Why Understanding Fluorochromes Is Important In Flow Cytometry. At the most basic level, a flow cytometer is photon counting device. It captures the emitted photons from fluorochromes present on targets — be they cells, beads, or other particles.
What type of fluorochromes are used in flow cytometry?
3.3 Fluorochromes used in flow cytometry In general, there are two classes of fluorochrome used in flow cytometry - those which bind non-covalently to structures within the cell and those which are covalently bound to other probes. The fluorescent proteins, such as Green Fluorescent Protein, (GFP) form a special category.
What are fluorochromes and why are they important?
Fluorochromes are key to identifying cells and their functions using flow cytometry. The ability for fluorochromes to fluoresce and emit light at defined wavelengths allows researchers to indirectly characterize a wide variety of particles and deeply advance knowledge of human, animal, and plant biology.
How does a flow cytometer work?
At the most basic level, a flow cytometer is photon counting device. It captures the emitted photons from fluorochromes present on targets — be they cells, beads, or other particles.
How do fluorochromes become fluorescent?
These fluorochromes can be attached to antibodies or proteins (like Annexin), free molecules that become fluorescent when bound to a target (DNA dyes), or have different fluorescent characteristics under different biological conditions (Indo-1, JC-1).

What is a fluorochrome and how is it used?
Fluorescent dyes (or fluorochromes) are commonly used as detection reagents in various applications such as cellular imaging and flow cytometry. Fluorochromes absorb light energy of a specific wavelength and re-emit it at a longer wavelength.
What is the meaning of fluorochrome?
Definition of fluorochrome : any of various fluorescent substances used in biological staining to produce fluorescence in a specimen.
What is the function of fluorochrome?
Fluorescent reporter labels (fluorochromes) are chemical molecules that have the ability to absorb light of a certain wavelength and then re-emit light at a longer wavelength. Light is emitted at longer wavelengths due to the molecule losing energy to its environment before fluorescing.
What are the types of fluorochrome?
In general, fluorochromes can be divided into 5 broad categories, which are discussed below.Fluorescent Proteins. Fluorescent proteins can be categorized into two groups. ... Synthetic Small Molecules. ... Quantum Dots. ... Polymer Dyes. ... Tandem Dyes.
What is fluorochrome staining?
Fluorochrome staining: The use of any fluorescent dye (e.g., auramine, rhodamine) used to label or stain. Must be viewed using a fluorescence microscope.
What is the difference between fluorophore and fluorochrome?
Yes, fluorophore and fluorochrome refer to the same thing. Fluorophores, or fluorochromes, are fluorescent chemical compounds that are capable of absorbing light from a laser and re-emitting the light within a range of wavelengths upon excitation.
Which dyes is used in flow cytometry?
A variety of fluorescent reagents are utilized in flow cytometry. These include, fluorescently conjugated antibodies, DNA binding dyes, viability dyes, ion indicator dyes and fluorescent expression proteins.
What is the principle of flow cytometry?
Flow cytometry (FCM) is a technique which enables rapid analysis of statistically significant number of cells at single cell level. The main principle of this technique is based on scattering of light and emission of fluorescence which occur when a laser beam hits the cells moving in a directed fluid stream.
How does a fluorescence quencher work?
Fluorescence quenching is a physicochemical process that lowers the intensity of emitted light from fluorescent molecules. When a molecule absorbs light, electrons in its constituent atoms become excited and are promoted to a higher energy level.
Can I use PE and FITC?
In some experiments FITC may be combined with other dyes, for example PE, that emit yellow and orange photons. In those cases the relative contribution of each fluorophore to the signal in a given detector must be determined (Figure 11).
What is FITC in flow cytometry?
Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) is a derivative of fluorescein used in wide-ranging applications including flow cytometry. First described in 1942, FITC is the original fluorescein molecule functionalized with an isothiocyanate reactive group (−N=C=S), replacing a hydrogen atom on the bottom ring of the structure.
What color is FITC?
greenFITC exhibits an excitation maximum at λ = 495 nm and emission maximum at approximately λ = 519 nm. The color of the compound is yellow while the emitted light is green.
What are Fluorochromes give an example?
Examples of fluorochromes used in the detection of art materials are: Berberine sulfate, Acridine orange, Acridine yellow, Auramine O, Blancophor R, Cycloheptaamylose dansyl chloride, Dichlorofluorescein, Fluorescein isothiocyanate, Lissamine Rhodamine B Sulfonyl Chloride, Primuline, Pyronine Y, Rhodamine B, Rosaniline ...
What is the purpose of immunofluorescence?
Immunofluorescence (IF) is an important immunochemical technique that allows detection and localization of a wide variety of antigens in different types of tissues of various cell preparations.
What is the purpose of flow cytometry?
Flow cytometry is a laser-based technique used to detect and analyze the chemical and physical characteristics of cells or particles. It is most commonly used to evaluate bone marrow, peripheral blood and other fluids in your body.
What are fluorochromes?
Fluorescent markers are known as fluorochromes, a term that is used interchangeably with fluorophore. Upon absorption of light from a laser, they become ‘excited’ and emit light at a longer wavelength to return to their original ‘ground’ energy state, which is known as fluorescence.
What is flow cytometry?
Flow cytometry is a popular cell biology laboratory method. It uses a laser for rapid analysis, quantification, and sorting of a suspension of live cells. In a matter of nanoseconds, profiles of the cell population’s properties are acquired, including size and granulation. This is based on the characteristic pattern of light refracted from the cells. It is then possible to purify the cell population by sorting them into distinct channels depending on their distinct properties.
What is the peak absorbance of fluorescein isothiocyanate?
For example, the most widely used fluorochrome, Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), has a peak absorbance of 494nm and a peak emission of 512nm corresponding to the colors blue and green. Exciting fluorochromes at their peak absorbance (rather than at the bottom end of their absorbance spectrum), enables more intense light emission.
Why do fluorochromes require overlapping emission/absorption spectra?
One advantage of this method is that it further increases the Stokes Shift for more distinguishable colors. It enables the use of several fluorochromes in a panel, producing many colors for analyzing multiple parameters.
Why is it important to use multiple fluorochromes?
Therefore, when using multiple fluorochromes, it is important to choose those that are non-overlapping. This allows differentiation of the cell features they are highlighting.
What is the purpose of antibodies tagged with fluorescent dyes?
When a more in-depth investigation of a cell population is required, antibodies tagged with fluorescent dyes are used to identify the presence or absence of particular cellular markers. Detecting specific proteins (such as CD markers) in a cell population may help to determine cell types, and this is known as immunophenotyping.
How are tandem dyes made?
Tandem dyes are made by covalently binding two different fluorochromes. One becomes the donor and the other an acceptor. The donor is ‘excited’ and emits light that is absorbed by the acceptor, due to Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET). For this to occur, the two fluorochromes require overlapping emission/absorption spectra.
What are the properties of fluorochromes?
The important properties of a fluorochrome are its absorption spectrum, its extinction coefficient at a wavelength convenient for excitation, its emission spectrum and its quantum efficiency. The latter is the number of photons emitted for every photon absorbed.
Why do fluorochromes bind to nucleic acids?
The fluorochromes described in this section bind stoichiometrically to nucleic acids so that they can be used for quantitative measurement. This is essential for the measurement of ploidy and the cell cycle (see Chapter 6 ).
How does fluorescence quench?
Fluorescence can also be quenched by an interaction with another molecule in which the energy is dissipated by a non-radiative transition. This can be illustrated by the bis-benzimadazole dye, Hoechst 33342, which binds to DNA giving blue fluorescence on excitation with UV. However, if DNA is labelled with 5'-bromodeoxyuridine, the fluorescence of the dye is quenched by the bromine atom. If a compound is over-labelled with a fluorochrome, fluorescence can also be quenched by interactions between the molecules of fluorochrome. This effect can be observed when liposomes are loaded with fluorescein; fluorescence decreases with increasing dye concentration above about 20 µM.
What happens when DNA is labelled with 5'-bromodeoxyuridine?
However, if DNA is labelled with 5'-bromodeoxyuridine, the fluorescence of the dye is quenched by the bromine atom. If a compound is over-labelled with a fluorochrome, fluorescence can also be quenched by interactions between the molecules of fluorochrome. This effect can be observed when liposomes are loaded with fluorescein;
Why is fluorescence detection so sensitive?
