NFPA 70E Arc Flash and Shock Hazard Boundaries
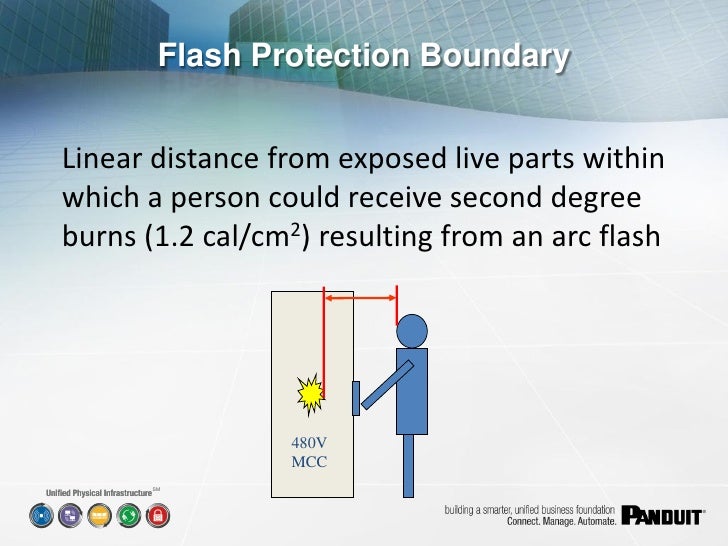
- Flash protection boundary (outer boundary) The flash protection boundary is the farthest established boundary from the energy source. ...
- Limited approach boundary The limited approach boundary is the minimum distance from an exposed live component where unqualified personnel may safely stand. ...
- Restricted approach boundary
What is the flash protection boundary of a building?
Flash protection boundary (outer boundary) The flash protection boundary is the farthest established boundary from the energy source. If an arc flash occurred, this boundary is where an employee would be exposed to a curable second degree burn (1.2 calories/cm2).
What is arc flash protection boundary (afpb)?
Arc Flash Protection Boundary – Distance and the Unprotected Person People that are not adequately protected must stay from a potential arc flash source by a minimum distance known as the Arc Flash Protection Boundary (AFPB). NFPA 70E defines the AFPB as:
What is the difference between flash boundary and limited approach boundary?
When an energized conductor is exposed, you may not approach closer than the flash boundary without wearing appropriate personal protective clothing and personal protective equipment. 2. Limited approach boundary The limited approach boundary is the minimum distance from an exposed live component where unqualified personnel may safely stand.
What is an arc-flash boundary?
An arc-flash boundary is a shock-hazard approach boundary that serves as a minimum safe distance from electrical equipment. An employer operating within the arc-flash boundary must use personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or other safety equipment.

What are the four protection boundaries?
The Prohibited Approach Boundary was removed from NFPA-70E in 2015.Flash protection boundary (outer boundary) The flash protection boundary is the farthest established boundary from the energy source. ... Limited approach boundary. ... Restricted approach boundary. ... References.
What are shock protection boundaries?
There are two shock protection boundaries; the Limited Approach Boundary (LAB) and the Restricted Approach Boundary (RAB), and one Arc Flash Boundary (AFB) that must be established in order to provide a safe distance for personnel from exposed, energized electrical components.
What is the distance to live electrical parts for the flash protection boundary?
All parts of the body inside the flash protection boundary have to be protected by suitable PPE. For example for voltage between 50 to 600 Volts, the flash protection boundary is 4 feet.
Why is the arc flash boundary defined?
The Arc Flash Boundary has been developed by NFPA70e to minimize the risk of arc flash injury to electrical workers, working in proximity to energized electrical equipment. The Arc Flash Boundary determines the distance from the equipment at which the Incident Energy of an arc flash would be 1.2 cal/cm².
What is the arc flash boundary distance?
