Effusion is the movement of gas molecules from one container to another through a tiny hole. Rates of effusion can be compared at the same temperature using Graham’s law. Diffusion is the movement of gas molecules through one or more other types of gas via random molecular motion.
What is the difference between diffusion and effusion rates?
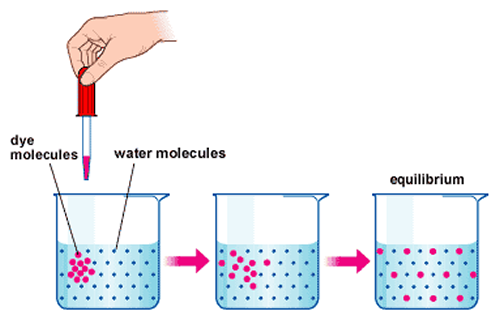
Although diffusion and effusion rates both depend on the molar mass of the gas involved, their rates are not equal; however, the ratios of their rates are the same. Figure 9.4. 2: Diffusion occurs when gas molecules disperse throughout a container.
What is effusion in chemistry?
A process involving movement of gaseous species similar to diffusion is effusion, the escape of gas molecules through a tiny hole such as a pinhole in a balloon into a vacuum (Figure 9.4. 1 ).
What happens during the process of diffusion?
During the process of diffusion, one gas tends to mix with the other generally by thermal random motion which results in the collision between each of the gases while it releases molecular energy. Effusion refers to the ability of the gas to travel through a tiny opening.
What is Graham's Law of diffusion and effusion?
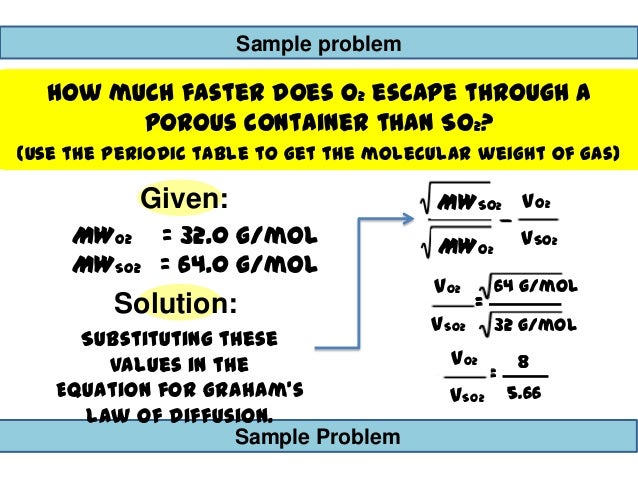
Graham's law of diffusion and effusion states the rate of diffusion or effusion for a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of the molar mass of the gas. r ∝ 1/(M)½. or. r(M)½ = constant. where. r = rate of diffusion or effusion. M = molar mass.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-975446322-1e590ef615bc48d5903bc15e65a49980.jpg)
What is the difference between diffusion and effusion?
Diffusion occurs when gas molecules disperse throughout a container. Effusion occurs when a gas passes through an opening that is smaller than the mean free path of the particles, that is, the average distance traveled between collisions.
What is effusion with example?
Effusion is defined as a loss of material across a boundary. A common example of effusion is the loss of gas inside of a balloon over time. The rate at which gases will effuse from a balloon is affected by a number of factors.
What is the effusion process?
In physics and chemistry, effusion is the process in which a gas escapes from a container through a hole of diameter considerably smaller than the mean free path of the molecules.
What is effusion of gases?
Effusion is a similar process in which gaseous species pass from a container to a vacuum through very small orifices. The rates of effusion of gases are inversely proportional to the square roots of their densities or to the square roots of their atoms/molecules' masses (Graham's law).
What is diffusion example?
A tea bag immersed in a cup of hot water will diffuse into the water and change its colour. A spray of perfume or room freshener will get diffused into the air by which we can sense the odour. Sugar gets dissolved evenly and sweetens the water without having to stir it.
What you mean by diffusion?
Diffusion is defined as the movement of individual molecules of a substance through a semipermeable barrier from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration [34].
What is the similarity between effusion and diffusion?
Similarities Between Diffusion and Effusion Diffusion and effusion are two mechanisms used by different types of molecules to move one to another place. Both methods occur through a concentration gradient. Moreover, the flow of molecules is constant and random.
