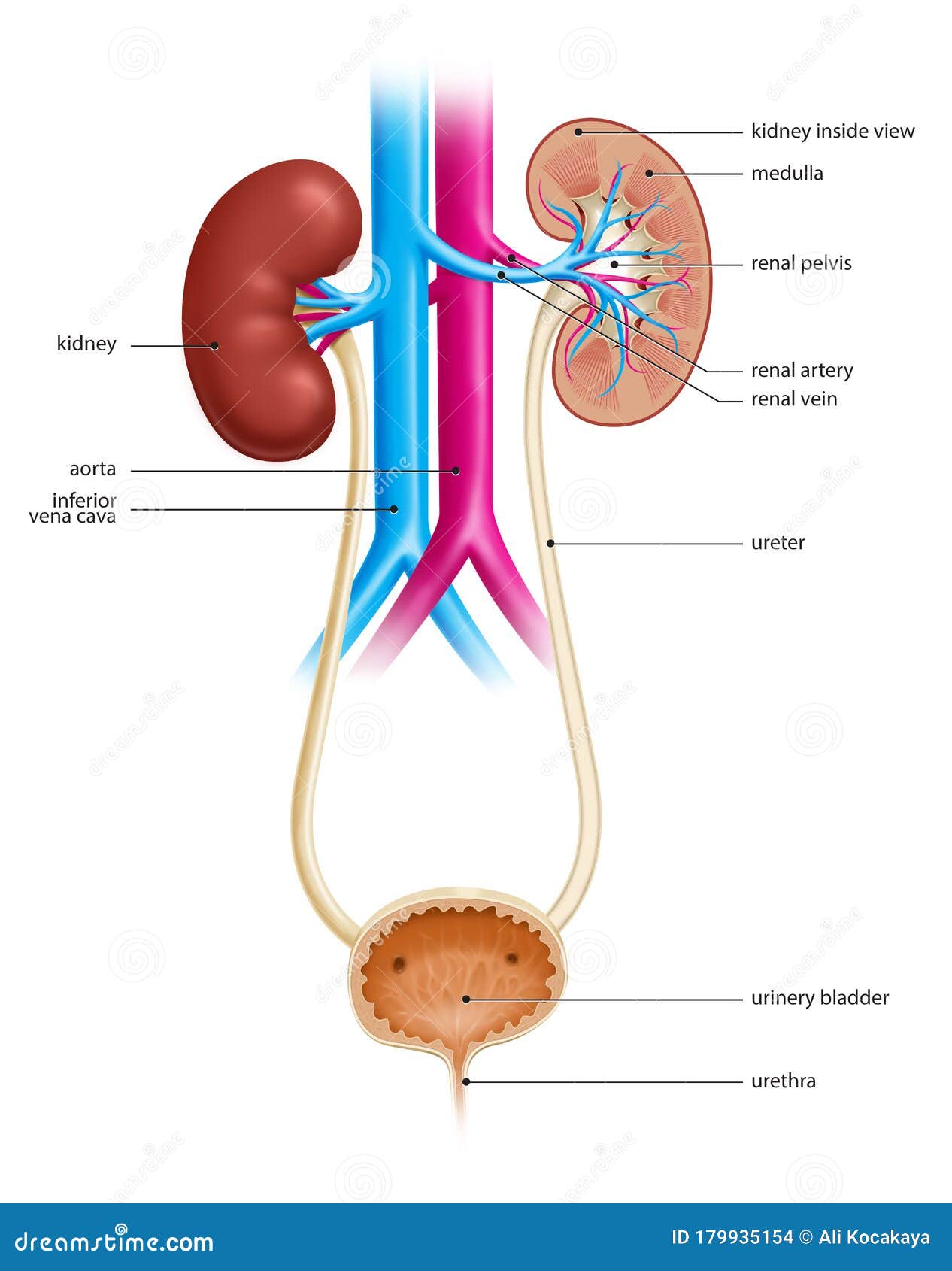
Urinary system. Following filtration of blood and further processing, wastes (in the form of urine) exit the kidney via the ureters, tubes made of smooth muscle fibres that propel urine towards the urinary bladder, where it is stored and subsequently expelled from the body by urination ( voiding ).
