Full Answer
What is dopamine sensitivity?
Dopamine is the brain's pleasure, motivation, and reward chemical. Improving dopamine sensitivity can have profound effects on many day-to-day functions, including motivation, memory, behavior, cognition, attention, sleep, mood, learning, and activities such as intense exercise.
What is a dopamine supersensitivity psychosis?
Dopamine supersensitivity psychosis may occur due to upregulation of dopamine 2 receptors (D2). The D2 receptor is the primary target of almost all antipsychotics, which oppose the action of the neurotransmitter dopamine at this receptor.
What causes dopamine receptors to be sensitive to antipsychotics?
Dopamine supersensitivity may be caused by the dopamine receptor D2 antagonizing effect of antipsychotics, causing a compensatory increase in D2 receptors within the brain that sensitizes neurons to endogenous release of the neurotransmitter dopamine.
Is there a relationship between dopamine receptor hypersensitivity and dyskinetic disorders?
The relationship of this phenomenon of dopamine receptor hypersensitivity and the clinical findings in dyskinetic disorders, is discussed; also some ideas for further research in this area are brought to light. Amphetamine* / pharmacology Amphetamines / administration & dosage
See more

How is dopamine supersensitivity treated?
Although the emergence of dopamine supersensitivity might be related to the upregulation of dopamine D2 receptor, which engenders tolerance to antipsychotics [Chouinard, 1991], no established treatment exists for this condition except for the use of clozapine [Kane et al.
What causes dopamine hypersensitivity?
Dopamine supersensitivity may be caused by the dopamine receptor D2 antagonizing effect of antipsychotics, causing a compensatory increase in D2 receptors within the brain that sensitizes neurons to endogenous release of the neurotransmitter dopamine.
What is dopamine receptor supersensitivity?
Abstract. Dopamine (DA) receptor supersensitivity refers to the phenomenon of an enhanced physiological, behavioral or biochemical response to a DA agonist.
Do antipsychotics upregulate dopamine?
Studies on cell cultures and animal models have shown that long-term antipsychotic use is linked to both an upregulation of dopamine D2-receptors in the striatum and the emergence of enhanced receptor affinity to endogenous dopamine.
How do I know if I have too much dopamine?
When certain parts of the brain are exposed to too much dopamine, for instance right after an individual takes illicit drugs, other behaviors may be present. These can include aggression, hallucinations, twitching, nausea and/or vomiting, and depression.
What is dopamine overactivity most like?
Given the tight correlation between the clinical potency and the D2-blocking action of the antipsychotic medications, dopamine overactivity could be the common denominator in the psychotic element of schizophrenia.
Can too much dopamine cause psychosis?
This research provided the first direct evidence that psychotic symptoms are promoted by excessive dopamine D2-receptor stimulation, a finding that is suggestive of an increased phasic activity of dopaminergic neurons in the subcortex.
Why do antipsychotics block dopamine?
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter, which means that it passes messages around your brain. Most antipsychotic drugs are known to block some of the dopamine receptors in the brain. This reduces the flow of these messages, which can help to reduce your psychotic symptoms. Affecting other brain chemicals.
Can antipsychotics make things worse?
First generation antipsychotics often have little effect on the negative symptoms. Some of their side effects may even make your negative symptoms worse. You may try different types of antipsychotic and find that they don't control your symptoms of schizophrenia.
What psych drugs increase dopamine?
What are common dopamine agonists and what do they treat?Bromocriptine (Parlodel). ... Cabergoline. ... Apomorphine (Apokyn). ... Pramipexole (Mirapex). ... Ropinirole (Requip). ... Rotigotine (Neupro).
Which antipsychotics increase dopamine?
Another property of second-generation antipsychotics is that some of them are 5HT1A agonists. This includes drugs such as ziprasidone, quetiapine and clozapine. What is the importance of this? 5HT1A agonism would increase dopamine release in the prefrontal cortex and also reduce glutamate release.
Can antipsychotics worsen psychosis?
As expected from previous studies [14], SP patients relapsing without drug discontinuation/dose reduction/switch of antipsychotics have a severe form of drug-induced psychosis: poor drug response, high chlorpromazine equivalent doses, and more residual negative symptoms. In addition, Fallon et al.
