What is the Gram stain made of?
The Gram stain involves staining bacteria, fixing the color with a mordant, decolorizing the cells, and applying a counterstain. The primary stain (crystal violet) binds to peptidoglycan, coloring cells purple. Both gram-positive and gram-negative cells have peptidoglycan in their cell walls, so initially, all bacteria stain violet.
Why is ethanol used in staining of Gram negative cells?
For the gram negative cells, ethanol causes the walls to be leaky and hence they cannot hold the large complexes of CV-L during de-colorization. In some of the staining processes using gram stain, a pattern of gram-variables are obtained, which is a mix of pink and purple.
Why ethyl alcohol is used to decolorize the sample after staining?
After staining the sample with crystal violet, ethyl alcohol is used to decolorize the sample. It achieves its purpose by dehydrating the peptidoglycan layer by tightening and shrinking it. In doing so, large crystal violet cannot penetrate the tightened layer of peptidoglycan, and hence it is trapped in the cell wall of gram positive bacteria.
What is the role of iodine in Gram staining?
Being a mordant, gram's iodine forms a complex with crystal violet in the stain that has attached more tightly to the cell wall of gram positive bacteria than that of the gram negative bacteria.

Why ethanol is used in Gram staining?
Ethyl alcohol is a nonpolar solvent, and thus penetrates the cell walls of Gram negative cells more readily and removes the crystal violet-iodine complex.
What is the purpose of the 95% ethanol step in the Gram staining procedure?
Gram-negative cells are stained with 95 percent ethanol in order to remove the main stain (crystal violet), which is a critical step in the staining procedure. This step must be performed to ensure that bacteria do not remain purple, which will result in a false positive.
What does the ethanol do to Gram-negative bacteria Why?
Gram-negative bacteria have an outer lipid membrane which is dissolved by ethanol, releasing the crystal violet stain.
What happens if you don't use ethanol in Gram stain?
The gram negative bacteria will retain their outer cell membrane, and stay purple when your staining is done. Thus both gram positive and negative bacteria will stain purple without the alcohol/acetone step.
What does alcohol do to Gram-positive bacteria?
A decolorizer such as ethyl alcohol or acetone is added to the sample, which dehydrates the peptidoglycan layer, shrinking and tightening it. The large crystal violet-iodine complex is not able to penetrate this tightened peptidoglycan layer, and is thus trapped in the cell in Gram positive bacteria.
What substance is used as the decolorizing agent in the Gram stain procedure?
The decolorizing agent, (ethanol or an ethanol and acetone solution), interacts with the lipids of the membranes of both gram-positive and gram-negative Bacteria.
What is the most important reagent in the Gram stain method?
crystal violetThe primary stain of the Gram's method is crystal violet. Crystal violet is sometimes substituted with methylene blue, which is equally effective. The microorganisms that retain the crystal violet-iodine complex appear purple brown under microscopic examination.
Can you use alcohol as Decolorizer for Gram stain?
Decolorizer-Alcohol Either acetone or ethyl alcohol can be used as the decolorizing agent. The alcohol dissolves lipids found in the outer cell membrane of Gram-negative bacteria, allowing the crystal violet-iodine complex to leak out of the thinner peptidoglycan layer.
Why is Decolorizing the most crucial step in Gram staining?
The length of decolorization is a critical step in gram staining as prolonged exposure to a decolorizing agent can remove all the stains from both types of bacteria. The final step in gram staining is to use basic fuchsin stain to give decolorized gram-negative bacteria pink color for easier identification.
What is the purpose of using alcohol acetone or acetone in the Gram stain procedure quizlet?
the alcohol and acetone in the decolorizer extracts the lipid making the gram negative wall more porous and incapable of retaining the crystal violet iodine complex thereby decolorizing it.
Which reagent is responsible for staining Gram-positive bacteria purple?
Reagents used in the gram stain reagents Crystal Violet (CV) is the Primary stain, and is used to color both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria purple.
What is the mordant in the Gram stain?
Gram staining is performed when the chemical dye crystal violet is mixed with the mordant iodine. Iodine and crystal violet form a large complex that precipitates out of solution. During the staining procedure, the bacteria are bathed in alcohol, which causes the cell walls to shrink.
What would be the consequence if you applied too much 95% ethanol in Gram staining technique?
95% ethanol, because it removes the primary stain (crystal violet) from Gram-negative cells. If missed, then the bacteria would remain purple and give a false positive result.
Why is decolorization important in Gram staining?