Where does filtration take place in the urinary system?
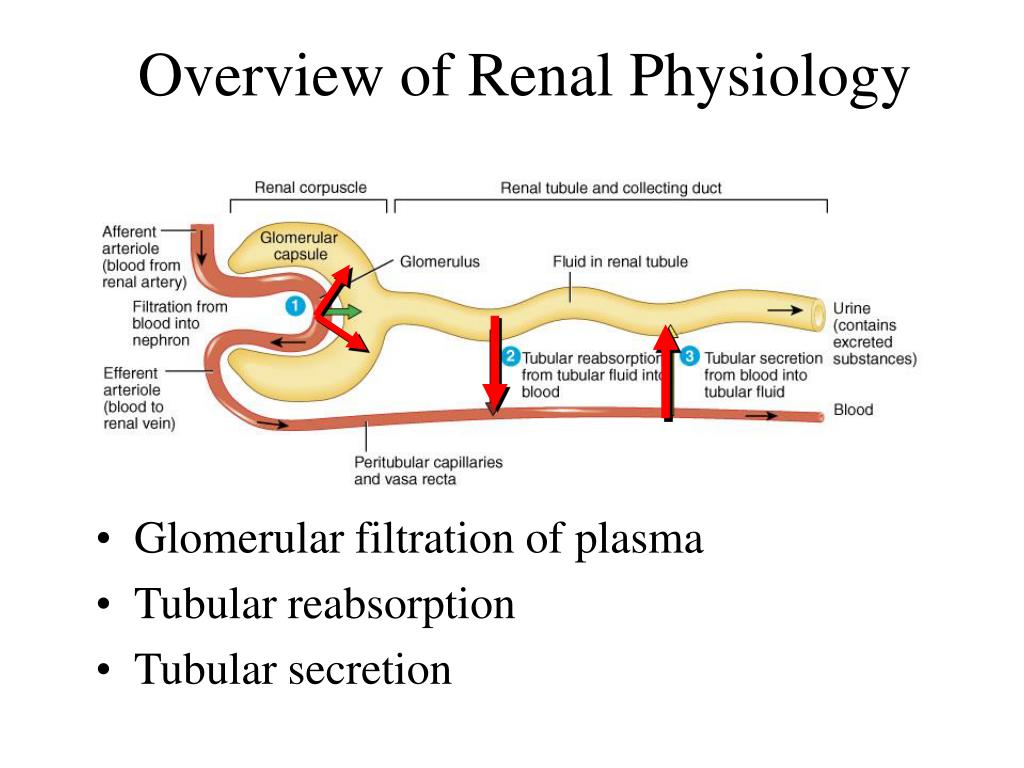
They wrap around the capillaries, but leave slits between them, known as filtration slits. A thin diaphragm between the slits acts as a final filtration barrier before the fluid enters the glomerular space. Together the glomerulus and glomerular capsule filtering unit are known as a renal corpuscle.
What is the best filtration system?
- Best Value Water Filter Pitcher For Most People: Brita Standard Metro Water Filter Pitcher
- Best Designed Water Filter Pitcher: Soma 10-Cup Pitcher
- Best Filter for Sink Faucet: PUR Faucet Mount Water Filtration System
- Best Under-Sink Water Filter System: Frizzlife Under Sink Water Filter System
Which part of the urinary system filters blood?
The kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra are the primary structures of the urinary system. They filter blood and remove waste from the body in the form of urine. The size and position of lower urinary structures vary with male and female anatomy. 1. Kidneys Filter Blood at the Top of the Urinary System.
When does filtrate become urine?
At the same time, waste ions and hydrogen ions pass from the capillaries into the renal tubule. This process is called secretion. The secreted ions combine with the remaining filtrate and become urine. The urine flows out of the nephron tubule into a collecting duct.

What is filtration in the urinary system quizlet?
filtration. function of the kidney; occurs in renal corpuscle, ultrafiltrate of plasma (filters blood; plasma, electrolytes, urea go into Bowman's capsule from glomerulus, albumins, RBCs, platelets remain in glomerulus) filters 180 L blood per day.
Where does filtration occur in the urinary system?
Each of your kidneys is made up of about a million filtering units called nephrons. Each nephron includes a filter, called the glomerulus, and a tubule. The nephrons work through a two-step process: the glomerulus filters your blood, and the tubule returns needed substances to your blood and removes wastes.
What happens during filtration in the kidney?
The glomerulus filters water and small solutes out of the bloodstream. The resulting filtrate contains waste, but also other substances the body needs: essential ions, glucose, amino acids, and smaller proteins. When the filtrate exits the glomerulus, it flows into a duct in the nephron called the renal tubule.
Which part is responsible for filtration?
The kidneys are the organs that filter waste from the blood and produce urine. This urine is then passed through the ureters and stored in the urinary bladder.
What organ is responsible for filtration?
Your kidneys are responsible for filtering both the body's blood and other waste materials that may enter the body, whether through food, drink or medicine. The waste leaves the body as urine.
What are the 3 stages of filtration?
There are three stages of filtration: mechanical, biological, and UV clarification.
How does filtration occur during the formation of urine?
During filtration, blood enters the afferent arteriole and flows into the glomerulus where filterable blood components, such as water and nitrogenous waste, will move towards the inside of the glomerulus, and nonfilterable components, such as cells and serum albumins, will exit via the efferent arteriole.
What happens when your kidneys don't filter properly?
When the kidneys aren't filtering properly, toxins stay in the blood rather than leaving the body through the urine. This can make it difficult to sleep.
How Does the Urinary System Work?
How the urinary system works is relatively simple, although the supplementary roles of the kidneys can be complex .
What muscle is involved in the expulsion of urine from the body?
The image below shows the stages of micturition and the muscles involved, namely the detrusor muscle of the urinary bladder, the internal urethral sphincter, and the pelvic floor muscle which surrounds the external sphincter.
What muscle is used to prevent urine from leaking out?
These only relax during micturition and otherwise prevent urine from constantly leaking out. The internal sphincter is an involuntary muscle; the external sphincter is voluntary. The urinary bladder is lined by a thick mucosa which forms folds when the bladder is empty but opens out as the bladder fills and expands.
What is the triangular shaped bladder?
The triangular shaped bladder is a large muscle into the top of which the two ureters empty the urine. Under the bladder, close to where it connects to a single urethra, lie two circular sphincters – internal and external. These only relax during micturition and otherwise prevent urine from constantly leaking out. The internal sphincter is an involuntary muscle; the external sphincter is voluntary. The urinary bladder is lined by a thick mucosa which forms folds when the bladder is empty but opens out as the bladder fills and expands.
Why do ureters get blocked?
Because the hollow areas are narrow, ureters can become blocked by debris such as salt crystals which have stuck together to create urinary stones. Complete blockage in one tube causes high pressures and urine buildup in its attached kidney and requires emergency surgery before permanent damage is done.
How long is the ureter tube?
Ureters are two narrow but relatively long tubes (approximately 25 – 30 cm) which leave the kidneys and enter the urinary bladder.
Why does urine not flow back to the kidneys?
Once the urine is transported into the bladder it does not flow back due to directional forces of the ureter muscle layers and the flattened ends of the ureters where ureter and bladder meet (the vesicoureteral junction). This flattening increases as the bladder fills, making it difficult for urine to flow back towards the kidneys. However, this can occur in cases of vesicoureteral reflux due to anatomical abnormalities in ureteral positioning at the vesicoureteral junction or in nerve disorders where peristalsis and muscle tone are affected.
How many ureters are there in the body?
There are two ureters in total. Each one is a muscular duct of 25 – 30 cm in length with narrow lumen, that carries urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder and also connects the two structures. The ureters run inferiorly from the apex of the renal pelves (pleural for pelvis) at the hila (pleural for hilum) of the kidneys, passing over the pelvic brim at the bifurcation of the common iliac arteries. They then run along the lateral wall of the pelvis and enter the urinary bladder, forming the upper two points of the urinary bladder trigone. The abdominal parts of the ureters adhere closely to the parietal peritoneum and are retroperitoneal throughout their course.
What is the function of the urinary bladder?
Urine production and the control of its composition is exclusively the function of the kidneys. The urinary bladder is responsible for storage of urine until it is voided. The ureters and urethra are simply passages for the transportation of urine into- and from the urinary bladder respectively. The two ureters and urethra form a trigone in the urinary bladder. This trigone indicates the three points of attachments of these passages to the urinary bladder.
What are the parts of the urinary system?
The system is divisible into upper and lower parts. The upper part located within the abdomen and consists of the kidneys and a large portion of the ureters. The lower part constitutes the pelvic urinary organs, and includes the short portion of the ureters, the urinary bladder and the urethra.
How to remove calculi?
The presence of calculi can often be confirmed by abdominal radiographs or an intravenous urogram. Ureteric calculi may be removed by open surgery, endoscopy (Endo-urology), or by lithotripsy.
How does the urinary system regulate blood pressure?
By eliminating fluid and waste, the urinary system regulates important physiological parameters, such are blood volume and consequently the blood pressure, the pH of the blood by eliminating acids and bases, and electrolyte balance by sophisticated mechanisms of reabsorbtion and excretion which depend upon the needs of the body.
Which part of the urinary system stores urine?
Lower (pelvic part) Urinary bladder - muscular sac that stores the urine which allows urination to be controlled. Urethra - tube that transports urine from the urinary bladder to outside of the body (in males additional function is to transport semen after ejaculation) Clinical relations.
Why is the kidney removed from the donor?
The kidney can be removed from the donor without damaging the suprarenal gland because of the weak septum of renal fascia that separates the kidney from this gland.
How does the urinary system work?
The urinary system's function is to filter blood and create urine as a waste by-product. The organs of the urinary system include the kidneys, renal pelvis, ureters, bladder and urethra.
What muscles help keep urine from leaking?
Two sphincter muscles. These circular muscles help keep urine from leaking by closing tightly like a rubber band around the opening of the bladder. Nerves in the bladder. The nerves alert a person when it is time to urinate, or empty the bladder. Urethra.
How many ureters are there in the body?
Two ureters. These narrow tubes carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. Muscles in the ureter walls continually tighten and relax forcing urine downward, away from the kidneys. If urine backs up, or is allowed to stand still, a kidney infection can develop. About every 10 to 15 seconds, small amounts of urine are emptied into the bladder from the ureters.
What tube allows urine to pass outside the body?
Urethra. This tube allows urine to pass outside the body. The brain signals the bladder muscles to tighten, which squeezes urine out of the bladder. At the same time, the brain signals the sphincter muscles to relax to let urine exit the bladder through the urethra.
How do kidneys remove urea from the blood?
Release hormones to regulate blood pressure. Control production of red blood cells. The kidneys remove urea from the blood through tiny filtering units called nephrons.
What is the ball of urine called?
Each nephron consists of a ball formed of small blood capillaries, called a glomerulus, and a small tube called a renal tubule. Urea, together with water and other waste substances, forms the urine as it passes through the nephrons and down the renal tubules of the kidney. Two ureters.
What is the function of the kidneys and urinary system?
The kidney and urinary systems help the body to eliminate liquid waste called urea, and to keep chemicals, such as potassium and sodium, and water in balance. Urea is produced when foods containing protein, such as meat, poultry, and certain vegetables, are broken down in the body. Urea is carried in the bloodstream to the kidneys, where it is removed along with water and other wastes in the form of urine.
What tests are used to determine the root cause of a urine problem?