Does high dopamine cause anxiety?
Among other effects, too much dopamine could lead the brain to weigh negative inputs too highly. This could result in paranoia, often seen in schizophrenia patients, or anxiety.
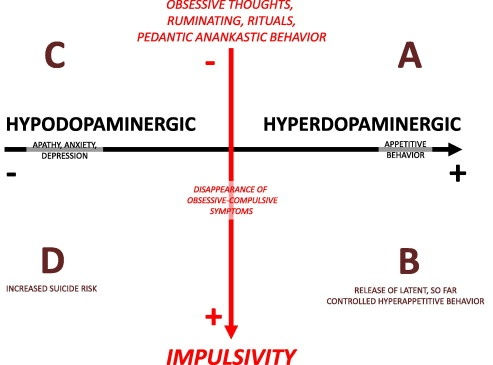
Is dopamine high or low in OCD?
Treatment with deep brain stimulation is effective in OCD, and response correlates with increased dopamine in the nucleus accumbens. Combined this evidence suggests that OCD may be associated with both increased and decreased dopamine signaling, or that a unidirectional model may not be adequate.
How do you reset your dopamine levels?
Things You Can Do to Reset Your Brain's Dopamine LevelsCreate exciting daily routines. Incorporate fun activities into your daily routine, even if they are mindless activities. ... Focus on perfecting your sleep schedule. ... Improve your diet. ... Exercise. ... Practice mindfulness. ... Listen to music.
What is the dopamine supersensitivity hypothesis?
Dopamine supersensitivity is often dismissed as an inconsequential factor in the progression of psychotic disorders by psychiatrists in the medical literature. The dopamine supersensitivity hypothesis was discussed by investigative journalist and author Robert Whitaker in his book Anatomy of an Epidemic, published in 2010.
What is the mechanism of dopamine supersensitivity?
Mechanism. Dopamine supersensitivity psychosis may occur due to upregulation of dopamine 2 receptors (D2) . The D2 receptor is the primary target of almost all antipsychotics, which oppose the action of the neurotransmitter dopamine at this receptor. The antagonizing or "blockade" of D2 by antipsychotics may cause neurons, ...
When was tardive psychosis discovered?
When supersensitivity psychosis was explored in 1978, a featured concern was increasing resistance to medication, requiring higher doses or not responding to higher doses. Some articles use the term tardive psychosis to reference to this specific concept. However, articles have disputed its validity. The condition has been discovered in very few people. Palmstierna asserts that tardive psychosis is a combination of "several different and not necessarily correlated phenomena related to neuroleptic treatment of schizophrenia."
What is the effect of D2 blockade?
The antagonizing or "blockade" of D2 by antipsychotics may cause neurons, a type of cell within the brain, to undergo compensatory changes to make up for the loss of activity at D2 receptors. The D2 signaling pathway within neurons is complex, and involves multiple enzymes and other secondary messengers.
Can tardive dyskinesia be caused by antipsychotics?
Tardive dyskinesia, a type of rare movement disorder that can be caused by antipsychotics, may also be caused by dopamine receptor sensitization. This may explain why, for people with tardive dyskinesia, increasing the dose of the antipsychotic may temporarily improve symptoms.
Can dopamine supersensitivity be a psychotic disorder?
It may sometimes be impossible to distinguish dopamine supersensitivity psychosis from psychosis that occurs "naturally" in the course of a primary psychotic disorder like schizophrenia, including cases in which the person was not taking their antipsychotic medication. Even in the presence of an alternative etiology, or when it is impossible to determine the precise etiology for a psychotic episode, it is possible that dopamine supersensitivity psychosis can play a role in the presentation. Recognizing the possible role of dopamine supersensitivity psychosis in a psychotic episode has implications for how to best manage someone's antipsychotic therapy.
How to increase dopamine sensitivity?
Junk foods like potato chips, candy, and cookies may make you feel momentarily happy, but they are not so good for your health or brain. Get rid of junk food, candy, and desserts, which are processed, concentrated sources of calories that hack your brain into pumping out large amounts of dopamine.
