What are the symbols in the Beer-Lambert law?
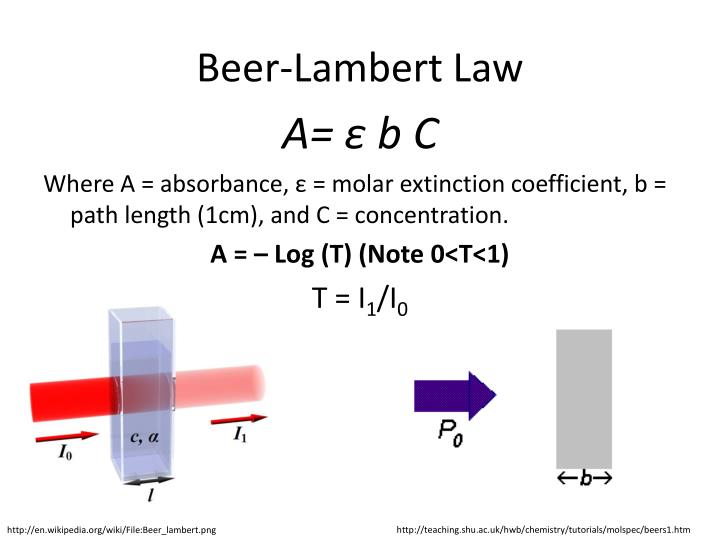
The Beer-Lambert Law. You will find that various different symbols are given for some of the terms in the equation - particularly for the concentration and the solution length. The Greek letter epsilon in these equations is called the molar absorptivity - or sometimes the molar absorption coefficient.
What is Beer-Lambert law in chemistry?
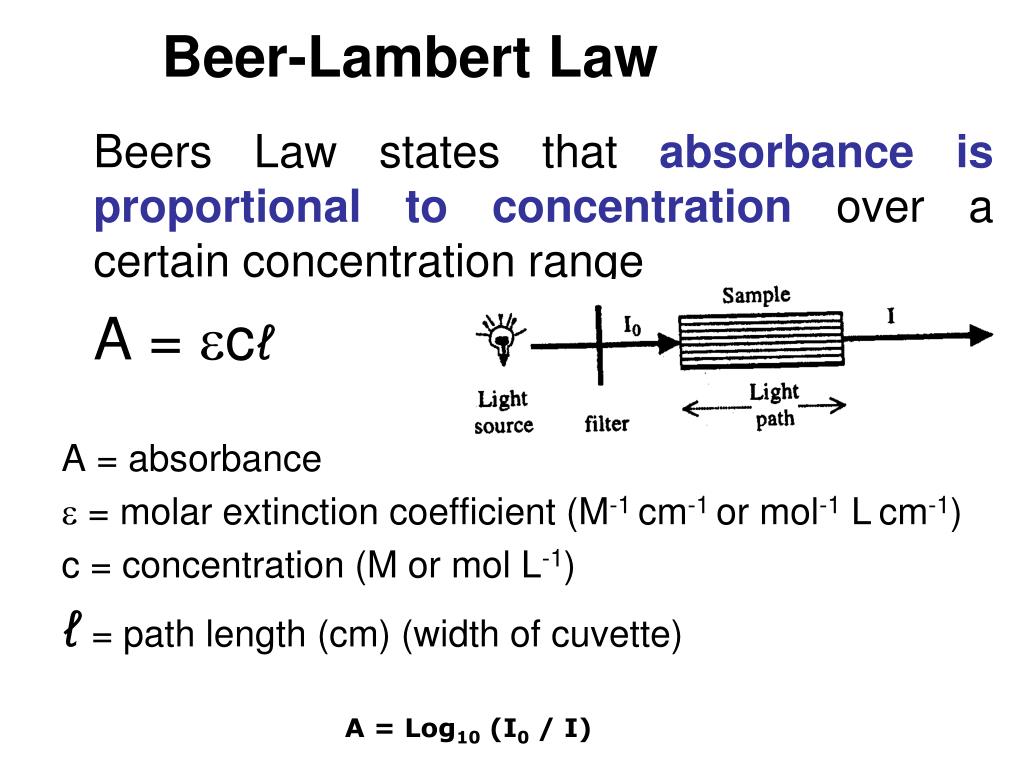
The Beer-Lambert law states that the absorbance of a solution is proportional to its concentration, absorption coefficient, molar, and optical coefficient. Beer law asserts that concentration and absorbance are exactly proportional to one other. Lambert law asserts that absorbance and path length are exactly related.
