
What does lateral ventricles mean?
The lateral ventricles are part of the ventricular system of the brain. Classified as part of the telencephalon, they are the largest of the ventricles. The lateral ventricles connect to the central third ventricle through the interventricular foramen of Monro.
What is normal right ventricle size?
These criteria classify the LV size as normal (men: 42 to 59 mm; women: 39 to 53 mm), mildly dilated (men: 60 to 63 mm; women: 54 to 57 mm), moderately dilated (men: 64 to 68 mm; women: 58 to 61 mm), or severely dilated (men: ≥69 mm; women: ≥62 mm). Secondly, what is a normal right ventricular ejection fraction? Abstract.
What is the medial partition between the lateral ventricles?
Septum pellucidum. The septum pellucidum is a thin, transparent membrane that forms the medial wall of the lateral ventricles. The term [septum] means “wall” or “partition” and [pellucidum] means “transparent”. The septum pellucidum is found most of the time as a single, median structure that is shared by both lateral ventricles and ...
What do the ventricles do in the brain?
Ultimately, the overarching function of ventricles is to circulate said fluid throughout the organ or body. In the case of the brain ventricular system, the fluid is CSF and the circulation occurs throughout the central nervous system, primarily the brain and spinal cord.
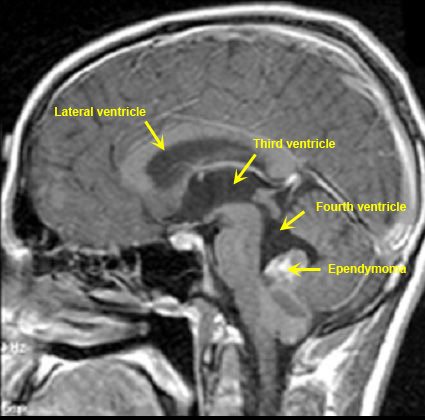
What causes dilated ventricles in the brain?
Two of the main factors that cause enlarged ventricles are: An injury or problem with brain development around the ventricles. A blockage or imbalance in the ventricular system which prevents spinal fluid from moving or being absorbed normally.
What happens when ventricles are dilated?
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a condition in which the left ventricle, the heart's main pumping chamber, is enlarged (dilated). As the chamber gets bigger, its thick muscular wall stretches, becoming thinner and weaker. This affects the heart's ability to pump enough oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body.
What is dilation of lateral ventricles?
Ventriculomegaly is a brain condition that mainly occurs in the fetus when the lateral ventricles become dilated. The most common definition uses a width of the atrium of the lateral ventricle of greater than 10 mm. This occurs in around 1% of pregnancies.
What happens if lateral ventricle is enlarged?
Mild enlargement of the lateral ventricles is a structural brain abnormality observed in neuropsychiatric disorders that are thought to be the result of abnormal prenatal brain development, including schizophrenia (1, 2), autism (3), and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder(4, 5).
How is dilated ventricle treated?
Treatment of dilated cardiomyopathy depends on the causes. The goals of treatment are to reduce symptoms, improve blood flow and prevent further heart damage. Dilated cardiomyopathy treatment may include medications or surgery to implant a medical device that helps the heart beat or pump blood.
How do you treat ventricular dilation?
TreatmentAngiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Also called ACE inhibitors, these medications widen blood vessels to lower blood pressure. ... Angiotensin II receptor blockers. ... Beta blockers. ... Calcium channel blockers. ... Water pills, also called diuretics.
How serious is a dilated right ventricle?
Living with right ventricular hypertrophy If left untreated, it can lead to some serious complications, including heart failure. If you have any symptoms of a heart problem, including chest pain, shortness of breath, or swelling in your legs, contact your doctor as soon as possible.
Can enlarged ventricles Go Away?
If your child has mildly enlarged brain ventricles or ventriculomegaly without other complications, the condition may resolve on its own. When hydrocephalus is more severe or progresses, timely treatment is important.
Can enlarged ventricles be normal?
There are spaces within the brain (ventricles) that are also filled with CSF. Ventriculomegaly is a condition in which the ventricles appear larger than normal on a prenatal ultrasound. This can occur when CSF becomes trapped in the spaces, causing them to grow larger.
Can enlarged heart ventricles go back to normal?
Some people have an enlarged heart because of temporary factors, such as pregnancy or an infection. In these cases, your heart will return to its usual size after treatment.