Fluorescence detection is a sensitive technique because a positive signal is observed against a negative background. The detection of up to 14 compounds fluorescing at different wavelengths permits multiparametric analysis of cells and has greatly increased the power of flow cytometry. The majority of applications use up to four fluorescences.
What happens to light after fluorescence?
The absorption and emission of light during fluorescence. After excitation by light absorption, the electron moves to an excited state of lower energy (red arrow). When it drops to the ground state (green arrow) light is emitted.
Does fluorescence decrease with dye concentration?
This effect can be observed when liposomes are loaded with fluorescein; fluorescence decreases with increasing dye concentration above about 20 µM. If two fluorochromes are closely associated, energy transfer can occur whereby excitation of one compound causes the other to fluoresce.
Why is fluorochrome important in flow cytometry?
At the most basic level, a flow cytometer is photon counting device. It captures the emitted photons from fluorochromes present on targets — be they cells, beads, or other particles. These fluorochromes can be attached to antibodies or proteins (like Annexin), ...
What are fluorochromes attached to?
These fluorochromes can be attached to antibodies or proteins (like Annexin), free molecules that become fluorescent when bound to a target (DNA dyes), or have different fluorescent characteristics under different biological conditions (Indo-1, JC-1). Fluorescent molecules are the tools of the trade in flow cytometry and, ...
What Are The 5 Classes Of Fluorochromes?
In general, fluorochromes can be divided into 5 broad categories, which are discussed below.
What is FlowJo in cytometry?
FlowJo is a powerful tool for performing and analyzing flow cytometry experiments, if you know how to use it to the fullest . This includes understanding embedding and using keywords, the FlowJo compensation wizard, spillover spreading matrix, FlowJo and R, and creating tables in FlowJo. Extending your use of FJ using these hacks will help organize your data, improve analysis and make your exported data easier to understand and explain to others. Take a few moments and explore all you can do with FJ beyond just gating populations.
What is fluorescent molecule?
Fluorescent molecules are the tools of the trade in flow cytometry and , with continued advances in chemistries, it is helpful to step back and review their essential properties.
Can fluorescent proteins be used as surrogates?
Many fluorescent proteins are commercially available in expression vectors to allow researchers to clone them into a vector expressing their favorite targets and follow the expression of the target by using the fluorescent surrogate.
What is fluorochrome used for?
Fluorochromes used in flow cytometry are essentially those that can attach in some way to biologically significant molecules and are excitable by the lasers commonly found on commercial flow cytometers.
How to visualize fluorochromes?
They can be visualized using a spectra viewer. Spectra viewers allow the researcher to understand the emission and excitation properties of a given fluorochrome and help them determine the best excitation and emission filter set to use for that fluorochrome.
What is fluorofinder?
FluoroFinder makes it easy to visualize and find the optimal fluorochrome from multiple suppliers with the flow cytometry panel builder, and on the spectra viewer.
How does fluorescence work?
Fluorescence is described in terms of excitation and emission. A fluorochrome may be excited by a laser at a defined excitation wavelength, at which time the molecule absorbs light photons.
Why are fluorochromes more desirable for fluorescent research?
Because the color of the exciting and emitting light are different , they can be separated from one another by using optical filters.
Why is brightness important in fluorochromes?
Brightness plays an important role when considering fluorochromes. Brighter fluorochromes should be reserved for critical markers of low expression, or rare events. While there are several resources and charts online with varying selections of fluorochrome brightness.
How many compounds can be detected in flow cytometry?
Experiments that were once limited to the detection of three to four parameters have increased to detect up to 40 compounds fluorescing at different wavelengths, permitting the multi parametric analysis of cells. As advanced fluorescence detection created added complexities in experimental design, it is helpful to step back and understand fluorescent molecules used in flow cytometry.
How to obtain optimal results from flow cytometry analysis?
Each fluorochrome has distinct properties and is characterized by specific excitation and emission wavelengths. First, the fluorochrome must be excited by the lasers available on the instrument. Second, the emission wave lengths are read by different detectors or photomultiplier tubes and the range of detection is limited by optical filters.
Which fluorochrome is used for the lowest expression?
Use the brightest fluorochrome, typically PE or PE based energy transfer conjugates, for the protein that has the lowest expression, and vice versa the dimmest fluorochrome for the most highly expressed protein.
