
Shigella causes bacillary dysentery and is classified into four species based on their antigen characteristics. This classification does not reflect genetic relatedness; in fact, Shigella species are so related to Escherichia coli , they should be classified as one distinctive species in the genus Escherichia.
What is Shigella infection?
Shigella infection (shigellosis) is an intestinal infection caused by a family of bacteria known as shigella. The main sign of shigella infection is diarrhea, which often is bloody. Shigella is very contagious. People get infected with shigella when they come in contact with and swallow small amounts of bacteria from the stool ...
Are Escherichia and Shigella motile?
Escherichiaare usually motile by peritrichous flagella and produce gas from fermentable carbohydrates. Escherichia and Shigella are gram-negative facultative, anaerobic, rod-shaped organisms, 2–6 μm long and 1.1–1.5 μm wide. Escherichia are usually motile by peritrichous flagella and produce gas from fermentable carbohydrates.
What is the difference between E coli and Shigella?
E. coli symptoms in adults are usually much milder and produce more typical gastrointestinal problems. Shigella, however, may produce serious bloody diarrhea both adults and children. Treatment may be complicated by the severity of the disease and by the fact that killing the bacteria can release more toxin.
What is the structure and classification of Shigella?
Structure, Classification, and Antigenic Types. Shigellae are Gram-negative, nonmotile, facultatively anaerobic, non-spore-forming rods. Shigella are differentiated from the closely related Escherichia coli on the basis of pathogenicity, physiology (failure to ferment lactose or decarboxylate lysine) and serology.
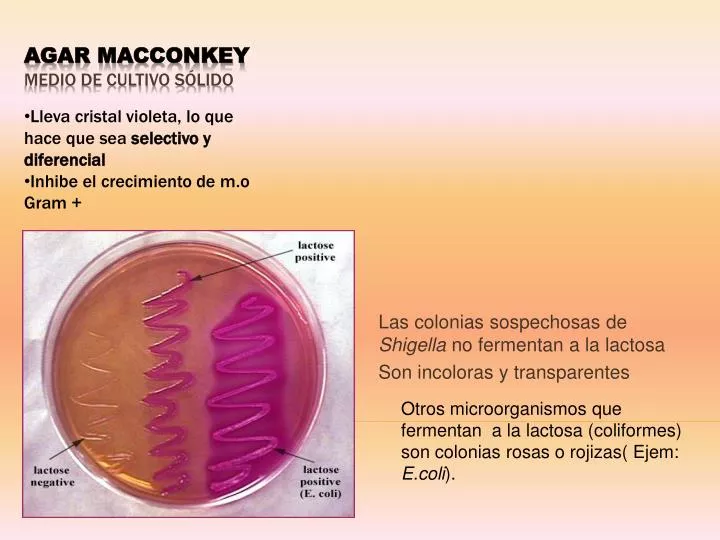
Is Shigella the same as E. coli?
Shigellae are phylogenetically E. coli that were later classified as separate species on the bases of biochemical characteristics and clinical relevance [3], [4]. Biochemical characteristics and serotyping are usually used to identify the species.
How do you get rid of Escherichia Shigella?
Antibiotics can shorten the time you have fever and diarrhea by about 2 days. Ciprofloxacin and azithromycin are two recommended oral antibiotics.
What foods is Shigella found in?
A wide variety of foods can be contaminated with Shigella. Foods that have been identified in Shigella outbreaks include salads (potato, shrimp, tuna, chicken, turkey, macaroni, fruit, and lettuce), chopped turkey, rice balls, beans, pudding, strawberries, spinach, raw oysters, luncheon meat, and milk.
How do you get Shigella bacteria?
Shigella can spread easily in environments such as day care facilities. People become infected with Shigella by: Eating food or drinking liquids contaminated by an infected person. Touching contaminated surfaces or objects and then touching their mouth or putting a contaminated object into their mouth.
What are the signs and symptoms of Shigella?
People with Shigella infection (shigellosis) usually start experiencing symptoms 1 to 2 days after contact with the germ. These symptoms include: Diarrhea that can be bloody....When to Contact Your DoctorFever.Bloody diarrhea.Severe stomach cramping or tenderness.Dehydration.
What happens when you get Shigella?
