
A duplicated chromosome therefore includes two identical strands joined along their length at corresponding lengths of DNA. Chromosomes are nothing more than distinct chunks of a substance called chromatin, which consists of very long molecules of DNA wrapped around special proteins known as histones.
What involves duplication of chromosomes?
pairing of homologs occurs, two divisions, four daughter cells produced, associated with sexual reproduction, involves duplication of chromosomes, chromosome number is halved, crossing over between homologous chromosomes may occur, daughter cells are not identical to parent cell, produces gametes, synapsis (forming tetrads) occurs in prophase.
Why do most humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes?
Humans have 23 sets of chromosomes because one set comes from each parent 2. What do the 23 chromosomes represent? The 23rd pair of chromosomes are two special chromosomes, X and Y, that determine our sex. Females have a pair of X chromosomes (46, XX), whereas males have one X and one Y chromosomes (46, XY).
What are DNA or chromosomes duplicate?
Chromosome duplication: Part of a chromosome in duplicate.A particular kind of mutation involving the production of one or more copies of any piece of DNA, including sometimes a gene or even an entire chromosome.A duplication is the opposite of a deletion.
How do chromosomes duplicate?
There are three main ways that genes can be duplicated:
- Through unequal crossing-over
- chromosomal duplication
- RNA duplication.
What happens if you have a duplicated chromosome?
Chromosomal Duplications Duplications may affect phenotype by altering gene dosage. For example, the amount of protein synthesized is often proportional to the number of gene copies present, so extra genes can lead to excess proteins.
Where is a duplicated chromosome?
2 duplication is a chromosomal change in which a small amount of genetic material within chromosome 16 is abnormally copied (duplicated ). The duplication occurs near the middle of the chromosome at a location designated p11. 2. This duplication can have a variety of effects.
What is a duplicated chromosome made of?
A replicated chromosome contains two identical double strand -DNA- molecules, the chromatids, that are joined at their centromere. Two single sets of pairs (daughter) chromosomes are formed by separation of the pair of chromatids during cell division (from anaphase on in mitosis and anaphase II in meiosis)
What is the difference between duplicated and unduplicated chromosomes?
a unreplicated chromosome has one DNA molecule; a replicated chromosome has two identical DNA molecules (sister chromatids) attached at the centromere.
Why do we have duplicate chromosomes?
Duplications typically arise from an event termed unequal crossing-over (recombination) that occurs between misaligned homologous chromosomes during meiosis (germ cell formation). The chance of this event happening is a function of the degree of sharing of repetitive elements between two chromosomes.
How do you know if a chromosome is duplicated?
A replicated chromosome (or equivalently, a duplicated chromosome) contains two identical chromatids, also called sister chromatids. The difference between a duplicated chromosome and a chromatid, strictly speaking, is that a chromosome contains two chromatids that are joined at a structure called a centromere.
What are two chromosomes called?
sister chromatidsThe two copies of a chromosome are called sister chromatids. The sister chromatids are identical to one another and are attached to each other by proteins called cohesins.
What is the difference between a single chromosome and a double chromosome?
Whether a chromosome is said to be single or double refers to the number of chromatids per chromosome. Not to whether the DNA in the chromosome is double or single stranded. The DNA is always double stranded. A 'single' or 'undoubled' chromosome does NOT contain single stranded DNA.
How many chromosomes are there in 2 duplicated chromosomes?
In total, there are 46 individual chromosomes (23 x 2) in each somatic cell; they are diploid. During S phase, each chromosome is replicated. This produces a second copy of each chromosome from the mother and a second copy of each chromosome from the father. These identical copies are known as sister chromatids.
Is a duplicated chromosome diploid?
Humans are diploid, meaning we have two copies of each chromosome. We inherited one copy of each chromosome from other mother, and one copy of each from our father. Gametes (sperm cells or egg cells) are haploid, meaning that they have just one complete set of chromosomes.