How do you find absorbance Using Beer-Lambert's law?
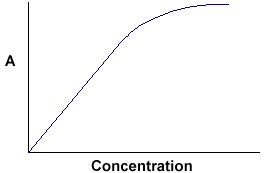
Answer: We can determine the absorbance of a chemical or biological molecule in a given sample by using Beer-Lambert’s law. Below is the graph of the absorbance versus concentration of the solution: The slope of this graph is ε x c; this product is the molar absorptivity coefficient.
What are the applications of Beer-Lambert's law in electromagnetic spectroscopy?
Answer: In electromagnetic spectroscopy, we find many applications on Beer-Lambert’s law. This law states the linear relationship between the absorbance and the concentration of a solution sample, which enables us to determine the molar concentration of any number of solutions.
What is the E in Beer's law?
The equation to be used (Beer-Lambert Law) is: A = E l C ; where A is the absorbance; C is the concentration and l is the cell's width, E (epsilon coefficient) and its unit is mol/dm3.
What is E in beer Lambert equation?
The Beer-Lambert law is expressed as: A = εLc. where, A is the amount of light absorbed for a particular wavelength by the sample. ε is the molar extinction coefficient.
What is E in absorption?
e = A / bc. In words, this relationship can be stated as "e is a measure of the amount of light absorbed per unit concentration". Molar absorbtivity is a constant for a particular substance, so if the concentration of the solution is halved so is the absorbance, which is exactly what you would expect.
Is E in Beer's law the slope?
The equation for Beer's law is a straight line with the general form of y = mx +b. where the slope, m, is equal to εl. In this case, use the absorbance found for your unknown, along with the slope of your best fit line, to determine c, the concentration of the unknown solution.
What is molar absorptivity extinction coefficient ε )?
The term molar extinction coefficient (ε) is a measure of how strongly a chemical species or substance absorbs light at a particular wavelength. It is an intrinsic property of chemical species that is dependent upon their chemical composition and structure.
How do you pronounce E in Beer-Lambert law?
0:020:26How to pronounce Beer-Lambert law - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipVerlander verlander verlander verlander verlander.MoreVerlander verlander verlander verlander verlander.
What is Epsilon chemistry?
The Greek letter epsilon in these equations is called the molar absorptivity - or sometimes the molar absorption coefficient. The larger the molar absorptivity, the more probable the electronic transition.
What is the relationship between absorptivity and molar absorptivity E?
In chemistry, the absorptivity and molar absorptivity are the same. Therefore, there is no difference between absorptivity and molar absorptivity because they express the same idea; it is the absorbance of a solution per unit path length and concentration.
What does Absorbancy mean?
: the quality or state of being able to draw in or soak up. absorbency. noun. ab·sor·ben·cy | \ əb-ˈsȯr-bən-sē , -ˈzȯr- \ plural absorbencies.
What is E in standard curve?
The slope/gradient or rate of a standard curve is the “e” value.
How do you calculate E from absorbance?
Here is an example of directly using the Beer's Law Equation (Absorbance = e L c) when you were given the molar absorptivity constant (or molar extinction coefficient). In this equation, e is the molar extinction coefficient. L is the path length of the cell holder....Concentration (M)Absorbances0.400.550.500.692 more rows
How do you solve Epsilon in Beer's law?
0:508:32Equil Constant Part 2: Epsilon and Standard Curve - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd concentration on the x axis as shown in this plot our slope should be equal to epsilon times LMoreAnd concentration on the x axis as shown in this plot our slope should be equal to epsilon times L that means epsilon can be calculated from slope.
1. How do you calculate the Absorbance?
We calculate the absorbance by using the following formula: \[Ay=-log(\frac{Io}{It})\] of a light with the wavelength ‘y’.Here, \[\frac{Io}{It}\] =...
2. How the Absorbance helps determine the concentration of a solution?
The value of the absorbance lies between 0.1 and 1. If the absorbance of material is greater than or equal to 1.0 (too high), then we can say that...
3. What is the slope of Beer’s Law Graph?
We can determine the absorbance of a chemical or biological molecule in a given sample by using Beer-Lambert’s law. Below is the graph of the absor...
4. What is the Beer-Lambert Law for absorption spectroscopy?
In electromagnetic spectroscopy, we find many applications on Beer-Lambert’s law. This law states the linear relationship between the absorbance an...