Can anxiety cause enlarged left ventricle?
Conclusion: Anxiety disorders are associated with elevated plasma adrenomedullin levels and increased left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with essential hypertension.
Can stress cause left ventricular enlargement?
Anything that puts stress on the heart's lower left chamber can lead to left ventricular hypertrophy. The lower left chamber is called the left ventricle. As the strain on the left ventricle increases, the muscle tissue in the chamber wall thickens.
How serious is a dilated right ventricle?
Living with right ventricular hypertrophy If left untreated, it can lead to some serious complications, including heart failure. If you have any symptoms of a heart problem, including chest pain, shortness of breath, or swelling in your legs, contact your doctor as soon as possible.
Can a dilated ventricle be reversed?
The results of the present study provide the first evidence that severe ventricular dilation due to idiopathic cardiomyopathy can be substantially reversed, even in the most advanced stages of heart failure.
Can enlarged heart ventricles go back to normal?
Some people have an enlarged heart because of temporary factors, such as pregnancy or an infection. In these cases, your heart will return to its usual size after treatment.
Can enlarged ventricles Go Away?
If your child has mildly enlarged brain ventricles or ventriculomegaly without other complications, the condition may resolve on its own. When hydrocephalus is more severe or progresses, timely treatment is important.
What are the lateral ventricles?
Lateral ventricles. The right and left lateral ventricles are structures within the brain that contain cerebrospinal fluid, a clear, watery fluid that provides cushioning for the brain while also helping to circulate nutrients and remove waste. Along with the structures known as the third ventricle and the fourth ventricle, ...
How to measure the volume of the lateral ventricles?
The volume of the lateral ventricles, and similar structures within the brain, can be measured through a CT scan. The scan allows doctors to measure not only the size of the ventricles but also the density of the cerebrospinal fluid that they contain.
What is the name of the abnormal accumulation of fluid in the ventricles?
This information can be used to diagnose potential problems within the brain, including hydrocephalus , an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the ventricles. Hydrocephalus can lead to progressive skull enlargement. Last medically reviewed on April 15, 2015.
What is the ventricular system?
The ventricular system acts as a continuation of the central canal of the spinal cord, a similar structure that contains cerebrospinal fluid and runs the length of the neck and trunk. The separate sections of the ventricular system are connected through small holes known as foramina.
Which ventricles connect through the cerebral aqueduct?
The lateral and third ventricles connect through the right and left interventricular foramina, while the third and fourth ventricles connect through a foramen known as the cerebral aqueduct.
What is the junction between the horns and the lateral ventricles?
Each lateral ventricle takes the form of an elongated curve, with an additional anterior-facing continuation emerging inferiorly from a point near the posterior end of the curve; the junction is known as the trigone ...
What is the structure that connects the third ventricle?
Below the putamen sits the globus pallidus, with which it connects. These structures bounding the lateral ventricles form a frame curving around the thalamus, which itself constitutes the main structure bounding the third ventricle.
What is the anterior horn of the lateral ventricle?
Anterior horns of lateral ventricle. Anterior horn shown in red. The anterior horn of the lateral ventricle is also known as the frontal horn as it extends into the frontal lobe. The anterior horn connects to the third ventricle, via the interventricular foramen.
What is the lateral ventricle?
Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy. The lateral ventricles are the two largest ventricles of the brain and contain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Each cerebral hemisphere contains a lateral ventricle, known as the left or right ventricle, respectively.
Which part of the ventricular curve forms the roof of the inferior horn?
As a continuation of the interior side of the ventricular curve, the floor of the body of the ventricle becomes the roof of the inferior horn, hence the tail of the caudate nucleus forms the lateral edge of the inferior horn's roof, until, at the extremity of the ventricle, the caudate nucleus becomes the amygdala.
What causes hydrocephalus in the ventricles?
If the production of cerebrospinal fluid is bigger than its reabsorption, or if its circulation is blocked – the ventricles may enlarge and cause hydrocephalus .
What happens to the central canal during prenatal development?
During the first three months of prenatal development, the central canal expands into lateral, third, and fourth ventricles, connected by thinner channels. In the lateral ventricles, specialized areas – choroid plexuses – appear, which produce cerebrospinal fluid.
What is normal pressure hydrocephalus?
