
What are the 3 types of angina?
There are three types of angina:Stable angina is the most common type. It happens when the heart is working harder than usual. ... Unstable angina is the most dangerous. It does not follow a pattern and can happen without physical exertion. ... Variant angina is rare. It happens when you are resting.
Is angina pectoris the same as unstable angina?
Unstable angina, also known as unstable angina pectoris, is a medical emergency with sudden chest pain or tightness that worsens over a short period of time.
Why is it called angina pectoris?
The term derives from the Latin angere ("to strangle") and pectus ("chest"), and can therefore be translated as "a strangling feeling in the chest".
Is angina pectoris the same as chest pain?
Angina pectoris is the medical term for chest pain or discomfort due to coronary heart disease. It occurs when the heart muscle doesn't get as much blood as it needs. This usually happens because one or more of the heart's arteries is narrowed or blocked, also called ischemia.
What are the 4 types of angina pectoris?
Types of AnginaStable angina.Unstable angina.Microvascular Angina.Vasospastic or variant angina.
Can ECG detect angina?
You may have tests to check if you have angina and assess your risk of more serious problems like heart attacks or stroke. You may have: an electrocardiogram (ECG) – a test to check your heart's rhythm and electrical activity.
What are four symptoms of angina pectoris?
These are the most common symptoms of angina:A pressing, squeezing, or crushing pain, usually in the chest under your breastbone.Pain may also occur in your upper back, both arms, neck, or ear lobes.Pain radiating in your arms, shoulders, jaw, neck, or back.Shortness of breath.Weakness and fatigue.Feeling faint.
What are three signs symptoms of angina?
Angina SymptomsAching.Burning.Discomfort.Dizziness.Fatigue.Feeling of fullness in your chest.Feeling of heaviness or pressure.Upset stomach or vomiting.More items...•
What is the treatment of angina pectoris?
Nitrates are often used to treat angina. Nitrates relax and widen the blood vessels so more blood flows to the heart. The most common form of nitrate used to treat angina is nitroglycerin. The nitroglycerin pill is placed under the tongue.
Can High BP cause angina?
Eventually, the muscle may become so thick that it does not get enough oxygen. This can cause angina (chest pain). Without appropriate blood pressure control, the heart can weaken over time and heart failure may develop. High blood pressure also leads to thickening of the blood vessel walls.
What is the fastest way to cure angina?
If you need immediate relief from your angina:Stop, relax, and rest. Lie down if you can. ... Take nitroglycerin.If the pain or discomfort doesn't stop a few minutes after taking nitroglycerin or if your symptoms become more severe, call 911 or let someone know that you need immediate medical assistance.
Can anxiety cause angina?
It can be challenging to distinguish between angina and an anxiety attack, especially because emotional distress can also increase the amount of oxygen the heart requires and trigger angina.
What is meant by unstable angina?
Unstable angina is a condition in which your heart doesn't get enough blood flow and oxygen. It may lead to a heart attack. Angina is a type of chest discomfort caused by poor blood flow through the blood vessels (coronary vessels) of the heart muscle (myocardium).
What are the categories of unstable angina?
Five different although not mutually exclusive causes of unstable angina are now recognized. These are (1) a nonocclusive thrombus on a preexisting plaque, (2) dynamic obstruction, (3) progressive mechanical obstruction, (4) inflammation, and (5) secondary unstable angina.
What are the two warning signs of unstable angina?
Symptoms of unstable angina include: Tight or crushing pain in your chest that may spread to other areas in your upper body. Chest pain that happens even when you're not exerting yourself.
How can you tell the difference between stable and unstable angina?
Stable and unstable angina Stable angina is when you get angina symptoms during moderate physical activity or when you are pushing yourself physically. These symptoms go away with rest and/or medication. Unstable angina is when you get angina symptoms while doing very little or resting.
What is angina pectoris?
Angina pectoris—or simply angina—is chest pain or discomfort that keeps coming back. It happens when some part of your heart doesn't get enough blood and oxygen. Angina can be a symptom of coronary artery disease (CAD). This occurs when arteries that carry blood to your heart become narrowed and blocked because of atherosclerosis or a blood clot. It can also occur because of unstable plaques, poor blood flow through a narrowed heart valve, a decreased pumping function of the heart muscle, as well as a coronary artery spasm.
Why is it important to treat angina?