What is the function of dopamine?
Improving dopamine sensitivity can have profound effects on many day-to-day functions, including motivation, memory, behavior, cognition, attention, sleep, mood, learning, and activities such as intense exercise.
What is the term for a decline in dopamine signaling?
Understand what dopamine desensitization is. Desensitization refers to long-term changes involving a decline in dopamine signaling and D2 receptors. A numbed pleasure response, or desensitization , is probably the best-understood brain change that addiction or addictive behaviors induce. The main physiological feature of reward circuitry desensitization is a decline in dopamine signaling. Desensitization is caused by a number of factors, including:
What causes desensitization?
Desensitization is caused by a number of factors, including: 1: Decline in dopamine (D2) receptors. Fewer D2 receptors mean less sensitivity to available dopamine, which leaves a person less sensitive to the pleasure normally found in experiences. 2: Decline in baseline (tonic) dopamine levels.
How do drugs increase dopamine levels?
Drugs can increase dopamine levels by decreasing the amount of dopamine uptake or increasing the amount of dopamine release. Drugs are so potent and stimulating that they can increase dopamine levels to over 1200% of their baseline levels.
What is the role of dopamine in the brain?
It plays important roles in mood, learning, sleep, attention, memory, movement, and anticipation. Dopamine dysfunction (as distinct from desensitization) is the cause of a handful of diseases, most notably Parkinson's disease which is caused by the death of dopamine-producing cells.
How many neurons are involved in dopamine?
Understand what dopamine is. There are close to 86 billion neurons in the brain. They communicate with each other via neurotransmitters, which are chemicals released by nerve cells. Dopamine is linked to many aspects of human behavior including pleasure-seeking, motivation, and addictions.
What is the cause of dopamine supersensitivity syndrome?
Dopamine Supersensitivity Syndrome is a neurological condition caused by a chemical imbalance in the brain, which is usually caused by chronic exposure to neuroleptic (anti-psychotic) drugs. Neuroleptic drugs work by blocking dopamine in the brain at the D2 receptors. Over time, the brain often responds to this assault by creating extra D2 ...
How does the brain respond to dopamine?
Over time, the brain often responds to this assault by creating extra D2 receptors and/or increasing the density and sensitivity of the receptors to dopamine. These changes in the brain are usually permanent.
What happens if you stop taking neuroleptic drugs?
The result is that the neuroleptic drugs lose their effectiveness and if they are stopped, the person's brain is overstimulated by the excessive dopamine activity and he/she develops mania, psychosis, and/or other symptoms characteristic of an amphetamine overdose.
What are the effects of tardive dyskinesia?
The only effects of it that they recognize (or acknowledge) though, are tardive dyskinesia (and accompanying insomnia), the development of new or worsening psychosis upon reduction or discontinuation of the anti-psychotic drug, and the development of tolerance to the anti-psychotic drug.
Does dopamine increase sensitivity?
Unfortunately though, increasing the drug will only cause the brain to develop even more extra receptors and further increased sensitivity to dopamine. Medical science recognizes this problem, but it has yet to be acknowledged as a syndrome.
What is dopamine in the brain?
Written by Erica Julson, MS, RDN, CLT on May 10, 2018. Dopamine is an important chemical messenger in the brain that has many functions. It’s involved in reward, motivation, memory, attention and even regulating body movements ( 1. Trusted Source.
When does dopamine release?
Animal studies show that dopamine is released in large amounts in the morning when it’s time to wake up and that levels naturally fall in the evening when it’s time to go to sleep. However, lack of sleep appears to disrupt these natural rhythms.
Why is dopamine important?
The Bottom Line. Dopamine is an important brain chemical that influences your mood and feelings of reward and motivation. It helps regulate body movements as well. Levels are generally well regulated by the body, but there are a few diet and lifestyle changes you can make to boost your levels naturally.
How to raise dopamine levels naturally?
4. Eat Velvet Beans. Velvet beans, also known as Mucuna pruriens, naturally contain high levels of L-dopa, the precursor molecule to dopamine. Studies show that eating these beans may help raise dopamine levels naturally, especially in people with Parkinson’s disease, a movement disorder caused by low dopamine levels.