The length of decolorization is a critical step in gram staining as prolonged exposure to a decolorizing agent can remove all the stains from both types of bacteria.
What are the steps of Gram staining?
The Gram staining process includes four basic steps, including:Applying a primary stain (crystal violet).Adding a mordant (Gram's iodine).Rapid decolorization with ethanol, acetone or a mixture of both.Counterstaining with safranin.
What is the purpose of Gram staining quizlet?
What is the purpose of Gram Stain? To be able to determine the composition of the cell wall. The advantage of this staining procedure is that those cells that decolorize can be differetiated from the cells that resist decolorization by alcohol.
What is Gram staining?
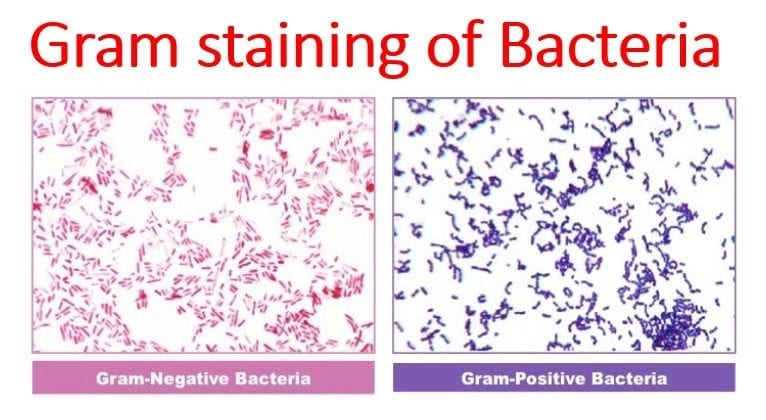
The Gram staining is one of the most crucial staining techniques in microbiology. It gets its name from the Danish bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram who first introduced it in 1882, mainly to identify organisms causing pneumonia. Often the first test performed, gram staining involves the use of crystal violet or methylene blue as the primary color. The term for organisms that retain the primary color and appear purple-brown under a microscope is Gram-positive organisms. The organisms that do not take up primary stain appear red under a microscope and are Gram-negative organisms.
What is the first step in gram staining?
The first step in gram staining is the use of crystal violet dye for the slide's initial staining. The next step, also known as fixing the dye, involves using iodine to form crystal violet- iodine complex to prevent easy removal of dye. Subsequently, a decolorizer, often solvent of ethanol and acetone, is used to remove the dye. The basic principle of gram staining involves the ability of the bacterial cell wall to retain the crystal violet dye during solvent treatment. Gram-positive microorganisms have higher peptidoglycan content, whereas gram-negative organisms have higher lipid content.
Do Gram negatives lose their primary stain?
Initially, all bacteria take up crystal violet dye; however, with the use of solvent, the lipid layer from gram-negative organisms is dissolved. With the dissolution of the lipid layer, gram negatives lose the primary stain. In contrast, solvent dehydrates the gram-positive cell walls with the closure of pores preventing diffusion of violet-iodine complex, and thus, bacteria remain stained. The length of decolorization is a critical step in gram staining as prolonged exposure to a decolorizing agent can remove all the stains from both types of bacteria.
What is the objective of gram stain?
This test differentiates the bacteria into Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria, which helps in the classification and differentiation of microorganisms. The Gram stain separates bacteria into two groups: (1) Gram-positive microorganisms that retain the primary dye (Crystal violet) and ...
What is Gram Staining?
Gram staining is a differential bacterial staining technique used to differentiate bacteria into Gram Positive and Gram Negative types according to their cell wall composition.
How to stain a specimen with gram stain?
The procedure/steps of Gram Stain. Prepare and fix the specimen to the microscope slide before staining. Cover the smear with crystal violet, the primary stain, for 20 seconds. Gently rinse off the stain with water. Cover the smear with Gram’s iodine, the mordant, for 1 minute. Pour off the excess Gram’s iodine.
How to do Gram stain?
The procedure/steps of Gram Stain 1 Prepare and fix the specimen to the microscope slide before staining. 2 Cover the smear with crystal violet, the primary stain, for 20 seconds. 3 Gently rinse off the stain with water. 4 Cover the smear with Gram’s iodine, the mordant, for 1 minute. 5 Pour off the excess Gram’s iodine. 6 Run the acid-alcohol decolorizer over the smear until the solution appears clear. 7 Gently rinse with water. 8 Cover the smear with safranin, the secondary or counterstain, for 20 seconds. 9 Gently rinse the stain with water. 10 Blot dry with bibulous paper.