Do duplicated chromosomes have the same genes?
Each pair are considered homologous, and carry the same genes in the same order, but the alleles for each trait may not be the same. An allele is one of two or more alternative forms of a gene that are found at the same locaion on homologous chromosomes. Different levels of DNA condensation: (1) Single DNA strand.
What is a non duplicated chromosome?
Chromosomes may exist as either duplicated or unduplicated. Unduplicated chromosomes are single linear strands, whereas duplicated chromosomes contain two identical copies (called chromatids or sister chromatids) joined by a centromere.
Are chromosomes duplicated in mitosis?
As mitosis progresses, the microtubules attach to the chromosomes, which have already duplicated their DNA and aligned across the center of the cell. The spindle tubules then shorten and move toward the poles of the cell. As they move, they pull the one copy of each chromosome with them to opposite poles of the cell.
Are chromosomes duplicated in mitosis or meiosis?
Mitosis creates two identical daughter cells that each contain the same number of chromosomes as their parent cell. In contrast, meiosis gives rise to four unique daughter cells, each of which has half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Are chromosomes duplicated in meiosis?
In meiosis, the chromosome or chromosomes duplicate (during interphase) and homologous chromosomes exchange genetic information (chromosomal crossover) during the first division, called meiosis I. The daughter cells divide again in meiosis II, splitting up sister chromatids to form haploid gametes.
Are chromosomes duplicated in interphase or mitosis?
interphaseThen, at a critical point during interphase (called the S phase), the cell duplicates its chromosomes and ensures its systems are ready for cell division. If all conditions are ideal, the cell is now ready to move into the first phase of mitosis.
What is chromosome 17p duplication?
Listen. Chromosome 17p duplication is a chromosome abnormality that occurs when there is an extra copy of genetic material on the short arm (p) of chromosome 17. The severity of the condition and the signs and symptoms depend on the size and location of the duplication and which genes are involved. Features that often occur in people ...
What are the characteristics of chromosome 17p duplication?
Features that often occur in people with chromosome 17p duplication include slowed growth both before and after birth; developmental delay; reduced muscle tone ( hypotonia ); congenital heart defects; and distinctive facial features. [1] [2] Most cases are not inherited and occur randomly when the parents’ sperm or egg cells formed, ...
Why is duplication better than polyploidy?
Duplication has an advantage over polyploidy because the genetic dis-balance due to the duplication of chromosomal segments is lesser as compared to polyploidy where the whole genome is duplicated.
When was duplication first discovered?
The term duplication was coined by Bridges in 1919, and the first duplications were described in Drosophila melanogaster.
What are the types of duplications?
In this article we will discuss about:- 1. Types of Duplications 2. Origin of Duplications 3. Chromosome Pairing 4. Phenotypic Effects of Duplications 5. Duplications in Human 6. Uses of Duplications.
What happens to the double bar during pachytene?
Unequal crossing over may occur in duplication heterozygotes leading further duplications of the concerned segment. For example, Bar eye locus of Drosophila gives rise to the double-Bar (ultra bar) eye following unequal crossing over; conversely, double-Bar may revert to Bar due to unequal crossing over (Fig. 13.2).
Why are duplicated loci important?
Duplications are believed to have played an important role in evolution. In Drosophila where salivary gland polytene chromosomes can be analysed accurately, numerous duplicated segments have been identified. Similarly, in many plants, many duplicated loci have been investigated. The duplicated segments may be large or very small. Duplications are proposed to have given rise to new gene functions.
What are the cytological effects of the Ds and Ac system?
The cytological effects produced by this system include various kinds of chromosomal aberrations, such as, deficiencies, duplications, translocations, inversions and ring chromosomes. The Ds and Ac both are capable of transposition to any chromosome or within the same chromosome.
Why does the wild type allele express like a mutant allele?
