Dichotomous Scale A dichotomous scale is a type of survey response scale that provides two options, which lie at opposite ends. On a dichotomous scale, the survey respondent can not give a neutral answer because it is a case of either one or the other.
What is a dichotomous scale in research?
More properly, it is a composite score of several survey questions that each measure the same attribute. A dichotomous scale is a type of survey response scale that provides two options, which lie at opposite ends.
When to use dichotomous questions in a survey?
When you are planning survey questions, there will be times when you want to clarify specific information or route participants; this is where dichotomous questions are beneficial. What are dichotomous questions?
What is the difference between nominal and Dichotomic scales?
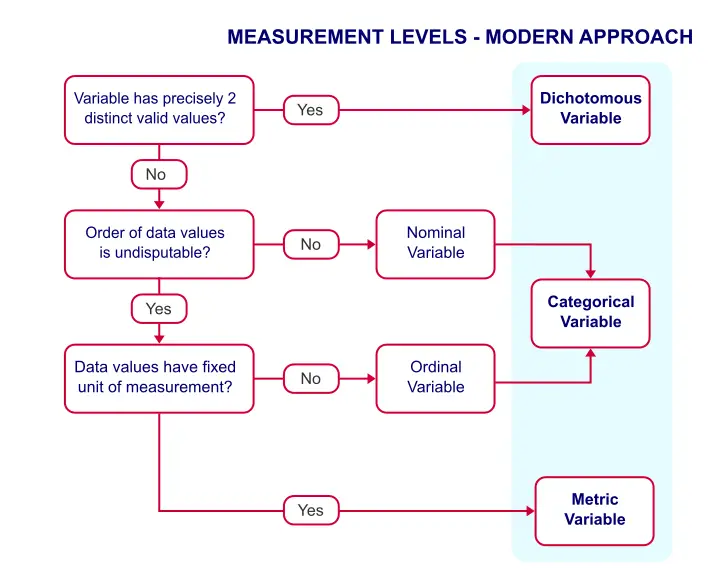
NOMINAL without order Scale for grouping into unique categories e.g. eye colour. DICHOTOMOUS As for nominal but two categories only e.g. male/female. In addition to the classification of measurement scales, other related terms are used to describe types of data:
What is a dichotomous variable?
(Definition & Example) A dichotomous variable is a type of variable that only takes on two possible values. These types of variables occur all the time in practice. For example, consider the following dataset that contains 10 observations and 4 variables:
What is dichotomous scale?
Why is dichotomous scale important?
What is a Survey Scale?
What is a rating scale?
What is a Likert scale?
Why are scales important in quantitative research?
What is a good example of rating scale?
See 2 more

What is a dichotomous question example?
For example, a good dichotomous question would be, “Are you taller than 6 feet?” While a bad dichotomous question would be, “Do you like the songs in album X? The respondent might not be able to express the way they feel through a Yes/No choice.
What is meant by Likert scale?
Definition: A Likert scale is a unidimensional scale that researchers use to collect respondents' attitudes and opinions. Researchers often use this psychometric scale to understand the views and perspectives towards a brand, product, or target market.
What is a scale in a questionnaire?
Survey scales are the indexes that measure those types of variables that are not directly observed but are instead inferred from the other variables that are directly measured. Likert Scale. One of these types of scales, called the Likert scale, is the most popular type of scale.
What is the best scale to use for surveys?
There's more variance in larger scales, which has made the Likert scale the most common survey scale. Dr. Rob Balon advises to “always use the 1–5 scale, with 5 being the positive end and 1 being the negative end. NEVER use 1 as the positive end.”
What is the 5 point Likert scale?
A type of psychometric response scale in which responders specify their level of agreement to a statement typically in five points: (1) Strongly disagree; (2) Disagree; (3) Neither agree nor disagree; (4) Agree; (5) Strongly agree.
What type of data is Likert scale?
Likert items are used to measure respondents' attitudes to a particular question or statement. To analyse the data it is usually coded as follows. One must recall that Likert-type data is ordinal data, i.e. we can only say that one score is higher than another, not the distance between the points.
What are the 3 types of scale?
Three Types of Scale:Fractional or Ratio Scale: A fractional scale map shows the fraction of an object or land feature on the map. ... Linear Scale: A linear scale shows the distance between two or more prominent landmarks. ... Verbal Scale: This type of scale use simple words to describe a prominent surface feature.More items...•
What are the four types of scales?
Each of the four scales (i.e., nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio) provides a different type of information. Measurement refers to the assignment of numbers in a meaningful way, and understanding measurement scales is important to interpreting the numbers assigned to people, objects, and events.
What are the different types of scales?
The four types of scales are: Nominal Scale. Ordinal Scale. Interval Scale....Nominal ScaleA nominal scale variable is classified into two or more categories. ... It is qualitative. ... The numbers don't define the object characteristics.
How do you read a dichotomous question?
The answers to dichotomous questions are either: Yes/No, Fair/Unfair, or Agree/Disagree. Dichotomous questions do not give room for ambiguity, and answers are usually direct and clear to everyone on which side the individual responding belongs.
What are the 5 rating scale?
ScaleRating5 points (Pass)Excellent. Exceptional Mastery. Much more than acceptable.4 points (Pass)Very Good. Full Performance Behaviours. Above average.3 points (Pass)Good. Acceptable. Satisfactory Average2 points (Fail)Weak. Less than Acceptable1 more row
Which scale is used for measuring?
