How does genetic information flow in an organism?
The information stored in the order of bases is organized into genes: each gene contains information for making a functional product. The genetic information is first copied to another nucleic acid polymer, RNA (ribonucleic acid), preserving the order of the nucleotide bases.
What are the effects of genetic drift and gene flow?
What are the effects of genetic drift and gene flow quizlet? Genetic drift, gene flow, and mutation can cause microevolution, or changes in allele frequencies. Gene flow occurs when fertile individuals or their gametes (sex cells) migrate between populations.
What is the complete set of genetic information called?
The genome is the complete set of genes in an organism. In other words, the total amount of genetic information in the chromosomes of an organism, including its genes and DNA sequences.
What is the flow of information from a DNA to a protein?
Francis Crick coined the phase "the Central Dogma" to describe the flow of information from nucleic acid to protein. Information encoded in DNA is transcribed to RNA, and RNA is translated to a linear sequence of amino acids in protein.
What is the flow of genetic information quizlet?
The flow of genetic information is from: synthesized on a DNA template. In transcription (DNA → RNA), the mRNA is: transcription occurs in the nucleus, and the messenger RNA is processed before it travels to the cytoplasm.
What are the steps in the genetic flow of information?
5: Flow of Genetic Information5.1: DNA Replication. The only way to make new cells is by the division of pre-existing cells. ... 5.2: DNA Repair. ... 5.3: Transcription. ... 5.4: Regulation of Transcription. ... 5.5: RNA Processing. ... 5.6: Translation.
What is the flow of genetic information in a eukaryotic cell?
In eukaryotic cells, DNA replication occurs in the nucleus, where the chromosomes reside. Genetic information in converted to RNA during the process of transcription. In eukaryotes, transcription occurs in the nucleus. Following RNA processing, RNAs exit the nucleus to the cytoplasm where they are utilized.
Why is the flow of genetic information so important to life?
For organisms to survive it is important that the information needed for survival is passed on through the generations. If a population has sufficient variation within its genetic information, it is more likely to respond successfully to changes in the environment.
How does genetic information flow from DNA to protein?
Francis Crick coined the phase “the Central Dogma” to describe the flow of information from nucleic acid to protein. Information encoded in DNA is transcribed to RNA, and RNA is translated to a linear sequence of amino acids in protein.
What is the correct flow of information from gene to protein?
The correct flow of information from gene to protein is the central dogma, which says DNA is copied to mRNA which is read to make protein.
What is the order of information flow in the nucleus?
The central dogma states that the pattern of information that occurs most frequently in our cells is: From existing DNA to make new DNA (DNA replication?) From DNA to make new RNA (transcription) From RNA to make new proteins (translation).
Who proposed genetic information flow in one direction?
This is the simplistic DNA → RNA → protein pathway published by James Watson in the first edition of The Molecular Biology of the Gene (1965). Watson's version differs from Crick's because Watson describes a two-step (DNA → RNA and RNA → protein) process as the central dogma.
What are the uses of genetic information?
Genetic information or genetic test results can be used to prevent the onset of diseases, or to assure early detection and treatment, or to make reproductive decisions. This information can also be used for nonmedical purposes, such as insurance and employment purposes.
What are the 4 steps of transcription?
The major steps of transcription are initiation, promoter clearance, elongation, and termination.
What are the main steps of transcription?
Stages of transcription. Transcription of a gene takes place in three stages: initiation, elongation, and termination.
What is the flow of information in the central dogma of biology?
Central dogma. The central dogma of molecular biology is a theory stating that genetic information flows only in one direction, from DNA, to RNA, to protein, or RNA directly to protein.
What are the three major pathways of information flow within the cell?
*What are the three major pathways of information flow within the cell? Replication, transcription, and translation—the components of the central dogma of molecular biology.
What is the purpose of RNA sequence?
The RNA sequence of messenger RNA is used to direct the synthesis of proteins in a process called translation .
What is the process of RNA production?
The actual formation of gene products requires RNA; the production of RNA on a DNA template is called transcription. The base sequence of DNA is reflected in the base sequence of RNA. Three kinds of RNA are involved in the biosynthesis of proteins. Of the three, messenger RNA (mRNA) is particularly important.
What is the function of mRNA?
Of the three, messenger RNA (mRNA) is particularly important. A sequence of three bases in mRNA specifies the identity of one amino acid in a manner directed by the genetic code. The process by which the base sequence directs the amino acid sequence is called translation. In nearly all organisms, the flow of genetic information is DNA - > RNA - > ...
What is the sequence of bases in DNA?
