
- Cancer screening: ELISA is widely used to determine the presence of cancer biomarkers in the body. ...
- Presence of drugs: The presence and concentrations of illegal drugs, like cannabinoids (morphine, heroin), amphetamines, opiates, cocaine, benzodiazepines (sedative drugs), and methadone, can be determined using ELISA in urine samples, and in blood.
What is the ELISA test and how does it work?
The Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is a technique used to detect antibodies or infectious agents in a sample. Antibodies are made in response to infection and so antibody ELISA testing can indicate whether or not an animal has been in contact with a certain virus. An antigen ELISA can tell whether an animal is infected with a virus by detecting it directly.
What are the different types of Elisa?
Types of ELISA (Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay) Tests
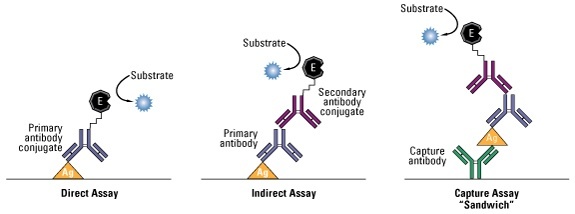
- Direct ELISA Assay. A direct ELISA is differentiated from other ELISA methods due to the fact the antigen is bound directly to the well of a microplate and the detection ...
- Indirect ELISA Assay. ...
- Sandwich ELISA Assay. ...
- Competitive ELISA. ...
- Multiplex ELISA. ...
How do you interpret ELISA results?
ELISA Test Results and Interpretation: ELISA test can be presented in the following 3 ways Quantitative – Data is interpreted in comparison to a standard curve. This method allows the concentration of antigens in different samples to be determined separately and precisely.
How to analyse ELISA results?
- Input ELISA data of standard into the software
- Choose the best fitting curve
- Calculate the concentration of target protein by interpolation
When would ELISA be used?
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an immunological assay commonly used to measure antibodies, antigens, proteins and glycoproteins in biological samples. Some examples include: diagnosis of HIV infection, pregnancy tests, and measurement of cytokines or soluble receptors in cell supernatant or serum.
Why ELISA test is used?
An ELISA test can help identify situations that lead your immune system to make antibodies. Certain diseases aren't easy to identify with other means like swab tests. In these cases, an ELISA blood test can help spot signs of infection or disease in your system.
What diseases is ELISA used for?
The assay used most widely to detect or diagnose virus infection, especially infection of blood borne viruses e.g. HBV, HCV, HIV and HTLV, is the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), whose sensitivity and practicability have rendered it the most common primary screening assay.
What is ELISA and what importance does this method serve?
ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) is a plate-based assay technique designed for detecting and quantifying peptides, proteins, antibodies, and hormones. In ELISA, an antigen must be immobilized to a solid surface and then complexed with an antibody that is linked to an enzyme.
Which disease is confirmed by ELISA test?
The most common HIV tests use blood to detect HIV infection. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) tests a patient's blood sample for antibodies. Oral fluid (not saliva), collected from the cheeks and gums, may also be used to perform an ELISA.
Which disease is quickly diagnosed by ELISA?
An ELISA test may be used to diagnose: HIV, which causes AIDS. Lyme disease.
What are two the most common applications of ELISA in healthcare?
From cancer screening to drug and pregnancy testing.
How is ELISA used for Ebola?
A common test used to detect if a patient has been exposed to a virus, such as Ebola, is called an ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay). This test takes advantage of the interactions between antigens and antibodies. Often compared to a lock and key, an antigen/antibody interaction is very specific.
Can ELISA detect autoimmune disease?
Conclusion: Dsg3, Dsg1 and BP ELISA is a sensitive, easy and quick reading tool for the diagnosis of the main autoimmune blistering diseases: pemphigus and bullous pemphigoid. More over, autoantibodies titre correlate with disease severity, and is useful to monitor treatment response.
Can ELISA detect STD?
Because the ELISA test is extremely sensitive, some people may test falsely positive. Other infections such as lupus, Lyme disease, and other STDs may cause a false positive for HIV on the ELISA test. Because of this, positive ELISA test results need to be confirmed through another test.
How to do an ELISA test?
The ELISA test involves taking a sample of your blood. First, a health care provider will cleanse your arm with an antiseptic. Then, a tourniquet, or band, will be applied around your arm to create pressure and cause your veins to swell with blood. Next, a needle will be placed in one of your veins to draw a small sample of blood. When enough blood has been collected, the needle will be removed and a small bandage will be placed on your arm where the needle was. You’ll be asked to maintain pressure at the site where the needle was inserted for a few minutes to reduce blood flow.
Why do doctors order ELISA?
ELISA is often used as a screening tool before more in-depth tests are ordered. A doctor may suggest this test if you’re having signs or symptoms of the conditions above. Your doctor may also order this test if they want to rule out any of these conditions.
What is an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay?
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, also called ELISA or EIA, is a test that detects and measures antibodies in your blood. This test can be used to determine if you have antibodies related to certain infectious conditions. Antibodies are proteins that your body produces in response to harmful substances called antigens.
What does it mean when an ELISA test is false positive?
False positives and false negatives can occur. A false-positive result indicates you have a condition when you actually don’t. A false-negative result indicates you don’t have a condition when you actually do. Because of this, you may be asked to repeat the ELISA again in a few weeks, or your doctor may order more sensitive tests to confirm or refute the results.
Is there a special preparation for blood draw?
There’s no special preparation for this test. The blood draw lasts only a few moments and is mildly uncomfortable. Tell your healthcare provider if you have a fear of needles or become lightheaded or faint at the sight of blood or needles.
Elisa Technique: Principle
Elisa Technique works on the principle of antigen-antibody binding. The principle requires two primary components, an analyte or ligand which is needed to be estimated quantitively and qualitatively, and a liquid or solid support media, on which the analyte is adsorbed.
Things to Remember
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, abbreviated as ELISA, is one of the most common assay techniques used in science to determine the presence or concentration of antibodies, hormones, proteins, and peptides, in the given sample.
Sample Questions
Ans. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, abbreviated as ELISA, is one of the most common analytical procedures used in science to check the presence or concentration of antibodies, hormones, proteins, and peptides, in the given sample. ELISA is an assay method. It is easy, simple, and efficient to perform.
How is an ELISA assay performed?
In the assay, the antigen of interest is immobilized by direct adsorption to the assay plate or by first attaching a capture antibody to the plate surface. Detection of the antigen can then be performed using an enzyme-conjugated primary antibody (direct detection) or a matched set of unlabeled primary and conjugated secondary antibodies (indirect detection).
How to optimize ELISA?
When developing a new ELISA for a specific antigen, the first step is to optimize the plate-coating conditions for the antigen or capture antibody. Begin by choosing an assay microplate (not tissue culture treated plates) with a minimum protein-binding capacity of 400 ng/cm 2. It is also important that the CV value (coefficient of variation) of the protein binding be low (<5% is preferred) so that there is limited deviation in values that should be identical in the assay results between wells and plates. The choice of plate color depends upon the signal being detected. Clear polystyrene flat bottom plates are used for colorimetric signals while black or white opaque plates are used for fluorescent and chemiluminescent signals. Visually inspect plates before use as imperfections or scratches in the plastic will cause aberrations when acquiring data from the developed assay. Thermo Scientific ELISA Plates are available with a variety of surfaces to optimize coating with the macromolecule of your choice. These plates are designed to deliver optimal results, lot-to-lot reliability, and well-to-well reproducibility.
What is an ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay)?
ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) is a plate-based assay technique designed for detecting and quantifying soluble substances such as peptides, proteins, antibodies, and hormones. Other names, such as enzyme immunoassay (EIA), are also used to describe the same technology. In an ELISA, the antigen (target macromolecule) is immobilized on a solid surface (microplate) and then complexed with an antibody that is linked to a reporter enzyme. Detection is accomplished by measuring the activity of the reporter enzyme via incubation with the appropriate substrate to produce a measurable product. The most crucial element of an ELISA is a highly specific antibody-antigen interaction.
What is sandwich ELISA?
There are several formats used for ELISAs. These fall into either direct, indirect, or sandwich capture and detection methods. The key step is immobilization of the antigen of interest, accomplished by either direct adsorption to the assay plate or indirectly via a capture antibody that has been attached to the plate. The antigen is then detected either directly (labeled primary antibody) or indirectly (such as labeled secondary antibody). The most widely used ELISA assay format is the sandwich ELISA assay, which indirectly immobilizes and indirectly detects the presence of the target antigen. This type of capture assay is called a “sandwich” assay because the analyte to be measured is bound between two primary antibodies, each detecting a different epitope of the antigen–the capture antibody and the detection antibody. The sandwich ELISA format is highly used because of its sensitivity and specificity.
What enzymes are used in ELISA?
The most commonly used enzyme labels are horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and alkaline phosphatase (AP). Other enzymes have been used as well; these include β-galactosidase, acetylcholinesterase, and catalase. A large selection of substrates is available commercially for performing ELISA with an HRP or AP conjugate.
Is sandwich ELISA specific for primary antibody?
In a sandwich ELISA, it is critical that the secondary antibody is specific for the detection of the primary antibody only (and not the capture antibody) or the assay will not be specific for the antigen.
Can ELISA plates be pre coated?
Pre-coated ELISA plates. For most antibodies and proteins, coating plates by passive adsorption usually works well. However, problems can arise from passive adsorption, including improper orientation, denaturation, poor immobilization efficiency, and binding of contaminants along with the target molecule.
What is an ELISA test?
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an immunological assay commonly used to measure antibodies, antigens, proteins and glycoproteins in biological samples. Some examples include: diagnosis of HIV infection, pregnancy tests, and measurement of cytokines or soluble receptors in cell supernatant or serum.
What is the step 3 of ELISA?
In step 3, detection antibody is added. This antibody is labelled with an enzyme, usually horse radish peroxidase or alkaline phosphatase. Detection antibody binds to any target antigen already bound to the plate. Finally, a substrate is added to the plate. ELISA assays are usually chromogenic using a reaction that converts the substrate (e.g. TMB or ABTS) into a coloured product which can be measured using a plate reader.
What is sandwich ELISA?
The ELISA pictured in Figure 1 is what is known as a sandwich ELISA, here two sets of antibodies are used to detect secreted products, e .g. cytokines. The method is stepwise in the order shown. The 1st step is to coat the ELISA plate with capture antibody, any excess, unbound antibody is then washed from the plate. The capture antibody is an antibody raised against the antigen of interest.
How does ELISA work?
In a direct ELISA, the primary detection antibody binds directly to the protein of interest. Next, the plate is rewashed to remove any unbound antibody and followed by the addition of a substrate/chromophore, such as alkaline phosphatase (AP) or Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) to the plate, which results in a color change. The color change of the sample occurs by either the hydrolysis of phosphate groups from the substrate by AP or by the oxidation of substrates by HRP. The advantages of using direct ELISA include eliminating secondary antibody cross-reactivity, and due to fewer steps, it is rapid compared to indirect ELISA. Its disadvantages include its low sensitivity compared to the other types of ELISA and its high cost of reaction. [2][8][3]
Who invented the ELISA method?
Two different research teams invented the direct ELISA simultaneously by scientists Eva Engvall and Peter Perlman and by Van Weemen and Schuurs. The ELISA was developed by the modification of the radioimmunoassay (RIA). This was done by conjugating tagged antigen and antibody with enzymes rather than radioactive iodine 125. The new method was first employed by determining the levels of IgG in rabbit serum. Within the same year, scientists were able to quantify human chorionic gonadotropin in urine by using horseradish peroxidase. Since then, the ELISA method has been used in many different applications and became a routine laboratory research and diagnostic method worldwide. [1]
What is the primary antibody used in ELISA?
ELISAs are performed in polystyrene plates, typically in 96-well plates coated to bind protein very strongly. Depending on the ELISA type, testing requires a primary and/or secondary detection antibody, analyte/antigen, coating antibody/antigen, buffer, wash, and substrate/chromogen. The primary detection antibody is a specific antibody that only binds to the protein of interest, while a secondary detection antibody is a second enzyme-conjugated antibody that binds a primary antibody that is not enzyme-conjugated. [2][3][4]
How to do an ELISA?
Both direct and indirect ELISAs begin with the coating of antigen to the ELISA plates. The first binding step involves adding antigen to the plates, which is incubated for one hour at 37 degrees C or can be incubated at 4 degrees C overnight. Once the incubation step is completed , the next step is to wash the plates of any potential unbound antibody and block any unbound sites on the ELISA plate using agents like BSA , ovalbumin , aprotinin, or other animal proteins. This second step is important because it prevents the binding of any non-specific antibodies to the plate and minimizes false-positive results. After adding the buffer, the plate is rewashed, and a selected enzyme-conjugated primary detection antibody is added. The plate is further incubated for one hour. [2][8][3]
What is an ELISA test?
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a labeled immunoassay that is considered the gold standard of immunoassays. This immunological test is very sensitive and is used to detect and quantify substances, including antibodies, antigens, proteins, glycoproteins, and hormones. The detection of these products is accomplished by complexing antibodies and antigens to produce a measurable result. An antibody is a type of protein produced by an individual’s immune system. This protein type has specific regions that bind to antigens. An antigen is a protein that can come from some foreign source and, when bound to an antibody, induces a cascade of events through the body’s immune system. This interaction is utilized in ELISA testing and allows for identifying specific protein antibodies and antigens, with only small amounts of a test sample. ELISA testing is used to diagnose HIV infection, pregnancy tests, and blood typing, among others. This article will discuss the basic principles, procedures, and clinical significance of the ELISA.[1][2][3][4]
How to do an indirect ELISA?
The steps of the indirect ELISA are identical to the direct ELISA, except for an additional wash step and the types of antibody added after the buffer is removed. Indirect ELISA requires two antibodies, a primary detection antibody that sticks to the protein of interest and a secondary enzyme-linked antibody complementary to the primary antibody. The primary antibody is added first, followed by a wash step, and then the enzyme-conjugated secondary antibody is added and incubated. After this, the steps are the same as the direct ELISA, which includes a wash step, the addition of substrate, and detection of a color change.
Why is ELISA important?
ELISA testing is an important part of medical care and scientific research. Collaboration between scientists, laboratory technicians, phlebotomists, physicians, nurses, and other medical professionals is necessary for appropriate specimen collection, testing, interpretation, diagnosis, and effective patient education and treatment planning. ELISA technologies continue to grow and play a major role in clinical research allowing for the development of more diagnostic and screening tests. The continued evolution of ELISA testing is promising for the future of medicine and has allowed for the improvement of early diagnosis of HIV and pregnancy detection.
What is the principle of ELISA?
Along with the enzyme-labelling of antigens or antibodies, the technique involves following three principles in combination which make it one of the most specific and sensitive than other immunoassays to detect the biological molecule: An immune reaction i.e. antigen-antibody reaction.
What is indirect ELISA?
The indirect ELISA detects the presence of antibody in a sample. The antigen for which the sample must be analyzed is adhered to the wells of the microtiter plate. The primary antibody present in the sample bind specifically to the antigen after addition of sample.
What is solid phase immunoassay?
It is also called solid-phase enzyme immunoassay as it employs an enzyme linked antigen or antibody as a marker for the detection of specific protein. An enzyme conjugated with an antibody reacts with a colorless substrate to generate a colored reaction product.
What is enzyme linked immunosorbent assay?
Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is a very sensitive immunochemical technique which is used to access the presence of specific protein (antigen or antibody) in the given sample and it’s quantification.
Can antigens be purified before measurement?
Suitable for complex (or crude/impure) samples as the antigen does not require purification prior to measurement.
What is ELISA used for?
ELISA is a biochemical technique as a useful diagnostic tool widely used in the field of immunology and serology. Home.
Who created the Elisa technique?
The technique of ELISA was created by Doctor Dennis E Bidwell and Alister Voller, and the first purpose was to detect various kind of diseases, such as Malaria, Chagas' disease, and Johne disease. For further detailed information about ELISA applications in disease diagnosis, please read about the section of ELISA related diseases. If you would like to know about some disease therapeutic targets, suggested here are some useful tools for research on diseases, including Cancer, Alzheimer's, Autoimmune disease, Diabetes, Heart disease, Vascular disease, Parkinson's, etc. Other applications of ELISA will be described respectively as following links.
What is the difference between ELISA and ELISA?
The only difference from general indirect ELISA is that what need to be doubling diluted are antisera (antibodies) other than antigens. In this type of ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbant Assay), the antigen (peptide or protein) is bound to the polystyrene microtiter plate first.
