What are the 7 functions of the cell membrane?
Cell membrane . What is the function of the cell membrane. Transport by formation of vesicles. Cellular input. Cellular excretion. Cell membrane installation. The mosaic model
What are facts about the cell membrane?
Here's Why:
- The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a thin layer that separates the inside of the cell from the outside. ...
- In order for the cell membrane to do its job properly, it needs to be semipermeable. ...
- In animals and humans, the cell membrane is the only layer between the cell and the outside. ...
What are some interesting facts about the cell membrane?
Other examples of organelles include:
- Nucleus - controls cell growth and reproduction.
- Mitochondria - provide energy for the cell.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum - synthesizes carbohydrates and lipids.
- Golgi Complex - manufactures, stores, and ships certain cellular products.
- Ribosomes - involved in protein synthesis.
- Lysosomes - digest cellular macromolecules.
What types of biomolecules are found in a cell membrane?
- Carbohydrates, proteins, fats are used as food stuffs in various forms.
- Volatile oils or essential oils are used for perfumes.
- Compounds like alkaloids, glycosides, tannins are used in medicine.
- Tannins are also used to tan (toughen) the leather in industry.

What is the cell membrane made of?
Cell Membrane Structure. The cell membrane is primarily composed of a mix of proteins and lipids. Depending on the membrane’s location and role in the body, lipids can make up anywhere from 20 to 80 percent of the membrane, with the remainder being proteins.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Its function is to protect the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances into the cell while keeping other substances out. It also serves as a base of attachment for the cytoskeleton in some organisms and ...
What is the role of cholesterol in animal cell membranes?
Cholesterol molecules are selectively dispersed between membrane phospholipids. This helps to keep cell membranes from becoming stiff by preventing phospholipids from being too closely packed together. Cholesterol is not found in the membranes of plant cells.
What are the functions of cell membrane receptor proteins?
Cell membrane receptor proteins help cells communicate with their external environment through the use of hormones, neurotransmitters, and other signaling molecules.
Why is the cell membrane important?
Thus the cell membrane also serves to help support the cell and help maintain its shape.
What is the function of the nucleus?
The nucleus and mitochondria are two examples. Another function of the membrane is to regulate cell growth through the balance of endocytosis and exocytosis. In endocytosis, lipids and proteins are removed from the cell membrane as substances are internalized. In exocytosis, vesicles containing lipids and proteins fuse with ...
Which bilayer of lipids is hydrophobic?
Phospholipids form a lipid bilayer in which their hydrophilic (attracted to water) head areas spontaneously arrange to face the aqueous cytosol and the extracellular fluid, while their hydrophobic (repelled by water) tail areas face away from the cytosol and extracellular fluid.
What is the cell membrane?
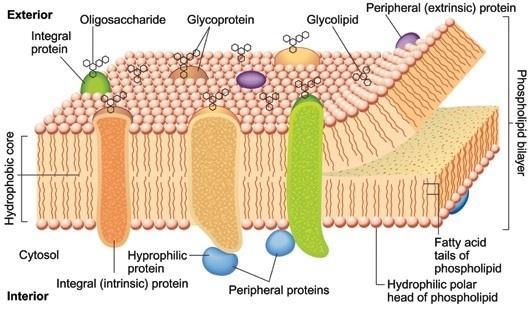
Definition. The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a double layer of lipids and proteins that surrounds a cell. It separates the cytoplasm (the contents of the cell) from the external environment. It is a feature of all cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic. a 3D diagram of the cell membrane.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
Function of the Cell Membrane. The cell membrane gives the cell its structure and regulates the materials that enter and leave the cell. It is a selectively permeable barrier, meaning it allows some substances to cross, but not others. Like a drawbridge intended to protect a castle and keep out enemies, the cell membrane only allows certain ...
What is the technical term for this double layer of phospholipids that forms the cell membrane?
The technical term for this double layer of phospholipids that forms the cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer. Structure of the cell membrane and its associated components.
What is the difference between hydrophobic and hydrophilic phospholipids?
When in water or an aqueous solution (including inside the body) the hydrophobic heads of phospholipids will orient themselves to be on the inside, as far away from the water as possible. In contrast, the hydrophilic heads will be on the outside, making contact with the water. The result is that a double layer of phospholipids is formed, with the hydrophobic heads clustering together in the center, and the hydrophilic tails forming the outside of the structure. The technical term for this double layer of phospholipids that forms the cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer.
What is the phospholipid bilayer?
