“Expiratory airflow” refers to how the volume and speed with which the lungs expel air during the exhalation (blowing out) portion of the breath cycle.
Full Answer
What is peak expiratory flow rate?
The measurement is also called the peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) or the peak expiratory flow (PEF). Peak flow measurement is mostly done by people who have asthma.
What is the difference between peak expiratory flow (PEF) and FEV1?
The forced expiratory flow averaged over the time during which 25 to 75% of the FVC is exhaled may be a more sensitive marker of mild, small airway airflow limitation than the FEV1, but the reproducibility of this variable is poor. The peak expiratory flow (PEF) is the peak flow occurring during exhalation.
What is the difference between normal and expiratory airflow?
However, when airflow is presented as a function of lung volume, it becomes apparent that airflow is actually higher than normal (as a result of the increased elastic recoil characteristic of fibrotic lungs). (A) Normal. Inspiratory limb of loop is symmetric and convex. Expiratory limb is linear.
What is expiratory flow limitation in COPD?
The expiratory flow limitation observed in COPD is due to pathological changes that result in reduced lung recoil and airway tethering, as well as intrinsic airway narrowing. The mechanical repercussions of expiratory flow limitation are important contributors to dyspnoea, and hence, exercise limitation.

What is expiratory air flow?
Expiratory (air) flow limitation (EFL) during tidal breathing is a well-defined, mechanical pathophysiological condition occurring, either during physical exercise or at rest, before in supine and later on in sitting-standing position, when expiratory flow cannot be further increased by increasing expiratory muscles ...
What is normal expiratory flow rate?
The peak expiratory flow emerges from the large airways within 100-102ms from the start of a forced expiration and it remains peaked for 10ms [3]. The normal peak flow is 450-550 L /min in adult males and it is 320-470 L/min in adult females.
What is expiratory airflow limitation?
Expiratory flow limitation (EFL) refers to a functional condition in which expiratory flow cannot increase and, hence, is maximal under the prevailing conditions. Many factors, alone or combined, may cause EFL. Among them, airway obstruction, expiratory flow rate and body posture are the most important.
What is the expiratory phase?
Expiratory phase begins when the ventilator cycles from inspiration to expiration; the expiratory valve opens, and the patient exhales passively. This phase is defined by airflow OUT of the patient. This phase is controlled by the PEEP variable.
What should my peak expiratory flow be?
Peak expiratory flow (PEF) is measured in litres per minute. Normal adult peak flow scores range between around 400 and 700 litres per minute, although scores in older women can be lower and still be normal. The most important thing is whether your score is normal for you.
What peak flow reading indicates COPD?
A peak expiratory flow rate of less than 80% will detect more than 90% of people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in the community, including all of those with moderate or severe disease—that is, patients most likely to benefit from treatment with bronchodilators.
Is wheezing expiratory?
Wheezing can be either expiratory, inspiratory, or both. Expiratory wheezing is more common and may mean that a person has a mild blockage causing the wheezing. If people have both expiratory and inspiratory wheezing, this may be because their airways are narrower, and it could indicate a more severe issue.
What is expiratory dyspnea?
Expiratory dyspnea. difficulty with the expiratory phase of breathing, often due to obstruction in the larynx or large bronchi, such as by a foreign body.
What does expiratory wheeze indicate?
Expiratory wheezing alone often indicates a mild airway obstruction. Inspiratory wheezing occurs when you inhale. In some people with asthma, you can only hear wheezing during the inspiratory phase. If you're wheezing when you exhale and inhale, you could have a more severe breathing issue.
What affects expiratory flow rate?
The expiratory flow rate depends on both air leaving the central airways during dynamic collapse as a result of the high intrathoracic pressure and the effect of high alveolar pressure, increased during the compressive phase and maintained at a high level by the contraction of the expiratory muscles.
What are the 3 phases of breathing?
The breathing cycle can be divided into three basic stages including rest, inspiration, and expiration which are discussed separately below.
What are the 4 phases of ventilation?
There are four stages of mechanical ventilation. There is the trigger phase, the inspiratory phase, the cycling phase, and the expiratory phase.
What is a normal FEV1 reading?
