
What is a simply way of explaining DNA?
DNA, short for deoxyribonucleic acid, is the molecule that contains the genetic code of organisms. This includes animals, plants, protists, archaea and bacteria. DNA is in each cell in the organism and tells cells what proteins to make. Mostly, these proteins are enzymes. DNA is inherited by children from their parents. This is why children share traits with their parents, such as skin, hair and eye color. The DNA in a person is a combination of the DNA from each of their parents. Part of an org
What is DNA and how does it work?
Like the one ring of power in Tolkien's "Lord of the Rings," deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the master molecule of every cell. It contains vital information that gets passed on to each successive generation. It coordinates the making of itself as well as other molecules (proteins). If it is changed slightly, serious consequences may result.
What are the two major functions of DNA?
The functions of DNA include:
- Replication
- Gene expression
- Mutation
- Transcription
- Translation
Does DNA stand for?
Your DNA is what makes you uniquely you. DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid, sometimes called "the molecule of life," as almost all organisms have their genetic material codified as DNA. Subsequently, question is, what is the full name of DNA? The full name of DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, gives you the name of the sugar present - deoxyribose.
What is DNA short explanation?
The molecule inside cells that contains the genetic information responsible for the development and function of an organism. DNA molecules allow this information to be passed from one generation to the next.
What is DNA in simple sentence?
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the hereditary material in humans and almost all other organisms. Nearly every cell in a person's body has the same DNA.
Why is DNA important simple explanation?
Why is DNA so important? Put simply, DNA contains the instructions necessary for life. The code within our DNA provides directions on how to make proteins that are vital for our growth, development, and overall health.
What is DNA explain to kids?
DNA is the genetic information inside the cells of the body that helps make people who they are. It's the instructions for how to make the body, like the code to a video game or blueprints for a house. If you used a very strong microscope, you would see that DNA looks like a twisting ladder.
What is DNA made of?
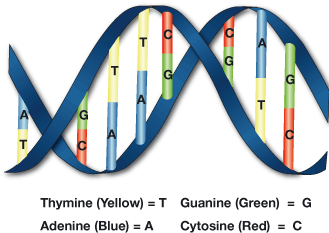
DNA is a linear molecule composed of four types of smaller chemical molecules called nucleotide bases: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). The order of these bases is called the DNA sequence.
What are the 3 purposes of DNA?
DNA now has three distinct functions—genetics, immunological, and structural—that are widely disparate and variously dependent on the sugar phosphate backbone and the bases.
What is DNA in simple words for kids?
DNA is the genetic information inside the cells of the body that helps make people who they are. It's the instructions for how to make the body, like the code to a video game or blueprints for a house. If you used a very strong microscope, you would see that DNA looks like a twisting ladder.
How is DNA like a sentence?
Genes are made of DNA The language of genetics has only four letters (A,T, C, and G). These four letters are combined into three-letter words. The words make up “genes,” which are like sentences. Each sentence has an important meaning or story to tell.
What is DNA made of?
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. It’s made up of units of biological building blocks called nucleotides. DNA is a vitally important molecule for not only humans, but for most other organisms as well. DNA contains our hereditary material and our genes — it’s what makes us unique.
What happens when your cells divide?
The cells of your body divide as a normal part of growth and development. When this happens, each new cell must have a complete copy of DNA.
How does DNA get split?
In order to achieve this, your DNA must undergo a process called replication. When this occurs, the two DNA strands split apart. Then, specialized cellular proteins use each strand as a template to make a new DNA strand. When replication is completed, there are two double-stranded DNA molecules.
What part of DNA is responsible for aging?
Another part of DNA that may be involved in aging are telomeres. Telomeres are stretches of repetitive DNA sequences that are found at the ends of your chromosomes. They help to protect DNA from damage, but they also shorten with each round of DNA replication.
Why are mutations bad?
They can sometimes be bad. This is because a change in the DNA code can have a downstream impact on the way a protein is made. If the protein doesn’t work properly, disease can result.
