elastic deflection The deflection of a structural element when a load is applied to it, and which recovers when the load is removed, as opposed to the deflection resulting from creep, 1. McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Architecture and Construction.
What is elastic deformation?
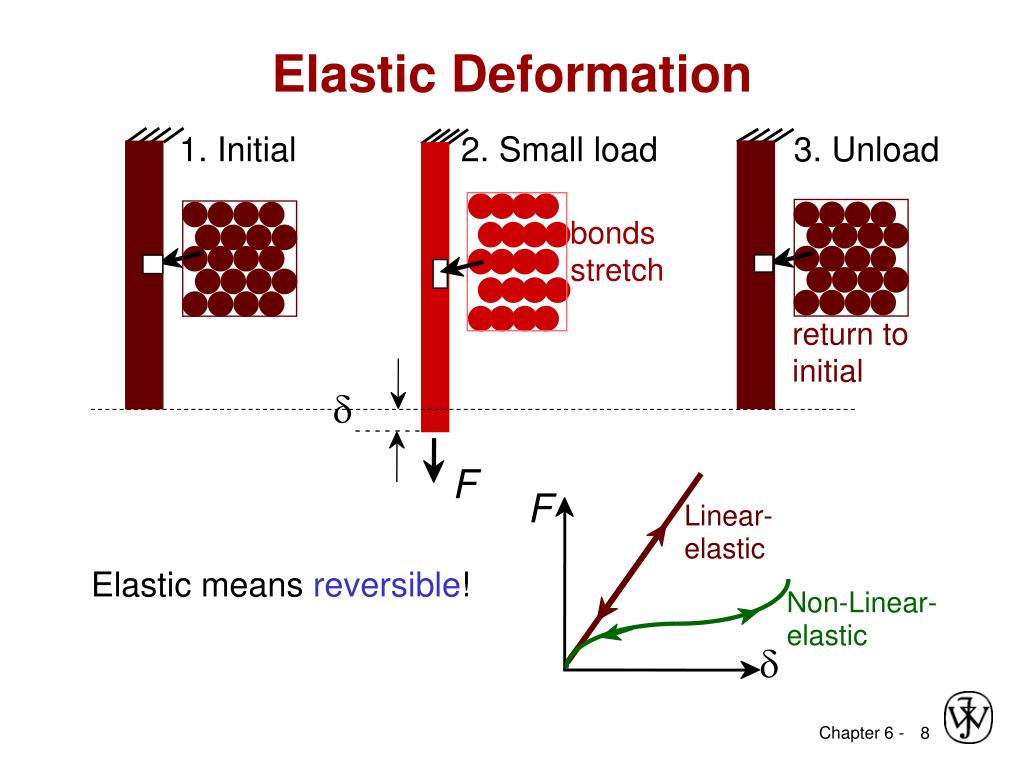
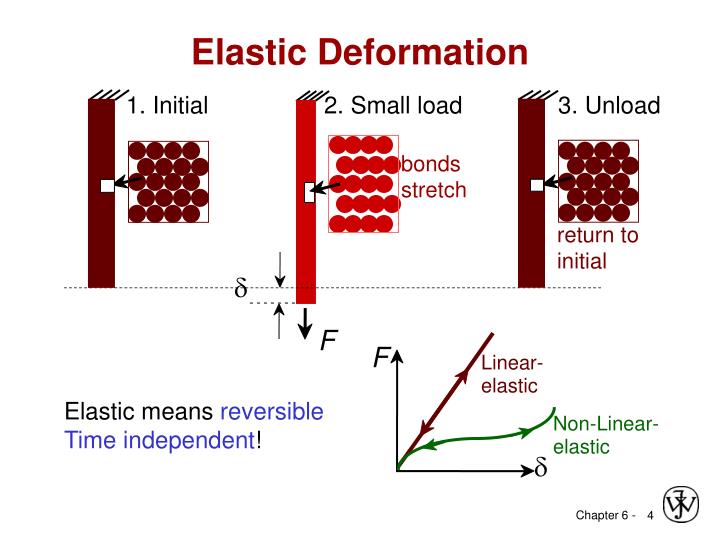
Elastic deformation is defined as deformation that is fully reversed (or recovered) when the load is removed.
What is the difference between creeping and elastic deflection?
Answer Wiki. As seen in the picture below, elastic deflection is the resulting bending of a structural element when a load is applied on a spot or uniformly distributed to an area of it. In contrast to creeping , the structural element recovers from an elastic deflection after the load is removed.
What is elastic deflection of smooth bodies?
Elastic deflections between smooth bodies was analysed by Hertz in 1882 for spheres in contact. Assuming two parallel cylindrical surfaces, the solution may be extended to a smooth grinding wheel in contact with the workpiece arc of contact as illustrated in Fig. 15.5.
What is the deflection distance?
It may refer to an angle or a distance. The deflection distance of a member under a load can be calculated by integrating the function that mathematically describes the slope of the deflected shape of the member under that load. Standard formulas exist for the deflection of common beam configurations and load cases at discrete locations.
Is elastic curve the same as deflection?
0:093:01Deflection and the Elastic Curve - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd the elastic curve or in other words how the internal. Moment can cause deflections of beams.MoreAnd the elastic curve or in other words how the internal. Moment can cause deflections of beams. When there is an internal moment the object will deflect how much depends on the geometry.
What does deflection mean in physics?
In physics, deflection is a change in a moving object's velocity, hence its trajectory, as a consequence of contact (collision) with a surface or the influence of a non-contact force field.
What is deflection of a material?
Introduction. Deflection – in engineering terms – is the degree to which an element of structure changes shape when a load is applied. The change may be a distance or an angle and can be either visible or invisible, depending on the load intensity, the shape of the component and the material from which it is made.
What causes deflection?
Deflection could be something a person learns as a child and is internalized over time (known as internalizing behavior). This can be from repression. Repression, or repressed memories, are thought to be a cause of deflection.
What deflection means?
a change of direction after/dɪˈflek.ʃən/ [ C or U ] a change of direction after hitting something: The second goal was from a deflection off the Liverpool defender. His shot took a deflection and sailed into the net.
What's meant by deflection?
Definition of deflection 1 : a turning aside or off course : deviation. 2 : the departure of an indicator or pointer from the zero reading on the scale of an instrument.
What are the types of deflection?
Types of DeflectionAxial Deflection.Lateral Deflection.Angular Deflection.Combined Deflection.Torsional Deflection.Cyclic Deflection and Cycle Life.Pressure Balancing Examples.Hinged or Gimbalpipe Expansion Joints.More items...
What is the difference between bending and deflection?
Bending is the general name of a class of phenomena, which includes - but is not limited to - beams and plates. Deflection is the displacement in a given point, resulting from an action which may or may not have caused bending.
What is the difference between deflection and deformation?
In engineering, deformation refers to the change in size or shape of an object. Displacements are the absolute change in position of a point on the object. Deflection is the relative change in external displacements on an object.
What is an example of deflection?
One of the most common examples of deflection is when someone changes the subject in the middle of an argument. Specifically, if their behavior is called into question, the deflector will redirect the conversation to focus on something the other person did wrong.
What affects deflection?
The deflection of a beam (beam deflection) is calculated based on a variety of factors, including materials, the moment of inertia of a section, the force applied, and the distance from support.
What is the function of deflection?
In structural engineering, deflection is the degree to which a part of a structural element is displaced under a load (because it deforms). It may refer to an angle or a distance.
What is deflection in a beam?
Deflection, in structural engineering terms, refers to the movement of a beam or node from its original position due to the forces and loads being applied to the member.
Is deflection the same as bending?
Deflection is the measure of bending caused due to a load or force in an element. (Eg. How much length the beam is bended from it original position?) Bending is the measure of internal changes caused by a load or force in an element.
Is deflection same as refraction?
The deflections of waves like light consist of reflection and refraction. Reflection is when light falls on any surface, and a part of that light is sent back to the same medium. Deflection is when light bounces back on the plane surface as it is bent by a gravitational force.
What is deflection in a magnetic field?
Magnetic coils are placed in pairs on the outside of the CRT to provide horizontal and vertical magnetic fields perpendicular to the electron flow. Current in these coils causes deflection of the electrons perpendicular to the magnetic field and to the direction of the electrons. Fig. 54. Magnetic deflection.
What is Elastic Collision?
An elastic collision is a collision in which there is no net loss in kinetic energy in the system due to the collision.
Does Elastic Collision conserve momentum?
Momentum is conserved in an elastic collision.
What is an example of an elastic collision?
When you throw a ball on the ground, and it bounces back to your hand, there is no net change in the kinetic energy, and hence, it is an elastic co...
What is the difference between elastic and inelastic collision?
Unlike the elastic collision, where the kinetic energy is conserved, the kinetic energy in an inelastic collision is not conserved. In an inelastic...