5. What is the significance of Beer-Lambert Law – Definition, Derivation, Applications and FAQs in s...
Spectroscopy is used in determining the concentration of a given solution using a device named an Ultraviolet (UV) Spectrophotometer. Many a time r...
6. How relevant is the topic of Beer-Lambert Law – Definition, Derivation, Applications and FAQs for...
Applied Chemistry is an application-based subject wherein whatever is being taught in Chemistry is directly applied in the labs during carrying out...
7. How long does it take to study Beer-Lambert Law – Definition, Derivation, Applications and FAQs?
Beer-Lambert Law – Definition, Derivation, Applications and FAQs is an extremely easy topic of very high significance and has a wide variety of app...
8. How can I study Beer-Lambert Law – Definition, Derivation, Applications and FAQs easily without a...
You can study Beer Lambert Law – Definition, Derivation, Applications and FAQs very easily from Vedantu’s website. All the information given on the...
9. What is the role of absorbance in Beer-Lambert Law – Definition, Derivation, Applications and FAQ...
Absorbance plays a very important role in Beer Lambert Law – Definition, Derivation, Applications and FAQs. This law states that there is a linear...
What is the Beer Lambert law?
The Beer-Lambert law relates the attenuation of light to the properties of the material through which the light is traveling. This page takes a brief look at the Beer-Lambert Law and explains the use of the terms absorbance and molar absorptivity relating to UV-visible absorption spectrometry.
What is the Greek letter epsilon in Beer-Lambert law?
The Greek letter epsilon in these equations is called the molar absorptivity - or sometimes the molar absorption coefficient.
How to find the absorbance of a solution?
The Absorbance of a Solution 1 The absorbance is directly proportional to the concentration ( c) of the solution of the sample used in the experiment. 2 The absorbance is directly proportional to the length of the light path ( l ), which is equal to the width of the cuvette.
Does ethanal absorb more than 290 nm?
The ethanal obviously absorbs much more strongly at 180 nm than it does at 290 nm. (Although, in fact, the 180 nm absorption peak is outside the range of most spectrometers.) You may come across diagrams of absorption spectra plotting absorptivity on the vertical axis rather than absorbance.
Why is the Beer-Lambert law called the Beer-Lambert law?
The reason for so many names is because more than one law is involved in it. In 1729 Pierre Bouger discovered the law and published it in Essai d’optique sur la gradation de la lumiere. In 1760 Lambert quoted the Bouger’s discovery in his Photometria which states that the absorbance of a sample is directly proportional to the path length of light. Lambert did not claim any discovery, but he was often credited with it. In 1852, August Beer discovered that absorbance is proportional to the sample concentration. Generally, beers law relates only to concentration while Beer-Lambert law relates absorbance to both concentration and thickness of a sample.
Why is Beer Lambert law considered a limiting law?
Presently, the Beer lambert law is declared as a limiting law because the absorbance is only nearly linear depending on the concentration. This is the reason that the attenuation coefficient also depends on concentration and density even if there are no interactions.
What did Lambert discover about the law of absorbance?
Lambert did not claim any discovery, but he was often credited with it. In 1852, August Beer discovered that absorbance is proportional to the sample concentration. Generally, beers law relates only to concentration while Beer-Lambert law relates absorbance to both concentration and thickness of a sample.
What is the deviation of Beer Lamberts law?
The law also deviates if non-monochromatic light is used. The change in temperature also leads to the deviation of Beer-lamberts’ law. The deviation may also occur if the width of the instrument is not proper.
Why is Beer's law important?
In chemistry Beers law is used to measure the concentration of chemical solutions , oxidation analysis and to measure the degradation of the polymer. Beer’s law also describes the attenuation of radiation through the Earth’s atmosphere.
What is the law of attenuation of solar radiation?
The attenuation of solar or stellar radiation is also described with the help of this law as it travels through the atmosphere. In this case, there is a scattering of radiation as well as absorption. The beer-lambert law for the atmosphere is written as:
What is Beer Lambert law?
Beer Lambert law is one of the popular topics in analytical chemistry. It relates the weakening of the intensity of the light to the characteristics of the medium through which it is traveling. Let’s say, we have a clear sample of a drug with a polished surface around its container. Now, passing electromagnetic radiation (incident radiation ...
What is Lambert's law?
Lambert’s Law. When monochromatic radiation (it can be UV rays) is passed through a medium, the intensity of the transmitted radiation decreases with the increase in the thickness of the absorbing medium, and it varies directly with the incident radiation. Mathematically, we can express this statement as:
What law states the linear relationship between the absorbance and the concentration of a solution sample?