The normal value for the FEV1/FVC ratio is 70% (and 65% in persons older than age 65). When compared to the reference value, a lower measured value corresponds to a more severe lung abnormality.
What peak flow indicates asthma?
A decrease in peak flow of 20 to 30 percent of your personal best may mean the start of an asthma episode. Your Asthma Action Plan may tell you to take your peak flow reading more often and to adjust your medicines. Use only one meter.
What affects expiratory flow rate?
The expiratory flow rate depends on both air leaving the central airways during dynamic collapse as a result of the high intrathoracic pressure and the effect of high alveolar pressure, increased during the compressive phase and maintained at a high level by the contraction of the expiratory muscles.
What causes airflow obstruction in bronchitis?
When airflow obstruction is more marked, coexisting emphysema is often the primary reason for the obstruction.
What are the factors that determine the lung volume?
Before a discussion of how lung volumes change in patients having the airway disease associated with COPD, it is useful to review the factors that determine the major lung volumes, namely, total lung capacity (TLC), functional residual capacity (FRC), and residual volume (RV). TLC is the point at which the force of the inspiratory muscles acting to expand the lungs is equaled by the elastic recoil of the respiratory system (primarily lung recoil) resisting expansion (see Chapter 1 ). At FRC, the resting point of the respiratory system, there is a balance between the elastic recoil of the lungs and the elastic recoil of the chest wall, which are acting in opposite directions—the lungs inward and the chest wall outward. The determinants of RV depend to some extent on age. In a normal young person, RV is the point at which the relatively stiff chest wall can be compressed no further by the expiratory muscles. With increasing age, a sufficient number of airways close at low lung volumes to limit further expiration, and airway closure is an important determinant of RV. In disease states in which airways are likely to close at low lung volumes, airway closure is associated with an elevated RV, even in young patients.
What are the pathophysiologic consequences of COPD?
The pathophysiologic consequences resulting from disease at each of these levels contribute to the overall clinical picture of COPD. In addition, the degree of airway reactivity, which probably is affected by genetic and environmental factors, appears to modify the clinical expression of disease in a given patient.
Why is RV increased in emphysema?
As in bronchitis, RV is substantially increased in emphysema because poorly supported airways are more susceptible to closure during a maximal expiration.
Does inhaled bronchodilator increase airway flow?
Use of inhaled bronchodilators may or may not result in significantly improved flow rates. Patients with asthmatic bronchitis and greater airways reactivity generally have the most striking improvement in flow rates after receiving an inhaled bronchodilator.
Which muscle is less efficient in obstructive lung disease?
However, it is clear that contraction of the diaphragm, the major muscle of inspiration, is less efficient and less effective in patients with obstructive lung disease. When FRC is increased, the diaphragm is lower and flatter, and its fibers are shortened even before the initiation of inspiration.
Does emphysema affect expiratory flow?
Coexistent small airways disease, emphysema, or both contribute significantly to decreased expiratory flow rates in chronic bronchitis. In patients who have a component of airway hyperreactivity contributing to their disease, the clinical expression often is more like asthmatic bronchitis.
What is peak expiratory flow rate?
What is a peak expiratory flow rate test? The peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) test measures how fast a person can exhale. The PEFR test is also called peak flow. This test is commonly performed at home with a handheld device called a peak flow monitor. For the PEFR test to be useful, you must keep continuous records of your flow rate.
How to test airflow speed?
When you blow air into the mouthpiece a small plastic arrow moves. This measures the airflow speed. To take the test, you will: Breathe in as deeply as you can. Blow into the mouthpiece as quickly and as hard as you can. Do not put your tongue in front of the mouthpiece. Do the test three times.
What is a spirometer?
A spirometer is a more advanced peak flow monitoring device. For this test, you will breathe into a mouthpiece connected to a spirometer machine that measures your breathing rates. Last medically reviewed on March 9, 2017.
Why does my peak flow rate decrease?
Flow rate lessens when the airways are blocked. If you notice a significant fall in your peak flow speed, it may be caused by a flare-up in your lung disease. People with asthma may experience low peak flow rates before they develop breathing symptoms.
How to determine peak flow rate?
To determine a “personal best,” you should measure your peak flow rate: 1 at least twice a day for two to three weeks 2 in the morning, upon awakening, and in the late afternoon or early evening 3 15 to 20 minutes after using an inhaled, quick-acting beta2-agonist
What does it mean when your airways are yellow?
