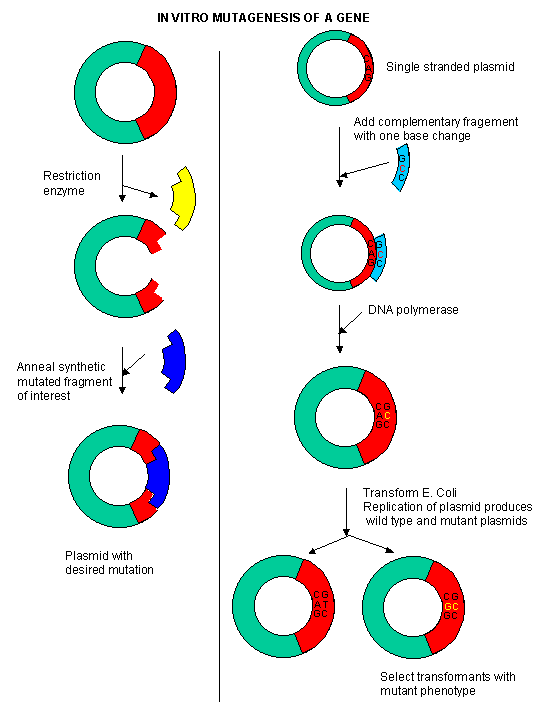
What is the process of mutagenesis?
Mutagenesis (/mjuːtəˈdʒɛnɪsɪs/) is a process by which the genetic information of an organism is changed by the production of a mutation. It may occur spontaneously in nature, or as a result of exposure to mutagens.
What is an example of mutagenesis?
DNA changes caused by mutagens may harm cells and cause certain diseases, such as cancer. Examples of mutagens include radioactive substances, x-rays, ultraviolet radiation, and certain chemicals.
Is mutagenesis and mutation same?
Mutagenesis is the process by which mutations are induced in the cells of organisms. Mutations can have beneficial effects, deleterious effects, or no consequences in organisms. Certain mutations have a positive effect on the organism.
What is the importance of mutagenesis?
Mutation breeding and plant mutagenesis play a significant role in increasing the genetic variability for desired traits in various food crops [1,2,3]. Induced mutagenesis is one of the most efficient tools used for the identification of key regulatory genes and molecular mechanisms.
What are the 4 types of mutagens?
There are three main types of mutagens: physical, chemical, and biological. Each type results in damage to DNA during the processes of replication and repair.
How do mutagens affect DNA?
Mutagens are agents that damage DNA and can, depending on the ability of an organism to repair the damage, lead to permanent changes (mutations) in the DNA sequence. But agents that damage DNA can also damage deoxynucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs), which are used by DNA polymerases to replicate DNA.
What is PCR mutagenesis?
PCR mutagenesis is a method for generating site-directed mutagenesis. This method can generate mutations (base substitutions, insertions, and deletions) from double-stranded plasmid without the need for subcloning into M13-based bacteriophage vectors and for ssDNA rescue.
What are the three main causes of mutations?
Mutations can result from errors in DNA replication during cell division, exposure to mutagens or a viral infection.
How do mutagens cause mutations?
Mutagens cause mutations in three different ways: Some act as base analogs and are mistakenly used as substrates when new DNA is synthesized at the replication fork. Some react directly with DNA, causing structural changes that lead to miscopying of the template strand when the DNA is replicated.
What are the types of mutagens?
Three different types of common mutagens are observed in nature- physical and chemical mutagens agents and biological agents.
Is mutagenesis reversible?
Mutagenesis is of concern because it may lead to irreversible effects that can affect fitness of organisms, which in turn may affect population-level processes.
What does a gene mutation affect?
Sometimes, gene variants (also known as mutations) prevent one or more proteins from working properly. By changing a gene's instructions for making a protein, a variant can cause a protein to malfunction or to not be produced at all.
What are the types of mutagenesis?
Two primary mutagenesis techniques are site-directed mutagenesis (SDM) and random-and-extensive mutagenesis (REM). These methods are largely accomplished by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and non-polymerase chain reaction (non-PCR).
What are 5 mutagens?
Some of the common examples of mutagens are- UV light, X-rays, reactive oxygen species, alkylating agents, base analogs, transposons, etc.
What is the most common mutagen?
The most commonly used chemical mutagens are alkylating agents such as ethylmethane sulfonate and N-methyl-N-nitrosourea that induce point mutations in DNA.
What is bacterial mutagenesis?
Mutagenesis. The process by which mutations are produced. Mutation reporter. A gene or set of genes in which mutations may yield mutantswith a selectable phenotype.
What are the advantages of amino acid mutagenesis?
Advantages: The role of an amino acid in the working of the protein is not required. Since a range of mutants are produced in this process some interesting and useful proteins may be generated. 3. Insertional Mutagenesis: Insertional Mutagenesis is produced by the insertion of one or more bases and can be produced. 1.
Which DNA type is oligonucleotide directed mutation?
a. Oligonucleotide Directed Mutagenesis With M13 DNA
What is a signature tagged mutation?
a. Signature Tagged Mutagenesis : Is used to study the function of genes using transposons.A transposon such as Drosophila melanogaster P -Element is made to integrate randomly in the genome of an organism. The mutants are then screened for any unusual phenotype.Any such phenotype is found suggests that the transposon has caused the inactivation of the phenotype related to that gene. Since the sequence of transposon is known the whole genome can be sequenced to identify the gene or PCR can be used to amplify the specific gene.
What is direct mutation?