Phospholipid Bilayer. The cell membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer. Phospholipids are lipid molecules made up of a phosphate group head and two fatty acid tails. Importantly, the properties of phospholipid molecules allow them to spontaneously form a double-layered membrane. The phosphate group head of a phospholipid is hydrophilic, ...
How does the cell control the rate of diffusion of substances?
Another way the cell membrane can bring molecules into the cytoplasm is through endocytosis. The reverse process, where the cell delivers contents outside the membrane barrier, is called exocytosis. Endocytosis includes phagocytosis (“cell eating”) ...
What is the process of endocytosis?
Endocytosis includes phagocytosis (“cell eating”) and pinocytosis (“cell drinking”). During these processes, the cell membrane forms a depression, surrounding the particle that it is engulfing. It then “pinches off” to form a small sphere of membrane called a vesicle that contains the molecule and transports it to wherever it will be used in ...
What are the three main types of substances that make up the cell membrane?
The cell membrane is made up of three main types of substances. They are lipids, proteins and carbohydrates.
What are the lipids that are found on the surface of the cell membrane?
Glycolipids are lipids located on the surface of the cell membrane with a carbohydrate chain covalently bonded to them. Glycolipids play an important role in cell recognition. They act as markers or tags that help cells to differentiate between other cells in the body. They are able to recognise foreign cells. This feature is the basis for rejection of foreign cells as it appears in the immune system.
What are glycolipids and glycoproteins?
Glycolipids and glycoproteins (proteins with a carbohydrate unit attached to them via covalent bonding) are the substances that associate the cell membrane with carbohydrates. They are collectively known as glycocalyx (Clegg and Mackean, 1994). Glycoproteins and glycolipids are found on the surface of the cell membrane. Glycocalyces help in cell-to-cell recognition, cell protection and uptake of molecules into the cell.
How does cholesterol make the cell membrane rigid?
Cholesterol makes the cell membrane rigid, by preventing interactions between fatty acid chains of phospholipids. The bent structure of cholesterol molecules immobilizes the neighbouring phospholipids, reducing the fluidity of the membrane but making it stronger. Depending on the type of cell, the amount of cholesterol in the cell membrane varies.
How thick is the cell membrane?
According to Campbell and Reece (2002), cell membranes are approximately 8 nm thick. Cell membranes or plasma membranes display extraordinary features in their structure and functions. They are composed of a bilayer of phospholipids with proteins and cholesterol molecules associated with them. As the cell membrane is a matrix containing varieties of substances that can move within it, it is described as a ‘fluid mosaic’.
What are the functions of proteins in the cell membrane?
According to the tasks they carry out, membrane proteins are categorized into different classes (e.g. structural proteins, transport proteins, receptor proteins). Campbell and Reece (2002), states that proteins determine most of the specific functions of the cell membrane. Some of these functions include transport of substances into the cell, communication of the cell with its outside environment, and cell recognition.
What is the outer layer of a cell?
The outer layer or membrane of a cell provides a boundary between the internal and external environment of the cell. It controls the passage of substances into and out of the cell. This permits the cell to uptake nutrients and eliminate waste products.
What is the membrane of a cell called?
Plasma Membrane (Cell Membrane) Plasma Membrane (Cell Membrane) =. The plasma membrane , also called the cell membrane, is the membrane found in all cells that separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. In bacterial and plant cells, a cell wall is attached to the plasma membrane on its outside surface.
Which membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell?
The plasma membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. The plasma membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell.
What are the proteins that interact with other cells?
Another is that the membrane of the cell, which would be the plasma membrane, will have proteins on it which interact with other cells. Those proteins can be glycoprotein, meaning there's a sugar and a protein moiety, or they could be lipid proteins, meaning there's a fat and a protein.
Is cholesterol in the plasma membrane?
And there are different types of plasma membranes in different types of cells, and the plasma membrane has in it in general a lot of cholesterol as its lipid component. That's different from certain other membranes within the cell.
What are membrane proteins?
These membrane proteins are responsible for many specialized functions; some act as receptors that allow the cell to respond to external signals, some are responsible for the selective transport of molecules across the membrane, and others participate in electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation.
What are the building blocks of the cell membrane?
The fundamental building blocks of all cell membranes are phospholipids, which are amphipathicmolecules, consisting of two hydrophobicfatty acid chains linked to a phosphate-containing hydrophilichead group (see Figure 2.7).
Why do unsaturated fatty acids increase membrane fluidity?
