
What's the difference between accountants and economists?
Sep 20, 2021 · Ecosystem accounting is a statistical framework for organising data, tracking changes in the extent and the condition of ecosystems, measuring ecosystem services and linking this information to economic and other human activity. It aims to illustrate the benefits society receives from ecosystems and their services.
Why choose ecosys for your project?
Environmental accounting is an important tool for understanding the role played by the Natural environment in the economy. Environmental accounts provide data which highlight both the contribution of natural resources to economic well-being and the costs imposed by pollution or resource degradation. Also, what are the objective of green accounting?
What is the importance of accounting?
Jul 22, 2017 · Eco-friendly or Environment Accountants. Green accountants are held accountable to determine and monitor green costs quite often working along with site, investigation and improvement, and manufacturing managers whenever planning their own budgets. Previously, such expenses were hidden in cost to do business preventing a definite picture from ...

What is environmental accounting example?
It is often cited as a key measure of our society's economic well-being. The term environmental accounting may refer to this national economic context. For example, environmental accounting can use physical or monetary units to refer to the consumption of the nation's natural resources, both renewable and nonrenewable.
What is the meaning of SEEA?
The System of Environmental-Economic Accounting (SEEA) is a framework that integrates economic and environmental data to provide a more comprehensive and multipurpose view of the interrelationships between the economy and the environment and the stocks and changes in stocks of environmental assets.
What is the purpose of environmental accounting?
Put in other words, environmental accounting is structured to identify, measure and communicate a company's activities based on its environmental conservation cost or economic benefit associated with environmental conservation activities, the company's financial performance which is expressed in monetary value, and its ...
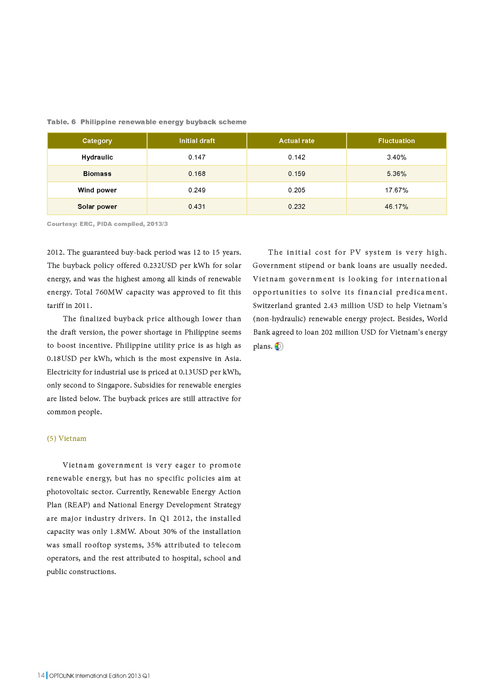
What is the meaning of green accounting?
Green accounting is a type of accounting that attempts to factor environmental costs into the financial results of operations. It has been argued that gross domestic product ignores the environment and therefore policymakers need a revised model that incorporates green accounting.
What is SNA and SEEA?
The SEEA framework follows a similar accounting structure as the System of National Accounts (SNA) and uses concepts, definitions and classifications consistent with the SNA in order to facilitate the integration of environmental and economic statistics.
When was SEEA created?
The SEEA Central Framework was adopted by the UN Statistical Commission as the first international standard for environmental-economic accounting in 2012. The SEEA Ecosystem Accounting offers a synthesis of current knowledge in ecosystem accounting.
What are the different types of environmental accounting?
There are four form of environmental accounting. These are; Environmental Financial Accounting (EFA), Environmental Cost Accounting (ECA), Environmental Management Accounting (EMA), and Environmental Nation Accounting (ENA).
What are the main approaches of environmental accounting?
Three main approaches to environmental accounting which are complementary and overlap each other are: (i) what is generally referred to as natural resource accounting, which focuses on accounts in physical terms; (ii) what is generally called monetary satellite accounting, which is linked to national accounts and is in ...
Who introduced green accounting?
It was first developed by Farr (1853), who estimated the capitalized value of earning capacity by calculating the present value of an individual's future earnings net of personal living expenses.
What is the difference between green accounting and environmental accounting?
Environmental accounting, also called green accounting, refers to modification of the System of National Accounts to incorporate the use or depletion of natural resources. Environmental accounting is a vital tool to assist in the management of environmental and operational costs of natural resources.
Who developed green accounting?
Professor Peter WoodThe term was first brought into common usage by economist and Professor Peter Wood in the 1980s. India's former Environment Minister Mr. Jairam Ramesh first time stressed the need and importance to bring Green Accounting practices to the forefront of accounting in India.Dec 24, 2018
What is eco friendly accounting?
According towards the EPA, eco-friendly or environment management sales is “the id, prioritization, quantification or even qualification, as well as incorporation associated with environmental expenses into company decisions. inch Green Administration Accounting utilizes “data regarding environmental expenses and overall performance for company decisions. This collects price, production, stock, and waste materials cost as well as performance with regard to business choices. It gathers cost, manufacturing, inventory, and waste materials cost as well as performance data within the accounting program to strategy, evaluate, as well as control. inch
When did green sales start?