It means your condition is under control. Yellow zone: 50 to 80 percent of your usual flow rate. Your airways may be starting to narrow. Talk to your doctor about how to handle yellow zone results. Red zone: less than 50 percent of your normal rate. Your airways are severely narrowing.
What is the normal flow rate for a blood test?
You can determine which category you fall in by comparing your past results. Green zone: 80 to 100 percent of your usual flow rate. This is the ideal zone.
What Does Research Say About the Potential Effect of Cannabis Consumption on Expiratory Airflow?
So, what does the clinical literature say about the connection, if any, between cannabis consumption (in the form of joints) and expiratory airflow?
Cannabis vs Tobacco: Differences in Effects on Lung Function
Harkening back to the earlier original reference to D.A.R.E.-style anti-cannabis propaganda campaigns, you might (if you are old enough) recall one particularly traumatic lesson imparted through these programs in the form of so-called “black lungs” displayed in glass jars – the ultimate effects of a lifetime spent smoking nicotine cigarettes (not cannabis)..
In Fact, a Joint a Day Might Keep the Doctor Away
Now that we’ve dispelled the myth of the pernicious dangers of cannabis to lung health, let’s survey some of the potential health benefits of a joint a day.
The Bottom Line on Joints and Lung Health
Barring pre-existing medical conditions, the evidence indicates that a vast majority of cannabis enthusiasts can likely light up a joint a day without worrying about any adverse effects in terms of lung function or long-term lung health.
What is the peak expiratory flow rate measurement test?
Peak expiratory flow rate measures lung strength using a handheld device, usually to diagnose or monitor asthma.
What is the name of the tube that opens up during inhalation?
Understanding the anatomy. During inhalation, air travels through the nose and/or mouth into the trachea (windpipe). The trachea further divides into two tubes (bronchi) that open into the lungs. Within the lungs, the bronchi branch out into smaller tubes called bronchioles.
Is PEFR contraindicated for asthma?
Children and young adults are also found to have poor compliance and or perform the test wrong. Moreover, there are no major contraindications for PEFR.
What is airflow obstruction?
Airflow obstruction has been defined using spirometric test results when the forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV 1) to forced vital capacity (FVC) ratio is below a fixed cutoff (<70%) or lower limits of normal (LLN) from reference equations that are based on values from a normal population. However, similar to other positive or abnormal diagnostic test results that are used to identify the presence of disease, perhaps airflow obstruction should be defined based on the values of FEV 1 /FVC for a population of individuals with known disease such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Unfortunately, we do not know such a distribution of values of FEV 1 /FVC for patients with COPD since there is no gold standard for this syndrome or condition. Yet, we have used this physiologic definition of airflow obstruction based on a normal population to identify patients with COPD. In addition, we have defined airflow obstruction as either being present or absent. Instead, we should use a different approach to define airflow obstruction based on the probability or likelihood that the airflow obstruction is present which in turn would give us the probability or likelihood of a disease state such as COPD.
What is spirometry in pulmonary function?
Pulmonary function testing including spirometry testing is performed in a clinical setting to evaluate patients who present with respiratory symptoms. The interpretation of spirometric test results can identify an abnormal pattern which may be associated with the presence of disease. One of the abnormal patterns of spirometric test results is airflow obstruction. Airflow obstruction refers primarily to a finding, by spirometry, of a reduced expiratory airflow compared to the total amount of air exhaled. This has been defined as a reduction in the ratio of forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV 1) to forced vital capacity (FVC). This is the physiologic definition of airflow obstruction. As such, the finding of airflow obstruction has been considered to be a critical element of certain diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). In fact, for many, the identification of the presence of COPD has required that physiologic airflow obstruction be present.
What is the goal of interpreting lung function testing?
The goal of interpreting lung function testing is to provide an expert opinion regarding the results of the test and how the test results are useful based on the clinical context to help in the evaluation of the patient. Knowing that our current approach to interpreting airflow obstruction is based on values of FEV 1 /FVC from normal populations is less than ideal for the identification of the presence of airway diseases in the patient.
