
Dorsal intercalated segment instability ( DISI ) is a form of instability involving the wrist. It occurs mainly after the disruption of the s capholunate ligament and is more often encountered than volar intercalated segment instability (VISI).
What is distal intercalated segment instability (DISI)?
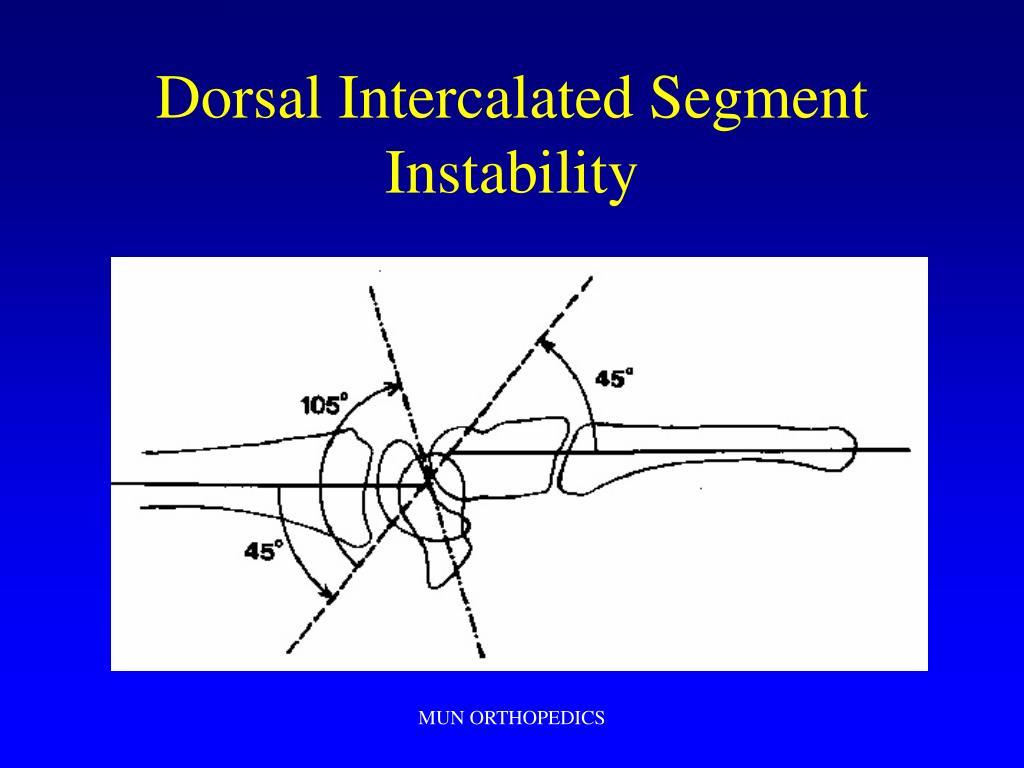
Dorsal intercalated segment instability (DISI) is one complication of chronic scapholunate dissociation. Over time, a rotational instability develops as the secondary stabilizers of the scapholunate joint, especially the radioscaphocapitate ligament, fail. The scaphoid moves into flexion and pronation.
What is the prognosis of dorsal intercalated segment instability?
Untreated dorsal intercalated segment instability eventually progresses to wrist osteoarthritis. For example, wrist osteoarthritis is present in about 85% of untreated cases of scapholunate instability after 36 months.
What is Disi carpal instability?
Dorsal Intercalated Segment Instability (DISI) The most common form of carpal instability. Secondary to disruption of the scapholunate ligamentous complex. The lunate is rotated into extension. As wrist flexes and/or radially deviates the scaphoid will flex and the lunate will extend and vice versa.
What is Disi deformity?
DISI deformity Dorsal intercalated segment instability A DISI deformity is a condition in which there is a mutual change in position of two carpal bones in the wrist joint. This causes symptoms in the wrist area, particularly when extending the wrist.

What is intercalated segment?
An “intercalated segment” would refer to 2 or more adjacent bones that are together acting as an intercalated link within an articulated series.
