What does an epidermal cell do?
What is the shape and function of the epidermal cells? The epidermis and its waxy cuticle provide a protective barrier against mechanical injury, water loss, and infection. Various modified epidermal cells regulate transpiration, increase water absorption, and secrete substances.
What are the essential functions of epidermal tissues?
- This system in the shoot checks excessive loss of water due to the presence of cuticle.
- Epidermis protects the underlying tissues.
- Stomata is involved in transpiration and gaseous exchange.
- Trichomes are also helpful in the dispersal of seeds and fruits, and provide protection against animals.
What is the primary function of the epidermis?
What does the epidermis do? The primary function of the epidermis is to protect your body by keeping things that might be harmful out and keeping the things your body needs to function properly in. Bacteria, viruses and other infectious agents are kept out, helping prevent infections on your skin. Asel Treffeisen Explainer
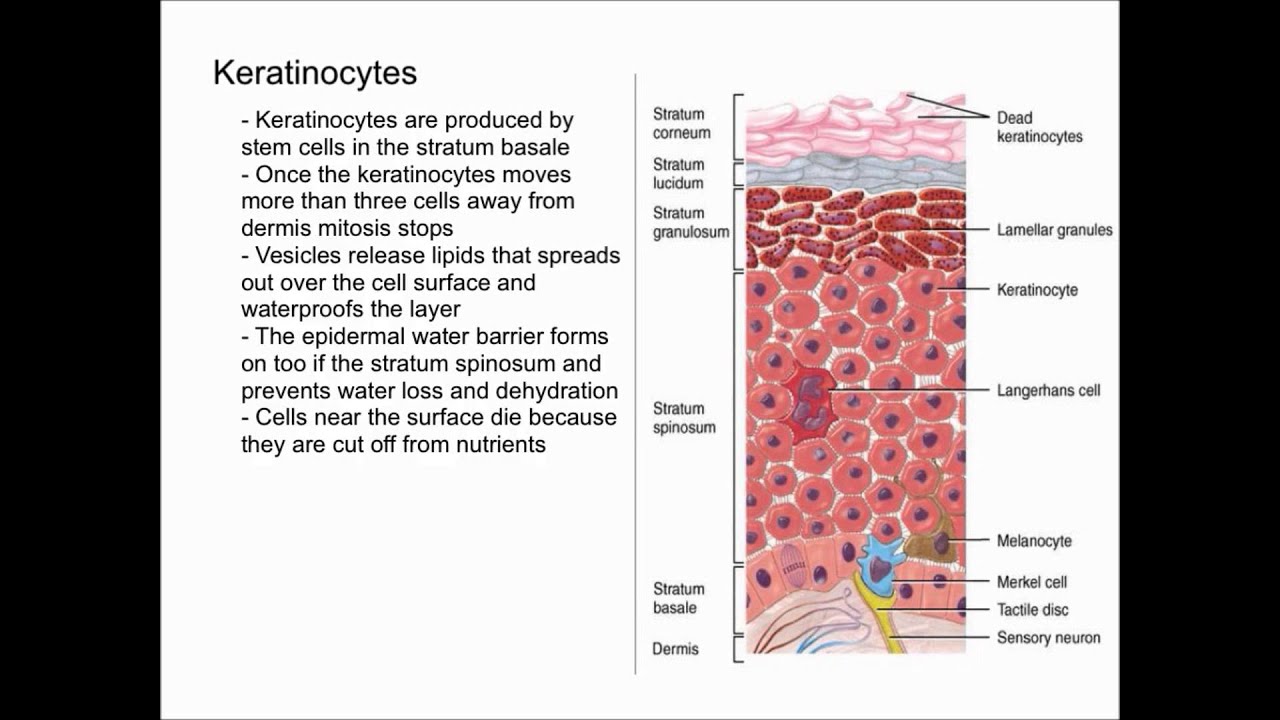
What cells are produced by or in the epidermis?
- Keratinocytes
- Melanocytes
- Langerhans’ cells
- Merkel’s cell
See more

What are the functions of epidermal cells?
Although they serve a number of important functions, their primary role is to protect from a variety of harmful factors (environmental stressors) including microbes, chemical compounds as well as ultraviolet light among others.
What is the epidermis of a plant?
Made up of epidermal cells, the epidermis in plants also serves as a protective layer that not only prevents various microorganisms from gaining entrance into the underlying tissue of leaves and stems, but also prevents excess water loss among a few other functions. Like the skin epidermis, epidermis of plants also consists of different types ...
