
What indicates the presence of an epiphyseal plate?
The presence of an epiphyseal plate indicates that. Used to water and cool climates, probably not thick coated or fluffy. they most likely have thin coats and have to survive to find food. sorry if this wasn't the answer you were looking for..: )
What happens when the epiphyseal plate is replaced by bone?
When the epiphyseal plate is replaced by bone, bone growth ends. Bone growth occurs when new bone tissue is laid in the epiphyseal plate, and this When the epiphyseal plate is replaced by bone and becomes an epiphyseal line? The epiphyseal plate allows the diaphysis of the bone to increase in length until early adulthood.
What disease is caused from thick epiphyseal plates?
acromegaly seen in adults - after epiphyseal plate has closed enlarged and thickened bones soft tissue can continue to grow chronic hyperglycemia results in diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis Hyposecretion of hGH
What does the epiphyseal plate represent?
What Are Growth Plates? The growth plate, which is also known by the name of epiphyseal plate, is an area of growing tissues along the end of the long bones in a child. Each long bone has two growth plates one at each end. The growth plate determines how the length and shape of the bone will be once the child attains puberty.

What is the epiphyseal plate and what is its function?
The epiphyseal growth plate is the main site of longitudinal growth of the long bones. At this site, cartilage is formed by the proliferation and hypertrophy of cells and synthesis of the typical extracellular matrix. The formed cartilage is then calcified, degraded, and replaced by osseous tissue.
What is epiphyseal plate made of?
They're made up of cartilage , a rubbery, flexible material (the nose, for instance, is made of cartilage). Most growth plates are near the ends of long bones.
Where is the epiphyseal plate?
metaphysisThe epiphyseal plate (or epiphysial plate, physis, or growth plate) is a hyaline cartilage plate in the metaphysis at each end of a long bone.
What is the epiphyseal plate and how did it form?
The epiphyseal bone plate is formed by ossification of the lower part of the epiphyseal cartilage after the development of the secondary ossification center. At the beginning, the secondary ossification center expands in all directions to form spongy bone trabeculae with a radial orientation.
What does epiphyseal mean?
: a part or process of a bone that ossifies separately and later becomes ankylosed to the main part of the bone. especially : an end of a long bone.
At what age growth plates close?
Typically, girls' growth plates close when they're about 14-15 years old on average. Boys' growth plates close by around the time they turn 16-17 on average. This occurs earlier in some individuals and later in others. Also, different bones' growth plates close at different times.
What causes epiphyseal plate?
Growth in height is driven by elongation of long bones due to chondrogenesis at the epiphyseal plates, also known as the growth plate. This process results from chondrocyte proliferation, hypertrophy, and extracellular matrix secretion.
What is the epiphyseal plate an example of?
SynchondrosesSynchondroses are joints that are connected by hyaline cartilage, while symphyses are joints that are connected by fibrocartilage. An epiphyseal plate is a plate of hyaline cartilage that connects the diaphysis to an epiphysis in juvenile long bones. Therefore, an epiphyseal plate is an example of a synchondrosis (c).
What happens if you break your epiphyseal plate?
If a fracture goes through a growth plate, it can result in a shorter or crooked limb. A growth plate fracture affects the layer of growing tissue near the ends of a child's bones. Growth plates are the softest and weakest sections of the skeleton — sometimes even weaker than surrounding ligaments and tendons.
How do epiphyseal plates grow?
Bones grow in length at the epiphyseal plate by a process that is similar to endochondral ossification. The cartilage in the region of the epiphyseal plate next to the epiphysis continues to grow by mitosis. The chondrocytes, in the region next to the diaphysis, age and degenerate.
What kind of joint is the epiphyseal plate?
cartilaginous jointThe epiphyseal growth plate is a temporary cartilaginous joint formed as the cartilage is converted to bone during growth and development. Cartilaginous joints are connected entirely by cartilage and allow more movement between bones than a fibrous joint, but less than the highly mobile synovial joint.
What type of tissue are epiphyseal plates?
The growth plate, also known as the epiphyseal plate is a thin layer of cartilage that lies between the epiphyses and metaphyses, and is where the growth of long bones takes place.
Is the epiphyseal growth plate cartilage?
The epiphyseal growth plate consists of a layer of cartilage present only during the growth period and vanishes soon after puberty in long bones. It is divided to three well-defined zones, from epiphyses; resting, proliferative, and hypertrophic zones.
What type of cartilage is found in the epiphyseal plate?
Epiphyseal cartilage is hyaline cartilage tissue with a gelatinous texture, and it is responsible for the longitudinal growth of the long bones in birds and mammals. It is located between the epiphysis and the diaphysis. Epiphyseal cartilage also is called a growth plate or physis.
Are epiphyseal plates made of spongy bone?
Answer and Explanation: This is false, the epiphyseal plate is a plate which is made of hyaline cartilage. Spongy bone, also called cancellous bone, is present at the epiphysis but the epiphyseal plate consists of hyaline cartilage and is a very narrow line which is present in long bones.
What is hereditary multiple exostoses?
Hereditary multiple exostoses is a genetic condition that is caused by growth irregularities of the epiphyseal plates of the long bones of the upper and lower limbs. It usually results in limb deformities and a certain degree of functional limitations.
What is the epiphyseal plate?
The epiphyseal plate (or epiphysial plate, physis, or growth plate) is a hyaline cartilage plate in the metaphysis at each end of a long bone. It is the part of a long bone where new bone growth takes place; that is, the whole bone is alive, with maintenance remodeling throughout its existing bone tissue, ...