What is the primary color of Gram stain?
Gram-positive organisms contain a highly cross-linked layer of peptidoglycan that retains the primary dye, crystal violet (CV), following the application of the mordant, iodine (I). The iodine and crystal violet form ...
What stain is used to make gram negative cells pink?
The cells appear colorless. To make the colorless cells visible, a secondary stain, safranin, is applied, leaving the gram-negative cells pink. Created with BioRender.com.
Can staining be precipitated?
The stain may form a precipitate with aging. Filtering through gauze will remove excess crystals.
What is Gram stain?
Gram stain is probably one of the most commonly used staining procedures used in the field of microbiology. It is one of the differential stains that are used to characterize bacteria in one of two groups: either gram positive bacteria or gram negative bacteria.
Why do we need to stain a gram positive?
Gram staining helps to characterize bacteria as gram positive or gram negative allowing microscopist enthusiasts/professionals to verify a bacterial cell's wall and membrane which in turn influences various facets of its pathogenicity and level of virulence .
Why do Gram positive bacteria stain violet?
Whereas the gram positive bacteria stain violet as a result of the presence of a thick peptidoglycan layer in the walls of their cell, the gram negative bacteria stain red, due to the thinner peptidoglycan layer in their cell wall (a thicker peptidoglycan layer allows for the retention of the stain, but a thinner layer does not).
How long to store crystal violet staining reagent?
Mix A and B so as to obtain crystal violet staining reagent and store for 24 hours.
Which bacteria have a stronger affinity for crystal violet?
Gram positive bacteria will typically have a stronger affinity for crystal violet on applying gram's iodine than the gram negative cell wall.
Does Clostridium stain Gram negative?
On the other hand in cultures of Clostridium and Bacillus, the reduced thickness of peptidoglycan during growth coincides with an increased number of cells that in turn stain gram negative.
Does safranin stain change color?
On the other hand, the outer membrane of the gram negative cells cannot retain the crystal violet iodine complex and hence the color is lost. Safranin is a lighter stain as compared to crystal violet and thus it does disrupt the purple coloration in the gram positive cells.
How does Gram stain work?
How the Gram Stain Works 1 The primary stain ( crystal violet) binds to peptidoglycan, coloring cells purple. Both gram-positive and gram-negative cells have peptidoglycan in their cell walls, so initially, all bacteria stain violet. 2 Gram's iodine ( iodine and potassium iodide) is applied as a mordant or fixative. Gram-positive cells form a crystal violet-iodine complex. 3 Alcohol or acetone is used to decolorize the cells. Gram-negative bacteria have much less peptidoglycan in their cell walls, so this step essentially renders them colorless, while only some of the color is removed from gram-positive cells, which have more peptidoglycan (60-90% of the cell wall). The thick cell wall of gram-positive cells is dehydrated by the decolorizing step, causing them to shrink and trapping the stain-iodine complex inside. 4 After the decolorizing step, a counterstain is applied (usually safranin, but sometimes fuchsine) to color the bacteria pink. Both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria pick up the pink stain, but it is not visible over the darker purple of the gram-positive bacteria. If the staining procedure is performed correctly, gram-positive bacteria will be purple, while gram-negative bacteria will be pink.
What is Gram staining?
The Gram stain is a differential method of staining used to assign bacteria to one of two groups (gram-positive and gram-negative) based on the properties of their cell walls. It is also known as Gram staining or Gram's method.
What is the primary stain for Gram positive bacteria?
The primary stain ( crystal violet) binds to peptidoglycan, coloring cells purple. Both gram-positive and gram-negative cells have peptidoglycan in their cell walls, so initially, all bacteria stain violet. Gram's iodine ( iodine and potassium iodide) is applied as a mordant or fixative. Gram-positive cells form a crystal violet-iodine complex.
How to get a crystal violet stain off a slide?
If too little heat is applied, the bacteria will wash off the slide during staining. Use a dropper to apply the primary stain (crystal violet) to the slide and allow it to sit for 1 minute. Gently rinse the slide with water no longer than 5 seconds to remove excess stain.
What is the primary stain for Gram staining?
The Gram stain involves staining bacteria, fixing the color with a mordant, decolorizing the cells, and applying a counterstain. The primary stain ( crystal violet) binds to peptidoglycan, coloring cells purple. Both gram-positive and gram-negative ...
Why is Gram stain important?
Because the bacteria are colored, not only is their Gram stain group identified, but their shape, size, and clumping pattern may be observed . This makes the Gram stain a valuable diagnostic tool for a medical clinic or lab.
