Fibrinolytic inhibitors, tranexamic acid, and ε-aminocaproic acid are the most commonly used treatments for bleeding in both inherited and acquired fibrinolytic disorders. These function by preventing binding of plasminogen to fibrin. The drugs can be given on demand or as prophylaxis for surgical or dental procedures.
Full Answer
What are the side effects of thrombolytic therapy?
- Anxiety
- blue lips and fingernails
- blue or pale skin
- blurred vision
- chest pain or discomfort
- chest pain, possibly moving to the left arm, neck, or shoulder
- convulsions
- cool, sweaty skin
- cough
- coughing that sometimes produces a pink frothy sputum
Are fibrinolytics and thrombolytics the same?
Yes and no. They are the same in that both break down blood clots. But, as the name implies, thrombolytics act on the entire thrombus (clot) while fibrinolytics break down the fibrin within the clot. Essentially fibrinolytic are a type of thrombolytic. Some drugs do both.
Are there side effects for thrombolytic therapy?
What are the side effects of thrombolytic therapy? Bruising or bleeding at the access site. Damage to the blood vessel. Migration of the blood clot to another part of vascular system. Kidney damage in patients with diabetes or other pre-existing kidney disease. Read rest of the answer.
What is thrombolytic therapy drugs?
Thrombolytics, also known as fibrinolytics or clot-busting agents are the type of drugs used to treat various conditions related to blood vessel occlusion done by a thrombus. This type of therapy begun in the middle of the 20 th century, but the modern way of thrombolytic agent use started in the 90’.

What is an example of a fibrinolytic drug?
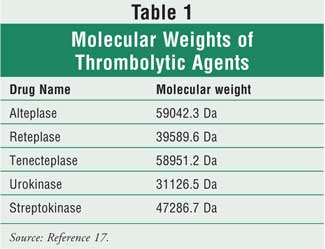
Alteplase, reteplase, and tenecteplase are “fibrin specific” drugs that selectively act on plasminogen which is fibrin bound.
What is fibrinolytic medicine?
Fibrinolytic therapy — or thrombolytic therapy — is an emergency treatment used to dissolve blood clots before they become fatal. If you or a loved one has a heart attack, stroke or another condition caused by a blood clot, fibrinolytic therapy can help prevent death and reduce long-term side effects.
Is aspirin a fibrinolytic drug?
Aspirin acetylates fibrinogen and enhances fibrinolysis. Fibrinolytic effect is independent of changes in plasminogen activator levels.
What is the difference between thrombolytic and fibrinolytic?
Fibrinolytic therapy, also known as thrombolytic therapy, is used to lyse acute blood clots by activating plasminogen, resulting in the formation of plasmin, which cleaves the fibrin cross-links causing thrombus breakdown.
When do you give fibrinolytic therapy?
Efficacy. For optimal results, fibrinolytic therapy should be administered as early as possible, preferably within the first 3 to 6 hours and potentially up to 12 hours after the onset of symptoms (Figure I in the Data Supplement). After 3 hours of symptom onset the clinical benefit of fibrinolysis markedly decreases.
Is fibrinolytic a blood thinner?
Fibrinolytic drugs work by activating the so-called fibrinolytic pathway. This distinguishes them from the anticoagulant drugs (coumarin derivatives and heparin), which prevent the formation of blood clots by suppressing the synthesis or function of various clotting factors that are normally present in the blood.
Does aspirin break down fibrin?
Aspirin alters the fibrin/fibrinogen properties and thereby influences the fibrin network structure, possibly through acetylation of the lysine residues in the fibrinogen molecule involved in cross-linking of fibrin (15–17).
Does aspirin dissolve fibrin?
Our previous studies have shown that aspirin treatment alters the fibrin network in non-diabetic individuals and increases the fibrin network permeability. The effect of aspirin on fibrin network formation in patients with diabetes is unclear.
Is heparin fibrinolytic therapy?
Intravenous administration of heparin seems justified, specially if rtPA is used as fibrinolytic agent. Potent new drugs capable of inhibiting platelets an the coagulation cascade emerge as a promising future.
What is the most common complication of fibrinolytic therapy?
Intracranial hemorrhage, the most devastating complication, occurs in 0.2-1% of patients treated with thrombolytic therapy.
Is heparin a thrombolytic?
Heparin administered intravenously appears to markedly attenuate the thrombin activity associated with thrombolysis and, in patients treated with tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA), prevents early recurrent coronary thrombosis.
What are contraindications to fibrinolytic therapy?
Contraindications to Fibrinolytic TherapyAbsolute contraindicationsAortic dissectionActive internal bleeding (not menses)Intracranial tumorPericarditisRelative contraindicationsBlood pressure > 180/110 mm Hg after initial antihypertensive therapy8 more rows
What should not be treated with fibrinolytic?
