What is a 3 on the ESI Scale?
Those rated 3, 4, or 5 are triaged to the labor and delivery area of the hospital. Overview of the Emergency Severity Index. The Emergency Severity Index (ESI) is a simple to use, five-level triage algorithm that categorizes emergency department patients by evaluating both patient acuity and resource needs.
What is the ESI and why is it important?
The ESI guides nurses’ in the evaluation of patient acuity and the resources that will be needed to treat the patient. Acuity is defined as the stability of a patient’s vital functions and the potential threat to life, limb or organ. Resources are defined as the number of resources to stabilize and initiate treatment.
What is a Level 2 ESI acuity?
ESI Level 2 As with assigning an ESI level-1 acuity, assigning an ESI level-2 acuity is based on the clinical condition of the patient, and it is not necessary to consider resource utilization in the decision.
What is the ESI algorithm?
In summary, the ESI is a five-level triage system that is simple to use and divides patients by acuity and resource needs. The ESI triage algorithm is based on four key decision points.
What is an ESI level 1?
Immediate physician involvement in the care of the patient is a key difference between ESI level-1 and ESI level-2 patients. Level-1 patients are critically ill and require immediate physician evaluation and interventions.
What are the 3 levels of acuity in hospital emergency departments?
The 3-level systems divide patients into the groups “emergent” (cannot safely wait until a space in the clinical area becomes available), “urgent” (can safely wait a short amount of time until a space in the clinical area becomes available), and “non-urgent” (can safely wait a long time until a space in the clinical ...
What are the 5 levels of triage?
The triage categories used in both systems are: Red (immediate evaluation by physician), Orange (emergent, evaluation within 15 min), Yellow (potentially unstable, evaluation within 60 min), Green (non-urgent, re-evaluation every 180 min), and Blue (minor injuries or complaints, re-evaluation every 240 min).
What does ESI level 2 mean?
There is a lack of studies examining distinctions between patients assigned to Level 2 (high risk) and Level 3 (lower risk) in the 5-level ESI triage system. Describing patients assigned to Level 2 and Level 3 may identify unique characteristics related to chief complaint, interventions, and resource needs.
What is the highest level of acuity?
Charts scored as levels 4, 5, or with associated critical care represent the highest acuity patients.
What are the 4 levels of triage?
The nursing triage is divided into 4 levels;critical, emergency, acute, and general.
What does acuity level 5 mean?
Acuity Level means a five-level emergency department triage algorithm that uses the Emergency Severity Index (ESI) developed by the Agency for Healthcare Research & Quality and provides clinically relevant stratification of patients into five groups from the most to the least urgent, with Level 1 life-threatening, ...
What are the 3 categories of triage?
TriageImmediate category. These casualties require immediate life-saving treatment.Urgent category. These casualties require significant intervention as soon as possible.Delayed category. These patients will require medical intervention, but not with any urgency.Expectant category.
Can you change ESI level?
The patients ESI level may change from the triage time to time of disposition (Briggs & Grossman, 2006). It may increase or decreased depending upon the outcome of the diagnosis and what is revealed during the exam as the nurse and doctor work together to determine the patients needs.
What is Level 3 in a hospital?
Level 3—Intensive care. Patients requiring two or more organ support (or needing mechanical ventilation alone). Staffed with one nurse per patient and usually with a doctor present in the unit 24 hours per day.
What does ESI mean in medical terms?
The Emergency Severity Index (ESI) is a five-level emergency department (ED) triage algorithm that provides clinically relevant stratification of patients into five groups from 1 (most urgent) to 5 (least urgent) on the basis of acuity and resource needs.
What are the benefits of ESI triage?
What are the advantages of using the ESI? The ESI has been found to be more accurate than other triage systems because it is simple and reduces subjectivity. One benefit is that it identifies patients in need of immediate attention more rapidly than other methods.
What is patient acuity level?
Definition. The levels of patient acuity equate to the number of hours needed for nursing staff to care for the offender's physical and mental health needs, therefore acuity assessment is a nursing function.
What is acuity rating?