If these have abnormal results, additional exams may be necessary to determine the root cause of the problem. Tests used for evaluating the urine system are generally referred to as urodynamic exams and can include uroflow tests, postvoid residual volume, cystometry, electromyography, and voiding pressure studies.
What organs are responsible for the flow of urine to the bladder?
Ureters: Once urine forms in the kidneys, it flows through small tubes (ureters) to the bladder. The ureters are typically between 8 and 10 inches in length. Muscles surrounding the ureters expand and contract to help urine flow to the bladder. Bladder: The bladder is a muscular organ that functions like a balloon.
What are the health problems of the urinary system?
Various health problems can arise in the urinary system. The most common conditions include: 1 Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or enlarged prostate: This occurs only in men and is a result of aging. The prostate is a walnut-sized gland that is located by the neck of the bladder, surrounding the urethra. As the prostate enlarges, it places pressure on the urethra. Such compression can cause the urethra to narrow and, in some cases, close completely. If this takes place, a patient may find it very difficult to urinate. 2 Kidney stones: Kidney stones are a common urological condition in both men and women. Kidney stones form when minerals and other solid substances accumulate in the kidneys or along any part of the urinary tract. When they're too large, these stones can block the flow of urine from the body. 3 Urinary tract infections (UTIs): Urinary tract infections also occur in both men and women. UTIs can be present in any part of the urinary system, from the kidney (pyelonephritis) to the bladder (cystitis) to the urethra (urethritis).
How long does urine stay in the bladder?
As the amount of urine in the bladder increases, the bladder will expand. The average bladder can hold up to 2 cups of urine for two to five hours.
Where do UTIs occur?
Urinary tract infections (UTIs): Urinary tract infections also occur in both men and women. UTIs can be present in any part of the urinary system, from the kidney (pyelonephritis) to the bladder (cystitis) to the urethra (urethritis).
Where does the urethra go when the bladder is full?
In men, the urethra travels through the penis and in women, the urethra ascends above the vaginal opening. When the bladder becomes full, nerves will send signals to the brain indicating that it is time to eliminate urine from the body.
Where does urine go when it is eliminated?
Elimination: Elimination occurs when urine moves from the bladder to the urethra and then out of the body.
Why is the arrangement of the glomerular capillaries in series with the peritubular capillaries important?
The arrangement of the glomerular capillaries in series with the peritubular capillaries is important to maintain a constant pressure in the glomerular capillaries , and thus a constant rate of filtration, despite momentary fluctuations in blood pressure.
What is the filtration process in the kidney?
Kidney Filtration. The glomerular capillaries, peritubular capillaries and the Bowman's capsule are all integral to the filtration process. In the nephron, approximately 20 percent of the blood gets filtered under pressure through the walls of the glomerular capillaries and Bowman's capsule. The filtrate is composed of water, ions (sodium, ...
Does blood appear in urine?
The filtrate only includes small molecules and water. No red blood cells get filtered. Therefore, no blood appears in the urine under normal conditions. If you find blood in your urine, you should contact your physician as soon as possible because it could be a sign of kidney problems.
How do uroliths form?
These compound uroliths form when factors promoting precipitation of one mineral type are superseded by factors promoting precipitation of a different type of mineral.
What is Bowman's space?
Bowman's space—The space between the visceral and parietal layers of Bowman's capsule into which the glomerular filtrate passes before emptying into the proximal convoluted tubule. Bowman's space is also called the capsular space.
What is the process of podocytes in the foot?
Foot processes of podocytes—Specialized cytoplasmic processes of podocytes that interdigitate to form filtration slits through which glomerular filtrate enters Bowman's space (uriniferous space)
Which cells are contractile and phagocytic and are able to synthesize collagen and mes?
Mesangial cells —Pluripotential modified pericytes that are contractile and phagocytic and are able to synthesize collagen and mesangial glycoprotein matrix
How many portals of entry/pathways of spread?
Portals of Entry/Pathways of Spread,637
What does ADH stand for in e-glossary?