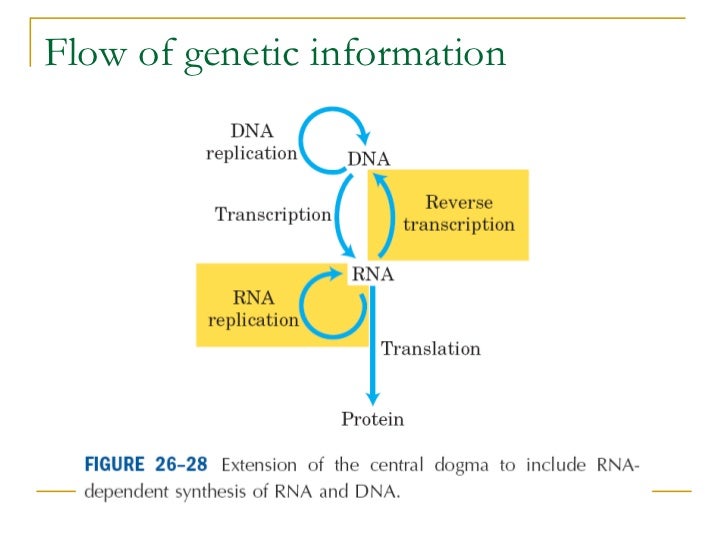
The sequence of bases in DNA encodes genetic information. The duplication of DNA, giving rise to a new DNA molecule with the same base sequence as the original, is necessary whenever a cell divides to produce daughter cells. This duplication process is called replication. The actual formation of gene products requires RNA; the production of RNA on a DNA template is called transcription. The base sequence of DNA is reflected in the base sequence of RNA. Three kinds of RNA are involved in the biosynthesis of proteins. Of the three, messenger RNA (mRNA) is particularly important. A sequence of three bases in mRNA specifies the identity of one amino acid in a manner directed by the genetic code. The process by which the base sequence directs the amino acid sequence is called translation. In nearly all organisms, the flow of genetic information is DNA - > RNA - > protein. The only major exceptions are some viruses (called retroviruses) in which RNA, rather than DNA, is the genetic material. In those viruses, RNA can direct its own synthesis as well as that of DNA. The enzyme reverse transcriptase catalyzes this process. (Not all viruses in which RNA is the genetic material are retroviruses, but all retroviruses have a reverse transcriptase. In fact, that is the origin of the term retrovirus, referring to the reverse of the usual situation with transcription.) In cases of infection by retroviruses, such as HIV, reverse transcriptase is a target for drug design. Figure 10.1 shows ways in which information is transferred in the cell. This scheme has been called the “Central Dogma” of molecular biology.
Is RNA the genetic material of a virus?
The only major exceptions are some viruses (called retroviruses) in which RNA, rather than DNA, is the genetic material. In those viruses, RNA can direct its own synthesis as well as that of DNA. The enzyme reverse transcriptase catalyzes this process. (Not all viruses in which RNA is the genetic material are retroviruses, ...
What is gene flow?
Gene flow is the exchange of alleles between two or more populations. For this reason it is sometimes referred to as allele flow or gene migration. While migrating animals often carry new alleles from one population to another, they must interbreed with the new population for gene flow to occur. In the image below, a beetle from a population ...
When does gene flow occur?
Migration occurs whenever an organism physically moves into a new area or joins a new population. However, gene flow only occurs when the populations interbreed. Even then, it is only considered gene flow if the populations are exchanging alleles and changing the allele frequency of one or both populations. 3.
What is the gene flow of a Labradoodle?
Gene flow, in this case, can be imagined as the Labradoodle. Or the half-Beagle, half-Pug mix: the Puggle. Gene flow is the Chiwe enie (Chihuahua/Dachshund), shown below. As one dog from a specific population is allowed to breed within a pure-breeding group, new alleles are brought into the mix. The gene pool is expanded, and new varieties are seen. Thus, the labradoodle has a Labrador mentality, but has Poodle hair. Artificial selection allows scientists and breeders to manipulate the timing and specifics of gene flow, to produce desirable traits.
How does gene flow affect birds?
Imagine a large population of birds on a mainland. When a big storm brews up, it forces some of the birds high into the air to avoid the storm. When the small flock comes down, they find themselves over the ocean. The wind carries them to a small island, where they set up a new home. The two populations are now sufficiently separated that they cannot regularly interbreed.
What is horizontal gene transfer?
These processes, like horizontal gene transfer, allow DNA to pass between organisms without the need for sexual reproduction. In fact, much of the diversity present in life today was caused by these gene transfers millions of years ago. The chart below shows gene flow between the different domains of life. Tree Of Life.
How do birds find themselves when the flock comes down?
When the small flock comes down, they find themselves over the ocean. The wind carries them to a small island, where they set up a new home. The two populations are now sufficiently separated that they cannot regularly interbreed. Over time, the environmental factors affecting the two different populations will differ.
Do birds interbreed with the main population?
Here, they can once again interbreed with the main population, and gene flow occurs as the new alleles from the island are introduced into the population. Likewise, if any birds go from the main population to the island population, they will bring with them the alleles selected for on the mainland.
What is the process of separating chromosomes in a cell?
Mitosis separates replicated chromosomes i to new cells; resulting cells are identical to the parent cell; and the majority of cells in body are somatic cells.
How are introns removed from mRNA transcripts?
Introns are removed from eukaryotic mRNA transcripts by splicesosomes.
What is the b sequence of a gene?
b (The nucleotide sequence of a gene usually codes for a polypeptide; some genes encode RNA molecules that are never translated, such as tRNA.)
How is RNA formed?
A molecule of RNA is formed based on the sequence of nucleotides in DNA.
Where does mRNA move?
b. mRNA moves from the nucleus to the cytoplasm following RNA processing.
