What is Bus Arbitration?
What are the two types of bus arbitration?
Why is distributed arbitration reliable?
What happens when a master bus relinquishes another bus?
How many arbitration schemes are there?
Can a computer have more than one bus master?
See 3 more
About this website
What is distributed arbitration?
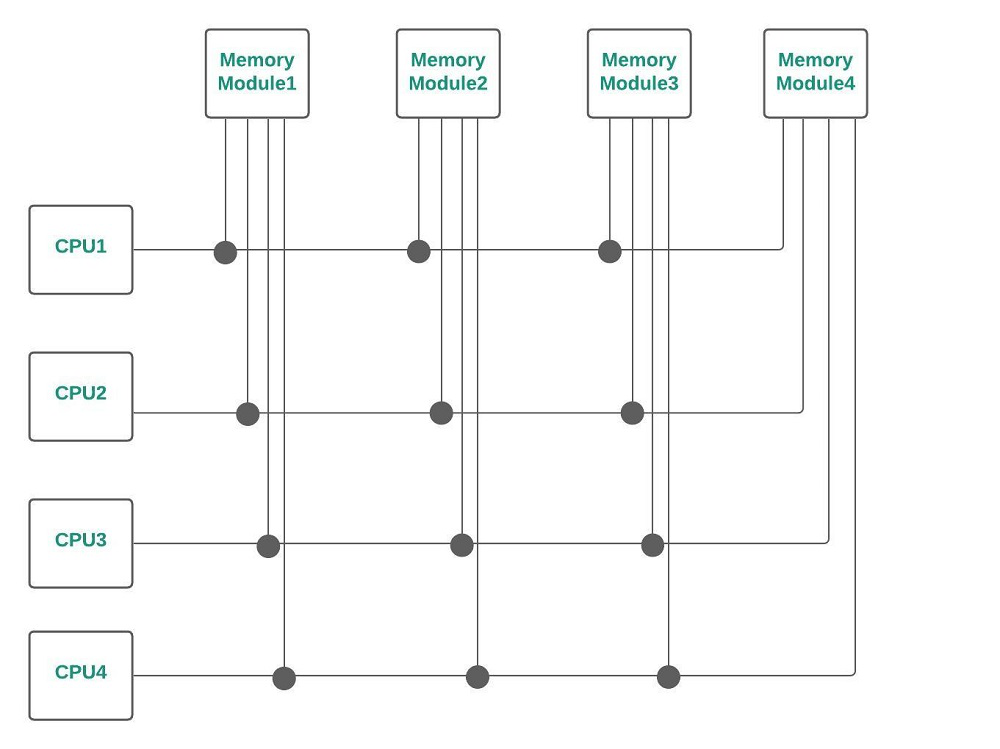
In distributed arbitration, all devices participate in the selection of the next bus master. In this scheme each device on the bus is assigned a4-bit identification number.
What are the four types of bus arbitration?
Bus arbitration schemes can be divided into four broad classes:Daisy chain arbitration.Centralized arbitration.Distributed arbitration by self-selection:Distributed arbitration by collision detection (e.g. Ethernet)
What is bus arbitration explain?
Bus Arbitration is the procedure by which the active bus master accesses the bus, relinquishes control of it, and then transfers it to a different bus-seeking processor unit. A bus master is a controller that can access the bus for a given instance.
What are the methods of bus arbitration?
Types of Bus Arbitration There are three arbitration schemes which run on centralized arbitration. a) Daisy Chaining − It is a simple and cheaper method where all the masters use the same line for making bus requests. b) Polling Method − In this method, the controller is used to generate address lines for the master.
What are the 3 types of buses?
Three types of bus are used.Address bus - carries memory addresses from the processor to other components such as primary storage and input/output devices. ... Data bus - carries the data between the processor and other components. ... Control bus - carries control signals from the processor to other components.
What are the characteristics of distributed bus arbitration?
Distributed BUS Arbitration : In this, all devices participate in the selection of the next bus master. Each device on the bus is assigned a 4bit identification number. The priority of the device will be determined by the generated ID.
What is the importance of bus arbitration?
Bus Arbitration And Message Priority The message arbitration (the process in which two or more CAN controllers agree on who is to use the bus) is of great importance for the readily available bandwidth for data transmission. Any CAN controller may start a transmission when it has detected an idle bus.
What is synchronous and asynchronous bus?
An synchronous bus works at a fixed clock rate whereas an asynchronous bus data transfer is not dependent on a fixed clock. Asynchronous buses take their timings from the devices involved in the data transfer (that is, the processor or system clock).
Which of the following is the fastest method of bus arbitration?
Which of the following is the fastest method of bus arbitration? Explanation: The independent request scheme is quite fast because each of the masters can independently communicate with the controller.
CAN bus arbitration example?
Main Rules of Bus Arbitration 1. This example uses three nodes in a CAN network, in this case represented by three transistors in open-collector configuration (“Wired And”). The bus level will be at low level (dominant) in case any number of transistors in the network output a dominant level.
What is a bus protocol?
Bus Protocols: The bus protocols can be used to transfer the data between to processors or buses. The serial protocols like SPI, I2C, USB can be used to exchange the data in the form of packets from one of the computational elements to other and vice versa.
What are the types of operands?
Three kinds of operands are generally available to the instructions: register, memory, and immediate.