The Patient Acuity Rating (PAR), a 7-point Likert score representing the likelihood of a patient experiencing a cardiac arrest or ICU transfer within the next 24 hours, was obtained from physicians and midlevel practitioners at the time of sign-out.
What does acuity rate mean?
By: admin December 28, 2019. Patient acuity is generally defined as a measurement of intensity of nursing care needed by a patient. For the proper development of a staffing plan for people receiving hospital care, patient acuity is a particularly critical benchmark.
What is a low acuity patient?
Many people who arrive are low acuity (i.e., looking for a test, showing no signs of the virus, and can be treated in their cars). Still, the facility is prepared to admit high-acuity patients who may need more complex care inside the facility.
What is ESI in emergency?
The Emergency Severity Index (ESI) is a five-level emergency department triage algorithm, initially developed in 1999. It is maintained by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ). ESI triage is based on the acuity of patients' health care problems and the number of resources their care is anticipated to require.
What is ESI triage?
ESI triage is based on the acuity of patients' health care problems and the number of resources their care is anticipated to require. This differs from standardized triage algorithms used in several other countries, such as the Australasian Triage Scale, which attempt to divide patients based on the time they may safely wait.
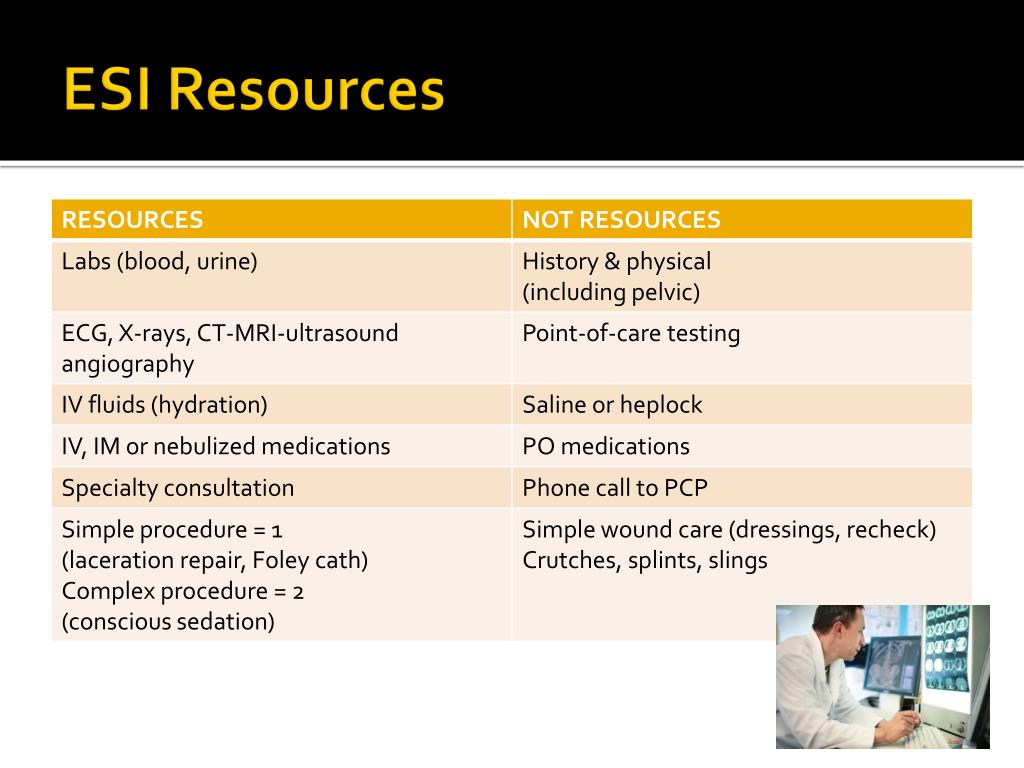
What are resources in ESI?
The concept of a "resource" in ESI means types of complex interventions or diagnostic tools, above and beyond physical examination. Examples of resources include X-ray, blood tests, sutures, and intravenous or intramuscular medications.
When was the ESI system developed?
The ESI triage system was developed in the late 1990s by American ED physicians Richard Wuerz and colleagues. 3 The physicians' initial goal was to make it easier to prioritize patients based on the urgency of the patient's clinical status and to improve patient streaming into the appropriate healthcare environment (such as a trauma room, fast-track ED, or an outpatient clinic).
