The due process in accounting refers to a series of procedures that entail the collection, processing, and communication of financial data at the end… What is a due process complaint? A due process complaint is a filing by a parent or a public agency on matters related to the: identification; evaluation; or. educational placement of a child; or. provision of FAPE to the child.
What is due process?
Due process is a requirement that legal matters be resolved according to established rules and principles, and that individuals be treated fairly. Due process applies to both civil and criminal matters.
What is due to account?
What is Due to Account? Due to Account is an accounting term that denotes a liability account. It is the amount of funds due to another party and is found in the general ledger
What is the Due Process Handbook used for?
The Due Process Handbook provides for comments or complaints from stakeholders about application of due process requirements, and these are also considered in public Due Process Oversight Committee meetings.
What is the due process for technical standards?
The process builds trust, legitimacy and global acceptance of the Standards. The Due Process Handbook outlines the requirements the Board and the Interpretations Committee must undertake in their technical standard-setting and lists possible additional steps. how the Board determines whether to add a project to its work plan;
What is due process FASB?
Due Process Procedures The Board votes on whether to add a project to the technical agenda, after consultation with stakeholders and others. The decision is subject to oversight by the FAF's Board of Trustees. The Board assigns the topic to its technical staff, its in-house group of experts, for research and analysis.
What are the steps in IFRS due process?
Due process stepsResearch programme.Developing a proposal for publication.Redeliberations and finalisation.Post-implementation reviews.
What are the 4 principles of IFRS?
There are a number of principles, but some of the most notable include the revenue recognition principle, matching principle, materiality principle, and consistency principle.
What is IFRIC accounting?
IFRIC (IFRS Interpretations Committee) is the interpretative body of the IFRS Foundation. Its mandate is to review on a timely basis widespread accounting issues that have arisen within the context of current International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRSs).
What does IFRS stand for?
International Financial Reporting StandardsInternational Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are a set of accounting standards that govern how particular types of transactions and events should be reported in financial statements. They were developed and are maintained by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB).
What is IFRS and process of IFRS standard setting?
IFRS - How we set IFRS® Standards. The IFRS Foundation is a not-for-profit, public interest organisation established to develop high-quality, understandable, enforceable and globally accepted accounting and sustainability disclosure standards.
What is difference between GAAP and IFRS?
IFRS is a globally adopted method for accounting, while GAAP is exclusively used within the United States. GAAP focuses on research and is rule-based, whereas IFRS looks at the overall patterns and is based on principle. GAAP uses the Last In, First Out (LIFO) method for inventory estimates.
What are golden rules of accounting?
Take a look at the three main rules of accounting: Debit the receiver and credit the giver. Debit what comes in and credit what goes out. Debit expenses and losses, credit income and gains.
What is IFRS and GAAP?
GAAP stands for Generally Accepted Financial Practices, and it's based in the U.S. IFRS is a set of international accounting standards, which state how particular types of transactions and other events should be reported in financial statements.
What is the difference between IFRIC and SIC?
SIC Interpretations agreed by the Standing Interpretations Committee (SIC) and ratified by the IASB were published between 1997 and 2001. IFRIC Interpretations agreed by the International Financial Reporting Interpretations Committee (IFRIC) and ratified by the IASB have been published since 2001.
What is the difference between IAS and IFRS?
What is IAS and IFRS? The IAS was a set of standards that was developed by the International Accounting Standards Committee (IASC). They were originally launched in 1973 but have since been replaced by the IFRS. IFRS is a set of standards that was developed by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB).
How many IFRS are there?
IFRS currently has complete profiles for 167 jurisdictions, including those in the European Union. The United States uses a different system, the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).
What are the steps in the standard setting process?
6 Stages of Standard Setting Process Of IASB :Setting the agenda : ... Planning the project: ... Developing and publishing the discussion paper: ... Developing and publishing the exposure draft (ED): ... Developing and publishing the standard:
What is an exposure draft IFRS?
The exposure draft in IFRS is a kind of statement that is periodically released by the IASB with proposed changes to this accounting method. It is meant to elicit feedback from relevant parties in the field.
Why is IFRS referred to as common accounting rules?