It is important to work with your healthcare provider to treat your underlying coronary artery disease, which causes angina. You need to control your risk factors: high blood pressure, cigarette smoking, high blood cholesterol levels, lack of exercise, excess weight, and a diet high in saturated fat.
What is the best medicine for angina?
You may also have shortness of breath, weakness, or fatigue. Nitroglycerin is the most common medicine prescribe for angina.
What is it called when your heart muscle does not get enough oxygen?
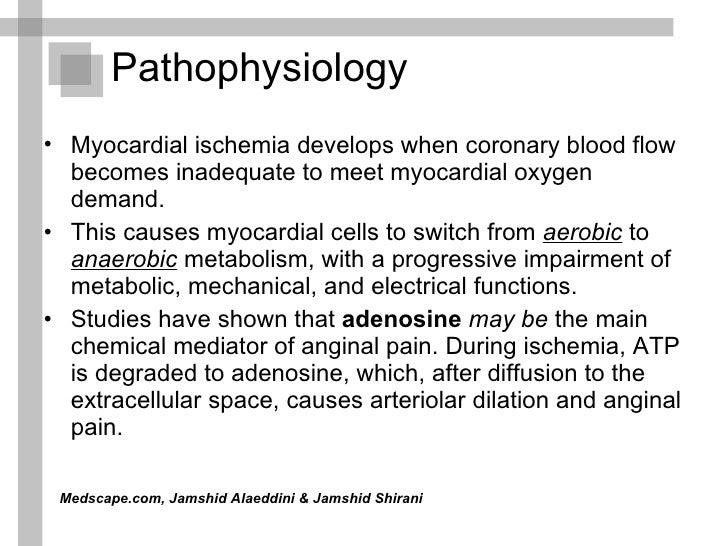
Angina pectoris occurs when your heart muscle (myocardium) does not get enough blood and oxygen for a given level of work. Insufficient blood supply is called ischemia.
Why does my heart get narrowed?
This occurs when arteries that carry blood to your heart become narrowed and blocked because of atherosclerosis or a blood clot. It can also occur because of unstable plaques, poor blood flow through a narrowed heart valve, a decreased pumping function of the heart muscle, as well as a coronary artery spasm.
How to relieve chest pain from angina?
Feeling faint. Angina chest pain is usually relieved within a few minutes by resting or by taking prescribed cardiac medicine, such as nitroglycerin. An episode of angina means some part of the heart is not getting enough blood supply. If you have angina, you have an increased risk for a heart attack.
Can angina be diagnosed from a medical history?
In addition to a complete medical history and medical exam, your healthcare provider can often diagnose angina from your symptoms and how and when they occur. Other tests may include:
What does it mean when you have angina pectoris?
People with angina pectoris or sometimes referred to as stable angina have episodes of chest pain. The discomfort that are usually predictable and manageable. You might experience it while running or if you’re dealing with stress.
When does angina pectoris occur?
Angina often occurs when the heart muscle itself needs more blood than it is getting, for example, during times of physical activity or strong emotions. Severely narrowed arteries may allow enough blood to reach the heart when the demand for oxygen is low, such as when you're sitting. But, with physical exertion—like walking up a hill or climbing stairs—the heart works harder and needs more oxygen.
What causes angina to be stable?
Possible triggers of stable angina include: Emotional stress – learn stress management. Exposure to very hot or cold temperatures – learn how cold and hot weather affect the heart. Heavy meals. Smoking – learn more about quitting smoking. Track your angina symptoms with our Angina Log.
Why does angina occur when you sit?
Angina often occurs when the heart muscle itself needs more blood than it is getting, for example, during times of physical activity or strong emotions. Severely narrowed arteries may allow enough blood to reach the heart when the demand for oxygen is low, such as when you're sitting.
What causes pain in the center of the chest?
Angina usually causes uncomfortable pressure, fullness, squeezing or pain in the center of the chest. You may also feel the discomfort in your neck, jaw, shoulder, back or arm. (Many types of chest discomfort — like heartburn, lung infection or inflammation — aren‘t related to angina. ) Angina in women can be different than in men.
What causes a paroxysmal pain in the chest?
Paroxysmal severe constricting pain or pressure in the chest due to myocardial ischemia; typically radiates from the precordium to one or both shoulders, neck, or jaw; often precipitated by exertion, exposure to cold, or emotional excitement.
Why does my chest hurt?