What is ESI triage?
The ESI triage system will help manage patient flow in EDs. Existing tri age systems aren't sufficient to address the growing problem of overcrowding in EDs nationwide and the resulta nt increase in wait time for patients. Older triage systems don't provide the discriminatory ability necessary to identify patient acuity when confronted with a high volume of patients. 2
What is the ultimate goal of implementing the ESI triage system?
The ultimate goal of implementing the ESI triage system is to improve patient care and patient outcomes. Patient acuity must be rapidly assessed and continually reassessed to ensure that only stable patients wait to be treated.
What are the benefits of standardizing the ESI triage system?
Advantages to standardizing the ESI triage system include providing data for benchmarking, facilitating various types of surveillance (such as bioterrorism, injury, and public health), and supporting clinical research . ESI triage system standardization will contribute to the understanding of how patient acuity relates to ED overcrowding and help ensure patient safety. 2
What are the disadvantages of ESI?
A primary disadvantage of ESI triage system standardization is the high cost of implementing the system nationwide. The educational and operational expenditures needed to implement the ESI triage system in every hospital would likely require millions of dollars. Also, ensuring interrater triage reliability across individual clinicians and hospitals is difficult. 2 One possible aspect that could hinder the system's reliability is its inherent subjectivity. Two equally experienced nurses, for example, may rate the same patient at different levels of acuity. A study conducted among 305 triage ratings was reviewed after all triage nurses had received a refresher course. The original nurses' ratings were compared with retrospective ratings assigned by an expert panel of ED triage nurses; the ratings agreed in about half of the cases. 1
How many levels of care are there in ESI?
The ESI triage system consists of five levels of care, with 1 as the most acute and 5 as the least acute. Each patient, after a brief but thorough assessment by an experienced triage nurse, is assigned a level number based on clinical status, vital signs, and how many resources are expected to be used to treat them. Consider a 90-year-old male who's pale, diaphoretic, and weak, with a heart rate of 30 beats/minute and BP of 80/45 mm Hg. He'd be immediately placed into a treatment room as an ESI level 1 because he needs immediate physician involvement.
What is level 1 in ESI?
The new level 1 criteria have been expanded to include patients who are intubated, apneic, pulseless, or unresponsive, as well as patients in imminent risk of death if lifesaving interventions aren't started. The new ESI version also has revised pediatric fever criteria. 4
What is ESI in nursing?
The ESI guides nurses’ in the evaluation of patient acuity and the resources that will be needed to treat the patient. Acuity is defined as the stability of a patient’s vital functions and the potential threat to life, limb or organ. Resources are defined as the number of resources to stabilize and initiate treatment. The result is a triage decision that stratifies patients’ need for emergency treatment into five levels of urgency. It was developed by a group of emergency nurses, physicians, managers, educators and researchers in collaboration with the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) who continue to update the tool and related training material.
What is an ESI algorithm?
The ESI is an algorithm that incorporates only four questions and the answers lead to a triage conclusion. The four questions are:
Why is ESI more accurate than other triage systems?
The ESI has been found to be more accurate than other triage systems because it is simple and reduces subjectivity. One benefit is that it identifies patients in need of immediate attention more rapidly than other methods. The ESI can help prioritize clinical staff attention and resources and it facilitates communication about patient acuity more effectively. It also has been used as the foundation for facility policy and procedure. The jail referred to at the beginning of this post has since drafted policy and procedure setting timeframes for response to each of the ESI levels. By keeping track of emergencies by ESI level the data can be used to determine if practices could be improved with targeted training or enhanced resources. Finally, the AHRQ maintains a website on the ESI that includes an implementation handbook that can be downloaded for free. There are also DVDs that include lectures and case studies that can be used to support training in use of the ESI. There is no charge for these materials but they must be requested from the site.
What is ESI level 3?
ESI level 3: Two or more resources. Abdominal pain in a 58-year-old male will require two or more resources. At a minimum, he will need labs and an abdominal CT.