Why do cells read the code 3 bases at a time?
Your cells read this code three bases at a time in order to generate proteins that are essential for growth and survival. The DNA sequence that houses the information to make a protein is called a gene. Each group of three bases corresponds to specific amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins.
Why is DNA damaged?
In fact, it’s estimated that tens of thousands of DNA damage events occur every day in each of our cells. Damage can occur due to things like errors in DNA replication, free radicals, and exposure to UV radiation. But never fear!
What are the chemicals that make up the sides of the DNA ladder?
Chemicals called phosphates and sugars make up the sides of the ladder. DNA also has chemicals called bases. Each base on one strand is joined to a base on the other strand. The linked bases form the rungs of the ladder.
How many strands are in DNA?
DNA has a complex structure. It is made of chemical substances that are linked together like a chain. Each piece of DNA has two long strands, or chains. The two strands are joined together. They form a shape like a ladder that has been twisted into a spiral.
Why does DNA work?
When DNA works correctly, it helps keep the body functioning properly. DNA helps cells to make the substances called proteins , which the cells need to live. DNA also allows living things to reproduce. The genes in DNA pass along physical traits from parents to children.
What is DNA in biology?
Introduction. DNA is the material that carries all the information about how a living thing will look and function. For instance, DNA in humans determines such things as what color the eyes are and how the lungs work. Each piece of information is carried on a different section of the DNA. These sections are called genes.
Why is the order in which the bases are arranged important?
The order in which the bases are arranged is very important. It forms a code that tells cells to make certain kinds of proteins. The differences in these proteins is what makes different living things—such as a cactus, a gerbil, and two different people—different. Print (Subscriber Feature)
Where is DNA found in a cell?
DNA is short for deoxyribonucleic acid. It is in every cell of every living thing. DNA is found in structures of the cell called chromosomes. Both DNA and chromosomes are tiny.
What are the bases of sugar?
Attached to each sugar is one of four bases--adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). The two strands are held together by bonds between the bases; adenine bonds with thymine, and cytosine bonds with guanine.
What is DNA made of?
The DNA molecule consists of two strands that wind around one another to form a shape known as a double helix. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups. Attached to each sugar is one of four bases--adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). The two strands are held together by bonds between the bases; adenine bonds with thymine, and cytosine bonds with guanine. The sequence of the bases along the backbones serves as instructions for assembling protein and RNA molecules.
What is the name of the structure of DNA?
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the central information storage system of most animals and plants, and even some viruses. The name comes from its structure, which is a sugar and phosphate backbone which have bases sticking out from it--so-called bases.
How many bases are in DNA?
The bases go by the names of adenine, cytosine, thymine, and guanine, otherwise known as A, C, T, and G. DNA is a remarkably simple structure. It's a polymer of four bases--A, C, T, and G--but it allows enormous complexity to be encoded by the pattern of those bases, one after another. DNA is organized structurally into chromosomes ...
Where do traits come from?
Functionally, it's organized into genes, of which are pieces of DNA, which lead to observable traits. And those traits come not from the DNA itself, but actually from the RNA that is made from the DNA, or most commonly of proteins that are made from the RNA which is made from the DNA.
Where do eye colors come from?
But for the most part, the observable traits of eye color or height or one thing or another of individuals come from individual proteins. Sometimes, we're learning in the last few years, actually, they come from RNAs themselves without being made into proteins--things like micro RNAs.
Can you add videos to your watch history?
Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations. To avoid this, cancel and sign in to YouTube on your computer.
How does DNA make proteins?
First, enzymes read the information in a DNA molecule and transcribe it into an intermediary molecule called messenger ribonucleic acid, or mRNA.
Why is DNA a chromosome?
Because the cell is very small, and because organisms have many DNA molecules per cell, each DNA molecule must be tightly packaged. This packaged form of the DNA is called a chromosome. During DNA replication, DNA unwinds so it can be copied.
What are the building blocks of DNA?