IFRS standards are issued and maintained by the International Accounting Standards Board and were created to establish a common language so that financial statements can easily be interpreted from company to company and country to country.
What are the three main areas in the practice of accountancy profession?
The accounting profession can be divided into three major categories: the practice of public accounting, private accounting and governmental accounting.
What is due process in accounting?
The due process comprises the requirements followed by the International Accounting Standards Board when setting IFRS Standards and developing the IFRS Taxonomy, and by the IFRS Interpretations Committee when working with the Board to support consistent application of those Standards.
Why is due process important?
The due process is essential both for developing high-quality IFRS Standards and for ensuring that stakeholders can be confident that all relevant views have been considered when the Standards are developed. The process builds trust, legitimacy and global acceptance of the Standards.
Why are due process committee meetings held?
The Due Process Oversight Committee’s meetings are held in public to enable stakeholders to follow any discussions about or updates on how the Board and the Interpretations Committee have delivered on its due process obligations.
What is the purpose of the Due Process Handbook?
The Due Process Handbook provides for comments or complaints from stakeholders about application of due process requirements, and these are also considered in public Due Process Oversight Committee meetings.
Who is responsible for maintaining the due process?
The Due Process Oversight Committee is also responsible for maintaining the due process to ensure it remains fit for purpose and reflects good practice. In August 2020, the Trustees published a revised version of the Due Process Handbook after a public consultation on proposed amendments.
Do you need to get permission from the Due Process Oversight Committee?
For example, if the Board would like a shorter consultation period than the minimum specified in the Handbook for a proposed amendment to an IFRS Standard, it must obtain permission from the Due Process Oversight Committee and, in some cases, from the Trustees. To meet stakeholders’ needs, the Board may need to work its way through the due process more quickly for some documents, for example as it did recently with an amendment to IFRS 16 on leases to help lessees accounting for covid-19-related rent concessions.
What is the difference between due to account and due from account?
The two are essentially opposites. Due to account is the money an organization owes to others, whereas due from account is the money the organization is owed. When a credit transaction occurs, the buying organization will record an entry to accounts payable, and the selling organization will record an entry to accounts receivable.
What does it mean when a company has a due to account?
The due to account is an extremely important item in a company’s balance sheet. If there is an increase in the due to account over a particular period, it means the organization is buying more goods or services on credit rather than paying cash.
What is credit balance in accounting?
The credit balance in the account will be the sum total of invoices recorded but are yet to be paid. The due to accounts are recorded as credit accounts and show the business the amount payable to another source. The reconciliation of all the accounts is the primary purpose of maintaining a general ledger within the accounting statement.
What is trial balance?
A trial balance is a document that helps a business record all its transactions in an orderly manner. It is used to prepare financial statements. Liability accounts are accounts that show the amount of money that is owed by the business. The trial balance rolls up the information from the general ledger, which includes all the financial accounts of a business. The ledger is divided into two columns; debit and credit. The two columns show the due to and due from accounts.
What is account payable?
The due to account is also known as account payable. Accounts Payable Accounts payable is a liability incurred when an organization receives goods or services from its suppliers on credit. Accounts payables are. .
What happens when an organization's financial statement decreases?
If it decreases, the organization is paying by cash rather than credit for goods and services. The correctness and completeness of an organization’s financial statements depend on the due to account (accounts payable) process. A good process will include:
What is a cash flow statement?
Cash Flow Statement A cash flow Statement contains information on how much cash a company generated and used during a given period.
What is FASAB due process?
Due Process. FASAB is subject to the Federal Advisory Committee Act and therefore follows Rules of Procedure (pdf) that meet or exceed the requirements of the Act. FASAB takes the following steps in considering accounting standards:
How long does it take to submit a proposed statement to the principals?
Submission of proposed Statement to the Principals for 90-day review (45 days for Interpretations)
How Does the DUE Process Model Work?
This criminal model aims to ensure a fair and equitable criminal process for everyone including a criminal system that respects constitutional rights. Moreover, the model claims that the system should look more like an “obstacle course” than a “conveyor”. The protection of human rights and freedoms is of great importance and is often more in line with liberal views.
Why is The DUE process Model Important?
For instance, NFL players who have been suspended or fined for domestic violence, child abuse or any other claim then there should be a “due process” before losing their job or income.