E-Glossary 11-1 Glossary of Abbreviations and Terms. ADH—Antidiuretic hormone. Azotemia—Excess of urea, creatinine, and other nitrogenous waste products in the blood. Bowman's capsule—Double-walled, cup-shaped dilation that surrounds the glomerulus and forms the beginning of the nephron.
Where are calculi formed?
Nephrolithiasis—The formation of calculi or stones (uroliths) within the kidney, typically within the renal pelvis
What is glomerular filtration?
Together they receive over a liter of blood each minute, and eliminate around 1.5 litres of urine per day, efficiently getting rid of excess water and waste products that would otherwise cause you some serious problems.
What is the first step in making urine?
Glomerular filtration is the first step in making urine. It is the process that your kidneys use to filter excess fluid and waste products out of the blood into the urine collecting tubules of the kidney, so they may be eliminated from your body.
What is the diaphragm between the slits?
A thin diaphragm between the slits acts as a final filtration barrier before the fluid enters the glomerular space. Together the glomerulus and glomerular capsule filtering unit are known as a renal corpuscle.
Why do the two arterioles change size?
The two arterioles change in size to increase or decrease blood pressure in the glomerulus. In addition, efferent arterioles are smaller in diameter than afferent arterioles. As a result, pressurized blood enters the glomerulus through a relatively wide tube, but is forced to exit through a narrower tube.
What is the glomerulus and glomerular capsule filtering unit?
Together the glomerulus and glomerular capsule filtering unit are known as a renal corpuscle.
How much blood does the heart supply to the kidneys?
Together, these unique features plus the fact that your heart is supplying your kidneys with over a liter of blood per minute (around 20% of its output) maintain a high glomerular capillary pressure and the filtration function of the kidney, regardless of fluctuations in blood flow.
How do kidneys work?
You can think of your kidneys as being your body’s natural blood filter. They are able to control the amount of water and substances dissolved in your body fluids (solutes) by reabsorbing what you need and producing urine to get rid of the rest. The production of urine is obligatory, meaning that it is made regardless of what is going on with your body; for example, you still make urine even when you are severely dehydrated. This occurs because of the need to remove various solutes from the body in order to keep internal conditions stable and relatively constant (homeostasis), so that your all of your body’s physiological processes continue operating effectively. Making urine is a complicated process, and to do it, each of your kidneys contain around a million specialized structures, called nephrons.
What is the first lesson about urine?
This lesson is about the first one. Urine is one of the body's waste products. It is primarily composed of water and urea. Urea is a special nitrogenous waste compound that the body must routinely remove. Urine formation occurs in the kidney in three stages: filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. 3:22.
What is the first stage of the kidney?
Stage 1: filtration . The kidney is the body's blood filtering system. Blood vessels visit the kidney and enter a special ball of capillaries called the glomerulus. The glomerulus is nestled within a region of the kidney called the Bowman's Capsule.
Why is antidiuretic hormone false?
False because the correct statement is: The antidiuretic hormone constantly regulates and balances the amount of water in the blood. True. True. False because the correct statement is: Toxic substances in the body do not go through filtration and reabsorption.
What is the name of the ball of capillaries within the kidneys?
Glomerulus: ball of capillaries within the kidneys. Bowman's Capsule: where filtration takes place. Filtrate: is made up of water, sugar, salts, and amino acids. Loop of Henle: where the filtrate loses and gains water and salt.
What is the substance that enters the kidney?
Water, sugar, salts, amino acids, nitrogenous wastes, and other tiny things enter the kidney as a substance called the filtrate. Cells and large blood proteins that cannot fit through remain in the blood vessels. The filtrate entering the kidney is like pre-pre-urine.
How does urine form in the kidney?
The first is filtering things out of the blood and into the filtrate. The next is reabsorbing the important stuff from the filtrate. Finally, anything that needs to be shipped right out of the body is secreted out.
Why is the kidney special?
This region of the kidney is special because many things can be removed from the filtrate. These valuable things are recollected, or reabsorbed, by the body. Glucose, certain salts, vitamins, hormones, and amino acids are restored to the body and will not be included in urine.