Lipids containing unsaturated fatty acidssimilarly increase membrane fluidity because the presence of double bonds introduces kinks in the fatty acid chains, making them more difficult to pack together. Figure 2.46. Mobility of phospholipids in a membrane.
Why are lipids important to the structure of membranes?
An important property of lipid bilayers is that they behave as two-dimensional fluids in which individual molecules (both lipidsand proteins) are free to rotate and move in lateral directions (Figure 2.46). Such fluidity is a critical property of membranes and is determined by both temperature and lipid composition. For example, the interactions between shorter fatty acid chains are weaker than those between longer chains, so membranes containing shorter fatty acid chains are less rigid and remain fluid at lower temperatures. Lipids containing unsaturated fatty acidssimilarly increase membrane fluidity because the presence of double bonds introduces kinks in the fatty acid chains, making them more difficult to pack together.
Why do phospholipids form bilayers?
Because their fatty acid tails are poorly soluble in water, phospholipids spontaneously form bilayers in aqueous solutions, with the hydrophobic tails buried in the interior of the membrane and the polar head groups exposed on both sides, in contact with water (Figure 2.45).
How are proteins anchored to the plasma membrane?
Proteins can also be anchored in membranes by lipidsthat are covalently attached to the polypeptidechain (see Chapter 7). Distinct lipid modifications anchor proteinsto the cytosolic and extracellular faces of the plasma membrane. Proteins can be anchored to the cytosolic face of the membrane either by the addition of a 14-carbon fatty acid (myristic acid) to their amino terminus or by the addition of either a 16-carbon fatty acid (palmitic acid) or 15- or 20-carbon prenyl groups to the side chains of cysteine residues. Alternatively, proteins are anchored to the extracellular face of the plasma membrane by the addition of glycolipids to their carboxy terminus.
How does cholesterol affect the membrane?
The rigid hydrocarbon rings of cholesterol therefore interact with the regions of the fatty acid chains that are adjacent to the phospholipid head groups. This interaction decreases the mobility of the outer portions of the fatty acid chains, making this part of the membrane more rigid. On the other hand, insertion of cholesterol interferes with interactions between fatty acid chains, thereby maintaining membrane fluidity at lower temperatures.
What is the cell membrane?
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a thin, flexible barrier protecting the cell. Cell membranes are an essential component of all cells. The membranes allow cells to separate their internal structures from the environment; this is important for maintaining homeostasis, a stable set of internal conditions despite a changing exterior.
What are the roles of membrane proteins in the cell?
Membrane proteins can also play an important role in cell structure and adhesion. Transmembrane proteins help anchor the cytoskeleton's internal components to the extracellular matrix or other cells; this helps create tight junctions in tissues between cells that create barriers and helps cells adhere to the extracellular matrix to secure tissues in place.
What happens when phospholipids are placed in water?
When placed in water, tails interacting with water are energetically unfavorable. As a result, individual phospholipids will arrange themselves into a bilayer where the tails are shielded from interactions with water. The result is a sphere where the heads face the aqueous internal and external environment, and the tails are hidden inside the membrane.
Why do phospholipids pass through the membrane?
The amphipathic nature of the phospholipids also allows the membrane to be semi-permeable or selectively permeable; this means that the membrane only lets certain things in and out of the cell. Because the lipids are packed tightly together, and due to their interactions, only tiny molecules can pass through the membrane freely. In addition, only hydrophobic molecules can pass freely through the membrane due to the hydrophobic nature of the tails inside the phospholipid leaflets. Thus, large or charged molecules, such as sugars, amino acids, or ions, cannot pass through the membrane without assistance.
What is the role of phospholipids in the transport of materials?
This process allows the cell to specifically regulate the transport of materials by regulating which proteins are distributed in the membrane and their transport process. For example, some channels only open at a certain membrane voltage or when a certain signal is in the environment. Five main types of transport occur across the membrane:
What is the role of cholesterol in the cell membrane?
Cholesterol, a type of sterol, are waxy fats that help to regulate membrane fluidity. Cholesterol fits in between the hydrophobic tails of phospholipids; this disrupts their interactions and helps the membrane maintain fluidity. Fluidity is necessary for the cell to be able to move in its environment.
How does osmosis work?
Osmosis is the passive movement of water from where there is a greater concentration to where there is a lesser concentration. Some water can diffuse directly across the membrane, but the process is slow. Cells that need to transport water in great volumes have specific proteins called aquaporins that create channels for osmosis. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from high to low concentration directly through the membrane; this only happens for small, hydrophobic molecules such as oxygen or carbon dioxide. Transports include pumps and channels and are proteins that help facilitate transport across the membrane. Endocytosis and exocytosis involve the invagination of the cell membrane to create vesicles or release them. Endocytosis brings large molecules into the cell in bulk, and exocytosis allows for their movement out of the cell.
What is the cell membrane?
Cell membrane (Plasma membrane) The outer thin membrane or the layer of the living cell is known as the cell membrane. It is also known as the plasma membrane in animal cells. In the plant cells, it is known as plasmalemma. The term cell membrane was given by Nageli and Cramer (1885) for the membrane covering of the protoplast.
How many types of cell membranes are there?
There are two types of cell membrane. They are:
What are the three types of lipids in the cell membrane?
Most of the cell membrane is composed of 40-50 % protein and 50-60 % lipids. Membrane lipids are of three types: a) Phospholipids b) Glycolipids c) Steroids. In the different membrane, the proportion of the lipid varies:
Which model suggests that the cell membrane is a solid and stable structure?
It was proposed by James Danielli and Hugh Davsan in the year 1935. This model suggests the cell membrane as the solid and the stable structure. Four molecular layers are present in it i.e. two phospholipids and two protein layers. It consists of the phospholipid.
Why is the cell membrane important?
Cell membrane helps to maintain homeostasis. It provides protection to all the internal organelles of the cell.
What is the interaction between lipids and proteins?
Between the lipids and the proteins, there is interaction which results in the fluidity of the membrane.
Where are respiratory enzymes found?
Some are involved in the biosynthesis of the cell wall. Incase of prokaryotes, respiratory enzymes are found in the plasma membrane.
Which cell membrane is the most thoroughly studied?
The Phospholipid Bilayer. The plasma membraneis the most thoroughly studied of all cell membranes, and it is largely through investigations of the plasma membrane that our current concepts of membrane structure have evolved. The plasma membranes of mammalian red blood cells (erythrocytes) have been particularly useful as a model for studies ...
What is the structure of the plasma membrane?
Like all other cellular membranes, the plasma membrane consists of both lipids and proteins. The fundamental structure of the membrane is the phospholipid bilayer, which forms a stable barrier between two aqueous compartments. In the case of the plasma membrane, these compartments are the inside and the outside of the cell.
Why are phospholipids impermeable?
Because the interior of the phospholipid bilayeris occupied by hydrophobicfatty acid chains, the membrane is impermeable to water-soluble molecules, including ions and most biological molecules. Second, bilayers of the naturally occurring phospholipids are viscous fluids, not solids.
How are integral membrane proteins released?
In contrast to the peripheral membrane proteins, integral membrane proteinscan be released only by treatments that disrupt the phospholipid bilayer. Portions of these integral membrane proteins are inserted into the lipid bilayer, so they can be dissociated only by reagents that disrupt hydrophobicinteractions.
How many transmembrane proteins are in the reaction center?
The reaction center consists of three transmembrane proteins, designated L (red), M (yellow), and H (green). The L and M subunits each have five transmembrane α helices, whereas the H subunit has only (more...) Although most transmembrane proteinsspan the membrane by α-helical regions, this is not always the case.
Why are transmembrane proteins so difficult to crystallize?
Because of their amphipathiccharacter, transmembrane proteinshave proved difficult to crystallize, as required for three-dimensional structural analysis by X-ray diffraction. The first transmembrane protein to be analyzed by X-ray crystallographywas the photosynthetic reaction center of the bacterium Rhodopseudomonas viridis, whose structure was reported in 1985 (Figure 12.7). The reaction center contains three transmembrane proteins, designated L, M, and H (light, medium, and heavy) according to their apparent sizes indicated by gel electrophoresis. The L and M subunits each have five membrane-spanning α helices. The H subunit has only a single transmembrane α helix, with the bulk of the polypeptidechain on the cytosolic side of the membrane. The fourth subunit of the reaction center is a cytochrome, which is a peripheral membrane protein bound to the complex by protein-protein interactions.
Which compartment of the cell is responsible for selective transport of molecules?
In the case of the plasma membrane, these compartments are the inside and the outside of the cell. Proteins embedded within the phospholipid bilayer carry out the specific functions of the plasma membrane, including selective transport of molecules and cell-cell recognition. The Phospholipid Bilayer. The plasma membraneis the most thoroughly ...