What are the guard cells in plants?
Stomatal Guard Cells. Stomatal guard cells are part of the epidermal tissue that serves several functions in plants. Depending on the type of plant, the spatial arrangement of these cells is not only dependent on size, but also the shape of air-space below them. Unlike pavement cells, guard cells are more specialized with a definitive shape ...
What is the shape of pavement cells?
For instance, in Arabidopsis thaliana, pavement cells have an irregular wavy shape that is produced during the development of leaves. In the leaves of many dicots, the shape resembles interlocking jigsaw puzzle pieces which provide some mechanical strength to the leaves.
Where is the cuticle located in a plant?
The cuticle, however, is located on the upper epidermis for the most part. In plants, this is the outermost part that is secreted by the epidermis.
Why are cells located close together?
These cells are situated very close together to prevent water loss as a protective mechanism. The cell layer covers the seeds, stem, root and leaves of a plant.
What is the outermost part of the plant?
In plants, this is the outermost part that is secreted by the epidermis. Here, it consists of a substance known as the cutin (polymerized esters of fatty acids). On the upper epidermis, the cuticle, which is waxy in nature, acts as a water-repellent. It is also shiny and thus helps reflect off excess sunlight.
Overview
Your skin has three main layers, and the epidermis (ep-uh-derm-us) is the outermost layer in your body. The other two layers of skin are the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis is the thinnest layer of skin, but it’s responsible for protecting you from the outside world, and it’s composed of five layers of its own.
Function
Each layer of your skin works together to keep your body safe, including your skeletal system, organs, muscles and tissues. The epidermis has many additional functions, including:
Anatomy
The epidermis is the top layer of your skin, and it’s what you see or feel when you look at or touch another person.
Conditions and Disorders
Some common conditions and disorders that affect the epidermis include:
Care
Establish a skin care routine, and follow your healthcare professional’s recommendations for keeping your skin healthy.
What is the epidermis?
As the tissue representing the outermost cell layer of the plant body, the epidermis consists of tightly packed cells that provide both strength and flexibility to the plant as it responds to sunlight, water intake, and growth. Epidermal cells in plants play an important role in both photosynthesis and the overall health of the plant. Epidermal tissue in plants is comprised of three main cell types: pavement cells, guard cells, and their subsidiary cells. These three cell types, along with the function of the epidermis, will be further discussed in detail as part of this lesson.
How many types of cells are there in the epidermis?
The epidermis contains three types of cells:
What is the outer layer of the plant?
The epidermis represents the outer layer of cells which helps to protect plants from the external environment. Epidermal cells secrete a lipophilic substance known as the cuticle, a waxy layer that protects the plant from water loss and pathogens. The epidermis is divided into two parts, the upper epidermis containing the cuticle and the lower epidermis consisting of stomata and guard cells. The three main cell types found in the epidermis include:
What is the role of the stomata in photosynthesis?
Despite the presence of the epidermis as a protective layer in plants, the stomata create openings in the dermal tissue that enable the passage of carbon dioxide, oxygen, and water. Both the stomata and ground tissue are therefore essential for the process of photosynthesis to occur in plants.
What is the cuticle?
The cuticle represents the first layer of the epidermis that interacts with the environment. Epidermal cells produce the cuticle as a waxy secretion that contains cutin, a polymer contributing to the lipophilic ("fat loving" or hydrophobic) characteristic of the cuticle. Due to this lipophilic quality, the cuticle is able to prevent water loss in plants.
What are the two layers of the epidermis?
The actual cells of the epidermis lie beneath the cuticle. The epidermis consists of two different cellular layers: the upper epidermis and the lower epidermis. The upper epidermis contains the cuticle, as well as cells lacking both stomata and chloroplasts. Stomata represent the tiny pore-like openings in leaves that facilitate gas exchange. Chloroplasts are plant organelles where photosynthesis takes place. By contrast, the lower epidermis is characterized by the presence of numerous stomata that control the absorption and release of carbon dioxide, oxygen, and water.
What is the role of the ground and vascular tissue in a plant?
While the epidermis is responsible for maintaining the overall structure of the plant, the ground and vascular tissue systems enable the plant to carry out metabolism and the transport of nutrients throughout the plant. The ground tissue and vascular system are sandwiched between the upper and lower epidermis.