Why is effusion faster than diffusion?
During the process of effusion, the particles tend to move faster than diffusion since there is no collision occurring between the molecules. The rate of diffusion is limited and depends on the size and the kinetic energy of the other particles. Effusion happens or is facilitated when there is a difference in pressure.
What is the difference between effusion and diffusion quizlet?
What is the difference between effusion and diffusion? Effusion is through a pinhole, and diffusion is through open space. How does the average kinetic energy (avg KE) of an ideal gas vary as the molar mass of the gas increases? avg KE is not dependent upon the molar mass of the gas.
What is called effusion?
Effusion in simple terms is the ability of gas to travel through a small opening. Diffusion is the ability of gases to mix with each other usually in the absence of a barrier. Effusion occurs when the size or aperture of the hole is smaller than the mean free path of the molecules.
What is diffusion of a gas?
Diffusion is the process whereby gaseous atoms and molecules are transferred from regions of relatively high concentration to regions of relatively low concentration. Effusion is a similar process in which gaseous species pass from a container to a vacuum through very small orifices.
Which is an example of gas diffusion?
The diffusion of gases allows the spread of the smell of a lot of things quickly. The smell of food, perfume, and fragrance of the incense stick diffuses in air.
What are three examples of diffusion?
Some examples of diffusion that occurs in our daily life are given below.The smell of perfumes/Incense Sticks.Opening the Soda/Cold Drinks bottle and the CO2 diffuses in the air.Dipping the tea bags in hot water will diffuse the tea in hot water.Small dust particles or smoke diffuse into the air and cause air pollution.More items...
What is effusion in biology?
Effusion occurs when the size or aperture of the hole is smaller than the mean free path of the molecules. Diffusion happens when there are no holes or if holes in the barrier are larger than the mean free path. Effusion occurs or is facilitated by a difference of pressures.
What is the difference between effusion and edema?
There are two types of swelling: edema – swelling that occurs primarily in the soft tissues of the body and effusion – swelling or fluid in the joint space. Edema and effusion are a result of the change in the fluid levels in and out of the cells.
What is effusion in a joint?
Fluid is normally found in joints such as knees, hips, and elbows. When too much fluid builds up around a joint in your body, it's called joint effusion. When you have this problem, your joint may look swollen.
What causes effusion?
Pleural effusion related conditions include congestive heart failure, kidney disease, pulmonary embolism, trauma, or infection. Patients with pleur...
What’s the difference between effusion and diffusion?
Diffusion happens as gas bubbles are spread all over a tube. Effusion happens as a gas travels into an area narrower than that of the particles’ me...
Why diffusion is faster in gases?
Diffusion is driven by concentration differences. When chemical substances like perfume are let loose in a room, their particles mix together with...
What is Graham’s law of effusion and diffusion?
Graham’s law states that the rate of effusion or diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molecular weight. Hence, th...
What are examples of simple diffusion?
In the cell, water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, ethanol, and urea are examples of molecules that can use quick diffusion to migrate in and out of the c...
1. What are the definitions of diffusion and effusion?
The definitions of diffusion and effusion are as follows. Diffusion: Diffusion is known as the process of the particles that tend to move from an a...
2. What is Graham’s law of diffusion and effusion?
According to Graham Law, the rate of the effusion or diffusion of the gas tends to be inversely proportional to the root of its total molecular wei...
3. How are effusion and diffusion different?
One of the major differences between Effusion and Diffusion is that Diffusion occurs through the spreading of gas bubbles all over a tube. But on t...
4. Is the rate of effusion and diffusion the same?
There are several factors that define the rate of Effusion and Diffusion like in Diffusion the surface area, increase and decrease in concentration...
5. What is Graham's law of effusion and diffusion all about?
Graham's Law "The rate of effusion of a gaseous substance is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass" is merely a relationship...
What is the difference between diffusion and effusion?
The primary difference between diffusion and effusion is the barrier , which filters the gas as it moves between the two volumes.
What is diffusion in biology?
Diffusion occurs when holes in a barrier are larger than the mean free path of a gas. If no barrier exists, consider a "barrier" with one large hole big enough to cover the boundary between the two volumes. Handy reminder: small holes = effusion, big holes = diffusion.