How to stimulate dopamine release in the brain?
7. Listen to Music. Listening to music can be a fun way to stimulate dopamine release in the brain. Several brain imaging studies have found that listening to music increases activity in the reward and pleasure areas of the brain, which are rich with dopamine receptors ( 42.
What does low dopamine do to motivation?
In contrast, low levels of dopamine are linked to reduced motivation and decreased enthusiasm for things that would excite most people ( 6 ).
How to increase dopamine levels?
Here are the top 10 ways to increase dopamine levels naturally. Share on Pinterest. 1. Eat Lots of Protein. Proteins are made up of smaller building blocks called amino acids.

Overview
Dopamine supersensitivity psychosis is a hypothesis that attempts to explain the phenomenon in which psychosis (e.g. having hallucinations, which can mean hearing or seeing things that other people do not see or hear) occurs despite treatment with escalating doses of antipsychotics. Dopamine supersensitivity may be caused by the dopamine receptor D2 antagonizing effect of antipsychotics, causing a compensatory increase in D2 receptors within the brain that sensitizes
Mechanism
Dopamine supersensitivity psychosis may occur due to upregulation of dopamine 2 receptors (D2). The D2 receptor is the primary target of almost all antipsychotics, which oppose the action of the neurotransmitter dopamine at this receptor. The antagonizing or "blockade" of D2 by antipsychotics may cause neurons, a type of cell within the brain, to undergo compensatory changes to make up for the loss of activity at D2 receptors. The D2 signaling pathway within neurons is complex, an…
Diagnosis
The original criteria for dopamine supersensitivity psychosis were the following:
• A. Continuous use of antipsychotics for at least 3 months.
• B. One of the following:
1. Rebound psychosis within 6 weeks of a change (e.g. dose reduction, or antipsychotic switching) in an oral antipsychotic regimen or 3 months for long-acting injectable antipsychotic…
History
When supersensitivity psychosis was explored in 1978, a featured concern was increasing resistance to medication, requiring higher doses or not responding to higher doses. Some articles use the term tardive psychosis to reference to this specific concept. However, articles have disputed its validity. The condition has been discovered in very few people. Palmstierna asserts that tardive psychosis is a combination of "several different and not necessarily correlated phen…
Society and culture
Dopamine supersensitivity is often dismissed as an inconsequential factor in the progression of psychotic disorders by psychiatrists in the medical literature. The dopamine supersensitivity hypothesis was discussed by investigative journalist and author Robert Whitaker in his book Anatomy of an Epidemic, published in 2010.
Research
As of 2017 , much of the evidence for dopamine supersensitivity psychosis comes from studies performed in animals. There is still a need for robust, human research.
In a cohort study of people taking chronic antipsychotic therapy with either schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder that presented for psychiatric care due to a relapse of their psychotic symptoms without a clear precipitating cause (e.g. new or worsening substance abuse, evidenc…
Further reading
• Chouinard G, Jones BD (1980). "Neuroleptic-induced supersensitivity psychosis: clinical and pharmacologic characteristics". Am J Psychiatry. 137 (1): 16–21. doi:10.1176/ajp.137.1.16. PMID 6101522.
• Steiner W, Laporta M, Chouinard G (1990). "Neuroleptic-induced supersensitivity psychosis in patients with bipolar affective disorder". Acta Psychiatr Scand. 81 (5): 437–40. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.1990.tb05477.x. PMID 1972608. S…
• Chouinard G, Jones BD (1980). "Neuroleptic-induced supersensitivity psychosis: clinical and pharmacologic characteristics". Am J Psychiatry. 137 (1): 16–21. doi:10.1176/ajp.137.1.16. PMID 6101522.
• Steiner W, Laporta M, Chouinard G (1990). "Neuroleptic-induced supersensitivity psychosis in patients with bipolar affective disorder". Acta Psychiatr Scand. 81 (5): 437–40. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.1990.tb05477.x. PMID 1972608. S2CID 36082613.{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint…