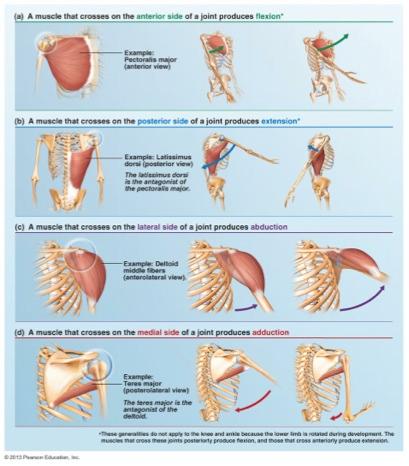
What does a fixator muscle do during exercise movement?
A fixator muscle is a muscle that acts as a stabilizer of one part of the body during movement of another part. An example: BICEP CURL: Agonist_Prime mover muscle: Biceps. Antagonist_Opposing muscle group: Triceps. Synergist_Helping muscle group (assists):Brachiradialis. Fixators_Prevents unecessary movement:Abs, Back,Shoulders and wrists.
What is the role of fixator muscle in human body?
- Concentric contraction : Any contraction where the muscle shortens under load or tension is known as a concentric contraction. ...
- Eccentric contraction : Muscles not only ‘shorten’ but can also lengthen under load or tension. ...
- Isometric contraction: Muscles don’t actually need to move (shorten or lengthen) at all to contract or develop tension. ...
What is fixator muscle is used when doing a press up?
What Is the Stabilizer Muscle During Pushups?
- Shoulders. The posterior deltoid and rotator cuff muscles act as stabilizers of the shoulder joint during the pushup.
- Back. There are two muscle groups of the back that function as stabilizers while you do pushups. ...
- Abdominals. The rectus abdominis acts as a stabilizer of the spine, opposite to the erector spinae, during the pushup.
- Hips and Legs. ...
What is the fixator muscle used in sit ups?
What is the fixator muscle in a sit-up? The abdominals can act as fixators to stabilise the body for hip and knee movements. What muscles are used in burpees? With burpees, the focus is on a full-body calisthenics workout that aims to build muscle strength and endurance in both your lower and upper body. A standard burpee exercise works to ...
What is a fixator muscle example?
The trapezius muscle can act as a fixator when the biceps is flexing the elbow joint. The abdominals can act as fixators to stabilise the body for hip and knee movements.
Where is fixator muscle?
The majority of fixator muscles are found working around the hip and shoulder joints. Many muscles are attached to more than one bone via tendons. When this happens the muscles are said to be 'multiarticulate' or 'multijoint muscles'.
What type of muscle is a fixator?
Fixator: The fixator in a movement is the muscle(s) that stabilises the origin of the agonist and the joint that the origin spans (moves over) in order to help the agonist function most effectively. In the bicep curl this would be the rotator cuff muscles, the 'guardians of the shoulder joint'.
What is a fixator and synergist muscle?
• Synergist: a muscle which assists the prime mover. • Fixator: a muscle or group of muscles which stabilises the body or a joint whilst a. movement is performed.
What is a fixator in PE?
Fixator. A muscle which acts as the stabilizer and helps the agonist work effectively of. one part of the body during movement of another part.
What is the fixator of the shoulder?
In the human body, we have so many examples of fixator muscles. The muscles attached to the shoulder girdle to the trunk acts as the fixator for the deltoid action. Fixators are not only fixing the bony component while the movement of agonists, antagonists or synergists and also have dynamic properties.
What is a fixator quizlet?
Fixator: when a synergist immobilizes a bone or a muscle's origin so that the prime mover has a stable base on which to act. Explain how a muscle's position relative to a joint affects its action.
What is shunt muscle?
A skeletal muscle with its proximal attachments near the joint or joints at which it acts, and its distal attachments at some distance from the joints, so that the greater part of its force is directed along the bones, tending to pull joint surfaces together. This makes shunt muscles good stabilizers.
What muscles stabilize joint activity?
Skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. Skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells.
What is the difference between synergist and fixators?
The terms synergist and antagonist relate to the action of single muscles on the movement about one axis of one joint; while the term fixator relates to the concerted action of several muscles (synergists and antagonists) on all possible movements of a joint.
What is synergist and antagonist?
Following contraction, the antagonist muscle paired to the agonist muscle returns the limb to the previous position. Synergist muscles act around a movable joint to produce motion similar to or in concert with agonist muscles, allowing for a range of possible movements.
What is the role of a synergist muscle?