What Is The Main Idea Of The DUE Process Model?
The main idea of the DUE crime control model is to reflect liberal values.
What is accounting process?
Accounting is a process that helps in recording the financial transactions which are necessary for the business. This process includes summarizing, analysing and reporting the transactions to give an overview to the agencies, regulators and tax collection entities. The financial statements that are used in accounting are in a concise summary format. Financial transactions which occurred over an accounting period summarizes the company's operations, the financial position and also the cash flows.
How Accounting Works?
Accounting is one of the most prior functions for almost any kind of business which may be handled by a bookkeeper or by an accountant at a small firm , or even by a sizable finance department with a dozen of employees at larger companies. The reports that are generated by various streams of accounting like cost accounting and managerial accounting are invaluable in helping the management to make an informed business decision.
What is interim accounting?
This accounting refers to the processes that are used to estimate the interim and annual financial statements. These results in all the financial transactions which occur during the accounting period. They are summarized into a balance sheet, an income statement and in a cash flow statement.
What is reversing entry in accounting?
Is to verify that all the transactions are designated as reversing entries in the preceding periods which have actually been reversed. Doing this will ensure that the transactions are not recorded twice in the same period. These transactions are generally tagged as being the reversing entries in the accounting software.
Why is cost accounting important?
Cost accounting helps the business to make decisions about costing. More importantly, cost accounting considers all of the costs related to producing a product .
What is a trial balance?
Prepare trial balance - The trial balance lists the balance left in all the accounts. The total of all the debit in the trial balance equals the total of all the credit, while in contrast to this, there is an error in the entry of the original transactions which must be researched and corrected.
What is adjusted trial balance?
Prepare an adjusted trial balance - This is an original trial balance, plus or minus and other such adjustments are to be subsequently made.
What is accounting in economics?
Definition of Accounting: Accounting is a set of concepts and techniques that are used to identify, measure, record, classify, summarize and report financial information of an economic unit to the users of the accounting information.
How old is accounting?
There are proofs which suggest that accounting might be more than 7000 years old.
Is an economic unit a legal entity?
The economic unit is considered as a separate legal entity. Accounting information is widely used by various types of parties for several different reasons. Few of them are;
What Is a Due From Account?
A due from account is an asset account in the general ledger used to track money owed to a company that is currently being held at another firm. It is typically used in conjunction with a due to account and is sometimes referred to as intercompany receivables .
Why separate outgoing and incoming funds?
Advantages of a Due From Account. The primary reason for separating the incoming and outgoing funds is for ease of accounting. This keeps all incoming payments focused in one account and outgoing in another.
Why is separating receivables and payables important?
The process of separating receivables and payables also helps in tax charges as movement in and out of due from accounts or due to accounts marks when funds were distributed and therefore the appropriate tax charge required on the funds.
Can due from accounts be negative?
Due from accounts and due to accounts should never be negative, which would signify bad data. Both accounts can, however, be zero.

Due to Account vs. Due from Account
- The due process comprises the requirements followed by the International Accounting Standards Board when setting IFRS Standards and developing the IFRS Taxonomy, and by the IFRS Interpretations Committee when working with the Board to support consistent application of those Standards. The process laid out in the Constitution and developed in consul...
Understanding The Accounting Point of View
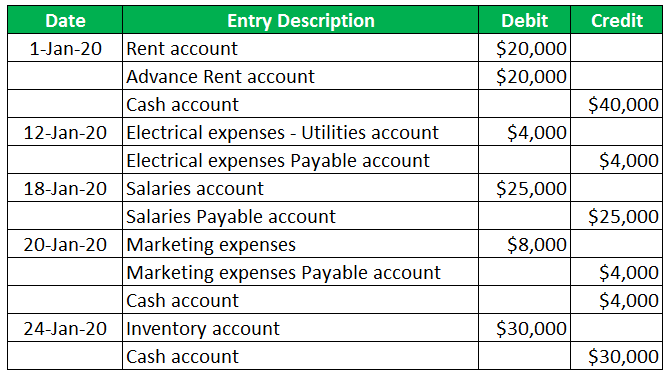
Practical Example
Additional Resources