Is cystic fibrosis a deadly disease?
It is often fatal in early adulthood. People with the disease have inherited two copies of the defective cystic fibrosis gene, one copy from each parent. More than 70,000 people live with cystic...
What is the best diet for cystic fibrosis?
You can do this by adding the following to your diet:
- Protein: Foods high in protein, such as beef, chicken, eggs, fish, and soy, are important for preventing muscle loss.
- Zinc: Foods high in zinc include kidney beans, beef, spinach, liver, eggs and seafood. ...
- Salt: People with CF have saltier sweat, which may cause electrolyte imbalance and dehydration. ...
Who is at risk with cystic fibrosis?
The greatest risk factor for cystic fibrosis is a family history of the disease, especially if either parent is a known carrier. The gene that causes cystic fibrosis is recessive. This means that in order to have cystic fibrosis, children must inherit two copies of the gene, one from each parent.
Why do cystic fibrosis patients get nasal polyps?
The thick mucus created by cystic fibrosis leads to chronic (constant, long-term) sinus congestion and frequent sinus infections, which doctors believe cause nasal polyps to develop. How are they diagnosed?

What does kidney fibrosis mean?
Kidney fibrosis is characterized by excessive production and deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins mainly in the kidney interstitium and results in structural damage, impairment of renal function, and eventually end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
How is kidney fibrosis treated?
Clinical Summary. There are currently no drugs for CKD and fibrosis in clinical use that would specifically target the kidney. Despite a number of potential anti-fibrotic treatment targets identified in preclinical studies, translation to clinical trials has remained remarkably poor.
Is kidney fibrosis reversible?
Can renal fibrosis be reversed? The simple answer is yes, areas of expanded extracellular matrix can regress. This has been demonstrated in some experimental models of self-limited kidney disease and in human diabetic nephropathy associated with mesangial matrix expansion.
How is kidney fibrosis diagnosed?
Biopsy is currently the gold standard for assessing fibrosis with histological techniques. Although this procedure has become safer over recent years, complications and limitations remain. Given these restrictions, new, noninvasive techniques are necessary for the evaluation and follow-up of CKD patients.
What are the first signs of kidney problems?
Generally, earlier stages are known as 1 to 3. And as kidney disease progresses, you may notice the following symptoms. Nausea and vomiting, muscle cramps, loss of appetite, swelling via feet and ankles, dry, itchy skin, shortness of breath, trouble sleeping, urinating either too much or too little.
What foods increase your GFR?
Avoid processed foods and choose fresh fruits and vegetables instead. Follow a low-salt diet. Salt should be limited especially if you have high blood pressure, protein in your urine, or swelling, or difficulty breathing. Eating less than 2000 mg a day of sodium is recommended.
What is the cause of fibrosis?
What causes pulmonary fibrosis? There are a number of known causes of pulmonary fibrosis. Exposure to toxins like asbestos, coal dust or silica (including workers in the coal mining and sandblasting industry) can lead to pulmonary fibrosis.
Does fibrosis cause kidney problems?
A final, common pathway in chronic kidney disease is fibrosis, the formation of internal scar tissue, which can cause devastating effects. In the kidneys, it can ultimately lead to end-stage kidney failure.
What is mild interstitial fibrosis kidney?
Kidney interstitial fibrosis (IF) can be defined as the accumulation of collagen and related molecules in the interstitium. Interstitial collagen is normally present in the kidney, particularly type I and III, which serve as structural scaffolding.
Will drinking water increase my GFR?
Water ingestion can acutely affect GFR, although not necessarily in the direction one might expect. Using 12 young, healthy individuals as their own controls, Anastasio et al. found increased water intake actually decreases GFR.
What should my GFR be for my age?
GFR Number by Age The normal range of Kidney Glomerular Filtration Rate is 100 to 130 mL/min/1.73m2 in men and 90 to 120mL/min/1.73m2 in women below the age of 40. GFR decreases progressively after the age of 40 years.
What is a normal GFR for a 70 year old?
However, we know that GFR physiologically decreases with age, and in adults older than 70 years, values below 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 could be considered normal.
Does fibrosis cause kidney problems?
A final, common pathway in chronic kidney disease is fibrosis, the formation of internal scar tissue, which can cause devastating effects. In the kidneys, it can ultimately lead to end-stage kidney failure.
What is the cause of fibrosis?
What causes pulmonary fibrosis? There are a number of known causes of pulmonary fibrosis. Exposure to toxins like asbestos, coal dust or silica (including workers in the coal mining and sandblasting industry) can lead to pulmonary fibrosis.
How do you get scarring on your kidney?
Kidney scarring, or 'fibrosis' is the primary cause of kidney disease and is triggered by factors including diabetes, autoimmune disease and high blood pressure, regular use of certain medications and prolonged infections.
Can UTI cause kidney scarring?
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a common bacterial illness in children. Acute pyelonephritis (APN) in children may lead to renal scarring, which results from a complex interactions between host and bacterial factors, leading to acute renal parenchymal damage and subsequent permanent damage1).
Kidney cirrhosis
Happens cirrhosis of the kidney in the beginning as a natural reaction to the body of the damage in the renal tissue, and the demise of the cause of the damage heals tissue and back to normal, but in the event of continuing cause of damage and kidney damage, accumulate scars and loses tissue properties In fact, pathological fibrosis occurs in the kidney tissues , and with the continuation of the fibrosis, the tissue loses its ability to heal, and the difficulty of blood supply to nourish the renal tissue increases, which ultimately leads to the occurrence of kidney failure, and it is worth noting that kidney cirrhosis may occur as a result of a person suffering from any of the chronic and progressive kidney diseases , especially in its advanced stages, as it is one of the main causes of the progression of chronic kidney disease to the stage The final stage , and fibrosis may affect many other organs in the body, such as the lungs and liver , and it should be noted that fibrotic diseases cause nearly half of the deaths in the developed countries of the world annually..
Kidney cirrhosis treatment
Scientists have not yet been able to find an effective treatment for cirrhosis or any of the other cirrhotic diseases that affect the various organs in the body, and because the fibrosis process is considered one of the vital repair processes that the body performs to try to reduce the damage to the tissues and repair it, it enters into this process There are many different factors and cells, and they are done in a very complex way, but there are some therapeutic methods that have been reached, or are currently being tested to reduce the progression of kidney cirrhosis, and these methods include the following:.
Symptoms of chronic kidney disease
Kidney cirrhosis is the main cause that leads to the development of chronic kidney disease into the final stage of disease . In fact, the progression of chronic kidney disease is accompanied by the appearance of some different symptoms and signs, including the following:
Causes of chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease occurs as a result of a disease or health condition that impairs kidney function , which leads to damage to it. Chronic kidney disease may develop over many months and years. Among the reasons that lead to the development of chronic kidney disease are the following:
Complications of chronic kidney disease
The progression of chronic kidney disease affects almost all parts of the body, and complications that accompany the progression of the disease include:
What is direct renal evidence?
Direct renal evidence comes from examining the histology in experimental renal infection and scarring. Being a primary tubulointerstitial model of injury, the glomeruli are largely unaffected during fibrosis, the density of glomeruli therefore providing a measure of parenchymal collapse.
What is renal scarring?
Renal fibrosis is a direct consequence of the kidney's limited capacity to regenerate after injury. Renal scarring results in a progressive loss of renal function, ultimately leading to end-stage renal failure and a requirement ...
What is the circulating uraemic serum?
The circulating uraemic serum consists of a complex mixture of more that 50 known or putative toxins [ 21 ]; including small water bound solutes, middle molecules and protein bound molecules [ 22 ].
Why are fibroblasts stimulated more directly in some diseases?
It is also likely that fibroblasts are stimulated more directly in some diseases because high glucose concentrations [ 12] and angiotensin II [ 13] stimulate in vitro renal cortical fibroblast proliferation and collagen production. Likewise the contraction of renal parenchyma is under cytokine control.
How many different cell types are there in the kidney?
Full size table. Firstly, and perhaps most importantly, is the inherent complexity of the kidney. The kidney consists of more than 20 different cell types. Not only does this exacerbate the in situ consequences of injury but it also affects the ability of the kidney to regenerate after an insult.
What are the three compartments of the kidney?
These variously affect the three functional compartments of the kidney; the vasculature, glomerulus and tubulointerstitium.
Where do myofibroblasts come from?
Myofibroblasts are probably derived from multiple sources, including not only resident fibroblasts, but also pericytes, blood borne precursors and transition of adjacent epithelial cells and endothelial cells, the relative importance of each being the subject of much conjecture [ 8 ].
Background
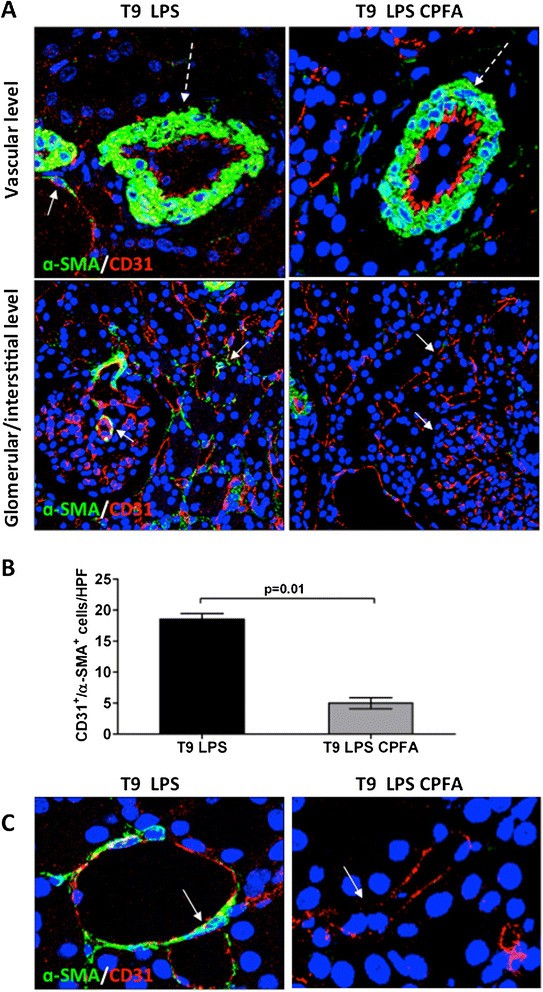
Chronic kidney disease is a growing global health concern, affecting about 10 percent of the world’s population. A final, common pathway in chronic kidney disease is fibrosis, the formation of internal scar tissue, which can cause devastating effects. In the kidneys, it can ultimately lead to end-stage kidney failure.
What the study found
HSCI faculty member Joseph Bonventre and his colleagues identified key factors involved in this cell cycle arrest and provided insight into its consequences. Based on these findings, they identified a structure within the cell that is involved in the cell cycle arrest and proposed new therapeutic targets for kidney fibrosis.
How they did it
Bonventre and colleagues studied the transition from acute to chronic kidney disease in mice, using extracted epithelial cells and analyzing which genes were active when.
Why it matters
By identifying a mechanism that triggers the formation of a compartment in kidney cells that facilitates the secretion of pro-fibrosis factors, the scientists have discovered a promising target for developing new therapies for patients with chronic kidney disease.
Discover more
This article originally appeared on the Brigham and Women's Hospital website. [Read the canonical version]
What is renal fibrosis?
Renal (interstitial) fibrosis is associated with previous or ongoing injury to the renal parenchyma,such as that associated with chronic interstitial inflammation. The amount of fibrosis dependson the inciting condition, the amount of damage to the renal parenchyma, and the chronicity of the lesion. Fibrosis results from a complex interaction ...
When is fibrosis secondary to another process?
When fibrosis is secondary to another process, such as inflammation, and both are present concurrently, the pathologist should use his or her judgment in deciding whether or not the fibrosis is prominent enough to warrant a separate diagnosis.
What causes renal allograft injury?
All causes of renal allograft injury, when severe and/or sustained, can result in chronic histological damage of which interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy are dominant features. Unless a specific disease process can be identified, what drives interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy progression in individual patients is often unclear. In general, clinicopathological factors known to predict and drive allograft fibrosis include graft quality, inflammation (whether "nonspecific" or related to a specific diagnosis), infections, such as polyomavirus-associated nephropathy, calcineurin inhibitors (CNI), and genetic factors. The incidence and severity of chronic histological damage have decreased substantially over the last 3 decades, but it is difficult to disentangle what effects individual innovations (eg, better matching and preservation techniques, lower CNI dosing, BK viremia screening) may have had. There is little evidence that CNI-sparing/minimization strategies, steroid minimization or renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade result in better preservation of intermediate-term histology. Treatment of subclinical rejections has only proven beneficial to histological and functional outcome in studies in which the rate of subclinical rejection in the first 3 months was greater than 10% to 15%. Potential novel antifibrotic strategies include antagonists of transforming growth factor-β, connective tissue growth factor, several tyrosine kinase ligands (epidermal growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor, vascular endothelial growth factor), endothelin and inhibitors of chemotaxis. Although many of these drugs are mainly being developed and marketed for oncological indications and diseases, such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, a number may hold promise in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy, which could eventually lead to applications in renal transplantation.