What is the process of dehydrating gram positive cells?
The thick cell wall of gram-positive cells is dehydrated by the decolorizing step, causing them to shrink and trapping the stain-iodine complex inside. After the decolorizing step, a counterstain is applied (usually safranin, but sometimes fuchsine) to color the bacteria pink.
What is Gram stain?
A Gram stain is a method used to visualize and identify the characteristics of a sample of bacteria. It can be used to identify if bacterial contamination or infection has occurred. Additionally, it gives a better understanding of the phenotypic features of bacteria from a culture or differentiates between the types of bacteria in a mixed sample.
What is the most important step in gram staining?
The most important step of gram staining is the decolorizing step. Over-decolorizing will wash the crystal violet off even from gram-positive cells, and under-decolorizing will leave the violet on all cells regardless of whether or not they have a cell wall.
Why do Gram positive bacteria have purple stains?
Gram-positive bacteria will have purple or blue stains by the crystal violet dye. On the other hand, Gram-negative bacteria will appear red or pink due to the safranin dye. The mechanisms through which this differentiation happens have been attributed to multiple different theories. Many think that the peptidoglycan in the cell walls of Gram-positive bacteria prevents the dye from being washed away, while others have attributed it to magnesium ribonucleate compounds on the wall and even the pH of the cytoplasm.
What differentiates stains from bacteria without cell walls?
The Gram stain differentiates stains bacteria with cell walls from bacteria without them.
Why are Gram negative bacteria red?
Gram-negative bacteria have thinner peptidoglycan layers, so they will be stained red or pink.
Which bacteria have more acidic cytoplasm than Gram-negative cells?
First, the "pH Theory" states that Gram-positive bacteria have more acidic cytoplasm than Gram-negative cells. It allows the cells to retain crystal violet more effectively, which helps with binding when the mordant is added.
Why do researchers use a cell identifier?
Researchers use it for the recognition and identification of contamination in cells or tissue samples.
What is Gram staining?
Gram staining is initially established by the physician Hans Christian Gram, which was from Denmark. He help to distinguish Klebsiella pneumonia to pneumococci. In short, the process of gram staining comprises the use of a solution of Gram iodine or Potassium iodide to the cells which are use to stain before with Crystal violet or Gentian violet.
What color are Gram positive cells?
Gram-positive cells resist decolorization and remain purple. The dye is released from Gram-negative cells. Counterstain (safranin) Add several drops of safranin to the smear and allow it to sit for one minute. Rinse the slide with water and blot dry. Gram-negative cells will be stained pink by the safranin.
How to make Gram positive and Gram negative cells purple?
Both Gram-positive and Gram-negative cells will be stained purple by the crystal violet dye. Add several drops of iodine to the smear and allow it to sit for 1 minute. Rinse the slide with water. Iodine “sets” the crystal violet, so both types of bacteria will remain purple.
What are the structural changes between the cell walls of Gram positive bacteria and Gram negative answerable in a way for the?
Some the structural changes between the cell walls of gram positive bacteria and gram negative answerable in a way for the Gram stain response ? In the Gram staining, an impenetrable crystal violet with gram iodine complexes is made inside the cell of bacteria, and this complexes is extracted by alcohol from gram negative bacteria but not from gram positive. Gram positive organisms are dehydrated by alcohol, they have very dense cell wall containing of many coatings of peptido-glycan. This creates the pores/holes in the cell wall to near, avoiding the insoluble crystal violet + gram iodine complexes from evasion. In gram negative alcohol eagerly infiltrates the lipid rich external layer, and the thin peptido-glycan coating does not stop solvent channel, therefore, the crystal violet + gram iodine complexes is simply detached or removed.
What is Gram positive bacteria?
Bacteria retain the crystal violet and gram iodine mixtures complexes after the wash in 95% ethanol solution in purple color and are named as Gram positive Bacteria, those which miss these complexes of solution are red in color by counter stain the safranin or 10% fuchsine are named as Gram negative Bacteria. Gram Staining Results.
What is the color of iodine?
This technique yields “ Iodine stain complex, purple color” in the cytoplasm of micro-organism for example bacteria. The cells that are previously stained with crystal violet and iodine are then treat with a decolorizing reagent like, Ethanol 95% or Acetone alcohol.
What is Gram positive?
Gram positive organisms are dehydrated by alcohol, they have very dense cell wall containing of many coatings of peptido-glycan. This creates the pores/holes in the cell wall to near, avoiding the insoluble crystal violet + gram iodine complexes from evasion.