An oppressive pain or pressure in the chest caused by inadequate blood flow and oxygenation to heart muscle. It is usually due to atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries and in Western cultures is one of the most common emergent complaints bringing adult patients to medical attention. It typically occurs after (or during) events that increase the heart's need for oxygen, e.g., increased physical activity, a large meal, exposure to cold weather, or increased psychological stress. See: illustration; table
What causes angina in the heart?
When you climb stairs, exercise or walk, your heart demands more blood, but narrowed arteries slow down blood flow. Besides physical activity, other factors such as emotional stress, cold temperatures, heavy meals and smoking also can narrow arteries and trigger angina.
What are the characteristics of unstable angina?
Characteristics of unstable angina (a medical emergency) Occurs even at rest. Is a change in your usual pattern of angina. Is unexpected. Is usually more severe and lasts longer than stable angina, maybe 30 minutes or longer. May not disappear with rest or use of angina medication. Might signal a heart attack.
What is the pain in the chest called?
Overview. Angina is a type of chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart. Angina (an-JIE-nuh or AN-juh-nuh) is a symptom of coronary artery disease. Angina, also called angina pectoris, is often described as squeezing, pressure, heaviness, tightness or pain in your chest. Some people with angina symptoms say angina feels like ...
How does stress affect your heart?
Stress. Stress can increase your risk of angina and heart attacks. Too much stress, as well as anger, also can raise your blood pressure. Surges of hormones produced during stress can narrow your arteries and worsen angina.
What is the risk of heart attacks and angina?
Cholesterol is a major part of the deposits that can narrow arteries throughout your body, including those that supply your heart. A high level of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, also known as "bad" cholesterol, increases your risk of angina and heart attacks. A high level of triglycerides, a type of blood fat related to your diet, also is unhealthy.
Why is my angina unstable?
Unstable angina can also be caused by blood clots that block or partially block your heart's blood vessels. Unstable angina worsens and isn't relieved by rest or your usual medications. If the blood flow doesn't improve, your heart is starved of oxygen and a heart attack occurs.
What is it called when your heart is narrowed?
Your heart (coronary) arteries can become narrowed by fatty deposits called plaques. This is called atherosclerosis. During times of low oxygen demand — when you're resting, for example — your heart muscle may still be able to function on the reduced amount of blood flow without triggering angina symptoms.
What is angina in a heart attack called?
Unstable angina is sometimes called “acute coronary syndrome, ” though heart attack itself also falls under this description. Acute coronary syndrome is a term for any group of diseases or conditions that can suddenly stop or restrict blood flow to the heart.
Why is angina so unpredictable?
This unpredictable type of angina is called “unstable angina” and is the more serious type of angina because it can indicate you’re going to have a heart attack.
What is the difference between stable and unstable angina?
The difference between stable angina and unstable angina lies partly in when the symptoms occur. Both types of angina cause chest pain or pressure, but the symptoms of unstable angina can occur when: You’re resting. You don’t feel stressed.
How long does it take for angina to get worse?
You don’t feel stressed. In addition, unstable angina usually comes on suddenly and gets worse rapidly over the course of 15 to 20 minutes. Other symptoms of unstable angina include: Chest pain that does not get better by taking nitroglycerin. Drop in blood pressure that occurs with the chest pain. Shortness of breath.
What is chest pain called?
Chest pain is called “angina” and can occur any time blood flow to the heart muscle becomes restricted. Sometimes, angina happens in a predictable pattern, such as when you’re exercising. Other times, angina occurs without warning or for no apparent reason. Knowing which type of angina you or a loved one is experiencing can help get emergency ...
What is stable angina?
Stable angina is the most common type and usually can be treated by resting and taking a medication like nitroglycerin.
Is unstable angina more common in men or women?
Unstable angina occurs more often in men than in women. Some of the other risk factors for unstable angina include:
What is chest angina?
We define chest angina as that pain or discomfort that we place in the chest area and that have as origin an insufficient blood supply to the heart. In the majority of the occasions this problem arrives as a consequence of the existence of a certain obstruction in the coronary arteries. In the event that this particular obstruction is only fleeting, that is, has a duration of minutes at most, and therefore the patient recovers after this time, it is considered angina pectoris.
What is the difference between angina and myocardial infarction?
Both have a common origin, which is the existence of some alteration at the level of the cardiac arteries. An alteration that influences a lack of oxygen, in addition to limiting the blood that reaches our heart. And is that myocardial infarction and angina have many features in common. However, there are also marked differences between both diseases of our vital engine. To understand what these differences are to which we refer, it is better to start by defining the specific concept of each disease:
What is myocardial infarction?