How is carpal instability treated?
A wrist brace can be placed in neutral and ulnar deviation. NSAID and splinting is the primary treatment option for acute ligamentous injuries. Isometric strengthening exercise of flexor carpi ulnaris and extensor carpi ulnaris is done.
What is volar intercalated segmental instability?
Volar intercalated segment instability (VISI) is a type of carpal instability featuring volar tilt of the lunate. It is less often encountered than dorsal intercalated segment instability (DISI).
What causes Scapholunate instability?
Causes. The scapholunate ligament usually tears when there is a lot of stress put on the wrist. A common cause is a fall onto the hand. Typically, the ligament is injured when the wrist is bent backward or into an unusual position.
What does carpal instability feel like?
Symptoms of Carpal Instability Loss of normal alignment of carpal bones. Changes in the range of motion. Pain and swelling of the wrist. Inability to grip objects.
How can I improve my wrist instability?
Place two fingers on your wrist, rotate your wrist inwards, resisting against your fingers. Using a rubber ball or other object that you can grasp in your hand, squeeze as tight as you can with your fingers and hold for 5 seconds. Push wrist upwards against resistance without changing the angle of your wrist.
What is SLAC wrist?
Scapholunate advanced collapse (SLAC) is a characteristic degenerative clinical wrist condition of progressive deformity, instability, and arthritis that affects the radiocarpal and mid-carpal joints of the wrist.
Why is lunate most commonly dislocated?
Mechanism. Lunate dislocations typically occur due to a fall on an outstretched hand (or during a motor vehicle injury) where there is forceful dorsiflexion of the wrist 3. There is injury of all of the perilunate ligaments, most significantly the dorsal radiolunate ligament.
What is scapholunate widening?
Widening of the scapholunate interval on imaging has been called the “Terry Thomas sign”, referring to the famous actor with a prominent gap in his front teeth [11]. MRI is useful in that in addition to diastasis, it may also directly show a scapholunate ligament tear (Fig. 2).
How do you fix scapholunate instability?
Partial injuries where there is no instability of the scapholunate joint are most commonly treated with splinting or casting, anti-inflammatories and hand therapy. Surgical treatments including arthroscopic debridement and thermal shrinkage of the ligament have been used.
What helps scapholunate instability?
3 Main Treatments for a Scapholunate Ligament InjuryImmobilization of the Wrist. Immobilization with a wrist orthosis in the acute stages is a common intervention provided by a therapist in the acute stage. ... Wrist Stabilization. Wrist stabilization involves strengthening the SL “friendly” muscles. ... Proprioceptive Exercise.
Do you need surgery for torn ligament in wrist?
Wrist Ligament Reconstruction may be necessary when a wrist ligament injury (WLI) is a severe or high grade tear, meaning that the ligament is completely torn or severely stretched. Different types of minimally invasive surgery are incorporated into the treatment algorithm including: Arthroscopy.
How is wrist instability diagnosed?
What may I experience?Clunking /clicking of wrist, or wrist feels like it's 'giving way'Pain with palpation over dorsum of wrist.Pain with end range or rotation.Pain with weightbearing, unable to push down through wrist to stand up.
What causes wrist instability?
Instability can occur as a result of ligaments tearing, or what are rarer, carpal bones fractures (1). Dorsal flexion instability is the most common type of carpal instability, and usually occurs in case of fall on prone, dorsal flexed wrist. It is manifested by a wide Scafo-lunate gap that is larger than 5 mm.
How is lunate instability treated?
3 Main Treatments for a Scapholunate Ligament InjuryImmobilization of the Wrist. Immobilization with a wrist orthosis in the acute stages is a common intervention provided by a therapist in the acute stage. ... Wrist Stabilization. Wrist stabilization involves strengthening the SL “friendly” muscles. ... Proprioceptive Exercise.
How do you treat carpal boss?
TreatmentA wrist splint to immobilize and rest the wrist.Icing of the painful area.Pain relievers such as Motrin or Tylenol.Steroid injection into the boss.Surgery.