Shigella bacteria cause an infection called shigellosis. Most people with Shigella infection have diarrhea (sometimes bloody), fever, and stomach cramps. Symptoms usually begin 1–2 days after infection and last 7 days. Most people recover without needing antibiotics.
Is Shigella worse than E. coli?
E. coli symptoms in adults are usually much milder and produce more typical gastrointestinal problems. Shigella, however, may produce serious bloody diarrhea both adults and children.
Who are most likely to get Shigella infection?
Young children are the most likely to get a Shigella infection, but people of all ages can be affected. Many outbreaks occur in childcare settings and schools. Infection commonly spreads from young children to their family members and other people in their communities because these bacteria spread easily.
How is Shigella transmitted through food?
Shigella spread very easily when a person eats food or drinks water contaminated with poop from an infected person. Food prepared by someone infected with Shigella can become contaminated and make other people sick. Shigella outbreaks have been linked to contaminated foods prepared by sick food workers.
Can Shigella be cured?
Shigella infection usually runs its course in five to seven days. Replacing lost fluids from diarrhea may be all the treatment you need, particularly if your general health is good and your shigella infection is mild.
Can Shigella cause death?
EPIDEMIOLOGY. Worldwide, Shigella is estimated to cause 80–165 million cases of disease and 600,000 deaths annually; of these, 20–119 million illnesses and 6,900–30,000 deaths are attributed to foodborne transmission.
Where is Shigella most commonly found?
Shigella outbreaks are more common in child care centers, community wading pools, nursing homes, jails and military barracks. Living or traveling in areas that lack sanitation. People who live or travel in developing countries are more likely to get shigella infection. Being a man who has sex with men.
Can Shigella clear on its own?
Most people who have shigella infection get better on their own and don't need to see a doctor. If you or your child has severe symptoms or a high fever, you may need treatment.
How long are you contagious with Shigella?
Wait to have sex (vaginal, anal, and oral) for one week after you no longer have diarrhea. Because Shigella germs may be in stool for several weeks, follow safe sexual practices, or ideally avoid having sex, for several weeks after you have recovered.
Can Shigella cause death?
EPIDEMIOLOGY. Worldwide, Shigella is estimated to cause 80–165 million cases of disease and 600,000 deaths annually; of these, 20–119 million illnesses and 6,900–30,000 deaths are attributed to foodborne transmission.
Where is Shigella most commonly found?
Shigella outbreaks are more common in child care centers, community wading pools, nursing homes, jails and military barracks. Living or traveling in areas that lack sanitation. People who live or travel in developing countries are more likely to get shigella infection. Being a man who has sex with men.
Is E. coli in the US?
The initial outbreak of E. coli in the US involved children that had eaten undercooked hamburgers at a fast food chain. More stringent requirements for cooking temperatures have reduced the risks. However, recent outbreaks have involved other meats, as well a various produce (bean sprouts, raspberries, lettuce) that is generally eaten raw. Frequently, these products have been imported from other countries where hygiene standards may be lower than those in the US. A recent E. coli outbreak at a fair in Florida highlighted some of the problems with E. coli disease. Apparently, limited contact with infected calves at a petting zoo produced disease in several children. The infectious dose appears to be very low for children, and any close contact with animals, particularly cattle that may be carriers, should be avoided.
Is E. coli a sign of Shigella?
SYMPTOMS and SIGNS. Both Escherichia coli ( E. coli) and Shigella spp. produce a potent shigatoxin during infection that causes severe and life-threatening disease. These species are very closely related and have some similarity in their symptomology, but E. coli infections are a particularly serious problem in children.
Can E. coli cause brain damage?
Even with treatment symptoms can progress to hemolytic uremic syndrome, which damages the kidney and leads to multiple organ failure, including brain damage. E. coli symptoms in adults are usually much milder and produce more typical gastrointestinal problems.
What is the genus of bacteria that is found in the large intestine?
a genus of gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria found in the large intestine of humans and other warm-blooded animals; most species are either nonpathogenic or opportunistic pathogens. E. co´li is the principal species and forms the greater part of the normal intestinal flora. Some strains of it may cause urinary tract infections, abscesses, conjunctivitis, and sometimes septicemia, as well as diarrheal diseases, especially in children.
What is a motile cell?