The wild type allele expresses like a mutant allele due to the heterochromatinization. However, the normal allele may escape repression due to heterochromatin in many cases and a variegated phenotype (a mixture of wild type and mutant type sectors) is produced.
What is chromosome 16p duplication?
Listen. Chromosome 16p duplication is a chromosome abnormality that occurs when there is an extra copy of genetic material on the short arm (p) of chromosome 16. The severity of the condition and the signs and symptoms depend on the size and location of the duplication and which genes are involved. Features that often occur in people ...
What are the characteristics of chromosome 16p duplication?
Features that often occur in people with chromosome 16p duplication include developmental delay, intellectual disability, behavioral problems and distinctive facial features. Most cases are not inherited, but people can pass the duplication on to their children. [1] .
What is the chromosome 4q duplication?
Chromosome 4q duplication is a chromosome abnormality characterized by an extra copy (duplication) of genetic material on the long arm (q) of chromosome 4. The severity and specific symptoms depend on the size and location of the duplication, and which genes are involved.
What is proximal duplication?
While very few cases have been described, it seems that those with a very small duplication of material close to the middle of the chromosome (called a proximal duplication) are usually healthy with developmental delay and/or learning difficulties.
How does 4q affect the long term?
The long-term outlook ( prognosis) for people with a chromosome 4q duplication depend s on the size and location of the duplication. This affects which specific genes are involved, and how many genes are duplicated. Some people with a 4q duplication may be born healthy and develop well, while others may be born with any of several types of birth defects that can lead to severe complications. Therefore, it is not possible to predict how one person will be affected. Additionally, people with the same 4q duplication (the same location and size) may be affected very differently - even within the same family. [1]#N#People with questions about prognosis for themselves or family members are encouraged to speak with their doctors about how their signs and symptoms may affect their health and quality of life.
What happens if you have a 4q deletion?
If a chromosome 4q duplication occurs with another chromosome abnormality (such as a deletion of part of another chromosome), the severity and features in an affected person may differ and will depend on the effects of the other chromosome abnormality as well. We encourage you to view Unique's guide for people and families with a chromosome 4q ...
