
Liquid control systems are safety systems in facilities that store chemicals while also moderating chemical fluids’ viscosities and compositions. When maintaining fluid levels, liquid control systems often need to deal with chemicals that are mixed, heated or cooled, which alters their properties.
What does a fluid control valve do?
control valve: A valve which controls the flow rate or flow direction in a fluid system. The final control element, through which a fluid passes, that adjusts the flow passage as directed by a signal from a cont-roller to modify the flow rate.
What are the components of fluid systems?
Fluid power systems consist of four basic components: reservoir/receiver (fluid storage); pump/compressor (converts mechanical power to fluid power); valve (controls direction and amount of flow); and actuators (converts fluid power to mechanical power, that is, cylinder and pistons). The connectors for these components consist of pipe, tube or ...
What are the hydraulics controls?
Hydraulic Controls, Inc. is committed to being a highly reliable local source for domestic and global fluid power products. Our goal is to be recognized by our customers as the one source that can and will meet their requirements without exceptions or excuses.
What is the purpose of hydraulic control system?
These include:
- System Overheat. The system exceeds its maximum allowable operating temperature and must be de-energized.
- Loss of System Pressure. Loss of system pressure can occur in two different ways; loss of fluid or failure of a hydraulic pump.
- Hydraulic Fluid Contamination. ...
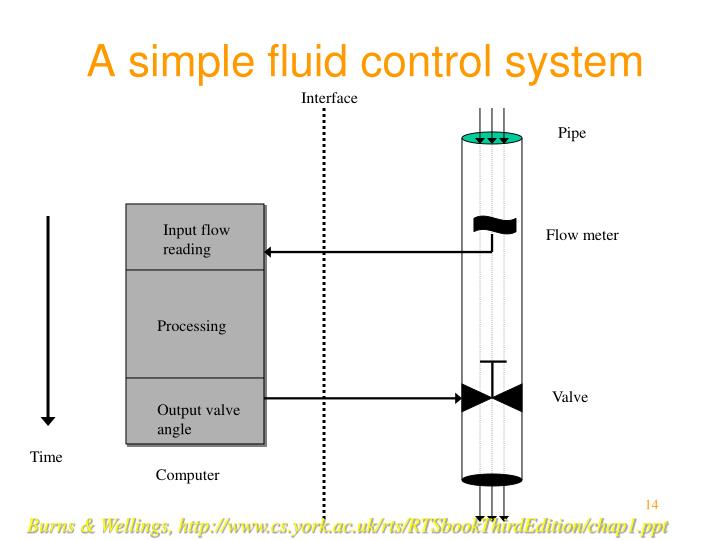
Why is fluid control important?
The control of fluid dynamics is essential to ensure efficient, reliable and safe operation of pumping systems. A pump puts fluid in motion by adding energy to it. This kinetic energy, observed as pressure, is carried in the fluid and slowly lost to friction in the piping system.
Are popularly used in fluid flow control in pipelines?
Piston Valves are mechanical devices used to control fluid flow through a pipe.
What are the six 6 types of valves?
Six types of valves and their applicationsGate valves.Butterfly valves.Globe valves.Needle valves.Check valves.
What are the three types of valve control?
There are three primary types of control valve trim:Snap Trim (also referred to as Quick-Opening trim)Nominal Trim (also referred to as Linear trim)Equal Percentage Trim.
What is fluids flow in pipes?
In fluid mechanics, pipe flow is a type of liquid flow within a closed conduit, such as a pipe or tube. The other type of flow within a conduit is open channel flow. These two types of flow are similar in many ways, but differ in one important aspect.
Which valve is used for fine control of flow in pipe line?
Globe valves and needle valves are standard designs used for flow control.
Which is used for controlling the flow rate?
Flow control valves control the volumetric rate of the fluid that flows through them. Generally, changing the size of the orifice is how the flow rate is set and adjusted. A tapered needle moving in and out of an orifice or opening and closing the gap inside a ball valve changes this rate.
What controls the direction of fluid flow?
Priority valves — A priority valve, Figure 7, is essentially a flow-control valve that supplies fluid at a set flow rate to the primary circuit, thus functioning as a pressure-compensated flow-control valve.
What is drilling fluid control system?
A drilling fluid control system is an automated system used to control the flow and processing of the drilling fluid. The complete system ensures that the consistency of drilling fluid, its retrieval, settlement and re-circulation into the drilling operation are done seamlessly in order to have a cost and time effective operation.
What is drilling fluid?
Drilling fluid is of prime importance in a drilling operation as it not only lubricates the borehole for easy drilling and installation but also helps remove cuttings and soil from the borehole to keep it clean.
What are the advantages of fluid power?
Fluid power systems, in general, tend to be inefficient, requiring much more energy input to the fluid than what is extracted at the points of use. When large amounts of energy need to be transmitted over long distances, electricity is a more practical medium for the task. However, fluid power systems enjoy certain advantages over electric power, a few of which are listed here: 1 Fluid power motors and cylinders do not overload at low speeds or under locked conditions 2 Fluid power systems present the little hazard of accidentally igniting flammable atmospheres (i.e. no sparks produced) 3 Fluid power systems present little or no fire hazard 4 Fluid power systems present no hazard of electric shock or arc flash 5 Fluid power systems are often easier to understand and troubleshoot than electric systems 6 Fluid power systems may be safely used in submerged (underwater) environments 7 Pneumatic systems are relatively easy to equip with back-up energy reserve (e.g. liquefied nitrogen serving as a back-up gas supply in the event of compressor shut-down) 8 Pneumatic systems are self-purging (i.e. enclosures housing pneumatic devices will be naturally purged of dust and vapors by leaking air)
Why is hydraulic fluid cool?
