,000 Americans have diabetic macular edema. Research shows that up to 10 percent of people with diabetes may develop the complication.
What causes macula to be affected?
In most cases, the macula is affected by the high levels of sugar in the bloodstream. This means that active steps need to be taken in order to control your blood sugar levels.
What is diabetic retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy affects people with diabetes, and occurs when high levels of sugar in the bloodstream cause progressive damage to the retina.
How is DME diagnosed?
Your eye doctor may utilize any of the following diagnostic tools to determine the presence of DME:
How is DME treated?
The treatment your eye doctor will recommend, will be dependent on the type of DME you have been diagnosed with. In some cases, more than one type of treatment will be required.
What causes DME in diabetics?
While DME is most commonly caused by diabetic retinopathy , it may also occur after eye surgery, from age-related macular degeneration, an inflammatory eye disease, or high blood pressure.
What is DME in medical terms?
Diabetic macular edema (DME) is a complication that can result from a diabetic ocular disease, called diabetic retinopathy.
How many people have DME?
Approximately 7.7 million Americans suffer from diabetic retinopathy, among those people, about 750,000 also have DME.
What is the risk factor for diabetic macular edema?
Chronic hyperglycemia is the major risk factor of diabetic macular edema. The incidence of DME over a 10 year period is 20% in patients with younger onset diabetes versus approximately 40% in older onset diabetes.
What is macular thickening?
Macular thickening with or without hard exudates as judged with stereobiomicroscopy; thickening can occur in various patterns: focal, multifocal, and diffuse areas of retina thickening Hard exudates (consisting of lipoproteins) in various patterns, e.g., circinate rings.
What is CSME in medical terms?
CSME is a clinical diagnosis and is defined bt the ETDRS (Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study) as: Retinal thickening within 500 µm of the macular center. Hard exudates within 500 µm of the macular center with adjacent retinal thickening. One or more disc diameters of retinal thickening, part of which is within one disc diameter of the macular center.
Is DME a neurovascular disease?
The exact pathogenesis of DME is still unclear. Recent evidence indicates that diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a neurovascular disease of the retina. Retinal neuronal abnormalities are present well before the retinal microvascular injury.
What Is Diabetic Macular Edema?
When you have diabetes, you have a lot to manage. High blood sugar can lead to other conditions, like eye problems.
What does a diabetic eye doctor look for in a diabetic eye?
They'll look for signs of disease, including damaged or leaking blood vessels, swelling, and fatty deposits on the retina. If your doctor thinks you have diabetic macular edema, you may also need one or both of these tests:
What happens when fluid seeps into your retina?
When fluid seeps into your retina, it can cause diabetic macular edema. The leaking makes your retina swell, which hampers the work of your macula, the special, sensitive part that gives you sharp vision.
Why does my retina swell?
Causes. High blood sugar weakens the blood vessels in your eyes. That can make them leak or grow out of control in your retina, the light-sensitive area at the back of your eye. This is called diabetic retinopathy. When fluid seeps into your retina, it can cause diabetic macular edema. The leaking makes your retina swell, ...
How to prevent diabetes from getting worse?
First, manage your diabetes by controlling your blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol. Diet changes, keeping a healthy weight, and exercise can all help you manage these problems.
How to protect your vision from diabetes?
Treatment can help you protect your vision. It can greatly decrease your chance of losing your vision. Stay on top of your diabetes, and stick with your treatment plan. You'll have the best chance of maintaining your sight and staying independent. Continued.
What is the procedure to remove a cloud from your eye?
Another treatment is a surgery called vitrectomy. This is usually done because of bleeding (not macular edema), and doctors take out the fluid that is clouding your vision and replace it with a clear solution.
What is DME in diabetics?
DME is a complication of diabetic retinopathy that can lead to vision loss and blindness. Diabetic retinopathy is a common diabetes-related eye disease. It’s estimated to affect about 1 in 3 people with diabetes over the age of 40, per the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
What is the cause of blindness in diabetics?
Diabetic macular edema is a complication of diabetes that can cause blindness.
Why do diabetics need a dilated eye exam?
People with diabetes should get a dilated eye exam every year to check for vision complications, according to the CDC. Diabetic macular edema (DME) is a complication of diabetic retinopathy, an eye disease related to diabetes. DME affects an estimated 750,000 people in the United States, according to the National Eye Institute.
What happens if you live with diabetes?
The longer you live with diabetes, the more likely you are to develop diabetic retinopathy or DME.
How many people are affected by DME?
DME affects an estimated 750,000 people in the United States, according to the National Eye Institute. The condition is the leading cause of blindness among people with diabetic retinopathy. There’s no cure for DME, but treatment can stop or slow its progression. Read on to learn more about DME, treatment options and goals, ...
How to treat DME?
The main treatment for DME is anti-VEGF injections into the eye. These injections stop the activity of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) to promote the growth of blood vessels. This can reduce leakage from damaged blood vessels and slow the progression of DME. Anti-VEGF drugs include:
What happens when you have too much fluid in your eye?
But when there’s too much fluid, you can experience swelling and thickening of the macula, an area in the center of the retina that helps you see clearly and precisely.
What is the condition where tiny bulges protrude from the vessel walls?
This condition is diabetic retinopathy. Sometimes, tiny bulges (microaneurysms) protrude from the vessel walls, leaking or oozing fluid and blood into the retina. This fluid can cause swelling (edema) in the central part of the retina (macula). This is a serious eye complication called diabetic macular edema that can cause vision problems ...
Can too much sugar cause edema?
In people with diabetes, too much blood sugar can damage the tiny blood vessels at the back inner wall of the eye (retina) or block them completely. This condition is diabetic retinopathy. Sometimes, tiny bulges (microaneurysms) protrude from the vessel walls, leaking or oozing fluid and blood into the retina. This fluid can cause swelling (edema) in the central part of the retina (macula). This is a serious eye complication called diabetic macular edema that can cause vision problems or blindness.