What is a defect in a lung?
a defect refers to the presence of an abnormal parameter such as airflow obstruction, restrictive lung defect, or mixed impairment
What is airflow platform?
Airflow is a platform to programmatically author, schedule and monitor workflows.
Is Airflow a data streaming solution?
Airflow is not a data streaming solution. Tasks do not move data from one to the other (though tasks can exchange metadata!). Airflow is not in the Spark Streaming or Storm space, it is more comparable to Oozie or Azkaban.
Is Airflow pipeline explicit?
Elegant: Airflow pipelines are lean and explicit. Parameterizing your scripts is built into the core of Airflow using the powerful Jinja templating engine.
What is peak expiratory flow?
The peak expiratory flow (PEF) is the peak flow occurring during exhalation. This variable is used primarily for home monitoring of patients with asthma and for determining diurnal variations in airflow.
What is inspiratory flow assessment?
In inspiratory flow and volume assessments, patients exhale as completely as possible, then forcibly inhale.
What percentage of FVC is exhaled?
The forced expiratory flow averaged over the time during which 25 to 75% of the FVC is exhaled may be a more sensitive marker of mild, small airway airflow limitation than the FEV1, but the reproducibility of this variable is poor.
How to measure inspiratory and expiratory flow?
Quantitative measures of inspiratory and expiratory flow are obtained by forced spirometry. Nose clips are used to occlude the nares.
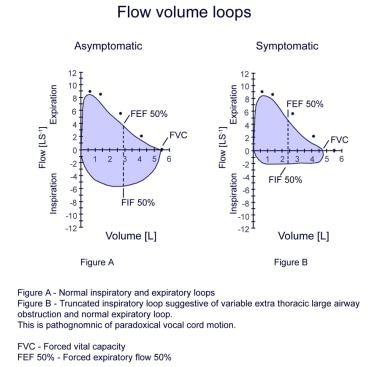
What is the flow volume loop?
In contrast to the spirogram, which displays airflow (in L) over time (in sec), the flow-volume loop (see Figure: Flow-volume loops) displays airflow (in L/second) as it relates to lung volume (in L) during maximal inspiration from complete exhalation (residual volume [RV]) and during maximum expiration from complete inhalation (TLC). The principal advantage of the flow-volume loop is that it can show whether airflow is appropriate for a particular lung volume. For example, airflow is normally slower at low lung volumes because elastic recoil is lower at lower lung volumes. Patients with pulmonary fibrosis have low lung volumes and their airflow appears to be decreased if measured alone. However, when airflow is presented as a function of lung volume, it becomes apparent that airflow is actually higher than normal (as a result of the increased elastic recoil characteristic of fibrotic lungs).
Why is airflow greater than normal at comparable lung volumes?
Airflow is greater than normal at comparable lung volumes because the increased elastic recoil of lungs holds the airways open. (D) Fixed obstruction of the upper airway (eg, tracheal stenosis, goiter). The top and bottom of the loops are flattened so that the configuration approaches that of a rectangle.
What is the advantage of flow volume loop?
The principal advantage of the flow-volume loop is that it can show whether airflow is appropriate for a particular lung volume. For example, airflow is normally slower at low lung volumes because elastic recoil is lower at lower lung volumes.
What is airflow limitation?
As a consequence, the term airflow limitation widely used to indicate the abnormal decrease of maximal expiratory flow rates at a given lung volume, as compared to predicted (i.e., airflow reduction or airflow obstruction), is inappropriate and should not be adopted unless the condition previously described is present (Figure 1 ).
What is tidal expiratory flow limitation?
When expiratory flow is maximal during tidal breathing and cannot be increased unless operative lung volumes move towards total lung capacity, tidal expiratory flow limitation (EFL) is said to occur. EFL represents a severe mechanical constraint caused by different mechanisms and observed in different conditions, but it is more relevant in terms of prevalence and negative consequences in obstructive lung diseases and particularly in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Although in COPD patients EFL more commonly develops during exercise, in more advanced disorder it can be present at rest, before in supine position, and then in seated-sitting position. In any circumstances EFL predisposes to pulmonary dynamic hyperinflation and its unfavorable effects such as increased elastic work of breathing, inspiratory muscles dysfunction, and progressive neuroventilatory dissociation, leading to reduced exercise tolerance, marked breathlessness during effort, and severe chronic dyspnea.
