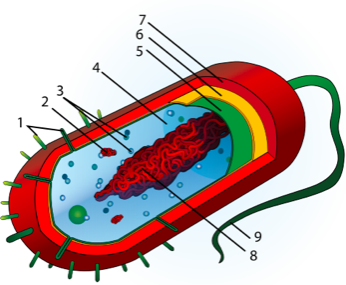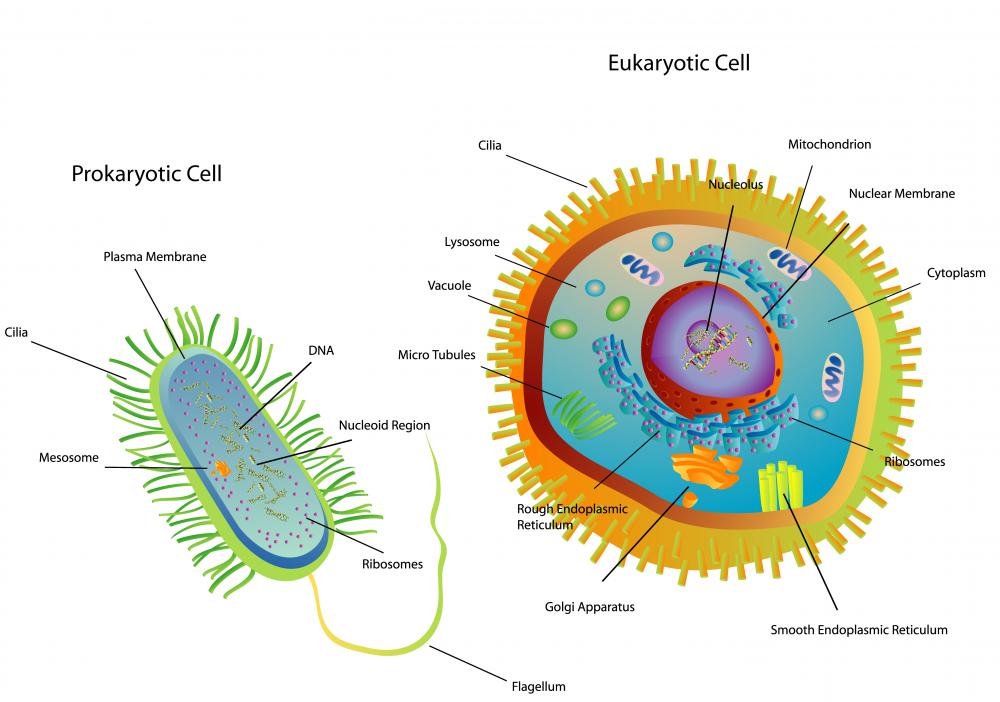
How can you tell a cell is an eukaryotic?
- Look for the nucleus of the cell. ...
- See if you can find organelles within the cytoplasm (the jelly-like interior of the cell). ...
- All eukaryotes have a plasma membrane and cytoplasm, and some (plants and fungi) have a cell wall. ...
- Although there are single-celled eukaryotes (protozoa), most are multi-cellular (animals and plants).
What is a typical eukaryotic cell?
Three Major Components Of A Typical Eukaryotic Cell
- Introduction to eukaryotic cells. By definition, eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus, a structural attribute that is not present in bacterial or archaeal cells.
- Chromatin and chromosomes. To understand also chromatin, it is advantageous to initially consider chromosomes. ...
- Ribosomes. ...
- Mitochondria. ...
What organisms have eukaryotic cells?
What are 4 examples of eukaryotic cells?
- The Protists. Protists are one-celled eukaryotes.
- The Fungi. Fungi can have one cell or many cells.
- The Plants. All of the roughly 250,000 species of plants -- from simple mosses to complex flowering plants -- belong to the eukaryotes.
- The Animals.
What are the two major parts of an eukaryotic cell?
Two major parts of a eukaryotic cell are the Nucleus and the Cytoplasm. 2.) Describe the steps in making, packaging and exporting a protein from a cell First, the ribosome makes a protein.

What is called eukaryotic cell?
Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. There is a wide range of eukaryotic organisms, including all animals, plants, fungi, and protists, as well as most algae. Eukaryotes may be either single-celled or multicellular.
What is eukaryotic cell short answer?
What is a Eukaryotic Cell? Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane and form large and complex organisms. Protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals all have eukaryotic cells. They are classified under the kingdom Eukaryota.
What are 3 examples of a eukaryote?
Organisms such as animals, plants, fungi, and protists are examples of eukaryotes because their cells are organized into compartmentalized structures called organelles, such as the nucleus.
What are 10 examples of eukaryotic cells?
10 examples of eukaryotic cells:Muscle cells.Stem cells.Bone cells.Cancer cells.Plant cells.Meristematic cells.Ova.Fungus cells.More items...•
What is eukaryotic and prokaryotic?
Prokaryotes are organisms made up of cells that lack a cell nucleus or any membrane-encased organelles. Eukaryotes are organisms made up of cells that possess a membrane-bound nucleus that holds genetic material as well as membrane-bound organelles.
What is eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell?
A eukaryotic cell is a cell that has membrane bound organelles and a nucleus which houses the genetic material. A prokaryotic cell is a cell that does not possess any membrane bound organelles and its genetic material is found floating freely within its cell wall.
What is prokaryotic cell example?
Prokaryotes are single celled, microscopic entities. They neither have specialized organelles nor a prominent nucleus with a membrane. Examples of prokaryotes include cyanobacteria, E. coli, mycoplasma etc.
What are 5 examples of prokaryotic cells?
Examples of Prokaryotes:Escherichia Coli Bacterium (E. coli)Streptococcus Bacterium.Streptomyces Soil Bacteria.Archaea.
What is an example of a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell?
Examples of prokaryotes are bacteria and archaea. Examples of eukaryotes are protists, fungi, plants, and animals (everything except prokaryotes). All prokaryote and eukaryote cells have plasma membranes.
What are 10 examples of prokaryotic cells?
1 AnswerEscherichia coli bacterium.Streptococcus bacterium.Sulfolobus acidocaldarius archeobacterium.streptococcus pyogenes.lactobacillus acidophilus.Cyanobacteria.Archaea.
What are the 2 types of eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells may be classified into two groups based on the number of cells that make an individual organism: (1) unicellular eukaryotic cells and (2) multicellular eukaryotic cells. Unicellular eukaryotes include the protists. Multicellular eukaryotes include a variety of plant, fungal, and animal species.
What are called prokaryotic cell?
Prokaryotes are organisms whose cells lack a nucleus and other organelles. Prokaryotes are divided into two distinct groups: the bacteria and the archaea, which scientists believe have unique evolutionary lineages. Most prokaryotes are small, single-celled organisms that have a relatively simple structure.
What is prokaryotic cell short answer?
Prokaryotes are organisms whose cells lack a nucleus and other organelles. Prokaryotes are divided into two distinct groups: the bacteria and the archaea, which scientists believe have unique evolutionary lineages. Most prokaryotes are small, single-celled organisms that have a relatively simple structure.
What makes eukaryotic cells?
Like a prokaryotic cell, a eukaryotic cell has a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and ribosomes. However, unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: a membrane-bound nucleus. numerous membrane-bound organelles (including the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria)
Where are eukaryotic cells found?
Eukaryotic cells are found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists. They generally have a nucleus—an organelle surrounded by a membrane called the nuclear envelope—where DNA is stored. There are a few exceptions to this generalization, such as human red blood cells, which don't have a nucleus when mature.
What are eukaryotic cells made of?
Definition. A eukaryotic cell contains membrane-bound organelles such as a nucleus, mitochondria, and an endoplasmic reticulum. Organisms based on the eukaryotic cell include protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals. These organisms are grouped into the biological domain Eukaryota.
Are eukaryotic cells unicellular or multicellular?
Eukaryotic cells may be unicellular or multicellular. Paramecium, Euglena, Trypanosoma, Dinoflagellates are unicellular eukaryotes. Plants and anim...
What is the most important characteristic of eukaryotic cells that distinguishes it from prokaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus. On the contrary, prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus, i.e., they have no nuclear membrane. Unlike...
Are viruses eukaryotes?
Viruses are neither eukaryotes nor prokaryotes. Since viruses are a link between living and non-living they are not considered in either category.
What are the salient features of a eukaryotic cell?
A eukaryotic cell has the following important features: A eukaryotic cell has a nuclear membrane. It has mitochondria, Golgi bodies, cell wall. It...
How does a eukaryotic cell divide?
A eukaryotic cell divides by the process of mitosis. It undergoes the following stages during cell division: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase...
When did the first eukaryotic cell evolve?
The first eukaryotic cells evolved about 2 billion years ago. This is explained by the endosymbiotic theory that explains the origin of eukaryotic...
What is the evidence for endosymbiotic theory?
The first evidence in support of the endosymbiotic theory is that mitochondria and chloroplast have their own DNA and this DNA is similar to the ba...
Describe the characteristics of eukaryotic cells.
Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria, Golgi complex, etc. The cell organelles and nucleus is embedd...
Eukaryotic cells have membrane bound organelles. 1. True 2. False
Organelles are the specialised and organised structures in a living cell. These may be bound by a single or double membrane (Exception is ribosomes...