Directed Mutagenesis is defined as the change in amino acid coding at the DNA level. A characterized 3D structure of the protein using X Ray crystallography and other analytical procedures helps in determining which amino acids of protein should be changed to attain specific property. However,this may not be possible for most of the proteins and hence a trial and error strategy is used to make changes in the nucleotides to yield a particular change in the protein. The encoded protein is then tested for the desired change in the protein.
What is the term for the fluctuation of the genome of an organism?
Mutagenesis refers to any fluctuation of the genome of the organisms by physical or chemical mutagens. The different types and their uses and drawbacks are discussed in the article...
Who developed the phenotype of the organism?
It was developed by Charlotte Auerbach. She was the first women scientist to study on the effect of chemical mutagens. This immediately found use as a genetic tool to induce mutations in specific ways which in turn can be used to determine the phenotype of the organism, the function of the genes and even the nucleotides.
What is mutation in biology?
Mutation. =. A mutation is a change in a DNA sequence. Mutations can result from DNA copying mistakes made during cell division, exposure to ionizing radiation, exposure to chemicals called mutagens, or infection by viruses.
Is mutation a narrator?
Narration. Mutation has been the source of many Hollywood movies, but it's really a simple process of a mistake made in a DNA sequence as it's being copied. Some of that's just the background noise that DNA copying is not perfect, and we should be glad of that or evolution couldn't operate. But mutation can also be induced by things like radiation ...
Can mutations be induced by radiation?
But mutation can also be induced by things like radiation or carcinogens in a way that can increase the risk of cancers or birth defects. But it's pretty simple; it's basically an induced misspelling of the DNA sequence. That's a mutation.
What causes DNA mutations?
These alterations can be caused by random mistakes in DNA replication or by environmental influences such as UV rays and chemicals.
What happens if a point mutation occurs in the third nitrogen base in a codon?
If the point mutation occurs in the third nitrogen base in a codon, then it has no effect on the amino acid or subsequent protein and the mutation does not change the organism. At most, a point mutation will cause a single amino acid in a protein to change.
What happens to amino acids after deletion?
Again, this causes the entire reading frame to change. It alters the codon and will also affect all amino acids that are coded for after the deletion .
What is frameshift mutation?
One type of frameshift mutation is called insertion. As the name implies, an insertion occurs when a single nitrogen base is accidentally added in the middle of a sequence. This throws off the reading frame of the DNA and the wrong amino acid is translated. It also pushes the entire sequence down by one letter, changing all codons that come after the insertion, completely altering the protein.
What is the least harmful type of mutation?
A point mutation—the change of a single nitrogen base in a DNA sequence —is usually the least harmful type of DNA mutation. Codons are a sequence of three nitrogen bases in a row that are "read" by messenger RNA during transcription. That messenger RNA codon is then translated into an amino acid that goes on to make a protein that will be expressed by the organism. Depending on the placement of a nitrogen base in the codon, a point mutation may have no effect on the protein.
What is a point mutation that is not harmless?
One example of a point mutation that is not harmless is the incurable blood disorder sickle cell anemia. This happens when a point mutation causes a single nitrogen base in a codon for one amino acid in the protein glutamic acid to code for the amino acid valine instead. This single small change causes a normally round red blood cell ...
How is DNA sequence read?
DNA Mutation Analogy. Much like reading text, the DNA sequence is "read" by messenger RNA to produce a "story" or an amino acid chain that will be used to make a protein. Since each codon is three letters long, let's see what happens when a "mutation" occurs in a sentence that uses only three-letter words.
What is deletion mutagenesis?
Deletion mutagenesis is when some bases are removed from the original/target DNA sequence. Inverse PCR is the best technique to produce deletion mutagenesis.
What is site-directed mutagenesis?
Site-directed mutagenesis: Site: specific location into the genome, Directed– performed by artificial techniques, Mutagenesis– Introduction of mutation.
What is the most common method of site directed mutagenesis?
The conventional PCR method is one of the most popular and easy methods for site-directed mutagenesis. The set up is simple; short, single-stranded oligonucleotide primers are designed in such a way that possess the mutation we wish to study.
Which polymerase is used in PCR?
DNA polymerases such as Pfu, Vent, and Phusion facilitate a higher amplification rate in site-directed mutagenesis. The Taq DNA polymerase is only used in the conventional PCR based method for introducing mutation.
What is the first step in mutagenesis?
The very first step in the mutagenesis process is to select the template DNA and mutation we wish to introduce. Several parameters prior to the experiment are evaluated such as template length, GC content, annealing temperature, template type, etc.
What is the purpose of introducing mutations?
The purpose of introducing a mutation is to study the function of a gene. Here in the present article, we are going to discussing different methods of introducing mutations or performing site-directed mutagenesis into the DNA, Why to do it and that is the purpose of it. The content of the article is, Introduction to site-directed mutagenesis.
Where to insert mutant bases in PCR?
The major recommendation for the conventional PCR based mutagenesis is to insert mutant bases up to several limits at the 5′ end of the primer or in the middle of the primer.
What is the term for a chemical or physical phenomenon that promotes errors in DNA replication?
Mutagen . A mutagen is a chemical or physical phenomenon, such as ionizing radiation, that promotes errors in DNA replication. Exposure to a mutagen can produce DNA mutations that cause or contribute to diseases such as cancer.
What is the name of the chemical or physical agent that has the ability to change our genetic code in a harmful way?
Narration. A mutagen is a chemical or physical agent that has the ability to change our genetic code in a harmful way. The change in the genetic code is called a mutation, and throughout our lifetime we actually accumulate many mutations within our cells.
Can mutations cause cancer?
Therefore, mutations are actually associated with the development of cancer.