What is EFL in tidal breathing?
Expiratory (air) flow limitation (EFL) during tidal breathing is a well-defined, mechanical pathophysiological condition occurring, either during physical exercise or at rest, before in supine and later on in sitting-standing position, when expiratory flow cannot be further increased by increasing expiratory muscles effort (i.e., by increasing pleural and alveolar pressure) because it is maximum at that tidal volume [ 1#N#N. B. Pride and J. Milic-Emili, “Lung mechanics,” in Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease, P. Calverley and N. B. Pride, Eds., pp. 135–160, Chapman Hall, London, UK, 1995. View at: Google Scholar#N#See in References#N#]. In other words, under the prevailing conditions, the respiratory system is globally limited as flow generator even during tidal expiration, and greater expiratory flow rates may be achieved just by increasing operating lung volumes, (i.e., moving progressively the end-expiratory lung volume (EELV) towards total lung capacity). In fact, the volume-related decrease of airway resistance and increase of elastic recoil are the only effective mechanisms to obtain higher expiratory flows in case of EFL [ 2#N#D. L. Fry and R. E. Hyatt, “Pulmonary mechanics. A unified analysis of the relationship between pressure, volume and gasflow in the lungs of normal and diseased human subjects,” The American Journal of Medicine, vol. 29, no. 4, pp. 672–689, 1960. View at: Google Scholar#N#See in References#N#].
Why do COPD patients develop DH?
During episodes of acute exacerbation and respiratory failure, COPD patients are prone to develop DH even in the absence of EFL because of increase in airway resistance with longer time constant in the respiratory system and rapid and shallow breathing with reduction of expiratory time [ 29.
What is EFL in COPD?
EFL represents a severe mechanical constraint caused by different mechanisms and observed in different conditions, but it is more relevant in terms of prevalence and negative consequences in obstructive lung diseases and particularly in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Does breathing at low volume cause EFL?
Breathing at low-lung volume (near residual volume), as frequently observed in great and massive obesity, chronic congestive heart failure, and sometimes in restrictive lung and chest wall disorders, intrinsically reduces the maximal expiratory flow rates in the tidal volume range, facilitating the EFL occurrence, mainly in the supine position.
Is isovolume a low lung volume?
Isovolume (low-lung volume) flow-pressure relationship in normal subjects, COPD without expiratory flow limitation (NFL) and COPD with expiratory flow limitation (FL). In any case, after , expiratory flow does not increase further on, and its driving pressure becomes . In COPD patients with high airflow resistance and very low , the occurs early, limiting expiratory flow in the tidal volume range.
How does a peak flow meter help asthma?
A peak flow meter can help you manage asthma. It can give you and your healthcare provider information about how open the airways are in your lungs. The PFM can detect small changes in the large airways before you start to wheeze. Using a PFM every day will let you know when your peak flows are starting to drop.
What is peak flow?
Peak flow measurement can show the amount and rate of air that can be forcefully breathed out of the lungs. The measurement should be started after a full lung inhalation. During the test, you blow forcefully into the mouthpiece of a device.
What is peak flow measurement?
Peak flow measurement is a quick test to measure air flowing out of the lungs. The measurement is also called the peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) or the peak expiratory flow (PEF). Peak flow measurement is mostly done by people who have asthma.
What happens during peak flow measurement?
Peak flow measurement is done 1 or more times daily at the same time of day, or whenever you are having early signs of an asthma attack. Or you should use it when directed by your healthcare provider. Use the peak flow meter (PFM) before taking asthma medicine. Your healthcare provider may advise other times when using a PFM is useful.
Why use a peak flow meter?
This slows the speed of air moving through the lungs. A peak flow meter can help show the narrowing of the airways well before an asthma attack happens.
When to measure peak flow?
Measure peak flows about the same time each day. A good time might be when you first wake up, or at bedtime. Clean and care for your meter as instructed. If you use a new peak flow meter, you will need to find your new personal best value on the new meter.
Can you use a PFM for asthma?
Your healthcare provider may not advise you use a PFM unless your asthma is moderate or severe and you are managing it with medicine. PFM can also be used to assess other lung problems, such as:
