Electronegativity
Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract electrons (or electron density) towards itself. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside fro…
What does the average electronegativity Tell Me?
What does the average electronegativity tell me? Average electronegativity ( χ) tells you the difference between covalent and metallic, or covalent and ionic. The example I like to use is silicon tetrafluoride vs. calcium sulfide. The one with the larger Δ χ is the covalent compound, because it has a high average χ.
What is the general trend in electronegativity across a period?
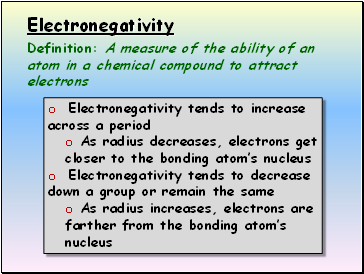
The trends for electronegativity is that the value increases across the periods (rows) of the periodic table. Lithium 1.0 and Fluorine 4.0 in period 2 The electronegativity also increases up a group (column) of the periodic table.
What has more electronegativity?
Which elements have the greatest electronegativity? Thus, fluorine is the most electronegative element, while francium is one of the least electronegative. (Helium, neon, and argon are not listed in the Pauling electronegativity scale, although in the Allred-Rochow scale, helium has the highest electronegativity.)
Which element has the lowest electronegativity?
Which element has the lowest electronegativity? The alkali metals as a group have the lowest electronegativities, with the values falling as the atomic number increases, so the winner is caesium (cesium), with a Pauling score of 0.79.
/chart-of-periodic-table-trends-608792-v1-6ee35b80170349e8ab67865a2fdfaceb.png)
What is the trend for electronegativity energy?
Electronegativity increases across a period and decreases down a group. Towards the left of the table, valence shells are less than half full, so these atoms (metals) tend to lose electrons and have low electronegativity.
What is the trend in electronegativity down a group?
From top to bottom down a group, electronegativity decreases. This is because atomic number increases down a group, and thus there is an increased distance between the valence electrons and nucleus, or a greater atomic radius.
What are the 2 trends in electronegativity?
Electronegativity values generally increase from left to right across the periodic table. Electronegativities generally decrease from the top to bottom of a group.
What is electronegativity in simple words?
Electronegativity is an index of the tendency of an atom to attract electrons. It is proportional to the difference between an atom's ionization potential and its electron affinity.
Why does electronegativity decrease down a group and increase across a period?
Electronegativity increases across a period because the number of charges on the nucleus increases. That attracts the bonding pair of electrons more strongly.
Why is electronegativity decreases down the group?
Moving down in a group, the electronegativity decreases due to increase in atomic size. With an increase in atomic size, the valence electron shell moves farther from the nucleus. Larger the distance, weaker is the attractive force, hence, lower is the the atom's tendency to attract the electrons.
What factors affect electronegativity?
The factors that affect electronegativity are atomic radius, nuclear charge, and shielding. As you go down a group in the periodic table, the electronegativity decreases. As you go across a period in the periodic table, the electronegativity increases.
Why does electronegativity increase from left to right?
Electronegativity increases as we move left to the right in the period because as we move across the period, the effective nuclear charge increases and the atomic size decreases. Therefore, the tendency to attract shared pairs of electrons increases, thereby increasing electronegativity.
How many trends are there in the periodic table?
There are four main periodic trends: electronegativity, atomic size, ionization energy, and electron affinity.
What is electronegativity and why is it important?
Electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract electrons (or electron density) towards itself. It determines how the shared electrons are distributed between the two atoms in a bond. The more strongly an atom attracts the electrons in its bonds, the larger its electronegativity.
What does high electronegativity mean?
Electronegativity refers to the ability of an atom to attract shared electrons in a covalent bond. The higher the value of the electronegativity, the more strongly that element attracts the shared electrons.
What is the importance of electronegativity?
Electronegativity helps us in predicting the polarity of covalent bonds. (i) The greater the electronegativity difference between the two bonded atoms, the greater is the polarity of the covalent bond.
Why does electronegativity decrease down group 7?
As the halogen atoms get bigger, any bonding pair gets further and further away from the halogen nucleus, and so is less strongly attracted towards it. In other words, as you go down the Group, the elements become less electronegative.
What determines the periodic trends down a group?
Moving down a group in the periodic table, the number of filled electron shells increases. In a group, the valence electrons keep the same effective nuclear charge, but now the orbitals are farther from the nucleus. Therefore, the nucleus has less of a pull on the outer electrons and the atomic radii are larger.
Why is electronegativity higher at the top of a group?
This is because as you go from top to bottom down a group, the atoms of each element have an increasing number of energy levels. The electrons in a bond are thus farther away from the nucleus and are held less tightly.
Why does Electropositivity increase down a group?
There is less attraction between the nucleus and the valence electrons due to this and valence electrons are easily lost. That is why as we move down a group, the electronegativity of an atom decreases and the electropositivity of an atom increases.
Which is the best definition of electronegativity?
Electronegativity is a function of an atom’s ability to attract an electrons binding pair. The most frequently used is the Pauling scale. Fluorine...
What is high electronegativity?
Electronegativity decrease as it moves from top to bottom and increases over time from left to right. The most electronegative element is, therefor...
What is the electronegativity difference?
The degree to which an atom attracts electrons in a chemical bond is described by electronegativity. If the difference in electronegativity is grea...
What is the difference between electron affinity and electronegativity?
The difference between the two is that electronegativity is a chemical property that shows how well an atom can attract electrons to itself as the...
Is electronegativity a relative quantity?
Electronegativity is an example of an atom’s ability to attract electrons. It is proportional to the difference between the potential for ionizatio...
How does electronegative vary along the period?
Electronegativity increases as we move left to the right in the period because as we move across the period, the effective nuclear charge increases...
How does electronegative vary in a group?
Electronegativity decreases as we move down the group because as we move down the group, the atomic size increases and the effective nuclear charge...
Name the most electronegative element and least electronegative element in the periodic table?
Fluorine is the most electronegative element, and caesium is the least electronegative element in the periodic table.
How does the electronegativity of an element affect its bonding?
The electronegativity of an element affects the bonding of an element. Elements with high electronegativity tend to form ionic bonds with other ele...
What is Electronegativity?
The tendency of an atom in a molecule to attract the shared pair of electrons towards itself is known as electronegativity.
Why is electronegativity important?
Electronegativity is an important quantity in determining the nature of bonds between elements and will be considered as the main factor in chemical bonding. The periodic table of elements with the electronegativity table is given below.
What is the power of an atom to attract electrons to itself?
Electronegativity is a chemical property that describes the power of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. There is a large difference in electronegativity for atoms from the left- and right-hand sides of the periodic table. Electronegativity is an important quantity in determining the nature of bonds between elements ...
What happens when a covalent bond is more electronegative?
In the covalent bonds featuring a large difference in the electronegativities of the bonded atoms, it is not uncommon for the more electronegative atom to gain complete control over the bond pair of electrons , resulting in the formation of two ions. Here, the more electronegative atom forms an anion and the more electropositive atom becomes ...
Why do covalent bonds become polarized?
This occurs because the more electronegative atom pulls the bond pair of electrons closer to itself, developing a partially negative charge in the process (which is usually denoted by the symbol -𝛿). At the same time, the more electropositive atom develops a partial positive charge (denoted by +𝛿). These partial charges are responsible for the polarity of the chemical bond.
How does electronegativity affect covalent bonds?
Impact of Electronegativity on Covalent Bonding. The strength of a covalent bond is highly dependent on the electronegativities of the two bonded atoms (especially the difference in the electronegativities of the bonded atoms). Homonuclear diatomic molecules feature relatively ‘pure’ covalent bonds since the electronegativities ...
What is the degree to which an atom attracts electrons in a chemical bond?
The degree to which an atom attracts electrons in a chemical bond is described by electronegativity. If the difference in electronegativity is greater than 1.7, the character of the bond will be ionic. If the difference in electronegativity is between 0.4 and 1.7, the character of the bond is polar covalent.
What is electronegativity?
Electronegativity is defined as an atom’s ability to attract electrons towards it in a chemical bond. There are several different ways of measuring it, the most common being the Pauling scale. Different elements have different electronegativities based on a number of factors such as size and number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. It is often viewed on an electronegativity chart of the elements, where trends and values can easily be seen. The higher the electronegativity, the stronger an atom attracts electrons. We will be exploring the electronegativity trends in the periodic table.
What are the factors that affect electronegativity?
There are a variety of factors that affect the electronegativity of an atom. Size is an important element of electronegativity. The positive protons in the nucleus “pull” on the negative electrons in the orbitals. The bigger the atom, the larger the distance, and the less effectively the protons are able to pull on the electrons. This leads to larger atoms with more electron shells having lower electronegativity. Attraction between protons and electrons means that atoms with a higher atomic number and number of protons have a higher electronegativity.
Why is electronegativity important?
Electronegativity can tell us a lot about how different elements will bond to each other and which type of bond it will be. If the electronegativity difference between the two elements involved in bonding is less than 0.4 then the bond will be nonpolar covalent. If the difference is between 0.4 and 1.7 then the bond is considered polar covalent. And finally, if the difference is greater than 1.7 then the bond will be ionic.
Which element has the highest electronegativity?
From top to bottom electronegativity decreases because of the increasing size of the atoms. As a result, Fluorine is considered the most electronegative element while cesium is the least electronegative element. Halogens are considered to have a high electronegativity, while it is low for the alkali metals and alkaline earth metals.
Is fluorine an electronegative element?
Fluorine is the most electronegative element on the electronegativity chart, followed by oxygen and then chlorine. This has several implications. Firstly, it means that fluorine is always negative when combined with other elements. Secondly, it means that oxygen always has a negative oxidation state, except in the very rare case where it forms a compound with fluorine. This also explains the high reactivity of fluorine, chlorine and oxygen. Fluorine is so electronegative, that it wants to rip an electron off anything it touches.
Do noble gases have an electronegativity?
No, they do not. It is not possible to measure electronegativity values for the noble gases, because they do not readily form bonds with other atoms.
What are the factors that affect electronegativity?
Factors that affect electronegativity include the nuclear charge and the number and location of electrons in an atom.
Which atom has the highest electronegativity?
The chlorine atom has a higher electronegativity than the hydrogen atom, so the bonding electrons will be closer to the Cl than to the H in the HCl molecule.
What happens when electrons are attracted to one atom?
Usually, the electrons in a chemical bond are more attracted to one atom (the more electronegative one) than to the other. This results in a polar covalent bond. If the electronegativity values are very different, the electrons aren't shared at all.
What is the property of an atom that increases with its tendency to attract the electrons of a bond?
Electronegativity is the property of an atom which increases with its tendency to attract the electrons of a bond. If two bonded atoms have the same electronegativity values as each other, they share electrons equally in a covalent bond. Usually, the electrons in a chemical bond are more attracted to one atom (the more electronegative one) ...
What is the tendency of an atom to attract electrons to itself in a chemical bond?
Electronegativity is an atom's tendency to attract electrons to itself in a chemical bond.
Which chemists studied the electronegativity of atoms?
The greater the difference between atom electronegativity values, the more polar the chemical bond formed between them. Avogadro and other chemists studied electronegativity before it was formally named by Jöns Jacob Berzelius in 1811. In 1932, Linus Pauling proposed an electronegativity scale based on bond energies.
Which element is the least electronegative?
The most electronegative element on the periodic table is fluorine (3.98). The least electronegative element is cesium (0.79). The opposite of electronegativity is electropositivity, so you could simply say cesium is the most electropositive element.
What is the electronegativity trend?
Electronegativity Trend, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom to attract a shared pair of electrons (electron density) towards itself. An atom’s electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus.
What determines the electronegativity of an atom?
On the most basic level, electronegativity is determined by factors like the nuclear charge (the more protons an atom has, the more “pull” it will have on electrons) and the number/location of other electrons present in ...
Why do elements on the right side of the periodic table have a higher ionization energy?
Generally, elements on the right side of the periodic table have a higher ionization energy because their valence shell is nearly filled.
What happens when the valence shell of an atom is less than half full?
If the valence shell of an atom is less than half full, it requires less energy to lose an electron than to gain one. Conversely, if the valence shell is more than half full, it is easier to pull an electron into the valence shell than to donate one.
Why do transition metals have a little variance?
This is because their metallic properties affect their ability to attract electrons as easily as the other elements.
Which gases do not attract electrons?
Important exceptions of the above rules include the noble gases, lanthanides, and actinides. The noble gases possess a complete valence shell and do not usually attract electrons. The lanthanides and actinides possess more complicated chemistry that does not generally follow any trends. Therefore, noble gases, lanthanides, and actinides do not have electronegativity values.
When was electronegativity first discovered?
Electronegativity Trend. The term “electronegativity” was introduced by Jöns Jacob Berzelius in 1811, though the concept was known even before that and was studied by many chemists including Avogadro. In spite of its long history, an accurate scale of electronegativity was not developed until 1932, when Linus Pauling proposed an electronegativity ...
Why is electronegativity important?
Electronegativity is important because it makes bonding between atoms possible. The higher the electronegativity, the greater an atom’s propensity to attract electrons.
What is the most common scale for electronegativity?
There are a number of different scales used to calculate electronegativity. The Pauling scale is by far the most common and widely accepted scale for calculating electronegativity and it’s the one that we will use in this article. The Pauling scale is a method of calculation originally proposed by Linus Pauling.
What scale is used to measure electronegativity?
The values underneath the elements give their electronegativity as measured by the Pauling scale.
Which elements are ordered in order of increasing electronegativity using the Pauling scale?
Sort the following elements in order of increasing electronegativity using the Pauling scale: barium, calcium, caesium, fluorine
Which element has the least electronegativity?
Caesium is the least electronegative element on the periodic table (with a Pauling score of 0.79); while fluorine is the most electronegative (3.98). The other methods of calculating electronegativity are the Mulliken electronegativity scale, the Allred-Rochow electronegativity scale, the Sanderson electronegativity equalization, ...
Which scale is used to calculate negativity?
The Allen electronegativity scale is typically considered the simplest way to calculate negativity, though it’s still not the one used most commonly.
Can you see electronegativity trends?
Looking at the chart above , you can see certain electronegativity trends on the electronegativity chart.
Why does electronegativity go down?
That is why electronegativity goes down as you go down a Group of the periodic table in the s and p blocks ...
Where are the most electronegative elements on the periodic table?
As a result, the most electronegative elements are found on the top right of the periodic table, while the least electronegative elements are found on the bottom left. Created by Sal Khan.
Which subshells are energetically stable?
Atoms are particularly energetically stable if the s and p subshells of their outermost electron shell are both completely full. Thus, the closer an element is to completing both its outermost p and s subshells, the more energetically favorable it is to gain an electron to help that process along.
Is electronegativity measurable?
Electronegativity is a derived quantity, so it is not directly measurable. It is just a calculation done on some other values. It is relative to hydrogen which was assigned a value of 2.20 on the Pauling scale. There are other electronegativity scales than Pauling, which use different means.
Does the d block have a periodic trend?
Thus, in the d- block you don't have a clear periodic trend for electronegativity as you do in the s and p blocks.
Where can you find the trend in electronegativity?
The trend in electronegativity can be seen on the periodic table and, more specifically, in the following graphs.
Why is electronegativity important?
Electronegativity is a very important chemical property that helps to explain how and why atoms create compounds. Electronegativity is defined as the ability to pull electrons from another atom and hold them tightly. The property is most often described using the values developed by Linus Pauling.
Why Does Electronegativity Decrease Down A Group?
A similar rationale can explain why electronegativity decreases from top to bottom on the periodic table. Moving down any group on the periodic table results in the gain of electrons that occupy energy shells that are farther and farther away from the nucleus.
Why do noble gases have electronegativity values of 0.0?
The reason that noble gases have electronegativity values of 0.0 stems from the fact that these atoms have full outer shells of electrons and they do not need to share or transfer electrons to gain stability.
What is the electronegativity of francium?
The electronegativity value of francium is close to 0, and it predicts that francium will not be able to attract or hold electrons very effectively - a property that is observed in nature.
Which side of the table has higher electronegativities?
The nonmetals on the right side of the table have higher electronegativities that the metals on the left.
Which element has greater electronegativity, potassium or phosphorus?
The correct response to the question is that phosphorus has the higher electronegativity.
What is electronegativity?
What is electronegativity? Electronegativity is how much an atom desires electrons. If an atom is highly electronegative, it will try to take electrons from its less electronegative neighbors. Electronegativity increases as you go to the right and up on the periodic table.
Which atom is the most electronegative?
Therefore, fluorine (shown on the periodic table above) is the most electronegative atom on the periodic table. When an electronegative atom like fluorine is next to a less electronegative atom, the more electronegative atom tends to hog or take some of the electrons. The result of this hogging is called induction, which occurs when partial charges appear on atoms as a result of a highly electronegative atom taking electrons.
Why do atoms get bigger as you move down the periodic table?
The atom therefore get larger simply because so many more protons (and therefore, more neutrons and electrons) are being added into the atoms orbitals.
Why does the atomic size decrease when you move to the right?
As you go to the right, the atomic size trend decreases because you are adding one more proton to the nucleus (the positively-charged center of the atom) each time you move one element to the right. More protons (and therefore more positive charge) in the nucleus produces a greater pull on the surrounding negatively-charged electrons causing them to reduce their radius.

Trend Periodic Table
Specific Examples of Electronegativity
- Strontium – Strontium is an alkaline earth metal with atomic number 38 and symbol Sr. It is found in Group 2 on the periodic table. Strontium was frequently used to made glass for cathode ray tube television, though as CRTs fall out of favor use of strontium is declining. It burns red when added to fireworks. Strontium has an electronegativity value of 0.95. Beryllium – Beryllium is a f…
Ionization Energy Trends
- Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom in its gaseous phase. Conceptually, ionization energy is the opposite of electronegativity. The lower this energy is, the more readily the atom becomes a cation. Therefore, the higher this energy is, the more unlikely it is the atom becomes a cation. Generally, eleme...