The contraindications for fibrinolytic therapy include previous intracranial hemorrhage, malignant intracranial neoplasm, known structural cerebrovascular lesion (e.g., arteriovenous malformation), ischemic stroke within 3 months except for acute ischemic stroke within 4.5 h, significant facial trauma or closed-head ...
Is tPA a thrombolytic or fibrinolytic?
The most commonly used drug for thrombolytic therapy is tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), but other drugs can do the same thing. Ideally, you should receive thrombolytic medicines within the first 30 minutes after arriving at the hospital for treatment. A blood clot can block the arteries to the heart.
How do fibrinolytic drugs work?
Fibrinolytic drugs work by activating the so-called fibrinolytic pathway. This distinguishes them from the anticoagulant drugs (coumarin derivatives and heparin ), which prevent the formation of blood clots by suppressing the synthesis or function of various clotting factors that are normally present in the blood.
What is the function of the fibrinolytic system?
The fibrinolytic system degrades fibrin and fibrinogen to products that act to inhibit the enzyme thrombin.
What is the enzyme that is involved in fibrinolytic process?
The active enzyme involved in the fibrinolytic process is plasmin , which is formed from its precursor, plasminogen, under the influence of an activating factor released from endothelial cells. If formed in the circulating blood, plasmin is normally inhibited by a circulating plasmin inhibitor.
What is the drug that inhibits fibrinogenolysis?
The antifibrinolytic drug aminocaproic acid is a specific antagonistof plasmin and inhibitsthe effects of fibrinolytic drugs.
What is the antifibrinolytic drug that inhibits plasmin?
The antifibrinolytic drug aminocaproic acid is a specific antagonist of plasmin and inhibits the effects of fibrinolytic drugs. Jeffrey S. Fedan.
What is the best treatment for occlusive clots?
Heparin, aspirin, dipyridamole, or a combination of these three drugs can be added to therapy to help prevent the recurrence of occlusive clots. An overdose of streptokinase may lead to bleeding from systemic fibrinogenolysis, which is the breakdown of the coagulation factors by plasmin.
What is the drug that prevents blood from clotting?
anticoagulant. Anticoagulant, any drug that, when added to blood, prevents it from clotting. Anticoagulants achieve their effect by suppressing the synthesis or function of various clotting factors that are normally present in the blood.
What is Fibrinolytic Therapy?
Fibrinolytic therapy, also known as thrombolytic therapy, is used to lyse acute blood clots by activating plasminogen. This results in the formation of plasmin, which cleaves the fibrin cross-links causing thrombus breakdown.
How do fibrinolytic drugs work?
Fibrinolytic medications, which prevent the formation of blood clots by suppressing the function of multiple clotting factors that are normal and present in the blood, are different from anticoagulants, which work by preventing normal clotting factors ...
What is the ST segment elevation for fibrinolytic therapy?
In patients with acute myocardial infarction, fibrinolytic therapy would be indicated if the ST-segment elevation is consistent with myocardial infarction of greater than or equal to 1mm in two or more contiguous leads. Contiguous leads are next to one another anatomically speaking, and they view the same general area of the heart (specifically the left ventricle).
What is the effect of fibrinolytic drugs on thrombosis?
And while there are similarities between these and anticoagulants, fibrinolytic drugs produce the therapeutic effect of breaking down the fibrin and fibrinogen matrix of a thrombosis (fibrinolysis), thus fragmenting the clot that is obstructing an artery and reestablishing distal blood flow.
How long does a fibrolytic last?
Fibrinolytic therapy may also be indicated if the signs and symptoms of a myocardial infarction last longer than 15 minutes and less than 12 hours and if PCI (percutaneous coronary intervention) is not available within 90 minutes of medical contact.
Can fibrinolytics be used in life support?
Although fibrinolytic medications are not usually found in advanced cardiac life support pharmacological drug cards, their use is extremely important to reperfusion therapies. The most common indications for the use of fibrinolytic therapy include the following: Acute myocardial infarction, also known as AMI.
Is fibrinolytic therapy time dependent?
Patients who have suffered from an acute ischemic stroke have a time-dependent benefit for fibrinolytic therapy similar to that of patients with STEMI, but this time-dependent benefit is much shorter. It should also be noted that the critical period for the administration of IV fibrinolytic therapy begins with the onset of symptoms.
Why is fibrinolytic therapy used in unstable angina?
Fibrinolytic therapy has also been used in unstable angina, because many such patients have coronary thrombi.
Is thrombolytic therapy contraindicated?
Thrombolytic therapy requires careful patient selection. It is contraindicated in all situations where the risk of bleeding is increased, such as— recent trauma, surgery, biopsies, haemorrhagic stroke or peptic ulcer, severe hypertension, aneurysms, bleeding disorders, diabetes, acute pancreatitis, etc. Its use in retinal vessel occlusion has been abandoned.
Do fibrolytics help with peripheral vascular disease?
Fibrinolytics have no role in chronic peripheral vascular diseases.
Drugs used to treat Fibrinolytic Bleeding
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
What is the best pharmacologic class for STEMI?
Fibrinolytic agents are the preferred pharmacologic class for the management of STEMI because of their ability to achieve reperfusion and to restore blood flow when administered within 12 hours of symptom onset.
What is the best treatment for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction?
Rapid reperfusion is the key treatment goal in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). The American College of Cardiology-American Heart Association (ACC-AHA) 2004 guidelines for the management of STEMI include recommendations for pharmacologic reperfusion with use of fibrinolytic agents. Fibrinolytic agents are the preferred pharmacologic class for the management of STEMI because of their ability to achieve reperfusion and to restore blood flow when administered within 12 hours of symptom onset. Four fibrinolytic agents are approved for the treatment of STEMI in the United States-streptokinase, alteplase, reteplase, and tenecteplase. Several clinical trials have demonstrated the beneficial effects of these therapies in reducing mortality rates in patients with suspected acute myocardial infarction. Alteplase is administered as an intravenous infusion. However, the relatively long half-lives of reteplase and tenecteplase enable bolus administration, which may be more convenient and less time consuming. Reteplase is administered as a double bolus, and dosing does not depend on the patient's weight; tenecteplase is administered as a single bolus, and dosing is weight based. Adherence to the ACC-AHA guidelines, as well as knowledge about the available fibrinolytic agents, is essential for physicians and pharmacists to make informed decisions regarding appropriate pharmacologic reperfusion strategies.
What is fibrinolytics?
Thrombolytics or fibrinolytics are a group of medications used in the management and treatment of dissolving intravascular clots. They are in the plasminogen activator class of drugs. This activity describes the indications, action, and contraindications for thrombolytics. This activity will highlight the mechanism of action and adverse event profile pertinent for members of the interprofessional team in the treatment of patients with intravascular clots such as Acute myocardial infarction, acute ischemic stroke, and related conditions.
How long does fibrinolysis take?
Local fibrinolysis usually takes 6 to 72 hours to achieve clot lysis; therefore, it is not suitable for patients with limb-threatening ischemia. [11][12]Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
What is thrombolytic treatment?
Thrombolytic treatment is also known as fibrinolytic or thrombolysis to dissolve dangerous intravascular clots to prevent ischemic damage by improving blood flow. Thrombosis is a significant physiological response that limits hemorrhage caused by large or tiny vascular injury. The physiological hemostatic response is well-controlled by intrinsic antithrombotic properties and fibrinolysis. Thrombus formation is supposed to be confined to localized areas of tissue injury. Any intravascular thrombus without damage that impedes the blood flow is considered abnormal. Any form of inherited or acquired hypercoagulable state may give rise to intravascular thrombus formation. Upon formation, an abnormal thrombus may propagate until complete blockage of the arterial lumen or may detach and travel to block downstream vascular lumen. Thromboembolism has the following clinical outcomes where a thrombolytic therapy can be used.
How are thrombolytic agents given?
There are two ways thrombolytic agents can be given: systemic administration through a peripheral IV or local release by a catheter after navigating to the site of the clot . Thrombolytic or fibrinolytic agents are often referred to as plasminogen activators. All of the available thrombolytic agents are serine proteases that cleave plasminogen into active plasmin. Currently, available thrombolytic agents include the following:
What is the process of thrombosis?
During thrombosis, circulating prothrombin is converted to its active form thrombin by activated platelets. Active thrombin then converts the fibrinogen into fibrin with the eventual formation of a fibrin matrix. This process is counterbalanced by plasmin derived from plasminogen, which gathers in the fibrin matrix. Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) is a natural fibrinolytic found in endothelial cells. It shows fibrin specificity and affinity. The end goal of this therapy is to convert plasminogen into plasmin which is accomplished at the location of the thrombus and on the surface of fibrin by the binding of tPA to plasminogen. This binding helps the conversion.
Is streptokinase a fibrinolytic agent?
Due to its relatively low cost with reasonable efficacy and safety, it is the most widely used fibrinolytic agent worldwide. While it has lower efficacy than alteplase, the risk of intracranial hemorrhage is less. Re-administration of streptokinase within six months is not considered safe due to its high antigenicity and associated high antistreptococcal antibody titer. It is not a plasminogen activator. However, after binding with free circulating plasminogen, it forms a complex that converts additional plasminogen to active plasmin. As it is produced from streptococcus, it often exerts febrile reactions and other allergic reactions. Dose dependant hypotension is another potential caution for this drug. [1]