A genus of aerobic, facultatively anaerobic bacteria containing short, motile or nonmotile, gram-negative rods. Motile cells are peritrichous. Glucose and lactose are fermented with the production of acid and gas. These organisms are found in feces; some are pathogenic to humans, causing enteritis, peritonitis, cystitis, and other disorders. It is the type genus of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The type species is Escherichia coli.
Where does Escherichia coli come from?
The genus Escherichia derives it name from Theodor Escherich, who first isolated this organism from faeces in 1885. The type strain of the genus is Escherichia coli, a common bacterium found in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and other vertebrates where most strains are nonpathogenic commensals.
What are the two types of bacteria that are found in the genus Escherichia coli?
The genus Escherichia consists of both motile and nonmotile bacteria, which conform to the definition of the family Enterobacteriaceae and the tribe Eschericherieae. Both acid and gas are formed from fermentable carbohydrates. Salicin is fermented by many species, but inositol is not utilized and adonitol is used by only one species. Lactose is rapidly fermented by most members, although there are also slow- or nonfermenting strains. Sodium acetate is frequently used as a sole carbon source. Escherichia coli (Migula) Castellani and Chalmers is the type strain of this genus.
How does E. coli affect laying hens?
Escherichia coli affects production and, potentially egg quality, in laying hens by causing colibacillosis associated with salpingitis ( Trampel et al., 2007 ). Other avian species such as ducks may also be affected ( Bisgaard, 1995 ). Many serotypes of E. coli are found in poultry but it is only the avian pathogenic E. coli (APEC) which possess specific virulence factors and are capable of causing salpingitis and peritonitis ( Landman and Cornelissen, 2006 ). Salpingitis may be caused by either a systemic infection or by ascending infection of the oviduct from the cloaca. The study of Ozaki and Murase (2009) reported postmortem findings of fibrinous exudates in the vagina, caseous exudates in the upper oviduct, degenerated ovaries and a thickened and oedematous oviduct mucosa. The stress associated with the onset of lay may act as a precipitating factor in colibacillosis outbreaks ( Zanella et al., 2000 ). Virulent Mycoplasma synoviae can act as a complicating factor in E. coli peritonitis syndrome ( Raviv et al., 2007 ). However, Vandekerchove et al. (2004) concluded that colibacillosis outbreaks are not necessarily associated with other respiratory pathogens.
What is the genus of E. coli?
Escherichia is the type genus of the family Enterobacteriaciae and E. coli is the type species of the genus Escherichia. E. coli causes colibacillosis in most avian species, with younger birds being most susceptible ( Barnes et al., 2008 ).
What are the most important things about E. coli?
In food safety, the most important E. coli are those that cause diarrhoeal diseases. Escherichia coli can also cause spoilage in dairy products, e.g. blowing of cheese, and ropiness in milk and cheese brines can be caused by E. coli growth. View chapter Purchase book. Read full chapter.
Where is E. coli found?
E. coli is commonly found in the intestines of poultry and is transmitted to eggs primarily by faecal contamination of the shell surface followed by entry into the egg.
Is Escherichia gram negative?
Escherichia and Shigella are gram-negative facultative, anaerobic, rod-shaped organisms, 2–6 μm long and 1.1–1.5 μm wide. Escherichia are usually motile by peritrichous flagella and produce gas from fermentable carbohydrates. In contrast, Shigella are non-motile, do not produce gas from carbohydrates, and do not decarboxylate lysine ...
What are the rectosigmoidal lesions of Shigellosis?
The rectosigmoidal lesions of shigellosis resemble those of ulcerative colitis. With frequencies indicated in Figure 22-2, there is proximal extension of erythema, edema, loss of vascular pattern, focal hemorrhage, and adherent layers of purulent exudate. Biopsy specimens from affected areas are typically edematous, with capillary congestion, focal hemorrhage, crypt hyperplasia, goblet cell depletion, mononuclear and polymorphonuclear (PMN) cell infiltration, shedding of epithelial cells and erythrocytes, and microulcerations.
What are the complications of Shigellosis?