The word, green sales, has existed since the actual 1980s, and is actually a management tool employed for a number of purposes, for example improving environment performance, managing costs, purchasing “cleaner” systems, developing “greener” procedures and items, and developing decisions associated with their company activities.
What is the system of environmental economic accounting?
As the agreed-upon international standard for natural capital accounting, the System of Environmental Economic Accounts (SEEA) provides a common framework for organising and presenting statistics on the environment and its relationship with the economy.
What is ecosystem account?
This set of ecosystem accounts measures the supply of ecosystem services as well as their corresponding use and beneficiaries, classified by economic sectors used in the national accounts. The ecosystem services accounts can be compiled in both physical and monetary terms.
Why is the Shea tree endangered?
The tree is under severe pressure and endangered due to overexploitation for timber, firewood and charcoal production.
What are the benefits of biodiverse ecosystems?
Biodiverse, healthy ecosystems provide essential contributions that humans depend upon in their daily lives – clean water , productive soils and flood control , to name just a few. But the economic contributions provided by this natural capital have too often been taken for granted when making important economic decisions.
Why is the SEEE EA important?
As a standard international framework, the SEEA EA is particularly well-suited to support important global environment and development initiatives. Its comparability across time and nations makes it ideal for use as a monitoring framework. Its rigorous foundation means that it can generate credible information for implementation plans. Its consistency promotes efficiency and helps avoid one-off initiatives that result in the duplication of effort.
What is the SEEA Ecosystem Accounting Framework?
The SEEA Experimental Ecosystem Accounting (SEEA EEA) framework was endorsed by the United Nations Statistical Commission in March 2013 as an important first step in the development of a statistical framework for ecosystem accounting. It was released in 2014 as a joint publication of the United Nations, European Commission, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development and the World Bank. It has been supplemented by a companion publication, The Technical Recommendations in support of the SEEA 2012 – Experimental Ecosystem Accounting, which provides guidance on implementation and clarifies some outstanding conceptual issues. Both publications are available on the SEEA website: seea. un.org. The SEEA EEA is currently undergoing a major revision with the goal of of moving beyond experimental status and being adopted as an official standard in 2021.
What is the importance of peatland?
Peatland covers around eight percent of Indonesia and is important for the cultivation of oil palm, a major export commodity, as well as timber production, and biomass production for pulp. It also delivers an important ecosystem service in the form of carbon sequestration.
Why is environmental accounting important?
Environmental accounting is a critical step in developing true costs for products and services and will identified. The value of these locally adapted genetic resources must be recognized, and better mechanisms must be developed to identify the rights of the communities and individuals whose collective action led to their creation and protection.
What are the key ecosystem flows?
The key ecosystem flows that must be understood include energy, water, and nutrients. Nutrient cycling is very important, because many native ecosystems are nutrient limited. In other ecosystems the most important factors may be energy and water flow and food webs as recovery). Natural capital may include both renewable (fish) and nonrenewable or finite (oil) resources. Unfortunately, most potentially renewable resources are currently being mined instead of sustainably managed. Sufficient research exists to understand only a few types of ecosystems well, which makes calculating the true environmental costs of impacts challenging. Even where there is considerable data it is often restricted to a few parameters that are easy and cheap to measure, such as biological oxygen demand. These may not, however, be very meaningful by themselves. The longer the time well as species reproduction, demographics (increase and series that can be developed, the better the chances to decrease by species), resilience to disturbance, or stability. Water flow and quality are two of the easiest functions to track and in many cases are good indicators of ecosystem health (Figure 6.2).
What is the purpose of evaluating the structure of an ecosystem?
comprehensively evaluate the organization’s performance Assessing the structure of an ecosystem includes the using both economic and environmental measures and to make improvements that reduce risks and wastes, eliminate unwanted costs, and provide new opportunities for adding value.
What are the problems of ecosystems?
Many problems in ecosystem function are poorly burning power plants and oil and natural gas produce thousands of tons of nitrogen oxides that are returned to understood and widely ignored by current accounting. As Earth in rain or as dry particulates falling as a dark, sticky noted in Chapter 4, nitrogen pollution is a perfect example. A growing concern about the enormous impact this seemingly innocuous nutrient and pollutant can have on terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems is largely confined to ecologists and environmental scientists. This is partially understandable because nitrogen gas (N2) is a major component of the atmosphere and seems innocent enough. Biologically available nitrogen, however, is a limiting factor in most natural ecosystems, and added nitrogen can wreak havoc.
What is the keystone species?
Keystone species (which play a critical role in the ecosystem) may be easy to track and can often provide useful information . Indicator species (which are particularly sensitive to change and reflect the overall health of an ecosystem) may help highlight changes that are significant.
How have ecosystems been disturbed?
Most ecosystems in the world have been disturbed and degraded by human activity. Often the first major disturbance or change was the arrival of tribal people. More changes took place when they died off after new invasions or were removed and their management practices were replaced by new managers, often with inappropriate strategies and ideas developed in very different ecosystems on other continents. These changes are seen throughout the western United States more than 100 years after the native people stopped managing the landscape (Figure 6.3). The open park-like forests of the 1800s have been replaced with dense stands (sometimes referred to as “dog hair” stands) that are much more vulnerable to fires and pests. The fierce wildfires in 2008 were in part a legacy of this long ago change in forest management. The scope and scale of these changes have been dramatic, and they are not well understood. For example, it is not known what the long-term consequences of the loss of 850 million tons of topsoil from the central plains during the Dust Bowl year of 1935 will be for future generations.
Why are honeybees in decline?
Also, many of these other pollinators are in decline as well, apparently as a result of misuse of pesticides and from the introduction of new pathogens.
What do accountants and economists do?
Both accountants and economists help businesses, industries, and governments to strategize and plan, make sound financial decisions, and set fiscal policies. Professionals in both fields base their analyses and projections on real-life markets, conditions, and events.
What is the difference between economics and accounting?
But accounting is a profession devoted to recording, analyzing, and reporting income and expenses, while economics is a branch of the social sciences that is concerned with the production, consumption, and transfer of resources.
What are the two main areas of economics?
Economics is broadly divided into two areas of study: 1 Macroeconomics is concerned with the distribution of resources within an ecosystem, such as a nation. It includes the tracking and study of the many factors that affect how efficiently the economy works, such as the inflation rate and the productivity rate. 2 Microeconomics is the study of the behavior of the individual within an economic ecosystem, or of any other single entity such as a business. It is concerned with the impact of individual decisions on the distribution of resources.
What do accountants do?
Accountants track the flow of money for businesses and individuals. Economists track the larger trends that drive money and the resources that money represents. Both help businesses and governments plan for the future, make sound financial decisions, and set fiscal policies.
What is the role of economists in the economy?
Economists have a critical role in developing economic policies for governments and projecting the impact of policy and regulatory changes.
What is macroeconomics?
Macroeconomics is concerned with the distribution of resources within an ecosystem, such as a nation. It includes the tracking and study of the many factors that affect how efficiently the economy works, such as the inflation rate and the productivity rate.
Why is GAAP important?
The accounting standards, known as GAAP, are critical for tax compliance and for accurate financial reporting to shareholders. In modern times, accounting operates according to principles of relevance, timeliness, reliability, comparability, and consistency of information or reports. Globally accepted accounting standards are followed in order ...
Digital Disruption is Coming to Capital Projects
There’s a compelling case for leaving the status quo behind and adopting an Enterprise Project Performance approach.
Efficiency, Predictability, and Control
By integrating project portfolio management, project controls and project management into a single enterprise solution, EcoSys quickly delivers more accurate insights. The result: better project performance.
Real-Time Insights with Enterprise Visibility
Say goodbye to data siloes and slow, error-prone spreadsheets. EcoSys drives better decisions with automated reporting and real-time data access.
Optimize Resources Across Your Project Portfolios
Finding a balance between resource capacity and project demand doesn’t have to be a struggle. Eliminate the guesswork and optimize your portfolios with close alignment of strategy and project delivery.
Ecosystem Accounting – How It Works
- The SEEA EA is built on five core accounts. These accounts are compiled using spatially explicit data and information about the functions of ecosystem assets and the ecosystem servicesthey produce. The five ecosystem accounts are: 1. ECOSYSTEM EXTENTaccounts record the total area of each ecosystem, classified by type within a specified area (ecosys...
Ecosystem Accounting Takes A Spatial Approach
- The SEEA EA takes a spatial approach to accounting, as the benefits a society receives from ecosystems depend on where those assets are in the landscape in relation to the beneficiaries. In contrast, the SEEA Central Frameworklooks at individual environmental assets (resources), such as water or energy resources. This spatial focus identifies the location and size of ecosystem as…
Seea Ecosystem Accounting - How It Can Be Used
- The SEEA EA has already been applied to a wide range of policies and decision making processes that support the global sustainability agenda. For example: 1. In Indonesia, carbon accounts have been used to assess the impacts of changes in peatland ecosystems (see World Economic Situation and Prospects 2020, Box II.4, page 86); 2. In South Africa, ecosystem extent and condit…
Projects That Supported Advancement of The Seea Ecosystem Accounting
- A range of international projects have contributed towards the development of the revised SEEA EA by testing and experimentation. These include: 1. The Natural Capital Accounting and Valuation of Ecosystem Services (NCAVES)project, funded by the EU 2. The Advancing Natural Capital Accounting Project (ANCA), funded by Norway 3. The Global Program for Sustainability (…
The Revision Process
- The SEEA EA revision process started in 2018 at the request of the UN Statistical Commission. More than 100 experts from a range of disciplines, sectors and countries were directly involved in its preparation and over 500 experts reviewed the final versions through a global consultation. For more on the revision process see the dedicated revision website.