DNA is made of chemical building blocks called nucleotides. These building blocks are made of three parts: a phos phate group, a sugar group and one of four types of nitrogen bases. To form a strand of DNA, nucleotides are linked into chains, with the phosphate and sugar groups alternating.
What are the four nitrogen bases found in nucleotides?
The four types of nitrogen bases found in nucleotides are: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). The order, or sequence, of these bases determines what biological instructions are contained in a strand of DNA. For example, the sequence ATCGTT might instruct for blue eyes, while ATCGCT might instruct for brown.
Why is DNA in its compact chromosome form?
But during cell division, DNA is in its compact chromosome form to enable transfer to new cells. Researchers refer to DNA found in the cell's nucleus as nuclear DNA.
How much of the DNA is made up of genes?
The size of a gene may vary greatly, ranging from about 1,000 bases to 1 million bases in humans. Genes only make up about 1 percent of the DNA sequence. DNA sequences outside this 1 percent are involved in regulating when, how and how much of a protein is made.
How many genes are in the DNA instruction book?
The complete DNA instruction book, or genome, for a human contains about 3 billion bases and about 20,000 genes on 23 pairs of chromosomes.
What are the four types of nucleotides in DNA?
The nitrogenous bases in DNA are of four types – adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine. The phosphate and the deoxyribose sugars form a backbone-like structure, with the nitrogenous bases extending out like rungs of a ladder.
How was DNA discovered?
DNA was isolated and discovered chemically before its functions became clear. DNA and its related molecule, ribonucleic acid (RNA), were initially identified simply as acidic molecules that were present in the nucleus. When Mendel’s experiments on genetics were rediscovered, it became clear that heredity was probably transmitted through discrete particles, and that there was a biochemical basis for inheritance. A series of experiments demonstrated that among the four types of macromolecules within the cell (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids ), the only chemicals that were consistently transmitted from one generation to the next were nucleic acids.
What is DNA in biology?
DNA Definition. Deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, is a biological macromolecule that carries hereditary information in many organisms. DNA is necessary for the production of proteins, the regulation, metabolism, and reproduction of the cell. Large compressed DNA molecules with associated proteins, called chromatin, ...
What material was transferred from one generation to the next?
As it became clear that DNA was the material that was transferred from one generation to the next, its functions began to be investigated.
What were the most important discoveries of the twentieth century?
By the turn of the twentieth century, molecular biology experienced a number of seminal discoveries that brought about an enhanced understanding of the chemical basis of life and cell division. In 1944, experiments by three scientists, (Avery, McCarty and McLeod) provided strong evidence that nucleic acids, specifically DNA, was probably the genetic material. A few years later, Chargaff’s experiments showed that the number of purine bases in every DNA molecule equaled the number of pyrimidine bases. In 1952, an elegant experiment by Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase confirmed DNA as the genetic material.
Why is DNA important in biology?
On another level, DNA’s role as genetic material and an understanding of its chemistry allows us to manipulate it and use it to enhance quality of life. For example, genetically modified crops that are pest or drought resistant have been generated from wild type varieties through genetic engineering. A lot of molecular biology is dependent on the isolation and manipulation of DNA, for the study of living processes.
How does life begin?
Life begins from a single cell. For humans, this is the zygote formed by the fertilization of an egg by a sperm. After this, the entire dazzling array of cells and tissue types are produced by cell division. Even the maintenance of normal functions in an adult requires constant mitosis.
What is DNA?
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid and is the familiar “double helix” molecule forming the building blocks of every living organism. In your body, DNA is tightly coiled up into chromosomes, and each chromosome contains a specific number of genes. The total number differs depending on the chromosome, of which there are 23 pairs or a total of 46. At conception, you get one set of chromosomes from your mother and another from your father, giving you a unique combination of characteristics expressed as what’s known as your genetic code.
Where is DNA Found?