What are the applications of the elastic collision?
The airbags in automobiles increase the collapse time and minimize the effect of force on objects during a collision.
What is inelastic collision?
An inelastic collision is a type of collision where this is a loss of kinetic energy. The lost kinetic energy is transformed into thermal energy, s...
State the law of conservation of linear momentum.
According to the law of conservation of linear momentum, if the net external force acting on a system of bodies is zero, then the system’s momentum...
Write some applications of conservation of linear momentum.
One of the applications of conservation of momentum is the launching of rockets. The rocket fuel burns are pushed the exhaust gases downwards, and...
What is elastic potential energy?
Elastic potential energy is energy stored as a result of applying a force to deform an elastic object. The energy is stored until the force is remo...
How many deflections are considered?
Only small deflections are considered (max deflection less than 1/10 of the span ).
What is the slope of a cantilever beam?
Cantilever beams have one end fixed, so that the slope and deflection at that end must be zero.
What is deflection in engineering?
In engineering, deflection is the degree to which a structural element is displaced under a load (due to its deformation ). It may refer to an angle or a distance.
How to represent deflected shape of beam?
The deflected shape of a beam can be represented by the moment diagram, integrated (twice, rotated and translated to enforce support conditions).
What is simply supported beam?
Simply-supported beams have supports under their ends which allow rotation, but not deflection.
Can you calculate deflection without knowing the beam?
If the beam is uniform and the deflection at any point is known, this can be calculated without knowing other properties of the beam.
Is a beam straight or curved?
Beams can vary greatly in their geometry and composition. For instance, a beam may be straight or curved. It may be of constant cross section, or it may taper. It may be made entirely of the same material (homogeneous), or it may be composed of different materials (composite). Some of these things make analysis difficult, but many engineering applications involve cases that are not so complicated. Analysis is simplified if:
What is an Elastic Collision?
When two bodies collide but there is no loss in the overall kinetic energy, it is called a perfectly elastic collision .
How do airbags reduce force?
Likewise, to minimize the force, the collision time must be increased. There are several real-world applications of these phenomena. The airbags in automobiles increase the collapse time and minimize the effect of force on objects during a collision. Airbag accomplishes this by extending the time required to stop the momentum of the passenger and the driver.
What happens to kinetic energy before and after an elastic collision?
In an elastic collision, the kinetic energy before the collision and after the collision remains the same. It is not converted to other forms of energy.
How to determine if a collision is elastic or inelastic?
To determine whether the collision is elastic or inelastic, calculate the total kinetic energy of the system both before and after the collision. Since the kinetic energy before the collision is equal to the kinetic energy after the collision (kinetic energy is conserved), this is an elastic collision.
What are some examples of inelastic collisions?
An example of an inelastic collision can be the collision of two cars.
How does collision time affect the force of an object?
The collision time affects the amount of force that an object experiences during a collision. The greater the time over which the collision occurs , the smaller the force acting upon the object. Thus, to maximize the force experienced by an object during a collision, the collision time must be decreased.
What is collision in science?
A collision occurs when two objects come in direct contact with each other. It is the event in which two or more bodies exert forces on each other in about a relatively short time. There are two types of collisions namely :
What is Figure 6.10?
Figure 6.10. Bioinspired ornithopter test platform wing in free flight: maximal occurring elastic deformation in the thrust flap region of the wing in the wing fixed reference frame CW.
What is the thermal deformation of a gas face seal?
Elastic deformation and thermal deformation of the gas face seal occur when seal pressure reaches several or even dozens of MPa; the thermo-viscosity effect, the pressure-viscosity of gases, and the choked flow effect of high-speed fluid will significantly change the law of seal performance, creating the problem of gas thermoelastohydrodynamic lubrication (TEHL). However, the TEHL problem of gas face seal is different from that of the liquid-lubricated bearing and gear, which presents mainly as a low-contact lubrication problem.
What is elastic deformation?
Elastic deformation is conventionally defined as a reversible deformation. Elastic deformation in metals commonly occurs by (small) changes in the shape of the atomic lattice (mainly by shear). Such elastic deformation is linear and therefore obeys the Hooke's law, which allows the determination of Young's modulus (in this chapter simply referred to as “elastic modulus”). An alternative mechanism of reversible deformation is a reversible martensitic transformation—the formation and vanishing of SIM upon loading and unloading, respectively—referred to as pseudoelasticity or superelasticity. Such reversible deformation is nonlinear and the elastic modulus cannot be unambiguously determined.