Why does effusion move particles faster?
Effusion typically transports particles more quickly because they don't have to move around other particles to reach their destination. Essentially, negative pressure causes quick movement.
What is diffusion in chemistry?
Effusion Definition Chemistry. In chemistry, diffusion and effusion are one of the most commonly used terms. However, they are nothing but two varying properties of the gases. When you study these terms, it can get quite confusing if you are just starting to study the gases. Both diffusion and effusion may sound quite similar to you, ...
When does effusion occur?
Effusion tends to occur when the aperture or size of the hole is much smaller when compared to the mean free path of the constituent molecules. Diffusion tends to occur when there are no holes present or when the holes in the barrier are much larger when compared to the mean free path. During the process of effusion, ...
What happens when gaseous molecules tend to escape through the pinhole into the vacuum?
Effusion happens when the gaseous molecules tend to escape through the pinhole into the vacuum.
How do gaseous molecules move?
This process is known as the process of effusion. If effusion has to occur, the diameter of the holes should be smaller than the mean path of the molecules. Also, the opening of the hole should be smaller than the molecule’s mean free path. Otherwise, the gaseous molecule would only move back and forth in the hole. We can define effusion as the continuous random motion of the particles. Over some time, this random motion would result in the passing of some of the molecules through the hole.
What is the process of particles that tend to move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration?
Ans: The definitions of diffusion and effusion are as follows. Diffusion : Diffusion is known as the process of the particles that tend to move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. The rate of this diffusion movement is a function of the size of the particles, viscosity of the medium and temperature.
Why do particles move faster during the process of effusion?
During the process of effusion, the particles tend to move faster than diffusion since there is no collision occurring between the molecules. The rate of diffusion is limited and depends on the size and the kinetic energy of the other particles. Effusion happens or is facilitated when there is a difference in pressure.
Does Graham's law allow heavier gases to diffuse?
It is essential to note that the heavier gases tend to diffuse at a slower rate. The complete theoretical explanation of this law was shown many years later with the help of the kinetic theory of gases. Graham’s Law provides us with a basis to separate the isotopes with the help of diffusion.
What is the difference between diffusion and effusion?
The main difference between diffusion and effusion is that diffusion is the movement of particles through a concentration gradient where as effusion is the movement of gas molecules through tiny holes. Furthermore, diffusion describes the movement of solid, liquid, and gas molecules while only gases undergo effusion.
What is diffusion in chemistry?
When considering gases, diffusion is the thermal random motion of molecules. Here, collisions that occur among gas molecules allows the release of molecular energy of the gas. Therefore, it becomes one of the major factors in reducing the efficiency of diffusion.
What is the process of gas molecules escaping through a pinhole into a vacuum?
What is Effusion . Effusion is a type of movement of gas molecules. It occurs with the escape of gas molecules through a pinhole into a vacuum. In simple terms, it describes the ability of gas molecules to move through a small opening. Here, the opening has to be smaller than the mean free path of the molecules.
What are the two mechanisms used by different types of molecules to move one to another place?
Diffusion and effusion are two mechanisms used by different types of molecules to move one to another place. Both methods occur through a concentration gradient. Moreover, the flow of molecules is constant and random. Besides, both do not use energy for the movement of molecules.
Why is diffusion important?
The main importance of diffusion is that it allows the mixing of molecules with each other in the space in the absence of a barrier. However, it mainly occurs due to the concentration gradient of molecules. But, it depends on the size and the kinetic energy of molecules.
What is the driving force of gas molecules?
Furthermore, the concentration gradient of gas molecules between either side of the opening generates a pressure gradient across the opening. And, this pressure gradient serves as the major driving force which moves the gas molecules from the higher concentration of gases to a lower concentration through the opening.
Is diffusion more efficient than effusion?
Moreover, diffusion is a less efficient method while effusion is more efficient due to the pressure difference involved in the process.
What is the difference between diffusion and effusion?
2: Diffusion occurs when gas molecules disperse throughout a container. Effusion occurs when a gas passes through an opening that is smaller than the mean free path of the particles, that is , the average distance traveled between collisions. Effectively, this means that only one particle passes through at a time.
How does diffusion work?