What causes short stature?
However, various other types of osteochondrodysplasias can cause short stature and generalized deformities of bones and joints due to abnormal function of growth plate cartilage cells.
What happens to chondrocytes in puberty?
In puberty increasing levels of estrogen, in both females and males, leads to increased apoptosis of chondrocytes in the epi physeal plate.
What is Salter Harris fracture?
Salter–Harris fractures are fractures involving epiphyseal plates and hence tend to interfere with growth, height or physiologic functions. Osgood-Schlatter disease results from stress on the epiphyseal plate in the tibia, leading to excess bone growth and a painful lump at the knee.
What is the most common defect in epiphyseal plate?
The most common defect is achondroplasia, where there is a defect in cartilage formation.
What is the role of endochondral ossification in bone formation?
Endochondral ossification is responsible for the initial bone development from cartilage in utero and infants and the longitudinal growth of long bones in the epiphyseal plate. The plate's chondrocytes are under constant division by mitosis. These daughter cells stack facing the epiphysis while the older cells are pushed towards the diaphysis. As the older chondrocytes degenerate, osteoblasts ossify the remains to form new bone. In puberty increasing levels of estrogen, in both females and males, leads to increased apoptosis of chondrocytes in the epiphyseal plate. Depletion of chondrocytes due to apoptosis leads to less ossification and growth slows down and later stops when the entire cartilage have become replaced by bone, leaving only a thin epiphyseal scar which later disappears.
What is a growth plate and where are growth plates located?
The growth plate, also known as epiphyseal plate or physis, is the area of growing tissue near the ends of our long bones.
When do teenagers stop growing taller?
As soon as teenagers stop growing, the epiphyseal plates' width decrease and harden into solid bones. This phenomenon occurs usually by the end of puberty, although the exact time is different for each individual.
How can parents check their kid's growth development?
In a safe and painless procedure, doctors can check the maturity of a child's skeletal system by performing an x-ray examination on the left wrist, hand, and fingers.
When does the epiphyseal plate disappear?
During childhood, the epiphyseal plate matures and its total width decreases. Eventually, it disappears at the end of puberty with complete replacement by bone along with the cessation of longitudinal growth. There are at least two growth plates on each end of the bones - for example in the shoulder, elbows, wrists, vertebrae, pelvis, thighs, ...
How many growth plates are there in the body?
There are at least two growth plates on each end of the bones - for example in the shoulder, elbows, wrists, vertebrae, pelvis, thighs, ankles, heels, fingers, and toes. The epiphyseal plate consists of cartilage, which is a rubbery, flexible material. The nose, for example, consists of the nasal bone, the upper lateral cartilage, ...
What is growth plate?
Growth plates are the softest and weakest sections of the skeleton and are decisive for the physical growth of children and teenagers. They are also vulnerable body parts to injuries and fractures.
Why do growth plates fracture?
How can a growth plate fracture occur? Most growth plate fractures occur because of stress on the bones, often caused by doing sports such as basketball, football, soc cer, skiing, skateboarding, or by traffic accidents .
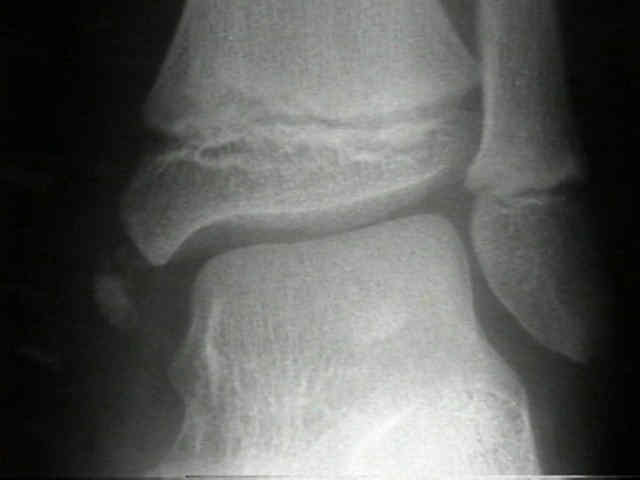
Overview
The epiphyseal plate (or epiphysial plate, physis, or growth plate) is a hyaline cartilage plate in the metaphysis at each end of a long bone. It is the part of a long bone where new bone growth takes place; that is, the whole bone is alive, with maintenance remodeling throughout its existing bone tissue, but the growth plate is the place where the long bone grows longer (adds length).
Structure
Endochondral ossification is responsible for the initial bone development from cartilage in utero and infants and the longitudinal growth of long bones in the epiphyseal plate. The plate's chondrocytes are under constant division by mitosis. These daughter cells stack facing the epiphysis while the older cells are pushed towards the diaphysis. As the older chondrocytes degenerate, osteoblasts ossif…
Clinical significance
Defects in the development and continued division of epiphyseal plates can lead to growth disorders collectively known as osteochondrodysplasia. The most common defect is achondroplasia, where there is a defect in cartilage formation. Achondroplasia is the most common cause of dwarfism or short stature and it also manifests in generalized deformities of bones and joints. However, various other types of osteochondrodysplasias can cause short stat…
Other animals
John Hunter studied growing chickens. He observed bones grew at the ends and thus demonstrated the existence of the epiphyseal plates. Hunter is considered the "father of the growth plate."
See also
• Human development (biology)
• Salter–Harris fracture
External links
• Normal bones at GetTheDiagnosis.org, showing the development of epiphyseal plates for different ages and bones.