On the other hand, and before specifying what are the differences between angina pectoris and infarction , it is necessary to know that myocardial infarction is that disease that has as main characteristic the death of an area of ??our heart as a consequence of the total obstruction of the heart. a coronary artery.
How long does angina pectoris pain last?
On the one hand, in the case of infarction, pain arises when the patient is in a resting state, lasts about 30 to 45 minutes. On the other hand, angina pectoris manifests a type of pain that arises when the patient is carrying out some kind of effort such as, for example, the practice of intense exercise, does not last more than five minutes and tends to disappear with rest. .
How long does it take for angina to disappear?
Angina pectoris tends to disappear at the time the patient is given a medication such as nitroglycerin. Angina pectoris tends to disappear after 10 minutes. The pain produced by angina pectoris is usually much less intense than that caused by a myocardial infarction.
Why do men have angina?
In many cases, angina can originate from a heart that is forced to increase its effort as well as a paralyzed organism in the face of the need to increase blood flow to its own motor. It is, in any way, a more frequent pathology than we think affects both genders equally, although in men it is more common after 30 years of age.
Can angina pectoris cause palpitations?
In addition to pain, the patient may suffer anxiety, sweating, paleness or palpitations in both angina pectoris and heart attack.
How to tell if it's heartburn?
Not sure if it's heartburn? "One of the best ways to tell if it's heartburn is to take some Pepto Bismol, " Ewy says. "If the chest pain is due to too much stomach acid, you'll feel so much better in a few minutes that it's like putting out a fire."
Is cardiac pain associated with exercise?
To know the difference, keep in mind that cardiac pain is most often associated with activity. "People notice it while they are walking or exercising," she says. "These put a greater demand on the heart. Pain from the pancreas or gall bladder is not associated with activity.".
Is heartburn on the left side?
True heartburn tends to be centered, not on the left side, says Narula. It can even go up into the throat area. It tends to not be associated with fatigue, sweatiness, and a moving pain that can radiate to the jaw. There's also something called unstable angina, Narula says.
Can angina be a sign of heartburn?
If sudden, new pain comes on and it feels very differently from earlier bouts of angina, it could even signal that a heart attack is impending. But those symptoms can also be similar to those from heartburn.
Can angina save your life?
Knowing the difference—and making a quick decision about treatment—could actually save your life. Diagnosing angina versus simple indigestion can be tricky. Here's what you need to know. Angina occurs when there's not enough blood flow to the heart.
Overview
- Angina (an-JIE-nuh or AN-juh-nuh) is a type of chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart. Angina is a symptom of coronary artery disease. Angina is also called angina pectoris. Angina pain is often described as squeezing, pressure, heaviness, tightness or pain in the chest. It may feel like a heavy weight lying on the chest. Angina may b...
Symptoms
- Angina symptoms include chest pain and discomfort. The chest pain or discomfort may feel like: 1. Burning 2. Fullness 3. Pressure 4. Squeezing Pain may also be felt in the arms, neck, jaw, shoulder or back. Other symptoms of angina include: 1. Dizziness 2. Fatigue 3. Nausea 4. Shortness of breath 5. Sweating The severity, duration and type of angina can vary. New or differ…
Causes
- Angina is caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. Blood carries oxygen, which the heart muscle needs to survive. When the heart muscle isn't getting enough oxygen, it causes a condition called ischemia. The most common cause of reduced blood flow to the heart muscle is coronary artery disease (CAD). The heart (coronary) arteries can become narrowed by fatty dep…
Risk Factors
- The following things may increase the risk of angina: 1. Increasing age.Angina is most common in adults age 60 and older. 2. Family history of heart disease.Tell your health care provider if your mother, father or any siblings have or had heart disease or a heart attack. 3. Tobacco use.Smoking, chewing tobacco and long-term exposure to secondhand smoke can damage the l…
Complications
- The chest pain that occurs with angina can make doing some activities, such as walking, uncomfortable. However, the most dangerous complication is a heart attack.
Prevention
- You can help prevent angina by following the same lifestyle changes that are used to treat angina. These include: 1. Not smoking. 2. Eating a healthy diet. 3. Avoiding or limiting alcohol. 4. Exercising regularly. 5. Maintaining a healthy weight. 6. Managing other health conditions related to heart disease. 7. Reducing stress. 8. Getting recommended vaccines to avoid heart complicat…