In general, we know that when a sample of gas is introduced to one part of a closed container, its molecules very quickly disperse throughout the container; this process by which molecules disperse in space in response to differences in concentration is called diffusion (shown in Figure 9.4. 1 ). The gaseous atoms or molecules are, of course, unaware of any concentration gradient, they simply move randomly—regions of higher concentration have more particles than regions of lower concentrations, and so a net movement of species from high to low concentration areas takes place. In a closed environment, diffusion will ultimately result in equal concentrations of gas throughout, as depicted in Figure 9.4. 1. The gaseous atoms and molecules continue to move, but since their concentrations are the same in both bulbs, the rates of transfer between the bulbs are equal (no net transfer of molecules occurs).
What is the process of moving gaseous species similar to diffusion?
A process involving movement of gaseous species similar to diffusion is effusion, the escape of gas molecules through a tiny hole such as a pinhole in a balloon into a vacuum (Figure 9.4. 1 ). Although diffusion and effusion rates both depend on the molar mass of the gas involved, their rates are not equal; however, the ratios of their rates are the same.
Why is gas diffusion now being replaced by gas centrifuge technology?
Because gaseous diffusion plants require very large amounts of energy (to compress the gas to the high pressures required and drive it through the diffuser cascade, to remove the heat produced during compression, and so on), it is now being replaced by gas centrifuge technology, which requires far less energy.
Why does a balloon deflate?
A balloon filled with helium (the green one) partially deflates because the smaller, light helium atoms effuse through small holes in the rubber much more readily than the heavier molecules of nitrogen and oxygen found in air. (credit: modification of work by Mark Ott)
How fast does hydrogen effuse?
Hydrogen effuses four times as rapidly as oxygen.
What is the rate of diffusion?
rate of diffusion = amount of gas passing through an area unit of time. The diffusion rate depends on several factors: the concentration gradient (the increase or decrease in concentration from one point to another); the amount of surface area available for diffusion; and the distance the gas particles must travel.
What is the difference between diffusion and effusion?
Figure 9.6.2. Diffusion occurs when gas molecules disperse throughout a container. Effusion occurs when a gas passes through an opening that is smaller than the mean free path of the particles, that is , the average distance traveled between collisions. Effectively, this means that only one particle passes through at a time.
How does diffusion work?
In general, we know that when a sample of gas is introduced to one part of a closed container, its molecules very quickly disperse throughout the container; this process by which molecules disperse in space in response to differences in concentration is called diffusion (shown in Figure 9.6.1). The gaseous atoms or molecules are, of course, unaware of any concentration gradient, they simply move randomly—regions of higher concentration have more particles than regions of lower concentrations, and so a net movement of species from high to low concentration areas takes place. In a closed environment, diffusion will ultimately result in equal concentrations of gas throughout, as depicted in Figure 9.6.1. The gaseous atoms and molecules continue to move, but since their concentrations are the same in both bulbs, the rates of transfer between the bulbs are equal (no net transfer of molecules occurs).
What happens when a mixture of gases is placed in a container with porous walls?
If a mixture of gases is placed in a container with porous walls, the gases effuse through the small openings in the walls. The lighter gases pass through the small openings more rapidly (at a higher rate) than the heavier ones (Figure 9.6.3). In 1832, Thomas Graham studied the rates of effusion of different gases and formulated Graham’s law of effusion: The rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of the mass of its particles:
What is the process of moving gaseous species similar to diffusion?
A process involving movement of gaseous species similar to diffusion is effusion, the escape of gas molecules through a tiny hole such as a pinhole in a balloon into a vacuum (Figure 9.6.2). Although diffusion and effusion rates both depend on the molar mass of the gas involved, their rates are not equal; however, the ratios of their rates are the same.
What is the definition of effusion rate?
Recall the definition of rate of effusion: rate of effusion = amount of gas transferred time rate of effusion = amount of gas transferred time and combine it with Graham’s law:
Which law states that the rate of diffusion and effusion of gases are inversely proportional to the square roots of?
Graham’s law of effusion: rates of diffusion and effusion of gases are inversely proportional to the square roots of their molecular masses
What is the rate of diffusion?
rate of diffusion = amount of gas passing through an area unit of time rate of diffusion = amount of gas passing through an area unit of time
Which law states that the rate of diffusion or effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square?