During forearm flexion, for example lifting a cup, a muscle called the biceps brachii is the prime mover. Because it can be assisted by the brachialis, the brachialis is called a synergist in this action (Figure 11.1. 1). A synergist can also be a fixator that stabilizes the muscle's origin.
What is the fixator of forearm flexion?
During forearm flexion, for example lifting a cup, a muscle called the biceps brachii is the prime mover. Because it can be assisted by the brachialis, the brachialis is called a synergist in this action (Figure 11.1. 1). A synergist can also be a fixator that stabilizes the muscle's origin.
What is a fixator quizlet?
Fixator: when a synergist immobilizes a bone or a muscle's origin so that the prime mover has a stable base on which to act. Explain how a muscle's position relative to a joint affects its action.
What is the fixator for elbow flexion?
The Orthofix Elbow Fixator is a unilateral humero- ulnar external fixation device designed to permit controlled movement about the centre of rotation of the elbow joint. It allows immediate pronation and supination and early flexion and extension of the forearm, thus preventing post-operative stiffness.
What is the role of the fixator muscle?
What Is the Role of a Fixator Muscle? The fixator muscles stabilize a section of the body when another section moves. The muscle allows the antagonist muscles to move effectively during normal movement or exercise. Some muscles attach to one or more bones.
Which muscle prevents the radius and scapula from moving during a curl?
The bicep connects to the bone in two places, and the fixator allows one area to move during the curl. As the bicep contracts, the radius and scapula come together. The fixator muscle prevents the scapula from moving in order ...
Which muscle prevents the scapula from moving?
The fixator muscle prevents the scapula from moving in order to achieve full movement of the radius area. Most fixator muscles surround the hip and shoulder bones. ADVERTISEMENT.
What is a fixator?
fixator. 1. A muscle being used to hold a body part in a certain position or to restrict its movement, usually so that other muscles may operate effectively. 2. A device, such as an EXTERNAL FIXATOR, used to maintain parts in alignment. Collins Dictionary of Medicine © Robert M. Youngson 2004, 2005.
What is the purpose of a fixator?
2. A muscle or muscle group that works to stabilize a joint or body region while other muscles initiate movement.
What is the best fixator for a distal fracture of the tibia?
Open proximal and distal fractures of tibia treated with Naseer Awais External Fixator with T-clamp
How long after fixator removal can you assess range of movement?
Range of movements was assessed at third month for one year after the fixatorremoval.
What is a rod in skeletal fixation?
A device providing rigid immobilization through external skeletal fixation by means of rods (f.'s) attached to pins that are placed in or through the bone.
What is an external fixator?
An external fixatorconstruct includes stainless steel pins that must engage both a near and far cortex of the bone.
How many pins are used for compound fracture?
All clinical cases of compound fracture were stabilized with epoxy external skeletal fixatorby inserting four trans fixation pins proximal to fracture and four distal to fracture.
Which muscle provides the major force to complete the movement?
1. Agonist: The agonist in a movement is the muscle (s) that provides the major force to complete the movement.
Which muscle is the antagonist in a movement?
2. Antagonist: The antagonist in a movement refers to the muscles that oppose the agonist. During elbow flexion where the bicep is the agonist, the tricep muscle is the antagonist.
What muscles are used in bicep curls?
In the bicep curl this would be the rotator cuff muscles, the ‘guardians of the shoulder joint’. The majority of fixator muscles are found working around the hip and shoulder joints.
Why do skeletal muscles contract isometrically?
Many skeletal muscles contract isometrically in order to stabilise and protect active joints during movement. So while the quadriceps muscles are contracting concentrically during the upward phase of the squat, and eccentrically during the downward phase, many of the deeper muscles of the hip contract isometrically to stabilise the hip joint during the movement.
What is the contraction of muscles that doesn't need to move?
3. Isometric contraction: Muscles don’t actually need to move (shorten or lengthen) at all to contract or develop tension. An isometric contraction refers to any contraction of muscles where little or no movement occurs. If during the squat the person stopped moving at a certain point (say halfway up) and held that position for 10 seconds, ...
Which muscle is the agonist in a bicep curl?
In the bicep curl which produces flexion at the elbow, the biceps muscle is the agonist, as seen in the image below. The agonist is not always the muscle that is shortening (contracting concentrically). In a bicep curl the bicep is the agonist on the way up when it contracts concentrically, and on the way down when it contracts eccentrically.
Why is it important to understand muscle contractions?
It will help you ensure your programme designs are specific to your clients ability and goals as well as keeping them safe with good technique.