How to solve thermal elastic deformation?
Thermal elastic deformation in continuum is solved by a coupling problem of heat-transfer problem and linear elastic problem. A solution of temperature to the heat-transfer problem is related to initial strain in the linear elastic problem. Hence, optimization problem of the boundary shape of the continuum involves coupling boundary value problems of partial differential equations as state equations. The present paper focuses on how to solve the boundary shape optimization problem consists of coupling boundary value problems.
What is ZW coordinate?
The zw-coordinate describes the deformation of the reference frame flapping around x with FA β.
What is QF in physics?
in which, qf is the vector of modal coordinates that describe elastic deformation of the body and Φ t p is the modal shape matrix.
What is the relationship between oxygen content and the resulting linear elastic deformation of a Ti alloy?
The relation between oxygen content and the resulting linear elastic deformation of a Ti alloy is predominantly related to the phase composition and stability of particular phases. The formation of α and ω iso phases should be avoided due to their high elastic modulus. Both phases are formed during annealing by the diffusion transformation; oxygen contributes to their stabilization and may increase their volume fraction [16,44].
Homework Statement
Calculate the deflection at the end of a rod whose dimensions are 1m x 0.1m x 0.1m, when a load of 100N is applied. The modulus of elasticity is given as 1 x 10 11 (N/m 2)
The Attempt at a Solution
I'm not sure if i've calculated that in the right order, or if I have missed any steps. I'm a little bit lost on how to approach this problem!
Answers and Replies
Your approach is fine, but your maths is not so good. The Area of the rod is 1 X 10 -2 m 2 (that is, 0.01 m 2 ). Please redo the maths and don't forget to note the units.
What is plastic deformation?
Under tensile stress, plastic deformation is characterized by a strain hardening region and a necking region and finally, fracture (also called rupture). During strain hardening the material becomes stronger through the movement of atomic dislocations. The necking phase is indicated by a reduction in cross-sectional area of the specimen. Necking begins after the ultimate strength is reached. During necking, the material can no longer withstand the maximum stress and the strain in the specimen rapidly increases. Plastic deformation ends with the fracture of the material.
What is elasticity in engineering?
Further information: Elasticity (physics) The study of temporary or elastic deformation in the case of engineering strain is applied to materials used in mechanical and structural engineering, such as concrete and steel, which are subjected to very small deformations.
How are strains and stress related?
Strains are related to the forces acting on the cube, which are known as stress, by a stress-strain curve. The relationship between stress and strain is generally linear and reversible up until the yield point and the deformation is elastic. The linear relationship for a material is known as Young's modulus.
What happens to an object when it is stressed?
Compressive stress results in deformation which shortens the object but also expands it outwards.
Why do cylinders bulge?
In the figure it can be seen that the compressive loading (indicated by the arrow) has caused deformation in the cylinder so that the original shape (dashed lines) has changed (deformed) into one with bulging sides. The sides bulge because the material, although strong enough to not crack or otherwise fail, is not strong enough to support the load without change. As a result, the material is forced out laterally. Internal forces (in this case at right angles to the deformation) resist the applied load.
What temperature does steel lose strength?
Note: When exposed to fire, steel first expands and then loses its strength, exceeding critical temperature at 538°C or 1000°F per ASTM E 119 unless treated with fireproofing.
Can stress strain curve be re-derived?
Since we disregard the change of area during deformation above, the true stress and strain curve should be re-derived. For deriving the stress strain curve, we can assume that the volume change is 0 even if we deformed the materials. We can assume that:

Overview
Beam deflection for various loads and supports
Beams can vary greatly in their geometry and composition. For instance, a beam may be straight or curved. It may be of constant cross section, or it may taper. It may be made entirely of the same material (homogeneous), or it may be composed of different materials (composite). Some of these things make analysis difficult, but many engineering applications involve cases that are not …
Structural deflection
Building codes determine the maximum deflection, usually as a fraction of the span e.g. 1/400 or 1/600. Either the strength limit state (allowable stress) or the serviceability limit state (deflection considerations among others) may govern the minimum dimensions of the member required.
The deflection must be considered for the purpose of the structure. When designing a steel frame to hold a glazed panel, one allows only minimal deflection to prevent fracture of the glass.
See also
• Slope deflection method
External links
• Deflection of beams
• Beam Deflections
• Calculation tools for Deflection & slope of beams