Can a patient wait to be seen for ESI level 2?
A yes answer to any of the above means that the patient cannot wait and so is triaged as ESI level 2. No further triage evaluation is necessary and the nurse’s focus shifts to ensuring prompt initiation of treatment. If the patient does not need to be seen urgently then proceed to the next question.
Is ESI a reliable measure?
The ESI has been found to be an easy, reliable and valid measure of patient acuity and resource need in multiple hospital settings and comparison groups. If you want to try it out, use your experience to determine the ESI rating for the patients in these four examples which come from the training material provided at the AHRQ site:
What is acuity based on?
The acuity based off of stability of patient, vital signs, potential for threat to life, limb, or organ, and estimated resources needed in treating the patient. Additionally a nurses own experiences, competence, and ability to recognize critical conditions is needed in determining the correct acuity for a patient.
What is level 1 acuity?
Level 1 acuity patients need treatment immediately in order to save their lives. This acuity level asks the question is the situation high risk, is the patient confused, lethargic, or disoriented, or in severe pain or distress.
Why is it important to reassess patient acuity?
An important thing to remember is that the patient acuity can change at any time! So it is important to reassess the patient, re-checking vitals, mental status, pain level etc., in order to ensure that acuity level is still appropriate for the patient.
What are some examples of level 2 acuity patients?
These patients tend to decompensate quickly without any intervention. Examples of level 2 acuity patients: Chest pain. Stroke like symptoms.
What is ESI version 4?
Any physician or nurse who treats acutely ill patients can benefit from reviewing The Emergency Severity Index (ESI) Version 4 which is available for download.*#N#The ESI is a five stage triage tool used in American emergency departments.
Is ESI level 2 high risk?
If the answer is yes, then the patient is assigned ESI Level 2. ESI Level 2 patients are at high risk and studies show that 20 to 30% of emergency department patients are Level 2. 3.
What is ESI in ED?
The ESI also has been used as the foundation for ED policies that address specific populations. For example, the psychiatric service at one site is expected to provide consults for level-2 and level-3 patients with psychiatric complaints within 30 minutes of notification and for level-4 and level-5 patients within 1 hour. At another site, the ESI has been incorporated into a policy for patients greater than 20 weeks pregnant who present to the ED. Patients rated at ESI levels 1 and 2 are treated in the ED by emergency medicine with an obstetrical consult. Those rated 3, 4, or 5 are triaged to the labor and delivery area of the hospital.
What is the ESI scale?
The ESI is a five-level triage scale developed by ED physicians Richard Wuerz and David Eitel in the U. S. Wuerz and Eitel believed that a principal role for an emergency department triage instrument is to facilitate the prioritization of patients based on the urgency of treatment for the patients' conditions. The triage nurse determines priority by posing the question, "Who should be seen first?" Wuerz and Eitel realized, however, that when more than one top priority patient presents at the same time, the operating question becomes, "How long can each patient safely wait?"
How many levels of acuity are there in ED?
Since 2000, there has been a trend toward standardization of triage acuity scales that have five levels:
What percentage of ED patients are ESI level 1?
Patients assessed as an ESI level 1 constitute approximately 1 percent to 3 percent of all ED patients upon arrival; the patient's condition requires immediate life-saving interventions from either the emergency physician and nurse or the trauma or code team. From ESI research we know that most ESI level-1 patients are admitted to intensive care units, while some die in the emergency department. A
Who developed the ESI?
The ESI is a five-level triage scale developed by ED physicians Richard Wuerz and David Eitel in the U. S. Wuerz and Eitel believed that a principal role for an emergency department triage instrument is to facilitate the prioritization of patients based on the urgency of treatment for the patients' conditions. The triage nurse determines priority by posing the question, "Who should be seen first?" Wuerz and Eitel realized, however, that when more than one top priority patient presents at the same time, the operating question becomes, "How long can each patient safely wait?"
What is the purpose of triage in the ED?
The purpose of triage in the emergency department (ED) is to prioritize incoming patients and to identify those who cannot wait to be seen . The triage nurse performs a brief, focused assessment and assigns the patient a triage acuity level, which is a proxy measure of how long an individual patient can