Popper gives the following definition of dialectic (Popper, 2002, p. 421): Dialectic is a theory which maintains that something – for instance, human thought – develops in a way characterised by the so-called dialectic triad: thesis, anti-thesis, synthesis. What is the Marxist dialectic and how does it work?
What is Popper’s view of Hegelian dialectics?
Popper thought that a core component of the quest for truth was criticism. Hegelian dialectics would lead to the destruction of criticism, because contradictions would not make any statement problematic, whereas actually contradictions should enable us to retransmit falsity back through an argument.
What is the difference between Popper's dialectics and dialectics?
In other words dialectics allows us to accept contradictory statments in the synthesis. whereas Popper thinks that contradictory statements should not be accepted: either one or the other statement has to be abandoned or both.
What is poppers?
“Poppers” is a slang term for this type of chemical when it's used recreationally. People inhale the strong-smelling, colorless liquid, often to enhance their senses during sex.
What is dialectic?
Dialectic or dialectics ( Greek: διαλεκτική, dialektikḗ; related to dialogue ), also known as the dialectical method, is at base a discourse between two or more people holding different points of view about a subject but wishing to establish the truth through reasoned arguments. Dialectic resembles debate,...

What is dialectic some remarks on Popper's criticism?
Abstract. Karl Popper famously opposed Marxism in general and its philosophical core – the Marxist dialectic – in particular. As a progressive thinker, Popper saw in dialectic a source of dogmatism damaging to philosophy and political theory.
What dialectic means?
a : any systematic reasoning, exposition (see exposition sense 2a), or argument that juxtaposes opposed or contradictory ideas and usually seeks to resolve their conflict : a method of examining and discussing opposing ideas in order to find the truth.
What is an example of a dialectic?
A dialectic is when two seemingly conflicting things are true at the same time. For example, “It's snowing and it is spring”. You might also see dialectics when in conflict with other people. I like to think of it as having an elephant in the room with two blindfolded people on opposite ends of the elephant.
What is meant by dialectical materialism?
dialectical materialism, a philosophical approach to reality derived from the writings of Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. For Marx and Engels, materialism meant that the material world, perceptible to the senses, has objective reality independent of mind or spirit.
What is a dialectical thinking?
Dialectical thinking is defined as seeing things from multiple perspectives. A fundamental principle of dialectical thinking is that everything is composed of opposites and that to understand things more fully, we need to understand their opposites.
What is dialectic reasoning?
Dialectic is a formal system of reasoning that arrives at the truth through the exchange of logical arguments. Dialectic is a process of examining an issue using very careful steps. A "thesis," or argument, is offered, followed by the "antithesis," or counterargument.
How do you use dialectic method?
0:011:17Dialectic Method - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIts correctness the dialectic method uses arguments and counter-arguments to correct contradictions.MoreIts correctness the dialectic method uses arguments and counter-arguments to correct contradictions. It seeks to find the truth through logic and rational thought rooted in Greek philosophy.
What is the opposite of dialectic?
adjective. ( ˌdaɪəˈlɛktɪk) Of or relating to or employing dialectic. Antonyms. internationalism nationalism.
What are the 3 basic laws of dialectics?
Three Laws of Dialectics Engels discusses three principal laws of dialectics: the law of the transformation of quantity into quality, and vice versa; the law of the interpenetration of opposites; and the law of the negation of the negation.
Why is dialectical materialism important?
A grasp of dialectical materialism is an essential prerequisite in understanding the doctrine of Marxism. Dialectical materialism is the philosophy of Marxism, which provides us with a scientific and comprehensive world outlook.
