What is the structure of fimbriae?
Jan 23, 2018 · The fimbriae are connected to the ovary. Small epithelial cells — those that line cavities throughout the body — with small, slender cilia …
What are fimbriae and pili made of?
Apr 07, 2022 · Like flagella, they are composed of protein. Fimbriae are shorter and stiffer than flagella, and slightly smaller in diameter. Generally, fimbriae have nothing to do with bacterial movement (there are exceptions, e.g. twitching movement on Pseudomonas).
What is the difference between sex pili and fimbriae?
Mar 05, 2022 · Fimbriae Characteristics The fimbriae tubae is made of finger-like projections that are located at the ends of Fallopian tubes near the ovaries. It is comprised of longitudinal muscle fibers. It...
Why are fimbriae important to bacteria?
Both fimbriae are composite structures composed of a thick, supporting shaft joined to a thin, adhesive tip fibrillum [41,42]. The supporting shaft of all of the E. coli fimbriae comprises a single strand composed of subunits arranged in a helical structure.

What do fimbriae contain?
Are fimbriae composed of protein?
The fimbriae and pili have a shaft composed of a protein called pilin. At the end of the shaft is the adhesive tip structure having a shape corresponding to that of specific glycoprotein or glycolipid receptors on a host cell (Figure 2.5C. 1).Apr 9, 2022
What are bacterial fimbriae made of?
What is the main protein component of fimbriae?
What are fimbriae microbiology?
What is glycocalyx made up of?
What are endotoxins made of?
Is fimbriae prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
What are fimbriae quizlet?
What type of bacteria have fimbriae?
Is fimbriae a virulence factor?
What role do fimbriae play in both biofilm formation?
Uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Rachel R. Spurbeck, Harry L.T. Mobley, in Escherichia coli (Second Edition), 2013
Haemophilus influenzae
Nicola J. High, ... Joseph D. Schwartzman, in Molecular Medical Microbiology (Second Edition), 2015
DISEASE STATES AND VACCINES: SELECTED CASES
FIM are also known as agglutinogens 2 and 3 because they induce antibodies able to agglutinate the bacterium (agglutinins). It is generally accepted that fimbriae are also involved in the adhesion of B. pertussis to the ciliated cells, although their precise role in the development of infection has not been clarified.
Urinary Tract Infections and the Mucosal Immune System
Ines Ambite, ... Catharina Svanborg, in Mucosal Immunology (Fourth Edition), 2015
Uropathogenic Escherichia coli
Farah Bahrani-Mougeot, ... Harry L.T. Mobley, in Escherichia Coli, 2002
Protein Secretion and Membrane Insertion Systems in Bacteria and Eukaryotic Organelles
Milton H. Saier, ... Ming Ren Yen, in Advances in Applied Microbiology, 2008
Escherichia coli: virulence, stress response and resistance
The other fimbriae referred to above are less well understood, compared with type-1 fimbriae but are considered to be virulence factors (Cassels and Wolf, 1995 ). Each type is associated with a limited number of serogroups of enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC).
Fimbriae Definition
The fimbriae or fimbria (Singular) are bristle-like short fibers occurring on the surface of several gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
Pili Definition
Pili or Pillus (Plural) are hair-like appendages which are seen on the surface of many gram-negative bacteria and archaea.
Type IV pili
Some of the pili is known as type IV pili (T4P), it generate motile forces.
Type V Pili
This is a unique type of pili which is mainly found in bacteria species of the class Bacteroidia.
Mechanism of Twitching Motility
Pre-PilA is occurred within the cytoplasm and then passes through the inner membrane.
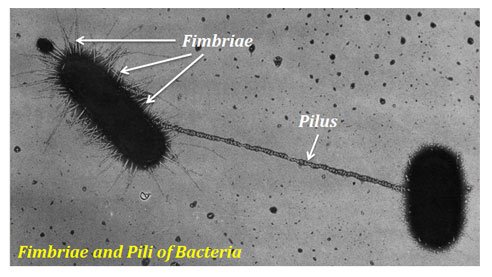
Structure and Function of Fimbriae and Pili
They are hair-like, filamentous, surface appendages present on the bacterial cell. The main characteristics are:
Fimbriae
Fimbriae are also called “short attachment pili”. They attach to the host surface and help bacteria colonise and cause infection. They are present on the overall surface or concentrated towards the poles.
Pili or Conjugative Pili
Pili are generally referred to as the appendages, which are involved in the conjugation. They are also known as long conjugative pili. They are longer than fimbriae and involved in the cell to cell attachment during conjugation for DNA transfer.
Type IV Pili
They are responsible for the twitching motility. They adhere to the surface and bring about the movement by contraction. Many archaea contain this type of pili, which help them to adhere to various surfaces.

Fimbriae Definition
- The fimbriae or fimbria (Singular) are bristle-like short fibers occurring on the surface of several gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
- It helps in attachment of bacterial cells on the surface of host cell and on some inanimate objects. For example, E. coliutilizes them to get attached to the mannose receptors.
- It is also known as “attachment pilus” and mainly found on Gram-negative and Gram-positive …
- The fimbriae or fimbria (Singular) are bristle-like short fibers occurring on the surface of several gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
- It helps in attachment of bacterial cells on the surface of host cell and on some inanimate objects. For example, E. coliutilizes them to get attached to the mannose receptors.
- It is also known as “attachment pilus” and mainly found on Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria.
- A single bacteria may contain 1,000 fimbriae.
Pili Definition
- Pili or Pillus (Plural) are hair-like appendages which are seen on the surface of many gram-negative bacteria and archaea.
- A special type of pili known as sex pili helps in bacterial conjugation.
- They are antigenic and also fragile and constantly replaced.
- These are visible under electron microscope.
Type IV Pili
- Some of the pili is known as type IV pili (T4P), it generate motile forces.
- The exterior ends of the pili adhere to a solid substrate, either the solid surface to which the bacterium is appended or to another bacteria. Then, during the pili contract, they forced the bacter...
- The structure of type IV pili is similar to the component flagellins of archaella (archaeal flagel…
- Some of the pili is known as type IV pili (T4P), it generate motile forces.
- The exterior ends of the pili adhere to a solid substrate, either the solid surface to which the bacterium is appended or to another bacteria. Then, during the pili contract, they forced the bacter...
- The structure of type IV pili is similar to the component flagellins of archaella (archaeal flagella) and both of them are associated to the Type II secretion system (T2SS).
- This type of pili mainly found in some Gram-positive bacteria (e.g., clostridia) and the majority of Gram-negative bacteria.
Type V Pili
- This is a unique type of pili which is mainly found in bacteria species of the class Bacteroidia.
- While the mechanism through which this structure is assembled is not clearly understood, researchers have suggested that it involves protease-mediated polymerization.
- Like Type IV pili, this pilus is also involved in adhesion and biofilm formation.
Mechanism of Twitching Motility
- Pre-PilA is occurred within the cytoplasm and then passes through the inner membrane.
- Pre-PilA is entered within the inner membrane.
- Next, a peptidase called PilD, separates a leader sequence, therefore producing the Pre-PilA shorter and into PilA, the central building-block protein of Pili.
- A NTP-Binding protein known as PilF supply energy for Type IV Pili Assembly.
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fimbria_(bacteriology)
- http://textbookofbacteriology.net/structure_3.html
- https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Microbiology/Book%3A_Microbiology_(Kaiser)/Unit_1%…
- https://byjus.com/neet/fimbriae-and-pili