Unlike eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells A. Lack in plasma membrane B. Do not have a nucleus C. Ha...
Eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles and have a true nucleus whereas prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus. The prokaryotic cells...
In eukaryotic cells, the chromosomes are located in?
In prokaryotes, the circular chromosomes are located in nucleoid which is present in the cytoplasm. In eukaryotes, the chromosome is stored inside...
What is an eukaryotic cell?
September 14, 2017 by Ranga.nr. Eukaryotic cells are the one which are advanced forms of cells. Almost all animals, including humans, have eukaryotic cells. A distinct nucleus identifies the eukaryotic cells with the genetic material enclosed inside it. They also have differences in the process of protein synthesis, RNA structures, etc.
Which organisms are single cell organisms?
12. Protozoans: Protozoa are are single-cell organisms having eukaryotic characters. They perform all their life activities within that single cell. They can also migrate from one place to another and even reproduce using that cell. amoeba picture. See for more on cells in the human body and types of cells.
What are germ cells with which sperm unite to form a zygote?
10. Ova : These cells are germ cells with which sperm unite to form a zygote. They are present in female animals.
What are the cells that are abnormal and have profuse multiplication and growth?
Cancer cells:These cells are abnormal animal cells that have profuse multiplication and growth. 7. Stem cells: These cells are germinal and are devoid of any physiology. But they can be totipotent to transform into another type of cells based on their body requirement. 8.
How many cells are there in animals?
1. Animals cells: There are millions of cells in animals, and all of them are eukaryotic.
Which cells help in electrical impulse conduction?
Neurons: These cells help in electrical nerve impulse conduction. They are quite long and branched, forming complex networks. Nerve cells with axon and dendrites. 4. Muscle cells: These cells help in the physical movement of the body. skeletal muscle cells.
Which cells are hard and give them rigidity?
Bone cells: Unlike other animal cells, these are hard cells with prominent calcification. They are made of calcium and phosphorous, which give them rigidity. 9. Meristematic cells: These cells are present in the tips or apex regions of plants. They multiply and help in the growth of a plant.
What are some examples of eukaryotic cells?
Examples of eukaryotic cells are plants, animals, protists, fungi. Their genetic material is organized in chromosomes. Golgi apparatus, Mitochondria, Ribosomes, Nucleus are parts of Eukaryotic Cells. Let’s learn about the parts of eukaryotic cells in detail.
Which organelle carries out sorting, tagging, packaging, and distribution of lipids and proteins?
Golgi apparatus carries out sorting, tagging, packaging, and distribution of lipids and proteins. Peroxisomes carry out oxidation reactions that break down fatty acids and amino acids. Vesicles and vacuoles are storage organelles. Apart from these organelles, the animal cell contains lysosomes and centrosomes.
What is the cytoplasmic membrane?
The plasma membrane is a semi-permeable membrane that separates the inside of a cell from the outside. Structure and Composition: In eukaryotic cells, the plasma membrane consists of proteins, carbohydrates and two layers of phospholipids (i.e.
How many membranes does the mitochondria have?
Structure: It has two membranes – outer and inner. The outer membrane forms a continuous boundary around the mitochondria. The inner membrane is semi-permeable and divided into folds called ‘cristae’. The membranes divide the lumen of the mitochondria into an inner and outer compartment.
Where is the nucleus located?
The nucleus is found in all eukaryotic cells except human RBCs and sieve cells of plants. Structure: A nucleus has the following parts: Nuclear envelope – It is a double membrane structure that surrounds the nucleus. The outer membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum.
What is the ER in a cell?
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Description: It is a network of small, tubular structures. It divides the space inside of Eukaryotic cells into two parts – luminal (inside ER) and extra-luminal (cytoplasm). Structure: ER can be of two types –.
Where is the cell wall located?
Description: The cell wall is a non-living, rigid structure outside the plasma membrane in plant cells and fungi. It is absent in Eukaryotic cells of animals
What is the unique characteristic of eukaryotic cells?
A eukaryotic cell has one unique characteristic that other cells do not. A Eukaryotic cell has a membrane-bound nucleus. The nuclear material in the cell or the DNA is contained within a double membrane. Bacteria are the only type of cells that are not eukaryotic, they are prokaryotic so they do not have DNA encased within a membrane.
Which animals have eukaryotic cells?
Animals such as cats and dogs have eukaryotic cells. 2. Plants such as apple trees have eukaryotic cells. 3. Fungi such as mushrooms have eukaryotic cells. 4. Protists such as amoeba and paramecium have eukaryotic cells. 5. Insects have eukaryotic cells.