Normal pressure hydrocephalus is characterized by gait impairment, cognitive impairment, and urinary incontinence, and is associated with disproportionate ventricular dilation. Here we report the distribution of ventricular volume relative to sulcal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) volume, and the association of increasing ventricular volume relative to sulcal CSF volume with a cluster of gait impairment, cognitive impairment, and urinary incontinence in a stroke-free cohort of elderly persons from the general population.
What is cerebellar infarct?
Cerebral infarcts were defined as lesions ≥4mm in the maximum diameter over a vascular distribution with typical MRI characteristics ( eg, a signal intensity that was isointense to that of cerebrospinal fluid), and that were distinguished from WMHs. Cerebellar infarcts had no size criteria, because lesions in this area can be very small. A neuroradiologist first examined the images for presence of cortical, subcortical, and cerebellar infarcts. Then, radiographers characterized the infarcts in more detail. WMH volume was assessed with a semiquantitative scale with known reliability and validity.35
What is bladder dysfunction?
Dysfunction, when present, was categorized into 1) urinary incontinence associated with an activity like coughing, lifting, standing up, or exercise; 2) urge incontinence where the subject cannot get to the toilet fast enough; and 3) urinary incontinence unrelated to coughing, sneezing, lifting, or urge. NPH type bladder dysfunction was defined as positive answers to questions 2 or 3, corresponding with descriptions in literature.4,10,34
Does ventricular dilation increase gait?
The prevalence and severity of gait impairment and cognitive impairment increases with ventricular dilation in persons without stroke from the general population, independent of WMH volume.
Where is the 4Faculty of Medicine?
4Faculty of Medicine, University of Iceland, Reykjavik, Iceland
What causes a heart to stop beating?
Dilated cardiomyopathy can cause your heart to suddenly stop beating. Blood clots (emboli). Pooling of blood in the left ventricle can lead to blood clots, which may enter the bloodstream and cut off the blood supply to vital organs. These blood clots can cause stroke, heart attack or damage to other organs.
What is dilated cardiomyopathy?
Dilated cardiomyopathy is a disease of the heart muscle that usually starts in your heart's main pumping chamber (left ventricle). The ventricle stretches and thins (dilates) and can't pump blood as well as a healthy heart can. Over time, both ventricles may be affected. The term "cardiomyopathy" refers to diseases that affect the heart muscle itself.
What are the risk factors for dilated cardiomyopathy?
Risk factors for dilated cardiomyopathy include: Long-term high blood pressure. Family history of dilated cardiomyopathy, heart failure or sudden cardiac arrest. Inflammation of the heart muscle from immune system disorders, such as lupus. Damage to the heart muscle from certain diseases, such as hemochromatosis.
What are the complications of late stage pregnancy?
Complications of late-stage pregnancy. Excessive iron in your heart and other organs (hemochromatosis) Certain infections. Other possible causes of dilated cardiomyopathy include: Alcohol abuse. Use of certain cancer medications. Use of illegal drugs, such as cocaine or amphetamines.
What does it mean when your heart beats?
Chest pain or feelings of having a fast-beating, fluttering or pounding heart (palpitations) Extra or unusual sounds heard when your heart beats (heart murmurs), which your doctor may find during a physical examination. Some people with dilated cardiomyopathy don't have any signs ...
What causes a backward flow of blood in the heart?
Heart valve regurgitation. Enlargement of the left ventricle may make it harder for your heart valves to close, causing a backward flow of blood and making your heart pump less effectively.
What is the term for damage to the heart muscle from certain diseases?
Damage to the heart muscle from certain diseases, such as hemochromatosis
What is Ventriculomegaly?
Ventriculomegaly is a condition in which the brain ventricles, or fluid-filled cavities, are enlarged due to build up of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). CSF is a fluid that protects the brain and spinal cord. The severity of ventriculomegaly depends on how enlarged the brain is. In some cases, fluid keeps building up, and the ventricles grow larger over time. This condition is known as hydrocephalus.
How is Does Ventriculomegaly Affect Delivery?
Babies diagnosed with ventriculomegaly should be delivered in a hospital that is prepared to treat babies with complex birth defects so they can have access to a team of specialists and a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU).
How is Ventriculomegaly Treated?
This can be done by placing a ventriculoperitoneal shunt or performing a surgery to reduce spinal fluid and create a hole in the floor of one the ventricles to bypass the blockage.
What are the Long-term Effects of Ventriculomegaly?