What are the types of operands?
Three kinds of operands are generally available to the instructions: register, memory, and immediate.
What is synchronous and asynchronous bus?
An synchronous bus works at a fixed clock rate whereas an asynchronous bus data transfer is not dependent on a fixed clock. Asynchronous buses take their timings from the devices involved in the data transfer (that is, the processor or system clock).
What are internal and external buses?
An internal bus enables the communication between internal components, such as a video card and memory. An external bus is capable of communicating with external peripherals, such as a USB or SCSI device.
CAN bus arbitration example?
Main Rules of Bus Arbitration 1. This example uses three nodes in a CAN network, in this case represented by three transistors in open-collector configuration (“Wired And”). The bus level will be at low level (dominant) in case any number of transistors in the network output a dominant level.
What is bus arbitration? Explain any two techniques of bus arbitration.
Bus Arbitration: The process of determining which competing bus master will be allowed access to the bus is called Bus Arbitration. Multiple devices may need to use the bus at the same time so must have a way to arbitrate multiple requests.
What is bus arbitration? Explain any two techniques of bus arbitration.
Bus Arbitration: The process of determining which competing bus master will be allowed access to the bus is called Bus Arbitration. Multiple devices may need to use the bus at the same time so must have a way to arbitrate multiple requests.
System Bus in Computer Architecture | Gate Vidyalay
Timing signals are used to synchronize the memory and I/O operations with a CPU clock. Typical control signals hold by control bus-Memory read – Data from memory address location to be placed on data bus. Memory write – Data from data bus to be placed on memory address location. I/O Read – Data from I/O address location to be placed on data bus. I/O Write – Data from data bus to be ...
What is bus arbitration?
Bus Arbitration refers to the process by which the current bus master accesses and then leaves the control of the bus and passes it to another bus requesting processor unit. The controller that has access to a bus at an instance is known as a Bus master .
Why is it difficult to add bus masters?
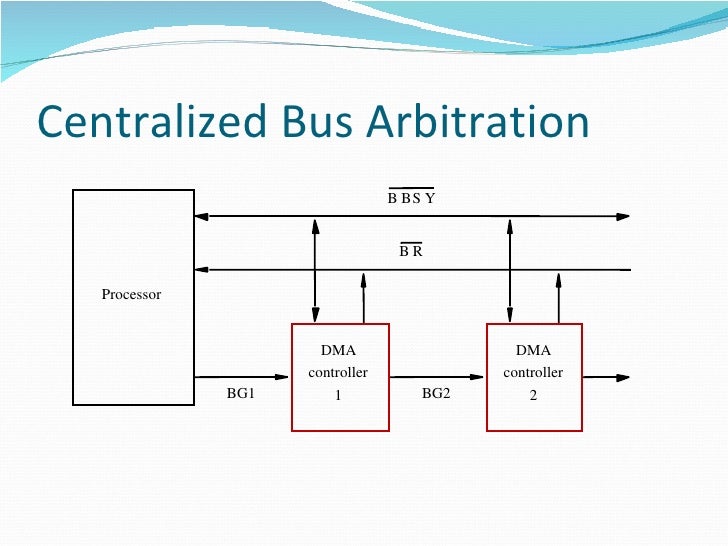
Adding bus masters is difficult as increases the number of address lines of the circuit. (iii) Fixed priority or Independent Request method –. In this, each master has a separate pair of bus request and bus grant lines and each pair has a priority assigned to it.
Can a DMA controller be a bus master?
A conflict may arise if the number of DMA controllers or other controllers or processors try to access the common bus at the same time, but access can be given to only one of those. Only one processor or controller can be Bus master at the same point in time.
What are the two types of bus arbitration?
There are two types of bus arbitration namely. Centralized Arbitration. Distributed Arbitration. Only single bus arbiter performs the required arbitration and it can be either a processor or a separate DMS controller. There are three arbitration schemes which run on centralized arbitration. a) Daisy Chaining: It is a simple ...
Why is distributed arbitration reliable?
The distributed arbitration is highly reliable because the bus operations are not dependant on devices.
How many arbitration schemes are there?
There are three arbitration schemes which run on centralized arbitration.
How do distributed systems work?
This is how distributed systems work. They divide the information (money in your case) and keep it on different machines (pockets and bags for us). This way if one of the machine goes down, we are not at a big loss. That is, we do not have a *single point of failure*
What is Bus Arbitration?
A device that initiates data transfers on the bus at any given time is called a bus master.
What are the two types of bus arbitration?
There are two types of bus arbitration namely. Centralised Arbitration. Distributed Arbitration. Only single bus arbiter performs the required arbitration and it can be either a processor or a separate DMS controller. There are three arbitration schemes which run on centralized arbitration.
Why is distributed arbitration reliable?
It does so by placing a 0 at the input of their drive. The distributed arbitration is highly reliable because the bus operations are not dependant on devices.
What happens when a master bus relinquishes another bus?
These devices share the system bus and when a current master bus relinquishes another bus can acquire the control of the processor.
How many arbitration schemes are there?
There are three arbitration schemes which run on centralized arbitration.
Can a computer have more than one bus master?
In a computer system, there may be more than one bus master such as a DMA controller or a processor etc. These devices share the system bus and when a current master bus relinquishes another bus can acquire the control of the processor.