There are different kinds of measurement scales, and the type of data being collected determines the kind of measurement scale to be used for statistical measurement. These measurement scales are four in number, namely; nominal scale, ordinal scale, interval scale, and ratio scale.
What is a scale of 1 to 10 called?
Likert scalesLikert scales typically range from 2 to 10 – with 3, 5, or, 7 being the most common. Further, this progressive structure of the scale is such that each successive Likert item is treated as indicating a 'better' response than the preceding value.
What are scale type questions?
In rating scale questions (sometimes referred to as ordinal questions), the question displays a scale of answer options from any range (0 to 100, 1 to 10, etc.). The respondent selects the number that most accurately represents their response. Net Promoter Score® questions are a good example of rating scale questions.
How do you use a 1 5 scale?
Example 1: Scaling down A 50mm line is to be drawn at a scale of 1:5 (ie 5 times less than its original size). The measurement 50mm is divided by 5 to give 10mm. A 10mm line is drawn.
What is a dichotomous variable?
A dichotomous variable is a type of variable that only takes on two possible values.
How to visualize dichotomous variables?
We typically visualize dichotomous variables by using a simple bar chart to represent the frequencies of each value it can take on.
What is point-biserial correlation?
Point-biserial correlation is used to measure the relationship between a dichotomous variable and a continuous variable.
Why are gender and won championship dichotomous?
The variables gender and Won Championship are dichotomous because they can each only take on two possible values: However, the variables Division and Average Points are not dichotomous because they can take on multiple values.
Can a dichotomous variable take two values?
You can remember that dichotomous variables can only take on two values by remembering that the prefix “di” is a Greek word that means “two”, “twice”, or “double.”.
Examples of dichotomous in a Sentence
Recent Examples on the Web Berlin, portrayed by Pedro Alonso in the original series, is a terminally ill, morally ambiguous jewel thief who quickly became a fan favorite, albeit a controversial one, thanks to his dichotomous personality. — Lester Fabian Brathwaite, EW.com, 1 Dec.
History and Etymology for dichotomous
borrowed from Late Latin dichotomos, borrowed from Greek dichótomos "cut in half, divided equally," from dicho- dicho- + -tomos, adjective derivative from the base of témnein "to cut" — more at tome
What is dichotomous question?
The dichotomous question is a question that can have two possible answers. Dichotomous questions are usually used in a survey that asks for a Yes/No, True/False, Fair/Unfair or Agree/Disagree answers.
Why are dichotomous questions useful?
Also, you can simplify the survey experience. Dichotomous questions have the advantage to ease responses and ease the analysis of the data. Here is another great article on why dichotomous questions are useful.
Can dichotomous questions be used to inquire about feelings?
Dichotomous questions (Yes/ No) may seem simple, but they have few problems both on the part of the survey respondent and in terms of analysis.
What is the term for data that is counted or measured using a numerically defined method?
Data that are counted or measured using a numerically defined method are called numerical (quantitative).
What is continuous data?
Continuous data are numerical data that can theoretically be measured in infinitely small units. For example, blood pressure is usually measured to the nearest 2mm Hg, but could be measured with much greater resolution of difference. The interval measurement scale is intended for continuous data. Sometimes continuous data are given discrete values at certain thresholds, for example age a last birthday is a discrete value but age itself is a continuous quantity; in these situations it is reasonable to treat discrete values as continuous. Remember that information is lost when continuous data are recorded only in ranges (ordered categories), and the statistical analysis of continuous data is more powerful than that of categorical data.
Is age a continuous quantity?
Sometimes continuous data are given discrete values at certain thresholds, for example age a last birthday is a discrete value but age itself is a continuous quantity; in these situations it is reasonable to treat discrete values as continuous.
Is categorical data discrete?
Discrete data arise from observations that can only take certain numerical values, usually counts such as number of children or number of patients attending a clinic in a year. Ordered categorical data are sometimes treated as discrete data, this is wrong. For example, using the Registrar General's classification of social class, it would be wrong to say that class I is five times the socio-economic status as class V, as there is not a strict numerical relationship between these categories. It follows, therefore, that average social class is a meaningless statistic. Thus, ordered categorical data should not be treated as discrete data for statistical analysis. Discrete data may be treated as ordered categorical data in statistical analysis, but some information is lost in doing so.
What is dichotomous scale?
A dichotomous scale is a type of survey response scale that provides two options, which lie at opposite ends. On a dichotomous scale, the survey respondent can not give a neutral answer because it is a case of either one or the other.
Why is dichotomous scale important?
It helps you gather direct and precise responses in research. It prevents vague or ambiguous answers that may not prove useful in the research. To a large extent, it results in a valid and objective survey data. Cons of Dichotomous Scale.
What is a Survey Scale?
A survey scale is an orderly arrangement of different survey response options. It typically consists of a specific range of verbal or numerical options that respondents can choose from as they provide answers to questions in a survey or questionnaire .
What is a rating scale?
A rating scale is a type of survey response scale that allows respondents to match specific qualitative values with different assertions, products, or features . With a rating scale, you simply answer the survey question by picking one of the rating options on the scale.
What is a Likert scale?
As we've mentioned earlier, a Likert scale is a type of rating scale. It is considered one of the most effective types of ranking scales; especially in social and educational research. Likert scales commonly have a 3-point, 4-point, or 5-point scale structure.
Why are scales important in quantitative research?
These scales help you to gather and organize large volumes of data during data collection; especially in quantitative research. At one point or the other, you must have come across a survey scale during data collection; whether as a survey respondent ...
What is a good example of rating scale?
A good example of this type of rating scale is the Likert scale .