What is a disi deformity?
A DISI deformity is a condition in which there is a mutual change in position of two carpal bones in the wrist joint. This causes symptoms in the wrist area, particularly when extending the wrist. In addition to DISI deformity, there is also VISI deformity (Volar Intercalated Segment Instability). However, this is much less common.
How to tell if you have a scapholunar joint?
The most important symptoms include: Pain when extending the wrist. Loss of strength. Pressure pain on the scapholunar joint. In addition, other symptoms can also occur, such as snapping or clicking during wrist movements and problems with gripping objects.
What are your tips for treating clients with a DISI deformity?
This blog is a discussion format. We have listed our views above but would love to know what you think, what your comments are or how you best treat DISI deformity in your practice. Feel free to email us at [email protected]
What happens if the scapholunate ligament is disrupted?
So, if the scapholunate ligament is disrupted, the lunate will displace dorsally with the triquetrum, i.e. DISI. If the lunotriquetral ligament is disrupted, the lunate will displace volarly with the scaphoid, i.e. VISI. A DISI may also be the result of an unstable scaphoid fracture.
What brace to use for disi cast removal?
My professional favourite for DISI post cast removal is: Jura Black Wrist Brace or the Procool D-ring wrist brace.
Is a grade 1 tear considered a disi?
With a Grade 1 tear, there will not be instability, thus this is not a DISI. Some Grade 2 tears do result in instability over time, but can be managed conservatively if diagnosed early. The goal of hand therapy for these clients is stability rather than mobility.
Can a scapholunate ligament tear cause disi?
Not all scapholunate ligament injuries result in DISI. Management depends on the severity of the tear, time since injury, and presence of arthritis. Severity increases from partial tears to dynamic instability to static instability to SLAC (scapho-lunate advanced collapse) wrist arthritis.
What is carpal instability?
Carpal instability occurs when the carpus is unable to maintain its normal alignment and motion under the influence of physiologic loads. Carpal instability must be differentiated from carpal misalignment. With carpal misalignment, the carpus may show deviation from normal radiographic alignment, but the joints will remain stable when loaded under physiologic conditions. [1]
What are the two most common types of carpal instability?
Due to the breadth of this topic, this article will focus on the two most common types of carpal instability: scapholunate and lunotriquetral dissociations. CIND-DISI and CIND-VISI will be elaborated on in the Complications section.
What determines if a lunate is a DISI?
The direction of the lunate relative to the axis of the radius determines whether DISI or VISI is present. For example, if the lunate is extended (dorsiflexed), then there is DISI. [2] [6] It must be noted that DISI or VISI deformities can occur as a consequence of chronic scapholunate or lunotriquetral dissociation, respectively. In this setting, the DISI or VISI is a dissociative malalignment. The third classification, CIC, is the consequence of perilunate or axial dislocations. It has features of both CID and CIND. [2]
How to treat lunotriquetral ligamentous complex injury?
Effective treatment of lunotriquetral ligamentous complex injury is dependent on chronicity and the presence of carpal instability. [19] In the patient with an acute injury (typically less than 6 weeks) without findings of instability on static radiographs, non-operative management should be attempted initially. [19] If the patient fails to respond to conservative treatment, arthroscopy is indicated to determine the extent of the lunotriquetral injury. The arthroscopic classification of the injury can assist in determining the next step in operative management. [19] [64] The management of chronic lunotriquetral ligament injuries is dependent on whether the carpal alignment is reducible or fixed (VISI). In a patient with lunotriquetral dissociation associated with positive ulnar variance and resulting ulnar abutment, an ulnar shortening osteotomy may be beneficial. [19]
How to test for lunotriquetral deviation?
[41] [40] Ulnar deviation with pronation and axial compression of the wrist can result in a painful snap. [19] The lunotriquetral ballottement test is another helpful physical examination test. The forearm is placed into neutral rotation with the elbow supported on the examination table. The lunate is stabilized in place by one of the examiner's thumb and index finger. The other thumb is placed over the triquetrum dorsally with the examiner's index finger placed volarly on the triquetrum/pisiform. The triquetrum is translated volarly and dorsally while the lunate is held in place. The test is considered positive if there is pain or increased motion compared to the contralateral, uninjured wrist. [40] [45]
What is secondary to ligamentous disruption?