Answer: In electromagnetic spectroscopy, we find many applications on Beer-Lambert’s law . This law states the linear relationship between the absorbance and the concentration of a solution sample, which enables us to determine the molar concentration of any number of solutions.
What is the value of absorbance?
Answer: The value of the absorbance lies between 0.1 and 1. If the absorbance of material is greater than or equal to 1.0 (too high), then we can say that the solution has a higher concentration.
What is Beer-Lambert Law?
The Beer-Lambert law, also known as the Beer-Lambert–Bouguer law, or the Beer's law, states that the absorbance of a solution is proportional to its concentration, absorption coefficient, molar, and optical coefficient.
Derivation and Mathematical Expression
ε denotes molar extinction coefficient or molar absorptivity (or absorption coefficient),
Applications of Beer-Lambert Law
The law finds application in analytical chemistry. Analytical chemistry is concerned with the separation, measurement, and identification of matter by the use of spectrophotometry. To obtain the results, no extensive pre-processing of the material is required.
Limitation of Beer-Lambert law
When the concentration is low, i.e. 10mM, it is simple to analyze the absorptivity coefficient of the sample using this rule, but as the concentration rises, i.e. >10mM, there is a deviation due to the increase of the electrostatic interactions.
Things to Remember
The Beer-Lambert law states that the absorbance of a solution is proportional to its concentration, absorption coefficient, molar, and optical coefficient.
Sample Questions
Ques. What role does absorbance play in determining a solution's concentration? 1 mark
What is the application of the Beer Lamberts law?
Answer 1: The application of the Beer-Lamberts law takes place to the analysis of a mixture by spectrophotometry. Furthermore, this application is without the need for extensive sample pre-processing. The Beer-Lambert law example includes the determination of bilirubin in blood plasma samples.
Why is Beer Lambert law inaccurate?
This is because the analyte’s molecules exhibit stronger electrostatics and intermolecular interactions.
What law states that light absorption is directly proportional to the concentration of a substance?
Beer Lambert law tells us that the absorption of a quantity of light by a substance that is dissolved in a fully transmitting solvent happens to be directly proportional to the substance’s concentration and the path length of the light via the solution.
How to measure Beer Lambert law?
It is possible to measure the Beer Lambert law by calculating the concentration of a solution by making use of the absorbancies. Another way is to plot a graph of various concentrations and then align them according to their appropriate or correct absorbencies. Afterwards, one must use a colourimeter to calculate the concentration ...
How does Beer Lambert law derivation take place?
Beer-Lambert law derivation can take place from an approximation for the absorption coefficient for a molecule. This happens by carrying out an approximation of the molecule by an opaque disk whose cross-sectional area is representative of the effective area seen by a frequency w photon.
Who developed the law of concentration?
The development of the law first took place by Pierre Bouguer before 1729. After its attribution to Johann Heinrich Lambert, the law included path length as a variable that had an effect on absorbance. ...
What is the Beer-Lambert law?
In theoretical physics, the Beer-Lambert Law is a solution to the Bhatnagar-Gross-Krook (BKG) operator, which is used in the Boltzmann equation for computational fluid dynamics.
What is the difference between Beer's Law and Beer-Lambert Law?
Technically, Beer's Law relates only to concentration, while the Beer-Lambert Law relates absorbance to both concentration and sample thickness.
Why is there so many names for beer law?
The reason there are so many names is because more than one law is involved. Basically, Pierre Bouger discovered the law in 1729 and published it in Essai D'Optique Sur La Gradation De La Lumière.
Why is Beer's law important?
Beer's Law is used in chemistry to measure the concentration of chemical solutions, to analyze oxidation, and to measure polymer degradation. The law also describes the attenuation of radiation through the Earth's atmosphere.
Who discovered the law of absorbance?
Basically, Pierre Bouger discovered the law in 1729 and published it in Essai D'Optique Sur La Gradation De La Lumière. Johann Lambert quoted Bouger's discovery in his Photometria in 1760, saying the absorbance of a sample is directly proportional to the path length of light.
What is the law of concentration?
The law states that the concentration of a chemical is directly proportional to the absorbance of a solution. The relation may be used to determine the concentration of a chemical species in a solution using a colorimeter or spectrophotometer. The relation is most often used in UV-visible absorption spectroscopy.