Possible complications of shigellosis include bacteremia, convulsions and other neurological complications, reactive arthritis, and hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Bacteremia occasionally accompanies S dysenteriaeserotype 1 infections in malnourished infants, but this complication is uncommon in otherwise healthy individuals. Convulsions have been reported in up to 25% of Shigellainfections involving children under the age of 4 years. Both high fever and a family history of seizures are risk factors for a convulsive episode. Ekiri syndrome, an extremely rare, fatal encephalopathy has also been described in Japanese children with S sonneior S flexneriinfections. Reactive arthritis, a self-limiting sequela of S flexneriinfection, occurs in an incidence as high as 2% in individuals expressing the HLA-B27 histocompatibility antigen. Hemolytic-uremic syndrome, characterized by a triad of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and acute renal failure, is a rare complication in children infected with S dysenteriaeserotype 1.
What is the S dysenteriaeserotype 1?
S dysenteriaeserotype 1 expresses Shiga toxin, an extremely potent, ricin-like, cytotoxin that inhibits protein synthesis in susceptible mammalian cells. This toxin also has enterotoxic activity in rabbit ileal loops, but its role in human diarrhea is unclear, since shigellae apparently express a number of enterotoxins. Experimental infection of rhesus monkeys with S dysenteriae1, and with a Shiga toxin-negative mutant, suggests that this cytotoxin causes capillary destruction and focal hemorrhage that exacerbates dysentery (see Table 22-1). More importantly, Shiga toxin is associated with the hemolytic-uremic syndrome, a complication of infections with S dysenteriae1. Closely related toxins are expressed by enterohemorrhagic E coli(EHEC) including the potentially lethal, food-borne O157-H7 serotype.
Is shigellosis a prodrome?
This disease differs from profuse watery diarrhea, as is commonly seen in choleraic diarrhea or in enterotoxigenic Escherichia colidiarrhea, in that the dysenteric stool is scant and contains blood, mucus, and inflammatory cells. In some individuals suffering from shigellosis, however, moderate volume diarrhea is a prodrome or the sole manifestation of the infection. Bacillary dysentery constitutes a significant proportion of acute intestinal disease in the children of developing countries, and this infection is a major contributor to stunted growth of these children. Shigellosis also presents a significant risk to travelers from developed countries when visiting in endemic areas, and sporadic food or water-borne outbreaks occur in developed countries.
Is shigellosis an inflammatory disease?
In summary, shigellosis can be characterized as an acute inflammatory bowel disease initiated by the uptake of only a few organisms into lymphoid follicles . Intracellular replication and intercellular spread leads to an amplified inflammatory cascade at the initial site of entry, and as this inflammation persists and expands, the infiltration of PMN facilitates the entry of additional bacteria into the epithelium. The inflammatory infiltrate can also cause detachment of sheets of epithelial cells in areas devoid of lymphoid structures or bacterial cells.
Is Shigellae a pathogen?
Shigellae are remarkably infectious enteric pathogenes that can cause disease after the ingestion of as few as 10 organisms. Nonetheless, shigellosis is normally an acute, self-limiting disease that exemplifies the regenerative capacity of the intestinal epithelium. Shigellavirulence probably reflects both the efficient uptake by the follicle associated epithelium (M cells) and the amplifying effect of the inflammatory cascade generated by apoptic macrophages. Tenesmus and evacuation of mucus by intestinal goblet cells may effectively eliminate both extracellular shigellae and infected enterocytes from the intestinal lumen, but this defensive response, in conjunction with PMN infiltration, also constitutes the definitive sign of bacillary dysentery.
Symptoms and Signs
- Both Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Shigella spp. produce a potent shigatoxin during infection that causes severe and life-threatening disease. These species are very closely related and have some similarity in their symptomology, but E. coli infections are a particularly serious problem in children. Symptoms include fever and bloody diarrhea. Even...
Treatment/Vaccine Availability
- Treatment may be complicated by the severity of the disease and by the fact that killing the bacteria can release more toxin. No vaccine is available for humans.
Causes and Relevance to Florida
- The initial outbreak of E. coli in the US involved children that had eaten undercooked hamburgers at a fast food chain. More stringent requirements for cooking temperatures have reduced the risks. However, recent outbreaks have involved other meats, as well a various produce (bean sprouts, raspberries, lettuce) that is generally eaten raw. Frequently, these products have been i…
Prevention
- CHILDREN SHOULD NOT EAT UNDERCOOKED MEATS. Hamburgers should be cooked well done with no pink. Washing hands and food products will reduce risk. Avoiding exposure to uncooked food of any kind may be advisable for small children. Children that lack toilet training should not participate in enclosed swimming activities because they present an opportunity for fecal conta…