DNA is housed inside all the cells of your body. Most of it resides in the nucleus of each cell and is called nuclear DNA. The rest is inside the mitochondria, the small organelles within cells responsible for energy production, and is known as mitochondrial DNA.
What is the Function of DNA?
Although over 99 percent of the bases in your DNA are identical to those in other people, the remaining fraction of a percentage is unique to you and influences everything from how cells differentiate in the womb to your risk for genetic diseases. Think of the letters representing the bases as an alphabet used to create the “words” making up your genetic sequence. With the exception of identical twins, no two people have exactly the same sequence of base pairs in their DNA. These differences have an influence on the outcomes of the two biggest functions DNA performs.
What happens when DNA is split?
When cells divide, the DNA double helix “unzips” down the middle to form two separate strands. Complimentary copies are made and attached to the unpaired bases, creating an identical strand of DNA for the new cell. If there’s an error in the process, the body usually destroys the mutation to prevent the error from replicating in the future. However, when this doesn’t happen, the resulting mutation can become the basis for disease. DNA errors like these may or may not cause problems depending on whether or not mutated genes are expressed when proteins are made.
How many bases are in a double helix?
Each DNA double helix is made up of two strands of nucleotides and a collection of nitrogenic bases. Nucleotides have three parts: The four bases, adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G), link together in various combinations of base pairs and determine the characteristics of the nucleotide.
Why is DNA packed into chromosomes?
The tight “packaging” of DNA into chromosomes makes it possible for this much genetic information to be contained in such a small space. Every time a cell divides, an identical copy of this lengthy double strand is made to ensure new cells have the same sequence of base pairs as the originals.
How do proteins work?
Proteins play a multitude of roles in your body, and it’s up to DNA to provide the code from which individual proteins are made. When a specific protein is required: 1 The DNA code is copied to create a single-stranded molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA) 2 Another type of RNA, known as transfer RNA (tRNA), “reads” the code from the mRNA in groups of three bases at a time 3 These groups, or codons, tell the body which amino acids are needed to make the protein
What is DNA?
- DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. It contains units of biological building blocks called nucleo…
DNA is a vitally important molecule for not only humans but also most other organisms. DNA contains our hereditary material and our genes, the things that make us unique.
What is the structure of DNA?
- A collection of nucleotides makes a DNA molecule. Each nucleotide contains three components:
•a sugar - •a phosphate group
•a nitrogen base
What does DNA do?
- DNA helps your body grow
Your cells read this code three bases at a time to generate proteins that are essential for growth and survival. The DNA sequence that houses the information to make a protein is called a gene. Each group of three bases corresponds to specific amino acids, which are the building blo… - How do you get from the DNA code to a protein?
First, the two DNA strands split apart. Then, special proteins within the nucleus read the base pairs on a DNA strand to create an intermediate messenger molecule. This process creates the messenger molecule RNA (mRNA). mRNA is another type of nucleic acid. It travels outside the …
DNA in health, disease, and aging
- The complete set of your DNA is called your genome. It contains roughly 3 billion bases, 20,000 …
You inherit one half of your DNA from your father and one half from your mother. This DNA comes from the sperm and egg, respectively. - Genes make up very little of your genome — only 1 percent. The other 99 percent helps regulat…
Scientists are still learning more and more about this “non-coding” DNA.
Where is DNA found?
- Eukaryotic cells
Humans and many other organisms have eukaryotic cells. This means that their cells have a membrane-bound nucleus and several other membrane-bound structures called organelles. In a eukaryotic cell, DNA is within the nucleus. A small amount of DNA is also in organelles called mi… - Prokaryotic cells
Organisms like bacteria are prokaryotic cells. These cells don’t have a nucleus or organelles. In prokaryotic cells, DNA resides in the middle of the cell, called a nucleoid, coiled tightly.
Takeaway
- DNA is pivotal to our growth, reproduction, and health. It contains the instructions necessary for …
Because DNA is so important, damage or mutations can sometimes contribute to disease development. However, it’s also important to remember that mutations can be beneficial and contribute to our diversity.