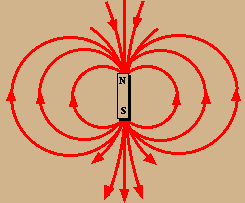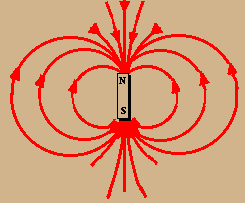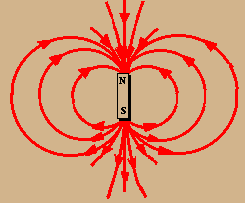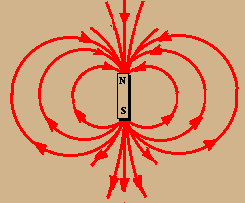
KS3 Electromagnetism and magnetism Magnets have a north pole and a south pole. Like poles repel but opposite poles attract. Electromagnets, motors, bells and compasses use magnetic fields.
What is electromagnetism?
Electromagnetism. Electromagnetism is a branch of Physics, deals with the electromagnetic force that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental forces and exhibits electromagnetic fields such as magnetic fields, electric fields, and light.
What is the other name of electromagnetic interaction?
Alternative Title: electromagnetic interaction. Electromagnetism, science of charge and of the forces and fields associated with charge. Electricity and magnetism are two aspects of electromagnetism. Electricity and magnetism were long thought to be separate forces.
What are the mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field?
There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. Most prominently, Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.
What are the force and conservation laws of electromagnetism?
The force and conservation laws are only two aspects of electromagnetism, however. Electric and magnetic forces are caused by electromagnetic fields. The term field denotes a property of space, so that the field quantity has a numerical value at each point of space. These values may also vary with time.
What is electromagnetism in simple terms?
Electromagnetism is a branch of Physics, that deals with the electromagnetic force that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental forces and exhibits electromagnetic fields such as magnetic fields, electric fields, and light.
What is electromagnetism kid definition?
Magnetism is created when electricity flows through metals. The magnetic force starts when the electricity flows, and stops if the electric current is disconnected. This kind of magnetism is called electromagnetism, and it is very useful for making magnets that can be switched on and off.
What is magnetism in physics ks3?
Magnets have a north pole and a south pole. Like poles repel but opposite poles attract. Electromagnets, motors, bells and compasses use magnetic fields. Physics.
How is electromagnetism used by students?
Electromagnets are very strong and have many uses in everyday life. For example, electromagnets are used in speakers to make sound. Electromagnets are also used in disc drives, generators, motors, and scrap yards. Electromagnets are used in modern medicine as well.
What are 3 facts about electromagnets?
5 Facts About Electromagnets#1) Controllable. Electromagnets are controllable. ... #2) Discovered In the 19th Century. Electromagnets were first discovered in the 19th century by Danish scientist and researcher Hands Christian Orsted. ... #3) Adjustable Power Level. ... #4) Used in MRI Machines. ... #5) Used in Generator.
What is electromagnetism BBC Bitesize?
Electromagnets. When an electric current flows in a wire, it creates a magnetic field around the wire. This effect can be used to make an electromagnet . A simple electromagnet comprises a length of wire turned into a coil and connected to a battery or power supply. A simple electromagnet.
How does a electromagnet work?
Electromagnets are made of coils of wire with electricity passing through them. Moving charges create magnetic fields, so when the coils of wire in an electromagnet have an electric current passing through them, the coils behave like a magnet.
What are the uses of electromagnets?
10 Uses of ElectromagnetsGenerators, motors, and transformers.Electric buzzers and bells.Headphones and loudspeakers.Relays and valves.Data storage devices like VCRs, tape recorders, hard discs, etc.Induction cooker.Magnetic locks.MRI machines.More items...
What is an electromagnet Grade 4?
An electromagnet is a material that turns into a temporary magnet when electricity runs through it.
What is the difference between a magnet and an electromagnet for kids?
An electromagnet is a magnet that uses electricity. The strength of an electromagnet can be changed by changing the amount of electricity that it is connected to. By taking away the electricity running through the electromagnet, it can be turned off.
What is the simplest form of an electromagnet?
The magnetic field around a straight wire forms concentric circles of magnetism. Because it creates a weak magnetic field, a straight wire could be considered the most basic form of an electromagnet.
Where do we use electromagnetism?
Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, electromechanical solenoids, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment.
What is Electromagnetism?
Electromagnetism is a branch of physics that involves the study of electromagnetic force. It is a type of interaction that occurs between electrica...
Define electromagnetic force?
The electromagnetic force is a force that acts between charged particles and is a combination of electrical and magnetic forces.
State Faraday’s Law?
Faraday’s Law states that whenever there is relative motion between magnetic field and conductor, the flux linkage changes and this change in flux...
Define electromagnetic induction?
Electromagnetic induction is the production of an electromotive force across an electrical conductor in a changing magnetic field.
How are electromagnetic waves propagated?
Electromagnetic waves are propagated by oscillating electric and magnetic waves at right angles to each other.
What are the advantages of electromagnets over magnets?
Electromagnets have some advantages over permanent magnets. For example: 1 they can be turned on and off 2 the strength of the magnetic field can be varied
How can electromagnets be reversed?
The magnetic field around an electromagnet is just the same as the one around a bar magnet. It can, however, be reversed by reversing the current (turning the battery around).
What is the effect of an electric current flowing through a wire?
When an electric current flows in a wire, it creates a magnetic field around the wire. This effect can be used to make an electromagnet. A simple electromagnet comprises a length of wire turned into a coil and connected to a battery or power supply. A simple electromagnet.
Why is there a limit to how much current can be passed through a wire?
There is a limit to how much current can be passed safely through the wire because the resistance of the wire causes heating. Dr Yan makes a powerful electromagnet by wrapping copper wire around pieces of iron and attaching a small battery. Electromagnets have some advantages over permanent magnets. For example:
Do magnets have north or south poles?
Electromagnetism and magnetism. Magnets have a north pole and a south pole. Like poles repel but opposite poles attract. Electromagnets, motors, bells and compasses use magnetic fields. Part of. Physics. Electromagnetism and magnetism. Add to My Bitesize. Revise.
How is electromagnetism created?
Electromagnetism is a process where a magnetic field is created by introducing the current in the conductor. When a conductor is electrically charged it generates magnetic lines of force of conductor. For example, if current i.e., positive charges moving in a wire, it produces the magnetic field along the wire, and the direction of magnetic lines and force can be determined using Right-hand Rule. Refer to the image for a detailed explanation.
What are some examples of electromagnetism?
Permanent Magnetic speakers commonly used in TV’s and Radios are perfect examples of Electromagnetic devices. Let’s see the operation of these devices which are based on the principle of electromagnetism. See the picture below.
What is Electromagnetic Force?
The electromagnetic force is a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. It acts between charged particles and is the combination of all magnetic and electrical forces. The electromagnetic force can be attractive or repulsive.
What are the properties of electromagnetic waves?
A few properties of electromagnetic waves are: 1 Electromagnetic waves are propagated by oscillating waves electric and magnetic waves oscillating at right angles to each other 2 They exhibit the properties of interference and diffraction 3 They travel at a speed of 3 × 10 8 m/s in a vacuum. 4 They are transverse waves. 5 The relationship between the wavelength (λ) and frequency (c) of an electromagnetic wave is given as follows:
What is the branch of physics that involves the study of the electromagnetic force?
What is Electromagnetism ? Electromagnetism is a branch of physics that involves the study of the electromagnetic force. It is a type of interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles.
How fast do electromagnetic waves travel?
They travel at a speed of 3 × 10 8 m/s in a vacuum. They are transverse waves.
How do Maglev trains work?
The Maglev trains or high-speed trains work on the principle of electromagnetism.
How do electric and magnetic fields work together?
Electric and magnetic forces can be detected in regions called electric and magnetic fields. These fields are fundamental in nature and can exist in space far from the charge or current that generated them. Remarkably, electric fields can produce magnetic fields and vice versa, independent of any external charge. A changing magnetic field produces an electric field, as the English physicist Michael Faraday discovered in work that forms the basis of electric power generation. Conversely, a changing electric field produces a magnetic field, as the Scottish physicist James Clerk Maxwell deduced. The mathematical equations formulated by Maxwell incorporated light and wave phenomena into electromagnetism. He showed that electric and magnetic fields travel together through space as waves of electromagnetic radiation, with the changing fields mutually sustaining each other. Examples of electromagnetic waves traveling through space independent of matter are radio and television waves, microwaves, infrared rays, visible light, ultraviolet light, X-rays, and gamma rays. All of these waves travel at the same speed—namely, the velocity of light (roughly 300,000 kilometres, or 186,000 miles, per second). They differ from each other only in the frequency at which their electric and magnetic fields oscillate.
How does electromagnetic energy affect modern life?
When a lightbulb is switched on, a current flows through a thin filament in the bulb, and the current heats the filament to such a high temperature that it glows, illuminating its surroundings. Electric clocks and connections link simple devices of this kind into complex systems such as traffic lights that are timed and synchronized with the speed of vehicular flow. Radio and television sets receive information carried by electromagnetic waves traveling through space at the speed of light. To start an automobile, currents in an electric starter motor generate magnetic fields that rotate the motor shaft and drive engine pistons to compress an explosive mixture of gasoline and air; the spark initiating the combustion is an electric discharge, which makes up a momentary current flow.
How are magnetic and electric forces different?
At a practical level, however, electric and magnetic forces behave quite differently and are described by different equations. Electric forces are produced by electric charges either at rest or in motion. Magnetic forces, on the other hand, are produced only by moving charges and act solely on charges in motion. Britannica Quiz.
What are some examples of electromagnetic waves traveling through space?
Examples of electromagnetic waves traveling through space independent of matter are radio and television waves, microwaves, infrared rays, visible light, ultraviolet light, X-rays, and gamma rays . All of these waves travel at the same speed—namely, the velocity of light (roughly 300,000 kilometres, or 186,000 miles, per second).
How does an electric starter work?
To start an automobile, currents in an electric starter motor generate magnetic fields that rotate the motor shaft and drive engine pistons to compress an explosive mixture of gasoline and air; the spark initiating the combustion is an electric discharge, which makes up a momentary current flow. Load Next Page.
What is the problem with electricity?
A common problem in electricity is determining the relationship between voltage and current or charge in a given physical situation. This article seeks to provide a qualitative understanding of electromagnetism as well as a quantitative appreciation for the magnitudes associated with electromagnetic phenomena.
Why do electric phenomena occur in neutral matter?
Electric phenomena occur even in neutral matter because the forces act on the individual charged constituents. The electric force in particular is responsible for most of the physical and chemical properties of atoms and molecules. It is enormously strong compared with gravity.
What type of energy travels in waves?
Electromagnetic energy travels in waves and spans a broad spectrum from very long radio waves to very short gamma rays. The human eye can only detect only a small portion of this spectrum called visible light. A radio detects a different portion of the spectrum, and an x-ray machine uses yet another portion.
What energy do you use when you tune your radio?
When you tune your radio, watch TV, send a text message, or pop popcorn in a microwave oven, you are using electromagnetic energy. You depend on this energy every hour of every day. Without it, the world you know could not exist.
What is the term for the wavelengths that pass through the atmosphere?
These regions of the spectrum with wavelengths that can pass through the atmosphere are referred to as "atmospheric windows.".
What was the first connection between electricity and magnetism?
In 1600, William Gilbert proposed, in his De Magnete, that electricity and magnetism, while both capable of causing attraction and repulsion of objects, were distinct effects. Mariners had noticed that lightning strikes had the ability to disturb a compass needle. The link between lightning and electricity was not confirmed until Benjamin Franklin 's proposed experiments in 1752. One of the first to discover and publish a link between man-made electric current and magnetism was Gian Romagnosi, who in 1802 noticed that connecting a wire across a voltaic pile deflected a nearby compass needle. However, the effect did not become widely known until 1820, when Ørsted performed a similar experiment. Ørsted's work influenced Ampère to produce a theory of electromagnetism that set the subject on a mathematical foundation.
What is the study of electromagnetic force?
Electromagnetism is a branch of physics involving the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force is carried by electromagnetic fields composed of electric fields and magnetic fields, and it is responsible for electromagnetic radiation such as light. It is one of the four fundamental interactions (commonly called forces) in nature, together with the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation. At high energy, the weak force and electromagnetic force are unified as a single electroweak force .
What did Hans Christian rsted discover?
In April 1820, Hans Christian Ørsted observed that an electrical current in a wire caused a nearby compass needle to move. At the time of discovery, Ørsted did not suggest any satisfactory explanation of the phenomenon, nor did he try to represent the phenomenon in a mathematical framework. However, three months later he began more intensive investigations. Soon thereafter he published his findings, proving that an electric current produces a magnetic field as it flows through a wire. The CGS unit of magnetic induction ( oersted) is named in honor of his contributions to the field of electromagnetism.
What is the weak force?
It is one of the four fundamental interactions (commonly called forces) in nature, together with the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation. At high energy, the weak force and electromagnetic force are unified as a single electroweak force .
Why is the CGS unit of magnetic induction named after Oersted?
The CGS unit of magnetic induction ( oersted) is named in honor of his contributions to the field of electromagnetism.
What are the peculiarities of electromagnetism?
One of the peculiarities of classical electromagnetism is that it is difficult to reconcile with classical mechanics, but it is compatible with special relativity. According to Maxwell's equations, the speed of light in a vacuum is a universal constant that is dependent only on the electrical permittivity and magnetic permeability of free space. This violates Galilean invariance, a long-standing cornerstone of classical mechanics. One way to reconcile the two theories (electromagnetism and classical mechanics) is to assume the existence of a luminiferous aether through which the light propagates. However, subsequent experimental efforts failed to detect the presence of the aether. After important contributions of Hendrik Lorentz and Henri Poincaré, in 1905, Albert Einstein solved the problem with the introduction of special relativity, which replaced classical kinematics with a new theory of kinematics compatible with classical electromagnetism. (For more information, see History of special relativity .)
What is the weak nuclear force?
the weak nuclear force, which binds to all known particles in the Standard Model, and causes certain forms of radioactive decay. (In particle physics though, the electroweak interaction is the unified description of two of the four known fundamental interactions of nature: electromagnetism and the weak interaction);