The Arc Flash Boundary marks the distance from the equipment at which the Incident Energy of an arc flash would be 1.2 cal/cm². At this energy level, an unprotected worker would probably receive second-degree burns as a result of an arc flash.
What are the limited restricted prohibited and flash protection boundaries?
Limited approach boundary A person crossing this line must be qualified to do the job/task. They must wear flash protective equipment. Unqualified workers are prohibited from crossing this boundary. Restricted approach boundary A person crossing this line enters into restricted space.
How is flash protection boundary calculated?
The arc flash boundary is calculated to 1.2 calories/cm2 of incident energy. That's the distance where a worker without appropriate PPE would receive second-degree burns. Sometimes this boundary is the furthest one from the exposed equipment, other times the limited approach boundary is the furthest out.
At what distance do you establish the working boundary?
Depending on the type of equipment, this “working distance” as it is called, is typically defined as either 18 or 36 inches however other distances may be used. Once the incident energy (IE) has been calculated, it can be used to select the appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
What are the 3 approach boundaries?
Under NFPA 70E, there are three boundaries that are observed—limited approach, restricted approach, (the shock protection boundaries) and arc flash boundary.
How does NFPA define the arc flash boundary?
NFPA 70E defines the arc flash boundary as “…a distance from a prospective arc source within which a person could receive a second degree burn if an electrical arc flash were to occur.” In more technical terms, it is defined as the distance at which, in the event of an arc flash, a worker would be exposed to a thermal ...
What is an arc flash boundary?
An arc-flash boundary is a shock-hazard approach boundary that serves as a minimum safe distance from electrical equipment. An employer operating within the arc-flash boundary must use personal protective equipment (PPE) and/or other safety equipment.
Is the arc flash boundary legal?
It is an OSHA-recognized consensus standard; therefore, the arc-flash boundary has legal weight as a boundary that must be observed in workplaces in order for employers to meet their general duty obligations for workplace safety. The NFPA prescribes specific calculations for determining the arc-flash boundary under Annex D of this standard.
How far is an AFPB?
Let’s say an arc flash study shows AFPBs from 0.5 feet to 5.3 feet. Using the simplified method, a standardized AFPB can be based on the largest value of 5.3 feet. Perhaps round it up to 6 feet. This makes the electrical safety program much easier.
What will the results of an arc flash calculation study produce?
The results of an arc flash calculation study will likely produce a different AFPB for each piece of equipment depending on its individual upstream protective device clearing time and the available short circuit current. With the possibility of so many different boundaries, it can be easy to make a mistake.
Does an arc flash drop off?
An arc flash in open air does drop off as the inverse distance squared. However, if the arc flash occurs inside an enclosure such as a panel or motor control center, the energy behaves more like it is being shot out of a cannon and a greater distance will be required. BUY NOW!
What is the flash protection boundary?
The flash protection boundary is the farthest established boundary from the energy source. If an arc flash occurred, this boundary is where an employee would be exposed to a curable second degree burn (1.2 calories/cm2).
What is the NFPA approach boundary?
As a result of accidents in the workplace related to arc flash, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) has developed specific approach boundaries designed to protect employees while working on or near energized equipment.
What temperature does an arc flash?
Arc flash temperatures can reach or exceed 35,000 °F (19,400 °C) at the source of the arc. The massive energy released in the fault rapidly vaporizes the metal conductors involved, blasting molten metal and expanding plasma outward with extraordinary force.
What is restricted approach?
The restricted approach boundary is the distance from an exposed part which is considered the same as making contact with the live part. Only qualified personnel wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), having specified training to work on energized conductors or components, and a documented plan justifying the need to perform this work may cross the boundary and enter the Restricted Space. Insulated gloves, tools, and equipment are required within this boundary.
How many pages are there in the Arc Flash Hazards Guide?
Our free 130-page Guide to Arc Flash Hazards is the most comprehensive resource in the industry and gives you practical advice to reduce accidents and keep employees safe. Download yours today!