Hydraulic fluid also acts as a heat-transfer medium, and as such must be kept cool enough to prevent thermal damage to components. Large hydraulic systems are equipped with coolers, which are just heat exchangers designed to extract heat energy from the fluid and transfer it to either cooling water or ambient air.
What can compromise the precise fit between the spool and the valve body?
Extreme cycles in temperature will also compromise the precise fit between the spool and the valve body. Pneumatic fluid power systems require cleanliness as well since any particulate contamination in the air will likewise cause undue wear in the close-tolerance compressors, motors, valves, and cylinders.
What happens when a spool valve is actuated in the other direction?
If the spool valve is actuated in the other direction, the spool piece inside the valve assembly shifts again, switching the directions of airflow to and from the cylinder. Compressed air still flows from the supply to the vent, but the direction within the cylinder is reversed.
How does a valving system work?
A valving system directs the main flow of compressed air through one of these desiccant chambers at a time, allowing the desiccant to absorb water vapor in the air. Meanwhile, the unused chamber is purged of its collected water by venting low-pressure air through it to the atmosphere.
What is the most common contaminant in instrument air systems?
Water is perhaps the most common contaminant in instrument air systems, causing corrosion of metal components and subsequent clogging of orifices. Special devices called air dryers installed in instrument air systems to use solid materials called desiccants to absorb water entrained in the compressed air.
Is fluid a mechanical power?
Given the ability of pressurized fluids to transmit force over long distances, it is not surprising that many practical “flu id power systems” have been built using the fluid as a mechanical power-conducting media. Fluid systems may be broadly grouped into pneumatic (, usually air) and hydraulic (, usually oil).
What are the advantages of fluid power?
When large amounts of energy need to be transmitted over long distances, electricity is the a more practical medium for the task. However, fluid power systems enjoy certain advantages over electric power, a few of which are listed here: 1 Fluid power motors and cylinders do not overload at low speeds or under locked conditions 2 Fluid power systems present little hazard of accidentally igniting flammable atmospheres (i.e. no sparks produced) 3 Fluid power systems present little or no fire hazard 4 Fluid power systems present no hazard of electric shock or arc flash 5 Fluid power systems are often easier to understand and troubleshoot than electric systems 6 Fluid power systems may be safely used in submerged (underwater) environments 7 Pneumatic systems are relatively easy to equip with back-up energy reserve (e.g. liquefied nitrogen serving as a back-up gas supply in the event of compressor shut-down) 8 Pneumatic systems are self-purging (i.e. enclosures housing pneumatic devices will be naturally purged of dusts and vapors by leaking air)
Why is hydraulic fluid cool?
Hydraulic fluid also acts as a heat-transfer medium, and as such must be kept cool enough to prevent thermal damage to components. Large hydraulic systems are equipped with coolers, which are just heat exchangers designed to extract heat energy from the fluid and transfer it to either cooling water or ambient air.
What happens when a spool valve is actuated in the other direction?
If the spool valve is actuated in the other direction, the spool piece inside the valve assembly shifts again, switching the directions of air flow to and from the cylinder. Compressed air still flows from the supply to the vent, but the direction within the cylinder is reversed.
Why do hydraulic pumps need a shunt regulator?
A “shunt” regulator is necessary because hydraulic pumps are positive displacement, meaning they discharge a fixed volume of fluid with every revolution of the shaft. If the discharge of a positive-displacement pump is blocked (as it would be if the spool valve were placed in its default “off” position, with no shunt regulator to bleed pressure ...
Can you use water instead of oil in a hydraulic system?
Note: While it would be technically possible to use water instead of oil in a hydraulic power system, oil enjoys some distinct advantages. First, oil is a lubricating substance, and non-corrosive, unlike water.
Is a pneumatic system self-purging?
Pneumatic systems are self-purging (i.e. enclosures housing pneumatic devices will be naturally purged of dusts and vapors by leaking air) Another important consideration for fluid power systems is the ongoing maintenance work they require for reliable operation.
Is water vapor a contaminant in pneumatic air?
Pneumatic (instrument air) systems must be free of water vapor and particulate contamination for much the same reason. Water is perhaps the most common contaminant in instrument air systems, causing corrosion of metal components and subsequent clogging of orifices.
What is flow control?
Flow control is an advancing field of fluid dynamics, that describes the flow of liquids, gases and plasmas. Flow control of fluids can be accomplished by passive (require no energy) or active devices (require energy).
What is flow measurement?
Flow measurement is the determination of bulk fluid movement. The flow of fluids can be measured in a variety of ways. Measuring the flow of fluids is a critical need in many industrial plants. This Technology Zone offers an insight into the latest innovations in fluid flow measurement and control.
What is liquid level control?
Liquid Level Control System is a system specifically designed to control the level of fluid in tanks. The main aim possessed by these systems is to control the rate with which the pump delivers fluid to the tank and so it can reach the desired level inside the tank.
What is the water level control system?
The crucial components of the water level control system are as follows: Fluid tank: Also known as a storage tank, used to hold the desired amount of fluid. Measurement system: Senses the level of the fluid inside the tank.
What are the fundamental parameters of a liquid level control system?
So, resistance, capacitance and inertance are regarded as the fundamental parameters of a liquid level control system. The term inertance corresponds to the inertia forces which comes into action in order to cause acceleration of the fluid through the pipes.
What happens when fluid outflows from a tank?
However, when the fluid outflows from the tank then there will be some resistance in its flow. The amount of resistance offered depends on the outlet through which the fluid comes out. In case of a hole as an outlet, the fluid will not flow out easily that causes the generation of resistance.