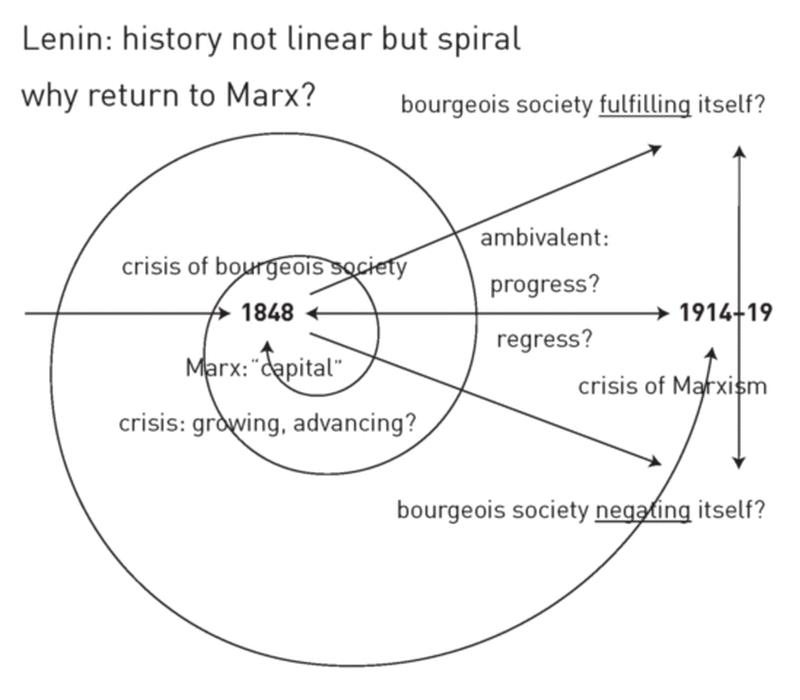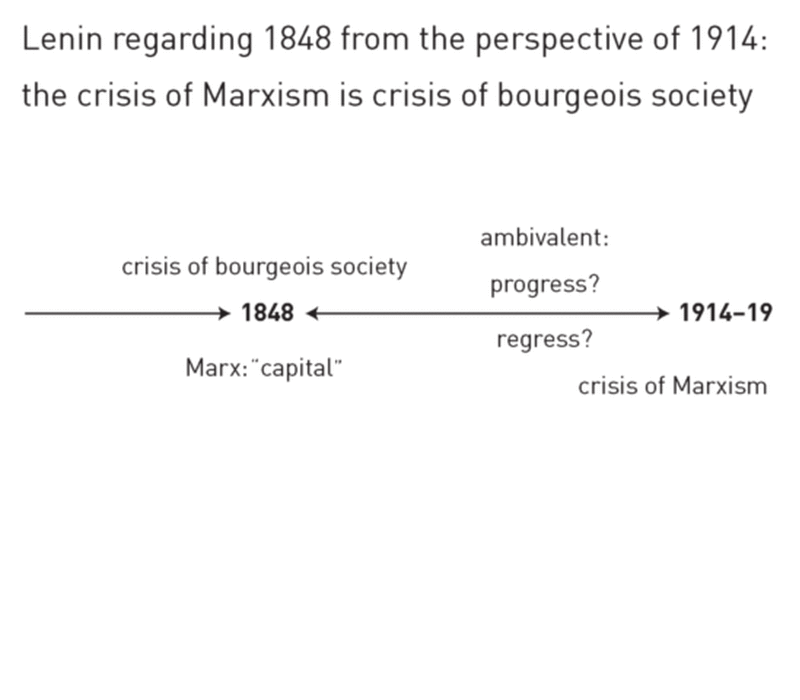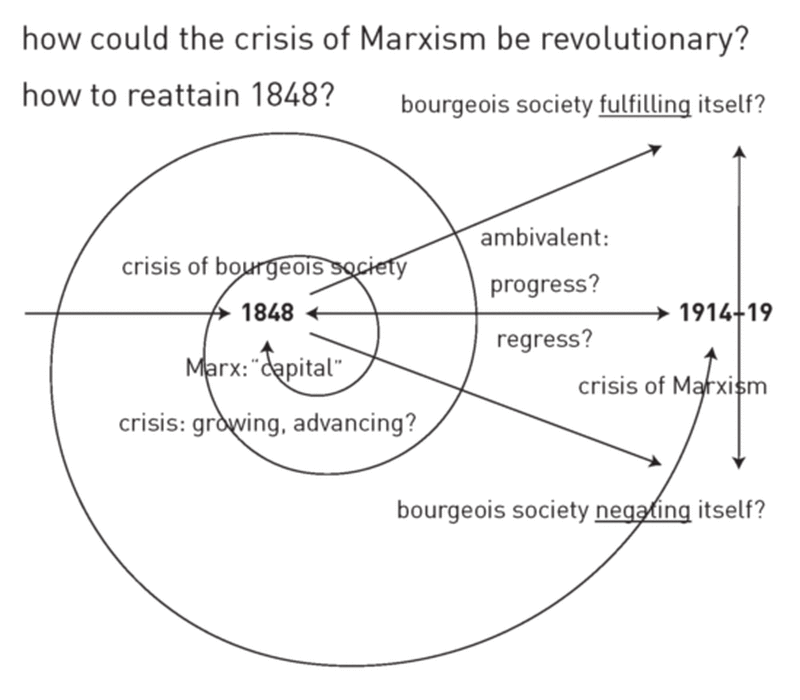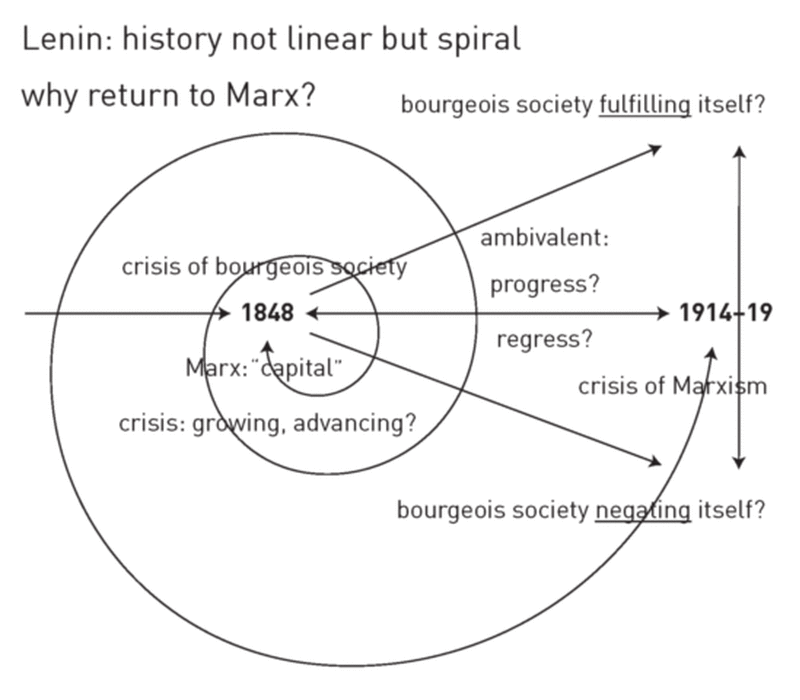
What are dialectics in Marxism?
Marxist dialectic is a form of Hegelian dialectic which applies to the study of historical materialism. It purports to be a reflection of the real world created by man. Dialectic would thus be a robust method under which one could examine personal, social, and economic behaviors.
Is dialectical materialism an ethical system?
The main methodological principles of Marxist-Leninist ethics are materialism and dialectics.
What is the opposite of dialectic?
adjective. ( ˌdaɪəˈlɛktɪk) Of or relating to or employing dialectic. Antonyms. internationalism nationalism.
What are the 3 basic laws of dialectics?
Three Laws of Dialectics Engels discusses three principal laws of dialectics: the law of the transformation of quantity into quality, and vice versa; the law of the interpenetration of opposites; and the law of the negation of the negation.
How do you use dialectics?
He has no other instrument than the dialectic of his compeers, and he is as far off as the rest from a criticism of the instrument, Socrates.
What is the main focus of dialectical approach?
In ancient and medieval times, both rhetoric and dialectic were understood to aim at being persuasive (through dialogue). The aim of the dialectical method, often known as dialectic or dialectics, is to try to resolve the disagreement through rational discussion.
Abstract
Karl Popper famously opposed Marxism in general and its philosophical core – the Marxist dialectic – in particular. As a progressive thinker, Popper saw in dialectic a source of dogmatism damaging to philosophy and political theory.
References (3)
This chapter presents a review of existing analytic frameworks for investigating interaction in learning sciences and reveals the lack of an analytic framework, which is applicable for analyzing interactions happening in networked language learning classrooms.