What is the NFPA 70E?
NFPA 70E is the major industrial standard for safe electrical work in the United States. It defines three protective boundaries around electrical equipment. One of the boundaries, called the Arc Flash Boundary, is based on the expected incident energy from an arc flash, and is intended to protect workers from burns if such an accident occurs. The other two are the Limited Approach Boundary and the Restricted Approach Boundary, which are based on the voltage of the equipment, and are intended to protect workers from electric shock.
Is an arc flash hazard a risk?
Most equipment that poses an arc flash hazard also presents a risk of electric shock. However, the two hazards need to be addressed separately. The two shock protection boundaries are intended to protect workers from this second hazard.
Can you get burns from an arc flash?
At this energy level, an unprotected worker would probably receive second-degree burns as a result of an arc flash. Second-degree burns are certainly not desirable, but they are still treatable. Third-degree, untreatable burns would be expected only for workers who are closer to the equipment, inside the Arc Flash Boundary.
What is the arc flash boundary?
While the other two boundaries deal with shock hazard, the arc flash boundary refers specifically to arc flash hazards and explains that 1.2 calories/cm 2 of incident energy, is the distance at which a worker will receive second-degree burns in the event of an arc flash incident without appropriate arc rated personal protective equipment.
What are the boundaries of NFPA 70E?
Under NFPA 70E, there are three boundaries that are observed—limited approach, restricted approach, (the shock protection boundaries) and arc flash boundary . These boundaries trigger multiple requirements in 70E including but not limited to determining the type and level of PPE and qualifications required to cross into each level. As part of a larger training and safety program, these boundaries are put in place to minimize risk through avoidance or the use of PPE.
What is the boundary of a shock?
The outer boundary at which a worker may be exposed to a shock hazard, the limited approach boundary, refers to the “stay back” distance for non-qualified workers. Qualified workers may cross this boundary after shock and arc flash risk assessments are performed with appropriate PPE if needed.
What is NFPA 70E?
NFPA 70E is a complicated document filled with many different practices and procedures, but even this document only does so much. While the document introduces and requires a safety program, programs are just that: Policies employees feel like they have to follow.
What is the arc flash boundary?
Originally this was referred to as the arc flash protection boundary… until someone realized it didn’t offer much protection.
Why do I need it and what do I do with it?
During any electrical job (that will expose people to an arc flash) the worker must set up a barricade at or beyond the boundary.
An example arc flash boundary calculation
Let’s say I’m racking out a 5kV circuit feeder breaker that is fed by another 5kV circuit breaker (which I’ll refer to as the main breaker). Above that is a transformer with an MVA equal to 10.
I hope this helps!
This should give you a handle on how to calculate arc flash boundaries. It’s not perfect, and remember that there are some limitation to this method, but when you have nothing else it will certainly do.
What is an arc flash?
Simply put, an arc flash is a phenomenon where a flashover of electric current leaves its intended path and travels through the air from one conductor to another, or to ground. The results are often violent and when a human is in close proximity to the arc flash, serious injury and even death can occur.
What is required to wear PPE for arc flash?
Employees must follow the requirements of the Arc Flash Hazard label by wearing the proper personal protective equipment (PPE), use of insulated tools and other safety related precautions. This includes not working on or near the circuit unless you are a “qualified” worker.

Equipment Considerations
The Right Tools For The Job
- Safety ratings:Test instruments must go through standardized testing in order to meet safety requirements. The CAT and voltage ratings listed on the test instrument and any accessories also need to match or exceed the electrical environment where you will use them. Look for tools that meet IEC standards with an independent lab testing verifying it. The lab’s symbol on the tool me…
Arc Flash vs Arc Blast
- Following these safety guidelines will help you stay safe in the event of an arc fault, but it’s important to also understand the how and what. How is an arc fault caused and what is the difference between arc flash and arc blast? Read arc flash vs arc blastfor more information.
Related Resources