Carpal instability secondary to ligamentous disruption is a broad, complex topic that includes a number of causes. This activity will cover the two most common carpal instabilities and their respective chronic complications: scapholunate dissociation, lunotriquetral dissociation, dorsal intercalated segment instability (DISI), and volar intercalated segment instability (VISI). This article will highlight anatomy, pathophysiology, evaluation, treatment, and highlight the role of the interprofessional team caring for patients with carpal instability .
Which ligaments move the scaphoid into flexion?
To a lesser extent, the lunate and triquetrum also move into flexion through the intact scapholunate and lunotriquetral ligaments. With ulnar deviation, the scaphoid is pulled into extension by the scaphotrapeziotrapezoid ligament. The lunate and triquetrum then follow the scaphoid into extension. [21] [22]
Why are the scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum intercalated?
The scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum are an intercalated segment due to the fact they have no tendon insertions and their movement is dictated by the surrounding articulations. They flex and extend as a group, however there is considerable multiplanar motion between each of the joints.
Which ligaments are in the distal row?
Distal row: trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate. Ligaments: Two major groups of ligaments cause stability of the carpus (Intrinsic and Extrinsic). The extrinsic ligaments are extracapsular and course between the carpal bones and the radius or metacarpals, whereas the intrinsic ligaments are intracapsular and originate and insert within ...
What is the V-shaped ligament that runs from the scaphoid and triquetrum to?
dorsal intrinsic intercarpal ligament (scaphoid to caitate and triquetrum) long palmar intrinsic ligament (aka "V" or "Deltoid" ligament) V-shaped ligament that runs from scaphoid and triquetrum to the capitate.
What is the triquetral column?
Triquetral is the ulnar column. Lunate and capitate with the remaining carpal bones making up the middle column. Navarro: modification of this with. Scaphoid, trapezium and trapezoid making up the radial column. Triquetral the ulnar column. Capitate and lunate along with the hamate the middle column.
Which ligaments are stronger, volar or extrinsic?
Ligaments: Two major groups of ligaments cause stability of the carpus (Intrinsic and Extrinsic). The extrinsic ligaments are extracapsular and course between the carpal bones and the radius or metacarpals, whereas the intrinsic ligaments are intracapsular and originate and insert within the carpus. The extrinsic ligaments are stiffer, while the intrinsic ligaments are capable of greater elongation before permanent deformation occurs. Likewise, the volar ligaments are stronger than the dorsal ligaments.
What is a Ligamentous Injury of the wrist?
Ligamentous injury of the wrist resulting in abnormal kinematics, pain, decreased grip strength, and, if untreated, degenerative joint disease. The most commonly affected joints are the scapholunate articulation (Dorsal Intercalated Segment Instability or DISI) followed by the lunatotriquetral articulation (Volar Intercalated Segment Instability or VISI).
How specific is SLIL?
94% sensitivity and 86% specificity for detecting SLIL tears when compared to arthroscopy as the gold standard for diagnosis
Description of The Condition
- radial or dorsal wrist pain, maximal on radial deviation and wrist extension
- weakness and/or instability
- clicking wrist
- positive Watson test: during ulnar to radial deviation, pressure applied to the volar aspect of the scaphoid elicits an audible and/or palpable clunk (due to dorsal subluxation of the scaph…
- radial or dorsal wrist pain, maximal on radial deviation and wrist extension
- weakness and/or instability
- clicking wrist
- positive Watson test: during ulnar to radial deviation, pressure applied to the volar aspect of the scaphoid elicits an audible and/or palpable clunk (due to dorsal subluxation of the scaphoid with...
Cause and Origin
Signs & Symptoms
Treatment
Dorsal intercalated segment instability (DISI) is a deformity of the wrist where the lunate angulates to the dorsal side of the hand.