How many chromophores does APC have?
APC has six phycocyanobilin chromophores per molecule, which make it a very bright fluorochrome that is highly suitable for flow cytometry applications. APC is excited by the red diode laser and excites in several tandem dyes including APC-Cy5.5 and APC-Cy7.
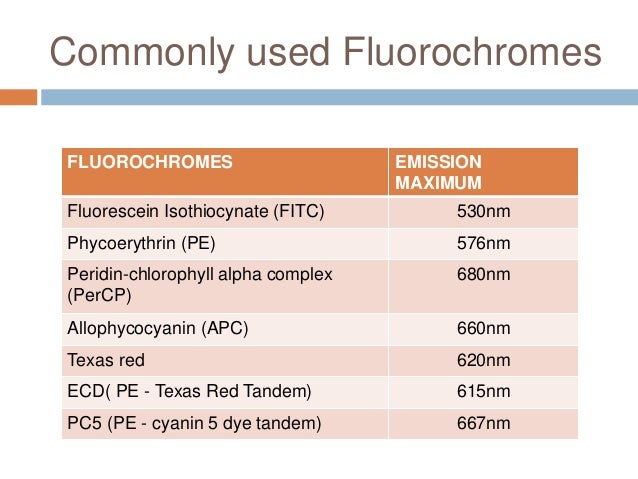
What is PE Cy5?
PE-Cy5 (Ex-Max 496 nm/Em-Max 667 nm): is a tandem conjugate that combines phycoerythrin and a cyanine dye. Because of its broad absorption range and the fact that its emission spectrum is equivalent to APC, PE-Cy5 is not recommended for simultaneous use with APC. The cyanine dyes are known to exhibit non-specific binding to Fc-receptors, which is most apparent on monocyte populations.
Can Alexa Fluor 647 and APC be used together?
Due to nearly identical excitation and emission properties, but different spillover characteristics, APC and Alexa Fluor 647 cannot be used simultaneously.
Is Alexa Fluor 488 a FITC?
Alexa Fluor 488 (Ex-Max 495 nm/Em-Max 519 nm): have nearly identical emission and excitation maxima as FITC. However, Alexa Flour 488 display higher photostability and is less susceptible to self-quenching. In addition, Alexa Flour 488 is pH insensitive (over a broad pH range) and tends to be brighter compared to FITC on most instruments. These properties, i.e. increased sensitivity and environmental stability, make Alexa Flour 488 suitable for intracellular staining.
Is FITC a fluorochrome?
FITC (Ex-Max 494 nm/Em-Max 520 nm): Fluorescein isothiocyanate - has a very high efficiency of energy transfer from absorbed to emitted light and is one of the most commonly used fluorochromes. However, FITC is highly sensitive to pH changes and photo bleaching. In addition FITC is relatively dim and should be reserved for highly expressed markers whenever possible.
Is Alexa Fluor 647 the same as APC?
The excitation and emission maxima are nearly identical to those of APC, albeit APC tends to be brighter. However, Alexa Fluor 647 is considered more optimal for intracellular applications. Due to nearly identical excitation and emission properties, but different spillover characteristics, APC and Alexa Fluor 647 cannot be used simultaneously.
Single Dyes
Single dyes such as FITC, PE, APC and PerCP have been available for many years, but there are now alternatives available from Alexa Fluor dyes, which offer users greater photostability and brighter fluorescence.
Starbright Dyes
StarBright Dyes are novel proprietary fluorescent nanoparticles specifically developed for flow cytometry. They are bright, photostable, have narrow excitation and emission profiles and do not require a special buffer when multiplexing.
Tandem Dyes
Tandem dyes comprise a small fluorophore covalently coupled to another fluorophore. When the first dye is excited and reaches its maximal excited electronic singlet state, its energy is transferred to the second dye (an acceptor molecule). This activates the second fluorophore, which then produces the fluorescence emission.
Fluorescent Proteins
Fluorescent proteins, such as green fluorescent protein (GFP), have become an integral tool for understanding protein expression in many scientific disciplines. Other fluorescent proteins, such as mCherry and yellow fluorescent protein, have also become widely used for flow cytometry analysis and cell sorting.