Graham's law states that the rate of diffusion or effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass. See this law in equation form below.
What is the relationship between the rate of effusion and the molar mass of a gas?
Graham's law expresses the relationship between the rate of effusion or diffusion of a gas and that gas's molar mass. Diffusion describes the spreading of a gas throughout a volume or second gas and effusion describes the movement of a gas through a tiny hole into an open chamber.
What is the inverse of the rate of effusion of a gas?
In 1829, Scottish chemist Thomas Graham determined through experimentation that a gas's rate of effusion is inversely proportional to the square root of the gas particle's density. In 1848, he showed that the rate of effusion of a gas is also inversely proportional to the square root of its molar mass. Graham's law also shows that the kinetic ...
Which isotope diffuses at a faster rate than U-238?
Through each effusion, the material passing through the pores becomes more concentrated in U-235 (the isotope used to generate nuclear energy) because this isotope diffuses at a faster rate than the heavier U-238. Cite this Article. Format. mla apa chicago.
How does diffusion work?
In general, we know that when a sample of gas is introduced to one part of a closed container, its molecules very quickly disperse throughout the container; this process by which molecules disperse in space in response to differences in concentration is called diffusion (shown in [link] ). The gaseous atoms or molecules are, of course, unaware of any concentration gradient, they simply move randomly—regions of higher concentration have more particles than regions of lower concentrations, and so a net movement of species from high to low concentration areas takes place. In a closed environment, diffusion will ultimately result in equal concentrations of gas throughout, as depicted in [link]. The gaseous atoms and molecules continue to move, but since their concentrations are the same in both bulbs, the rates of transfer between the bulbs are equal (no net transfer of molecules occurs).
What happens to the effusion rate of two gases at the same temperature?
This means that if two gases A and B are at the same temperature and pressure, the ratio of their effusion rates is inversely proportional to the ratio of the square roots of the masses of their particles:
Why is gas diffusion being replaced?
Because gaseous diffusion plants require very large amounts of energy (to compress the gas to the high pressures required and drive it through the diffuser cascade, to remove the heat produced during compression, and so on), it is now being replaced by gas centrifuge technology, which requires far less energy. A current hot political issue is how to deny this technology to Iran, to prevent it from producing enough enriched uranium for them to use to make nuclear weapons.
What is the process of moving gaseous species similar to diffusion?
A process involving movement of gaseous species similar to diffusion is effusion, the escape of gas molecules through a tiny hole such as a pinhole in a balloon into a vacuum ( [link] ). Although diffusion and effusion rates both depend on the molar mass of the gas involved, their rates are not equal; however, the ratios of their rates are the same.
What happens when a mixture of gases is placed in a container with porous walls?
If a mixture of gases is placed in a container with porous walls, the gases effuse through the small openings in the walls. The lighter gases pass through the small openings more rapidly (at a higher rate) than the heavier ones ( [link] ). In 1832, Thomas Graham studied the rates of effusion of different gases and formulated Graham’s law of effusion: The rate of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of the mass of its particles:
What happens when gas molecules disperse throughout a container?
Diffusion occurs when gas molecules disperse throughout a container. Effusion occurs when a gas passes through an opening that is smaller than the mean free path of the particles, that is, the average distance traveled between collisions. Effectively, this means that only one particle passes through at a time.
How is UF 6 pumped?
In a diffuser, gaseous UF 6 is pumped through a porous barrier, which partially separates 235 UF 6 from 238 UF 6 The UF 6 must pass through many large diffuser units to achieve sufficient enrichment in 235 U.
Which law states that the rate of diffusion or of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the?
Graham’s law states that the rate of diffusion or of effusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its molecular weight.
Which gas is the fastest to effuse?
The gas with the lowest molecular weight will effuse the fastest. The lightest, and therefore fastest, gas is helium.
Which law states that atoms with lower molecular mass will effuse faster than atoms with higher mo?
According to Graham’s Law, at constant pressure and temperature, molecules or atoms with lower molecular mass will effuse faster than the higher molecular mass molecules or atoms. Thomas even found out the rate at which they escape through diffusion.
Is rate of diffusion or effusion inversely proportional to molecular mass?
It states that rate of diffusion or effusion is inversely proportional to its molecular mass.