What are the factors that drive allograft fibrosis?
In general, clinicopathological factors known to predict and drive allograft fibrosis include graft quality, inflammation (w hether "nonspecific" or related to a specific diagnosis), infections, such as polyomavirus-associated nephropathy, calcineurin inhibitors (CNI), and genetic factors.
Can pulmonary fibrosis be used for renal transplant?
Although many of these drugs are mainly being developed and marketed for oncological indications and diseases, such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, a number may hold promise in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy, which could eventually lead to applications in renal transplantation.
How long does it take for nephrogenic fibrosis to appear?
Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis can begin days to months after exposure to gadolinium-containing contrast. Some signs and symptoms of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis may include: Thickening and hardening of the skin, typically on the arms and legs and sometimes on the body, but almost never on the face or head.
What is a rare disease that occurs mainly in people with advanced kidney failure with or without dialysis?
Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is a rare disease that occurs mainly in people with advanced kidney failure with or without dialysis. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis may resemble skin diseases, such as scleroderma and scleromyxedema, with thickening and darkening developing on large areas of the skin. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis can also affect ...
What is the highest risk of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis after gadolinium exposure?
The highest risk of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis after gadolinium exposure occurs in people who: Have moderate to severe kidney disease. Have had a kidney transplant, but have compromised renal function. Are receiving hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. Have acute kidney injury.
Can nephrogenic fibrosis cause shortening of muscles?
Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis can also affect internal organs, such as the heart, kidneys and lungs, and it can cause a disabling shortening of muscles and tendons in the joints (joint contracture). For some people with advanced kidney disease, being exposed to certain gadolinium-containing contrast agents during magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI) ...
Can gadolinium be used for kidney disease?
The Food and Drug Administration ( FDA) recommends avoiding gadolinium-containing contrast agents in people with acute kidney injury or chronic kidney disease. Other conditions that may lead to or promote the disease when severe kidney disease and exposure to gadolinium-containing contrast are present include:
Can gadolinium cause nephrogenic systemic fibrosis?
The exact cause of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis isn't fully understood. Exposure to gadolinium-containing contrast agents during magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI) has been identified as a trigger for development of this disease. The Food and Drug Administration ( FDA) recommends avoiding gadolinium-containing contrast agents in people ...
What causes fibrosis scars?
Repeated injuries, chronic inflammation and repair are susceptible to fibrosis where an accidental excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix components, such as the collagen is produced by fibroblasts, leading to the formation of a permanent fibrotic scar.
What is the process of scarring called?
Physiology. Fibrosis is similar to the process of scarring, in that both involve stimulated fibroblasts laying down connective tissue, including collagen and glycosaminoglycans. The process is initiated when immune cells such as macrophages release soluble factors that stimulate fibroblasts.
What is the term for the pathological accumulation of fibrous tissue?
Fibrosis can be used to describe the pathological state of excess deposition of fibrous tissue, as well as the process of connective tissue deposition in healing. Defined by the pathological accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, fibrosis results in scarring and thickening of the affected tissue, it is in essence an exaggerated wound ...
What is fibroma in biology?
In response to injury, this is called scarring, and if fibrosis arises from a single cell line, this is called a fibroma. Physiologically, fibrosis acts to deposit connective tissue, which can interfere with or totally inhibit the normal architecture and function of the underlying organ or tissue. Fibrosis can be used to describe ...
What are the two types of myocardial fibrosis?
Myocardial fibrosis has mainly two forms: 1 Interstitial fibrosis, which has been described in congestive heart failure, hypertension, and normal aging. 2 Replacement fibrosis, which indicates an older myocardial infarction.
What are the mediators of fibrosis?
Other soluble mediators of fibrosis include CTGF, platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), and interleukin 10 (IL-10).
What is bridging fibrosis?
Bridging fibrosis An advanced stage of liver fibrosis seen in the progressive form of chronic liver diseases. The term “bridging” means ‘the formation of “bridge” (by the band of mature & thick fibrous tissue) obliterating portal area to central vein’, leads to the formation of pseudolobules. Long-term exposure to hepatotoxin (e.g. thioacetamide, carbon tetrachloride, diethylnitrosamine) results in the bridging fibrosis in experimental animal models.