Can you predict how one person will be affected by 4q duplication?
Therefore, it is not possible to predict how one person will be affected. Additionally, people with the same 4q duplication (the same location and size) may be affected very differently - even within the same family. [1]
Is balanced translocation inherited?
Most cases are inherited from an unaffected parent with a chromosomal rearrangement called a balanced translocation. Some cases are not inherited and occur sporadically. Treatment is based on the signs and symptoms present in each person. [1] Last updated: 5/18/2016.
Can 4q duplication be severe?
Since few cases of 4q duplication have been described in the literature, it is difficult to predict severity or the specific features that a person will have. Someone with a small duplication may be very mildly affected and have no developmental delays.
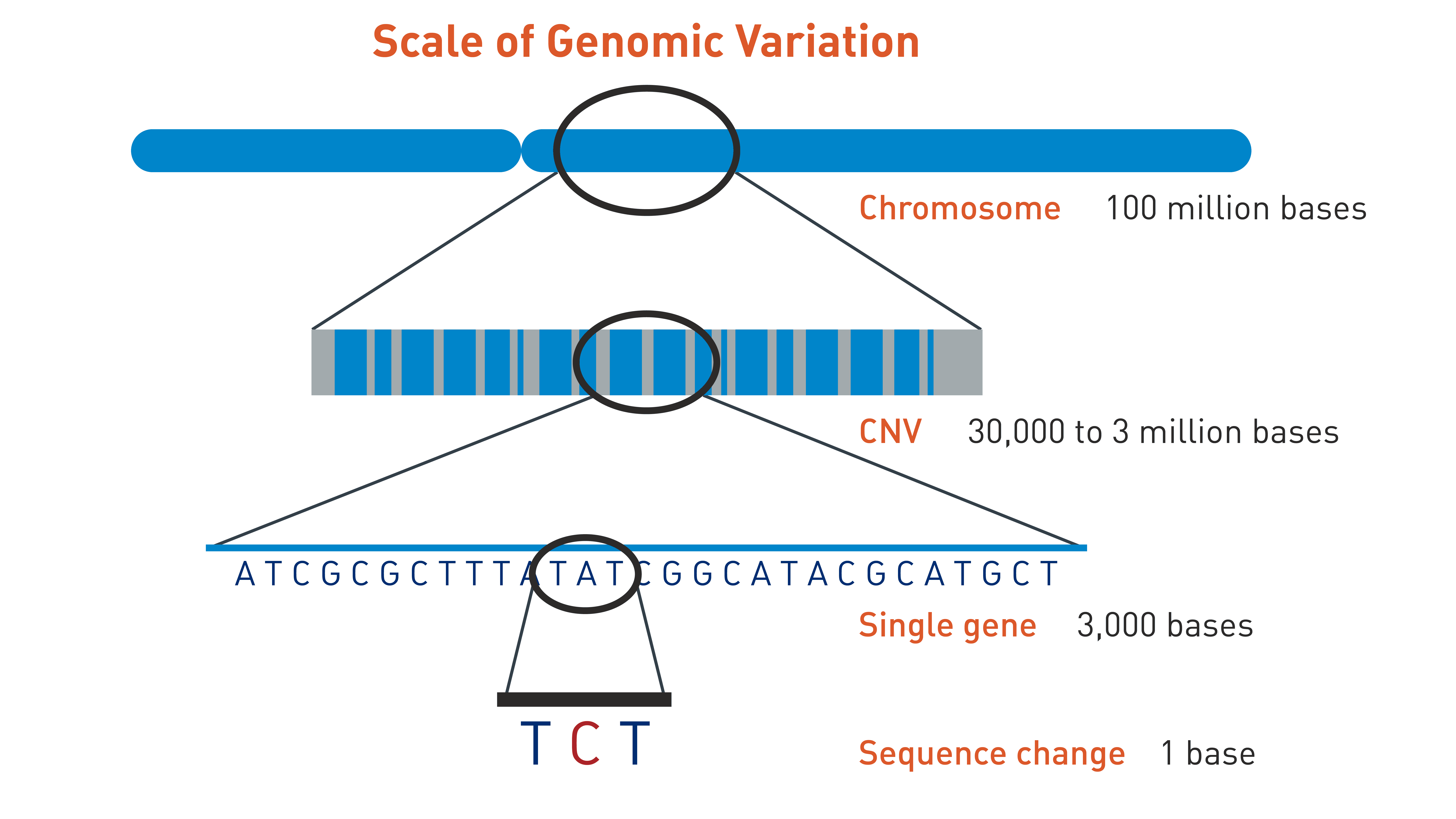
What is a chromosome duplication?
See additional information. Chromosome duplication: Part of a chromosome in duplicate. A particular kind of mutation involving the production of one or more copies of any piece of DNA, including sometimes a gene or even an entire chromosome. A duplication is the opposite of a deletion.
Why are duplications important?
Duplications have been important in the evolution of the human genome (and the genomes of many other organisms). Duplications typically arise from an event termed unequal crossing-over (recombination) that occurs between misaligned homologous chromosomes during meiosis (germ cell formation).
How do duplicates occur?
Duplications occur when there is more than one copy of a specific stretch of DNA. This can occur in several different contexts. During a disease process, extra copies of the gene can contribute to a cancer. Genes can also duplicate through evolution, where one copy can continue the original function and the other copy of the gene produces a new function. On occasion, whole chromosomes are duplicated. In humans this causes disease. Throughout evolution, there have been several occasions, both in fish and plants, where whole genomes have been duplicated.
What is the process of producing one or more copies of a gene?
Duplication . Duplication is a type of mutation that involves the production of one or more copies of a gene or region of a chromosome. Gene and chromosome duplications occur in all organisms, though they are especially prominent among plants. Gene duplication is an important mechanism by which evolution occurs.
Can a whole genome be duplicated?
Genes can also duplicate through evolution, where one copy can continue the original function and the other copy of the gene produces a new function. On occasion, whole chromosomes are duplicated. In humans this causes disease. Throughout evolution, there have been several occasions, both in fish and plants, where whole genomes have been duplicated.
What is the final pair of chromosomes?
The final pair is called the "sex chromosomes.". Sex chromosomes determine an individual's sex: females have two X chromosomes (XX), and males have an X and a Y chromosome (XY). The mother and father each contribute one set of 22 autosomes and one sex chromosome.
What are chromosomes?
Chromosomes are the structures that hold genes. Genes are the individual instructions that tell our bodies how to develop and function; they govern physical and medical characteristics, such as hair color, blood type and susceptibility to disease.
What are chromosome abnormalities?
There are many types of chromosome abnormalities. However, they can be organized into two basic groups: numerical abnormalities and structural abnormalities.
Where are chromosomes found in the body?
Your body has many different kinds of cells, such as skin cells, liver cells and blood cells. In the center of most cells is a structure called the nucleus. This is where chromosomes are located.
How many chromosomes do humans have?
The typical number of chromosomes in a human cell is 46: 23 pairs, holding an estimated total of 20,000 to 25,000 genes. One set of 23 chromosomes is inherited from the biological mother (from the egg), and the other set is inherited from the biological father (from the sperm).
How do scientists study chromosomes?
For a century, scientists studied chromosomes by looking at them under a microscope. In order for chromosomes to be seen this way, they need to be stained. Once stained, the chromosomes look like strings with light and dark "bands," and their picture can be taken. A picture, or chromosome map, of all 46 chromosomes is called a karyotype. The karyotype can help identify abnormalities in the structure or the number of chromosomes.
What is a picture of all 46 chromosomes called?
A picture, or chromosome map, of all 46 chromosomes is called a karyotype. The karyotype can help identify abnormalities in the structure or the number of chromosomes. To help identify chromosomes, the pairs have been numbered from 1 to 22, with the 23rd pair labeled "X" and "Y.".
What is the name of the strands of DNA that are unzipped?
DNA Condensing: Most of the time, the DNA molecules in each of your cells do not look like chromosomes, but instead are in very long strands called chromatin. When the DNA is undergoes the process of replication, it must be in these long chromatin strands, so that the double-stranded molecule can be "unzipped" and read. But when the cell prepares to divide, it must “pack” its DNA for the move. So prior to cell division, the chromatin condenses. This prevents the DNA from getting tangled up when it is sorted into two cells during mitosis.
How many chromosomes are in a somatic cell?
Every somatic cell in your body has 46 chromosomes. You received a set of 23 from your mother’s egg and a set of 23 via your father’s sperm, and now these chromosomes are the genetic material inside nearly every cell of your body.
How many sets of homologous chromosomes do sexual reproducers have?
Article Summary: Sexual reproducers have two sets of homologous chromosomes; one from mom and one from dad. What is the difference between homologous and duplicated chromosomes?
How many copies of DNA are there in each cell?
This replicated DNA molecule, in its condensed form, is now referred to as a chromosome. But, remember, there are two copies attached to each other until the genetic material is split so that each new cell gets a copy. During prophase and metaphase of mitosis, we have 22 pairs of homologous, duplicated autosomes.
What is the name of the cell that is not a sperm cell?
Most of the cells in our bodies are somatic , the cells that aren't eggs or sperm. Somatic cells have a diplod (2n) chromosome number, meaning that chromosomes come in pairs called homologues.
Why do DNA strands separate?
DNA molecule replicating: Strands separating so that the DNA can be read and replication can occur.
What is an allele in biology?
An allele is one of two or more alternative forms of a gene that are found at the same locaion on homologous chromosomes.