Most children with mild, nonprogressive cases that do not involve brain damage or developmental anomalies will not have any long-term health effects. More severe cases may need surgery. These children would be more likely to have neurological disabilities.
What is the term for a condition in which the brain ventricles are enlarged due to build up of cere?
Ventriculomegaly is a condition in which the brain ventricles, or fluid-filled cavities, are enlarged due to build up of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
How to diagnose ventriculomegaly?
Ventriculomegaly is often diagnosed through prenatal ultrasound when the brain ventricles are measured. Sometimes a fetal MRI is also done to give more detailed images.
How many pregnancies are there with ventriculomegaly?
Ventriculomegaly is the most common fetal brain abnormality, occurring in up to 1.5 per 1,000 pregnancies.
How to diagnose biatrial enlargement?
Biatrial enlargement is diagnosed based on an electrocardiogram (least accurate for diagnosis), an echocardiogram, a cardiac MRI, or a cardiac CT scan. If you have not had an echocardiogram, we will first request for echocardiogram to look for causes like heart-failure, valvular heart disease or atrial septal defect.
What causes a pulmonary artery to enlarge?
The right atrium and ventricle (RA and RV) pump blood through the lungs. There are 3 basic reasons why they may get enlarged: 1 some abnormal “plumbing” resulting in blood going through the lungs more than once for every time going through the body. The most common is a “hole in the heart” called as ASD but there can be an abnormal vein connection called APVD. 2 Increased resistance to blood going through the lungs (called PAH) which can be caused by blood clots (multiple pulmonary emboli) or can just develop for no obvious reason. 3 Something causing weakness of the heart muscle or leaking of the valv
What causes a sinificant heartbeat?
Usually it’s just an incidental finding on echocardiogram. If sinificant, it could be caused by raised pulmonary artery pressure (though this would generally be detected at the same time), increased blood flow through the right heart e.g. due to ASD or APVD (developmetal abnormalities allowing flow of blood from left to right), specific muscle disease mainly affecting the right ventricle (RV cardiomyopathy) or tricuspid or pulmonary valve disease.
What is restricted cardiomyopathy?
Restricted cardiomyopathy: seen in diseases (such as sarcoidosis and amyloidosis) that infiltrate the muscle with fibrosing damage, stiffening and ‘restricting’ the heart muscles motion. Dilated cardiomyopathy: also called non-ischemic cardiomyopathy to distinguish it from #1, the most common.
Why does dilation occur in the heart?
Dilation of the heart chambers is due the muscle fibers losing their normal organised , and cohesive relationship to each other . Both at a cellular and larger level of function, this creates an inefficient function of pumping blood and the result is a burden from fluid backing up into the lungs, as well as body cavities, and legs.
What happens when you have right ventricular hypertrophy?
When a person suffers from right ventricular hypertrophy, the right ventricle,which is the lower chamber of the heart, dilutes itself. This means that it becomes weaker.
Why is alcohol bad for the heart?
Alcohol is especially prominent in it's damage because, while the heart is failing to pump, cirrhosis is damaging the liver, too. The combination of a bad pump and a clogged filter compound the reasons for fluid to back up and accumulate. There is probably a dietary deficiency of thiamine (aka wet beriberi) that leads to the cardiomyopathy of alcoholism.

Overview
The lateral ventricles are the two largest ventricles of the brain and contain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Each cerebral hemisphere contains a lateral ventricle, known as the left or right ventricle, respectively.
Each lateral ventricle resembles a C-shaped cavity that begins at an inferior horn in the temporal lobe, travels through a body in the parietal lobe and frontal lobe, …
Structure
Each lateral ventricle takes the form of an elongated curve, with an additional anterior-facing continuation emerging inferiorly from a point near the posterior end of the curve; the junction is known as the trigone of the lateral ventricle. The centre of the superior curve is referred to as the body, while the three remaining portions are known as horns (cornua in Latin); they are usually referred to by th…
Clinical significance
The volume of the lateral ventricles is known to increase with age. They are also enlarged in a number of neurological conditions and are on average larger in patients with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder and Alzheimer's disease.
Asymmetry as an anatomical variation, in the size of the lateral ventricles is found in about 5–12% of the population. This has been associated with handedness, where right-handed people have b…
Additional images
• Position of lateral ventricles (shown in red).
• Drawing of a cast of the ventricular cavities, viewed from above.
See also
• Colpocephaly
• Choroid plexus